Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Avaya IPOCC Port Matrix - 101012811
Uploaded by
James HavocOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Avaya IPOCC Port Matrix - 101012811
Uploaded by
James HavocCopyright:
Available Formats
Avaya Port Matrix:
IP Office Contact Center
9.1.6.0
Issue 1.0
February 23, 2016
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 1
ALL INFORMATION IS BELIEVED TO BE CORRECT AT THE TIME OF
PUBLICATION AND IS PROVIDED "AS IS". AVAYA INC. DISCLAIMS ALL
WARRANTIES, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE AND FURTHERMORE, AVAYA INC. MAKES NO REPRESENTATIO NS
OR WARRANTIES THAT THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HEREIN WILL
ELIMINATE SECURITY THREATS TO CUSTOMERS’ SYSTEMS. AVAYA
INC., ITS RELATED COMPANIES, DIRECTORS, EMPLOYEES,
REPRESENTATIVES, SUPPLIERS OR AGENTS MAY NOT, UNDER ANY
CIRCUMSTANCES BE HELD LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL,
PUNITIVE, EXEMPLARY, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HEREIN.
THIS INCLUDES, BUT IS NOT LIMITED TO, THE LOSS OF DATA OR LOSS OF
PROFIT, EVEN IF AVAYA WAS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES. YOUR USE OF THIS INFORMATION CONSTITUTES ACCEPTANCE
OF THESE TERMS.
© 2016 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved. All trademarks identified by the ®
or ™ are registered trademarks or trademarks, respectively, of Avaya Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 2
1. IP Office Contact Center Components
Component Interface Description
IP Office Contact User Interface Home: Displays the home area.
Center Telephony: Displays the telephony area.
Realtime information: Displays the real time information
area.
Reporting: Displays the reporting area.
Agent Status Reports: Displays the agent evaluation area.
Contact Detail Reports: Displays the contact evaluation
area.
Error list: Displays the date time, code, and the error
description.
Configuration: Displays the standalone Configuration
module.
UI Config: Displays the UI configuration area.
Task Flow Editor: Displays the standalone Task flow editor
module
IVR Editor: Displays the standalone IVR editor module.
Dialer: Displays the standalone Dialer module.
Email Configuration: Displays the Email administration
module.
Text Block Administration: Displays the Text block
administration module.
Address Book Administration: Displays the Address book
configuration module.
IP Office Contact Web UI Web interface with Telephony, Email, Chat, real time and
Center (Chrome and historical reporting
Browsers)
IP Office Contact Web Admin Web based administration interface
Center
IP Office Contact Web Service Programming interface
Center
IP Office Contact Wallboard Real time monitoring
Center
IP Office Contact TTrace Console, Trace interface
Center
IP Office Contact WebLM Standard Avaya WebLM
Center
IP Office Contact WebChatDialog Application managing Chat sessions with customer Web
Center Servers
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 3
2. Port Usage Tables
2.1 Port Usage Table Heading Definitions
Source System: System name or type that initiate connection requests.
Source Port: This is the default layer-4 port number of the connection source. Valid values include: 0 – 65535. A
“(C)” next to the port number means that the port number is configurable.
Destination System: System name or type that receives connection requests.
Destination Port: This is the default layer-4 port number to which the connection request is sent. Valid values
include: 0 – 65535. A “(C)” next to the port number means that the port number is configurable.
Network/Application Protocol: This is the name associated with the layer-4 protocol and layers-5-7 application.
Optionally Enabled / Disabled: This field indicates whether customers can enable or disable a layer-4 port
changing its default port setting. Valid values include: Yes or No
“No” means the default port state cannot be changed (e.g. enable or disabled).
“Yes” means the default port state can be changed and that the port can either be enabled or disabled.
Default Port State: A port is either open, closed or filtered.
Open ports will respond to queries
Closed ports may or may not respond to queries and are only listed when they can be optionally
enabled.
Filtered ports can be open or closed. Filtered UDP ports will not respond to queries. Filtered TCP will
respond to queries, but will not allow connectivity.
Description: Connection details. Add a reference to refer to the Notes section after each table for specifics on
any of the row data, if necessary.
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 4
2.2 Port Tables
Below are the tables which document the port usage for this product.
Table 1. Ports for IP Office Contact Center
Source Destination
Netw ork / Optionally Default
System Port System Port Application Enabled / Port Description
(Configurable (Configurable Protocol Disabled? State
Range) Range)
IP Office Contact SMTP
25 25 TCP Yes Open C3000, SMTP module, Voice Unit
Center
IP Office
SMTP 25 Contact 25 TCP Yes Open C3000, SMTP module, Voice Unit
Center
IP Office Contact POP3
110 110 TCP Yes Open POP3IMAP4_connector (POP3)
Center
IP Office
POP3 110 Contact 110 TCP Yes Open POP3IMAP4_connector (POP3)
Center
IP Office Contact IMAP POP3IMAP4_connector (IMAP)
143 143 TCP Yes Open
Center
IP Office POP3IMAP4_connector (IMAP)
IMAP 143 Contact 143 TCP Yes Open
Center
IP Office Contact LDAP Address Book Server/ Address Book Admin for
389 389 TCP Yes Open
Center LDAP import
IP Office Contact SMTPS
465 465 TCP Yes Open C3000, SMTP module, Voice Unit
Center
IP Office
SMTPS 465 Contact 465 TCP Yes Open C3000, SMTP module, Voice Unit
Center
IP Office Contact SMTP
587 587 TCP Yes Open C3000, SMTP module, Voice Unit
Center
IP Office
SMTP 587 Contact 587 TCP Yes Open C3000, SMTP module, Voice Unit
Center
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 5
Source Destination
Netw ork / Optionally Default
System Port System Port Application Enabled / Port Description
(Configurable (Configurable Protocol Disabled? State
Range) Range)
IP Office Contact IMAPS POP3IMAP4_connector (IMAP)
993 993 TCP Yes Open
Center
IP Office POP3IMAP4_connector (IMAP)
IMAPS 993 Contact 993 TCP Yes Open
Center
IP Office Contact POP3S POP3IMAP4_connector (POP3)
995 995 TCP Yes Open
Center
IP Office POP3IMAP4_connector (POP3)
POP3S 995 Contact 995 TCP Yes Open
Center
IP Office Contact SMTP C3000, SMTP module (only used in our Google
2525 2525 TCP Yes Open
Center cloud product - SendGrid)
IP Office CORBA Naming service
User Interface 2809 Contact 2809 TCP Yes Open Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
Center open this port in both direction
IP Office Contact IP Office SIP Signaling (Unsecure – only used in Google
5056 5056 TCP Yes Open
Center Cloud behind firewall)
IP Office Contact IP Office SIP Signaling (unsecure)
5060 5060 TCP Yes Open
Center
IP Office Incoming SIP Extension Signaling
IP Office 5100 Contact 5100 TCP Yes Open
Center
XMPP Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol
IP Office Contact (XMPP) client connection
5222 (External or 5222 TCP Yes Open
Center
IP Office)
XMPP IP Office Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol
(External or 5222 Contact 5222 TCP Yes Open (XMPP) client connection
IP Office) Center
XMPP Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol
IP Office Contact (XMPP) client connection over SSL
5223 (External 5223 TCP Yes Open
Center
Only)
XMPP IP Office Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol
5223 Contact 5223 TCP Yes Open (XMPP) client connection over SSL
(External only) Center
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 6
Source Destination
Netw ork / Optionally Default
System Port System Port Application Enabled / Port Description
(Configurable (Configurable Protocol Disabled? State
Range) Range)
Database Used by Web Admin, TaskReporting view er,
PostgreSQL 5432 5432 TCP Yes Open AddressBook Server, Chat Task Server, C3K
Server, UMR client Adapter
IP Office TCP Server Edition SyncProcess
IP Office Contact HTTP
7070 7070 No Open
Center
HTTPS
IP Office Core WebApplications (multiple applications)
User Interface 8080 Contact 8080 TCP No Open Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
Center open this port in both direction
IP Office Contact IP Office IP500V2 SyncProcess
8443 8443 TCP/HTTPS No Open
Center Core WebApplications (HTTPS Port)
IP Office Contact WebLM WebLM
8443 8443 TCP/HTTPS No Open
Center
WebLM WebLM
User Interface 8443 8443 TCP No Open Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office Contact Watchdog Internal
10001 10001 TCP No Open
Center
IP Office Trace
User Interface 10300 Contact 10300 TCP No Open Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
Center open this port in both direction
IP Office Trace
TTrace Console 10300 Contact 10300 TCP No Open
Center
IP Office Console
TTrace Console 10301 Contact 10301 TCP No Open
Center
IP Office Contact TomCat Web Service Collection
18080 18080 TCP/HTTP No Open
Center
IP Office Contact TomCat Web Service Collection
18443 18443 TCP/HTTPS No Open
Center
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 7
Source Destination
Netw ork / Optionally Default
System Port System Port Application Enabled / Port Description
(Configurable (Configurable Protocol Disabled? State
Range) Range)
Web Admin IP Office TomCat
CRM Connector Contact
Center
Wallboard/DirectWS
WebUI (ChromeApp 28080 28080 TCP/HTTP No Open
and Brow sers)
StatView er
WebChatDialog
Web Admin IP Office TomCat
CRM Connector Contact
Center
Wallboard/DirectWS
WebUI (ChromeApp 28443 28443 TCP/HTTPS No Open
and Brow sers)
StatView er
WebChatDialog
IP Office SIP Extension RTP ports
IP Office 40750-50750 Contact 49152-53247 RTP/UDP No Open
Center
IP Office Autodialer service
Contact Used by IPOCC UI
User Interface 49901 Center 49901 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office database access service
Contact Used by IPOCC UI
User Interface 49906 Center 49906 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office Database access service
Contact Used by IPOCC UI
User Interface 49910 Center 49910 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office callflow configuration
Contact Used by IPOCC UI
User Interface 49919 49919 TCP No Open
Center Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 8
Source Destination
Netw ork / Optionally Default
System Port System Port Application Enabled / Port Description
(Configurable (Configurable Protocol Disabled? State
Range) Range)
IP Office Task Manager service
Contact Used by IPOCC UI
User Interface 49921 Center 49921 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office Internal
IP Office Contact
49922 Contact 49922 TCP No Open UM database access service
Center
Center
IP Office Internal
IP Office Contact
49923 Contact 49923 TCP No Open UM database access service
Center
Center
IP Office Monitoring Service
Contact Used by IPOCC UI
User Interface 49924 Center 49924 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office IPO Taskserver
User Interface 49940 Contact 49940 TCP No Open
Center
IP Office Contact Direct TAPI IP Office port
50796 50796 TCP Yes Open
Center port (secure)
IP Office Contact Direct TAPI IP Office port
50797 50797 TCP Yes Open
Center port
IP Office UI SessionManager (UMR-Client, StatView er,
Contact TRView er)
User Interface 51000 Center 51000 TCP No Open Used by IPOCC UI, Chrome App and WSC
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office Messaging service
51001 - Contact 51001 - Used by IPOCC UI and Chrome App
User Interface Center TCP No Open
51003 51003 Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office UMR Admin
User Interface 51011 Contact 51011 TCP No Open
Center
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 9
Source Destination
Netw ork / Optionally Default
System Port System Port Application Enabled / Port Description
(Configurable (Configurable Protocol Disabled? State
Range) Range)
IP Office User Interface observes Addressbook Admin
Contact Application.
User Interface 51013 Center 51013 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office User Interface observes UMR Textblock Admin
Contact Application.
User Interface 51014 Center 51014 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office Addressbook server
Contact Used by IPOCC UI
User Interface 51015 Center 51015 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office Chat Taskserver
User Interface 52000 Contact 52000 TCP No Open Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
Center open this port in both direction
IP Office WSC DirectoryWS
Web Service
52100-52109 Contact 52100-52109 HTTP No Open
Application
Center
IP Office WSC TaskWS
Web Service
52110-52119 Contact 52110-52119 HTTP No Open
Application
Center
IP Office WSC MonitoringWS
Web Service
52120-52129 Contact 52120-52129 HTTP No Open
Application
Center
IP Office WSC ManagementWS
Web Service
52130-52139 Contact 52130-52139 HTTP No Open
Application
Center
IP Office WSC UMRWS
Web Service
52140-52149 Contact 52140-52149 HTTP No Open
Application
Center
IP Office Contact WebLM Only used in Cloud System
52233 52233 TCP No Open
Center
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 10
Source Destination
Netw ork / Optionally Default
System Port System Port Application Enabled / Port Description
(Configurable (Configurable Protocol Disabled? State
Range) Range)
IP Office Report generator service
Contact Used by IPOCC UI and Chrome App
User Interface 53002 Center 53002 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office Media Store database Server
User Interface 53009 Contact 53009 TCP No Open Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
Center open this port in both direction
IP Office Customer history view
Contact Used by IPOCC UI
User Interface 53010 Center 53010 TCP No Open
Using CORBA Bidirectional GIOP. Firew alls must
open this port in both direction
IP Office Used by Wallboard
Wallboard 55100 Contact 55100 TCP No Open
Center
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 11
2.3 Port Table Changes
Table 2. Port Changes From IP Office Contact Center 9.1.2.0 to 9.1.6.0
Source Destination
Netw ork / Optionally Default
System Port System Port Application Enabled / Port Description
(Configurable (Interface) Protocol Disabled? State
Range)
IP Office Contact SMTP C3000, SMTP module (only used in our Google
2525 2525 TCP Yes Open
Center cloud product - SendGrid)
WebUI (Brow sers) IP Office Tomcat – Agent Web UI and Customer Web Page
28080 Contact 28080 TCP/HTTP No Open chat
WebChatDialog Center
WebUI (Brow sers) IP Office Tomcat - Agent Web UI and Customer Web Page
28443 Contact 28443 TCP/HTTPS No Open chat
WebChatDialog Center
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 12
3. Port Usage Diagram
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 13
Appendix A: Overview of TCP/IP Ports
What are ports and how are they used?
TCP and UDP use ports (defined at http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers) to route traffic
arriving at a particular IP device to the correct upper layer application. These ports are logical descriptors
(numbers) that help devices multiplex and de-multiplex information streams. Consider your desktop PC.
Multiple applications may be simultaneously receiving information. In this example, email may use
destination TCP port 25, a browser may use destination TCP port 80 and a telnet session may use
destination TCP port 23. These logical ports allow the PC to de-multiplex a single incoming serial data
packet stream into three mini-streams inside the PC. Furthermore, each of the mini-streams is directed to
the correct high-level application because the port numbers identify which application each data mini-
stream belongs. Every IP device has incoming (Ingress) and outgoing (Egress) data streams.
Ports are used in TCP and UDP to name the ends of logical connections which carry data flows. TCP
and UDP streams have an IP address and port number for both source and destination IP devices. The
pairing of an IP address and a port number is called a socket (discussed later). Therefore, each data
stream is uniquely identified with two sockets. Source and destination sockets must be known by the
source before a data stream can be sent to the destination. Some destination ports are “open” to receive
data streams and are called “listening” ports. Listening ports actively wait for a source (client) to make
contact to a destination (server) using a specific port that has a known protocol associate with that port
number. HTTPS, as an example, is assigned port number 443. When a destination IP device is
contacted by a source device using port 443, the destination uses the HTTPS protocol for that data
stream conversation.
Port Type Ranges
Port numbers are divided into three ranges: Well Known Ports, Registered Ports, and Dynamic Ports
(sometimes called Private Ports).
Well Known Ports are those numbered from 0 through 1023.
Registered Ports are those numbered from 1024 through 49151
Dynamic Ports are those numbered from 49152 through 65535
The Well Known and Registered ports are assigned by IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) and
are found here: http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers.
Well Known Ports
For the purpose of providing services to unknown clients, a service listen port is defined. This port is
used by the server process as its listen port. Common services often use listen ports in the well known
port range. A well known port is normally active meaning that it is “listening” for any traffic destined for a
specific application. For example, well known port 23 on a server is actively waiting for a data source to
contact the server IP address using this port number to establish a Telnet session. Well known port 25 is
waiting for an email session, etc. These ports are tied to a well understood application and range from 0
to 1023.
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 14
In UNIX and Linux operating systems, only root may open or close a well-known port. Well Known Ports
are also commonly referred to as “privileged ports”.
Registered Ports
Unlike w ell know n ports, these ports are not restricted to the root user. Less common services register ports in this range. Avaya uses ports
in this range for call control. Some, but not all, ports used by Avaya in this range include: 1719/1720 for H.323, 5060/5061 for SIP, 2944 for
H.248 and others. The registered port range is 1024 – 49151. Even though a port is registered w ith an application name, industry often uses
these ports for different applications. Conflicts can occur in an enterprise w hen a port w ith one meaning is used by tw o servers with different
meanings.
Dynamic Ports
Dynamic ports, sometimes called “private ports”, are available to use for any general purpose. This means there are no meanings associated
w ith these ports (similar to RFC 1918 IP Address Usage). These are the safest ports to use because no application types are linked to these
ports. The dynamic port range is 49152 – 65535.
Sockets
A socket is the pairing of an IP address w ith a port number. An example w ould be 192.168.5.17:3009, w here 3009 is the socket number
associated w ith the IP address. A data flow, or conversation, requires two sockets – one at the source device and one at the destination
device. The data flow then has two sockets with a total of four logical elements. Each data flow must be unique. If one of the four elements is
unique, the data flow is unique. The follow ing three data flow s are uniquely identified by socket number and/or IP address.
Data Flow 1: 172.16.16.14:1234 - 10.1.2.3:2345
Data Flow 2: 172.16.16.14.1235 - 10.1.2.3:2345
Data Flow 3: 172.16.16.14:1234 - 10.1.2.4:2345
Data flow 1 has tw o different port numbers and tw o different IP addresses and is a valid and typical socket pair.
Data flow 2 has the same IP addresses and the same port number on the second IP address as data flow 1, but since the port number on the
first socket differs, the data flow is unique.
Therefore, if one IP address octet changes, or one port number changes, the data flow is unique.
Socket Example Diagram
Client HTTP-Get Source 192.168.1.10:1369 Destination 10.10.10.47:80 Web Server
TCP-info Destination 192.168.1.10:1369 Source 10.10.10.47:80
Figure 1. Socket example showing ingress and egress data flows from a PC to a web server
Notice the client egress stream includes the client’s source IP and socket (1369) and the destination IP
and socket (80). The ingress stream has the source and destination information reversed because the
ingress is coming from the server.
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 15
Understanding Firewall Types and Policy Creation
Firewall Types
There are three basic firewall types:
Packet Filtering
Application Level Gateways (Proxy Servers)
Hybrid (Stateful Inspection)
Packet Filtering is the most basic form of the firewalls. Each packet that arrives or leaves the network has
its header fields examined against criterion to either drop the packet or let it through. Routers configured
with Access Control Lists (ACL) use packet filtering. An example of packet filtering is preventing any
source device on the Engineering subnet to telnet into any device in the Accounting subnet.
Application level gateways (ALG) act as a proxy, preventing a direct connection between the foreign
device and the internal destination device. ALGs filter each individual packet rather than blindly copying
bytes. ALGs can also send alerts via email, alarms or other methods and keep log files t o track
significant events.
Hybrid firewalls are dynamic systems, tracking each connection traversing all interfaces of the firewall and
making sure they are valid. In addition to looking at headers, the content of the packet, up through the
application layer, is examined. A stateful inspection firewall also monitors the state of the connection and
compiles the information in a state table. Stateful inspection firewalls close off ports until the connection
1
to the specific port is requested. This is an enhancement to security against port scanning .
Firewall Policies
The goals of firewall policies are to monitor, authorize and log data flows and events. They also restrict
access using IP addresses, port numbers and application types and sub-types.
This paper is focused with identifying the port numbers used by Avaya products so effective firewall
policies can be created without disrupting business communications or opening unnecessary access into
the network.
Knowing that the source column in the following matrices is the socket initiator is key in building some
types of firewall policies. Some firewalls can be configured to automatically create a return path through
the firewall if the initiating source is allowed through. This option removes the need to enter two firewall
rules, one for each stream direction, but can also raise security concerns.
Another feature of some firewalls is to create an umbrella policy that allows access for many independent
data flows using a common higher layer attribute. Finally, many firewall policies can be avoided by
placing endpoints and the servers that serve those endpoints in the same firewall zone.
1
The act of systematically scanning a computer's ports. Since a port is a place where information goes into and out of a
computer, port scanning identifies open doors to a computer. Port scanning has legitimate uses in managing networks, but
port scanning also can be malicious in nature if someone is looking for a weakened access point to break into your computer.
Avaya – Proprietary
Use pursuant to the terms of your signed agreement or Avaya policy.
February 2016 Avaya Port Matrix: IP Office Contact Center 9.1.6.0 16
You might also like
- Valvoline Product Catalog 2015 LRDocument59 pagesValvoline Product Catalog 2015 LRJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager TCP and UDP Port UsageDocument18 pagesCisco Unified Communications Manager TCP and UDP Port UsageJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Liqui Moly P001117 Long-Life-Antifreeze - Summer-CoolantDocument1 pageLiqui Moly P001117 Long-Life-Antifreeze - Summer-CoolantJames HavocNo ratings yet
- General MaintenanceDocument14 pagesGeneral MaintenanceJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Manual Transaxle: Precaution Components RepairDocument40 pagesManual Transaxle: Precaution Components RepairJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 5Document60 pagesCisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 5James HavocNo ratings yet
- MaintenanceDocument42 pagesMaintenanceJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Installation GuideDocument132 pagesInstallation GuideJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Engine Mechanical: Precautions and Preparations Timing ChainDocument88 pagesEngine Mechanical: Precautions and Preparations Timing ChainJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Status and Future Scope of Floriculture in SLDocument10 pagesStatus and Future Scope of Floriculture in SLJames HavocNo ratings yet
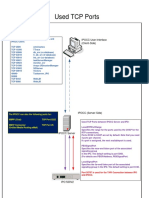
- Used TCP Ports IPOCCDocument1 pageUsed TCP Ports IPOCCJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Ec QG16Document320 pagesEc QG16James Havoc100% (1)
- Avaya Switch - NN47203-300!02!01 - QuickInstallGuideDocument2 pagesAvaya Switch - NN47203-300!02!01 - QuickInstallGuideJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Ports IP OfficeDocument3 pagesPorts IP OfficeJesús CHuy Jiménez RuizNo ratings yet
- DC Motor EMI SuppressionDocument37 pagesDC Motor EMI SuppressionJames HavocNo ratings yet
- ADSL PresentationDocument14 pagesADSL PresentationJames HavocNo ratings yet
- Acer At2621Document34 pagesAcer At2621James HavocNo ratings yet
- China - Haier HT 2199 tnp87ck38n tb1238n La4275 La7830Document1 pageChina - Haier HT 2199 tnp87ck38n tb1238n La4275 La7830James HavocNo ratings yet
- Technics Sa Dx950Document54 pagesTechnics Sa Dx950James HavocNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Anonymous IRC, Track Defenses, Hacking and PrivacyDocument16 pagesAnonymous IRC, Track Defenses, Hacking and PrivacyRafael BressanNo ratings yet
- RAC 12c OptimizationDocument65 pagesRAC 12c OptimizationBikuNo ratings yet
- DVR 4 Canales CNB HDF1212DVDocument1 pageDVR 4 Canales CNB HDF1212DVTecnoSmartNo ratings yet
- Building Service PDFDocument35 pagesBuilding Service PDFamirahNo ratings yet
- Manufactured by Smith & Company 1361 Newton Street Los Angeles, California 90021 TEL: 213-748-6361 FAX:213-748-1683Document45 pagesManufactured by Smith & Company 1361 Newton Street Los Angeles, California 90021 TEL: 213-748-6361 FAX:213-748-1683Jeffrey Michael AtencioNo ratings yet
- Cloudera HiveDocument106 pagesCloudera HivediegocueNo ratings yet
- Precedent StudyDocument6 pagesPrecedent StudyNathawut TangjitpeanshokeNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint DocumentationDocument42 pagesFingerprint DocumentationHen DryNo ratings yet
- Iran (Persian) Architecture & Folk Arts: Shan Jasper O. TorresDocument24 pagesIran (Persian) Architecture & Folk Arts: Shan Jasper O. TorresGlenda DenosoNo ratings yet
- Daewoo FR - 530kt-fr - 590kt (ET)Document36 pagesDaewoo FR - 530kt-fr - 590kt (ET)khaled1512No ratings yet
- Linux Ethernet Bonding HOWTODocument45 pagesLinux Ethernet Bonding HOWTOjwtvenNo ratings yet
- CMA CGM Full Fledge PDFDocument135 pagesCMA CGM Full Fledge PDFNaeem ChNo ratings yet
- Android Custom GridView With Images and TextDocument8 pagesAndroid Custom GridView With Images and TextKurniawan PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Lighting System DesignDocument2 pagesLighting System DesignReybin AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor Plan Second Floor Plan: Project Tittle: Approved By: Sheet Contents: Sheet No.: RevisionsDocument16 pagesGround Floor Plan Second Floor Plan: Project Tittle: Approved By: Sheet Contents: Sheet No.: RevisionsMaria Christina Abadu TagacayNo ratings yet
- RFC3227 - Guidelines For Evidence Collection and ArchivingDocument10 pagesRFC3227 - Guidelines For Evidence Collection and ArchivingPyroargerNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Concepts of ABAP PDFDocument16 pagesObject-Oriented Concepts of ABAP PDFPrerna DesaiNo ratings yet
- A Novel Peer-To-Peer Payment System: Despoina PalakaDocument6 pagesA Novel Peer-To-Peer Payment System: Despoina PalakaRubinaNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 1Document7 pagesIndividual Assignment 1Yuevitra KalaiselvanNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Study of Pedestrian Movement Over Foot Over BridgesDocument9 pagesPreliminary Study of Pedestrian Movement Over Foot Over BridgesAshis karmakarNo ratings yet
- E Commerce NotesDocument52 pagesE Commerce NoteschsureshchandraNo ratings yet
- Rescue ElevatorDocument3 pagesRescue Elevatorthanggimme.phanNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Drawing Strategy - Diagram Diaries Update 0511208 PDFDocument194 pagesConceptual Drawing Strategy - Diagram Diaries Update 0511208 PDFEndyYudhoPrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 9 - Dynamic VoiceXML and JSPDocument19 pages9 - Dynamic VoiceXML and JSPAjay MishraNo ratings yet
- The Hindu - Property Plus Chennai - Planning Construction CostsDocument4 pagesThe Hindu - Property Plus Chennai - Planning Construction CostsAaditya Pratap SanyalNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument1 pageEducationAnonymous N0v1qjAZyNo ratings yet
- Gabinetes para Area de ServiçoDocument9 pagesGabinetes para Area de Serviçohd1000No ratings yet
- What Light Source To Choose?: IncandescentDocument4 pagesWhat Light Source To Choose?: IncandescentSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- PoC For MDMDocument27 pagesPoC For MDMsvmglpNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeosyntheticsDocument45 pagesIntroduction To GeosyntheticsShakti Dubey100% (1)