Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supraspinatus muscle anatomy and trigger points
Uploaded by
Daniel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views1 pagerotator cuff lab notes
Original Title
Supra Spin at Us
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentrotator cuff lab notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views1 pageSupraspinatus muscle anatomy and trigger points
Uploaded by
Danielrotator cuff lab notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
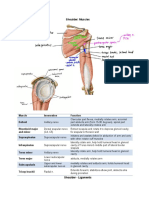
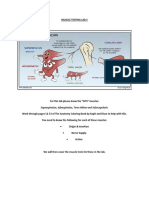
O: Supraspinous fossa of
scapula
SUPRASPINATUS
I: Greater tuberosity of humerus
(superior facet)
A: Abduction of arm.
N: Suprascapular nerve; C5. C6
TrPs: Concentrating in the mid-
deltoid Often extending down the
arm and forearm, sometimes
focuses over the lateral
epicondyle. This helps to
distinguish supraspinatus from
infraspinatus TrPs.
NOTES ON MM TEST:
NOTES:
The middle deltoid, upper trapezius and rhomboids are synergistic with the supraspinatus during abduction of the arm.
The infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis assist the supraspinatus to position and stabilise the head of the humerus accurately in the
glenoid fossa during abduction.
The latissimus dorsi, teres major and lower fibres of the pectoralis major can act as antagonists to the supraspinatus.
You might also like
- UPPER EX - UNODocument16 pagesUPPER EX - UNOrsbagtasNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action: Pectoralis MajorDocument7 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action: Pectoralis MajorChinnyChin ChynNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Shoulder and ArmDocument2 pagesMuscles of Shoulder and ArmEdreyn DellosaNo ratings yet
- The Upper ExtremityDocument9 pagesThe Upper ExtremityHiruzaminNo ratings yet
- 01 Muscle Tables Upper LimbDocument7 pages01 Muscle Tables Upper LimbhawkreadNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Muscles & AnatomyDocument4 pagesShoulder Muscles & AnatomySheila Setiawati TanzilNo ratings yet
- Muscles of the Upper Limb: Anatomy and ActionsDocument7 pagesMuscles of the Upper Limb: Anatomy and ActionsKris GulleyNo ratings yet
- Back, Upper Limb, Thorax and Abdomen Muscles, Nerves and ArteriesDocument4 pagesBack, Upper Limb, Thorax and Abdomen Muscles, Nerves and Arteries品錞RenéeNo ratings yet
- Muscle Page Upper Trapezius 1Document2 pagesMuscle Page Upper Trapezius 1Yuleidy LopezNo ratings yet
- 03 Muscles of Upper LimbDocument40 pages03 Muscles of Upper LimbbnvjNo ratings yet
- Muscles of RabbitDocument19 pagesMuscles of RabbitshanleymojaresNo ratings yet
- Regio ColliDocument38 pagesRegio ColliKrisna MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy HWDocument4 pagesAnatomy HWTassnime SebaeiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderDocument10 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderAdam IrsyaddyraNo ratings yet
- Muscle origins insertions actions and namesDocument2 pagesMuscle origins insertions actions and namesAlyssa JacobsNo ratings yet
- Leher DAN PunggungDocument38 pagesLeher DAN Punggung21-028 Farrahany Diva Az ZahraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Hand 30pDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Hand 30pBui Nguyen Hoang HaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Hand 30pDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Hand 30pBui Nguyen Hoang HaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Hand 30pDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Hand 30pSu SuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Hand 30pDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Hand 30pnote9 DataNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Hand 30p PDFDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Hand 30p PDFNguyễn Thị Hồng Khánh100% (2)
- Anatomy of The Hand 30pDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Hand 30pton tai khongNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Chart Upper ExtremityDocument12 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Chart Upper ExtremityKaren ManlapazNo ratings yet
- UL Bone AnatomyDocument34 pagesUL Bone AnatomyMejNo ratings yet
- Upper Extermity: A. SkeletalDocument24 pagesUpper Extermity: A. SkeletalDinda BiolawatikaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Chart Muscles of Upper Extremity Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action InnervationDocument11 pagesMuscle Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Chart Muscles of Upper Extremity Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action InnervationNurul Afiqah Fattin AmatNo ratings yet
- 1D-19 GRSANA Reviewer 1.04 - Muscles of The Shoulder RegionDocument16 pages1D-19 GRSANA Reviewer 1.04 - Muscles of The Shoulder RegionShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- U.L MusclesDocument4 pagesU.L Muscles54ytkq9mtgNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Upper Limb: Wang HaoDocument22 pagesMuscles of Upper Limb: Wang Haoapi-19641337100% (2)
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomyfarahjurdi8No ratings yet
- Palm and Joints of HandDocument33 pagesPalm and Joints of HandGaurav ThapaNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 UL Forarm Anterior CompartmentDocument32 pagesLec 11 UL Forarm Anterior CompartmenthusseinNo ratings yet
- Origins and InsertionsDocument12 pagesOrigins and InsertionsFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Surface Landmarks and Body PositionsDocument2 pagesSurface Landmarks and Body PositionsLesNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Arm & ShoulderDocument4 pagesMuscles of Arm & ShoulderDavid BadaruNo ratings yet
- Shoulder: Rhomboids and Levator Scapulae Levator ScapulaeDocument4 pagesShoulder: Rhomboids and Levator Scapulae Levator ScapulaeHilary ByrthNo ratings yet
- Body Parts and Functions Pictorial GuideDocument8 pagesBody Parts and Functions Pictorial GuideKent GaliciaNo ratings yet
- UE and LE AnaDocument123 pagesUE and LE AnaPatrick JohnNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Muscles, Vessels and Nerves 2021 PDFDocument96 pagesUpper Limb Muscles, Vessels and Nerves 2021 PDFGeetNo ratings yet
- Chart Muscles For Small Animal ForelimbDocument7 pagesChart Muscles For Small Animal ForelimbAlliNo ratings yet
- Muscles of UlpDocument40 pagesMuscles of UlpAdinda DindaNo ratings yet
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Document6 pagesSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴No ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy Lab ChecklistDocument2 pagesGross Anatomy Lab ChecklistKeyla M Ramos PrattsNo ratings yet
- ANPH 111 LAB REPORT MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument6 pagesANPH 111 LAB REPORT MUSCULAR SYSTEMHannah MaeNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Mnemonics 2Document8 pagesUpper Limb Mnemonics 2KaiyoorNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic For Forearm Muscles and BoneDocument2 pagesMnemonic For Forearm Muscles and BoneLaura Tapia89% (28)
- Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesMuscular SystemKylaNicole SierrasNo ratings yet
- MoinaDocument43 pagesMoinaMoo MinNo ratings yet
- Pulse PointsDocument4 pagesPulse PointsZnieh ZniehNo ratings yet
- Innervations of Muscles TableDocument22 pagesInnervations of Muscles TableEslie NájeraNo ratings yet
- Review List of Structures WebsiteDocument4 pagesReview List of Structures WebsiteboissonfishNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Circulation and NervesDocument35 pagesUpper Extremity Circulation and NervesMarie100% (1)
- Anatomy Exam 1 Review - Muscles of the Back, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm & HandDocument27 pagesAnatomy Exam 1 Review - Muscles of the Back, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm & Handgdubs215No ratings yet
- Bones of The Thoracic LimbDocument10 pagesBones of The Thoracic LimbDelfin UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Fascia of Upper LimbDocument4 pagesFascia of Upper Limb김원재No ratings yet
- List of Mnemonics For Upper Limbs-1Document6 pagesList of Mnemonics For Upper Limbs-1chitrojan142269% (13)
- Clavicular Part: Flexes and Acromial Part: AbductsDocument1 pageClavicular Part: Flexes and Acromial Part: AbductsMihaelaNo ratings yet
- Middle and Lower TrapsDocument1 pageMiddle and Lower TrapsDanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 4Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 4DanielNo ratings yet
- CoracobrachialisDocument1 pageCoracobrachialisDanielNo ratings yet
- Pectoralis MinorDocument1 pagePectoralis MinorDanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 8: (1) Tibialis Anterior (2) Tibialis Posterior (3) REVIEW: Glute Max, Glute Med and MinDocument1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 8: (1) Tibialis Anterior (2) Tibialis Posterior (3) REVIEW: Glute Max, Glute Med and MinDanielNo ratings yet
- Erector SpinaeDocument1 pageErector SpinaeDanielNo ratings yet
- Teres MinorDocument1 pageTeres MinorDanielNo ratings yet
- Upper TrapeziusDocument1 pageUpper TrapeziusDanielNo ratings yet
- Upper TrapeziusDocument1 pageUpper TrapeziusDanielNo ratings yet
- DeltoidDocument1 pageDeltoidDanielNo ratings yet
- Tricep BrachiiDocument1 pageTricep BrachiiDanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 4Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 4DanielNo ratings yet
- The IliopsoasDocument1 pageThe IliopsoasDanielNo ratings yet
- Upper TrapeziusDocument1 pageUpper TrapeziusDanielNo ratings yet
- Coraco BrachialisDocument1 pageCoraco BrachialisDanielNo ratings yet
- Biceps BrachiiDocument1 pageBiceps BrachiiDanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 4Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 4DanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 4Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 4DanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 4Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 4DanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 3Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 3DanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 4Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 4DanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 6Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 6DanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 2Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 2DanielNo ratings yet
- Muscle Testing Lab 1Document1 pageMuscle Testing Lab 1DanielNo ratings yet
- The Four Layers of Strength PDFDocument73 pagesThe Four Layers of Strength PDFWil Arz100% (1)
- Way of The Warrior Kid QuizDocument6 pagesWay of The Warrior Kid QuizKelly Collins100% (2)
- An Exclusive Look Into My Daily Fitness and Productivity RoutineDocument2 pagesAn Exclusive Look Into My Daily Fitness and Productivity RoutineDanielNo ratings yet
- Ric Mma PDFDocument11 pagesRic Mma PDFDaniel100% (1)
- A Book For The Seriously StressedDocument2 pagesA Book For The Seriously StressedDanielNo ratings yet