Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Institute of Nursing: Far Eastern University
Uploaded by
aleccespiritu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
403 views3 pagesHeart failure, also called congestive heart failure, occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. Causes of heart failure include congenital heart disease, rheumatic heartdisease, endocarditis. Pulmonary edema, pulmonary emboli, refractory heart failure, and myocardial failure. After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient was able to display vital signs within acceptable limits, dysrhythmias controlled and no symptoms of failure
Original Description:
Original Title
ncp CO
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHeart failure, also called congestive heart failure, occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. Causes of heart failure include congenital heart disease, rheumatic heartdisease, endocarditis. Pulmonary edema, pulmonary emboli, refractory heart failure, and myocardial failure. After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient was able to display vital signs within acceptable limits, dysrhythmias controlled and no symptoms of failure
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
403 views3 pagesInstitute of Nursing: Far Eastern University
Uploaded by
aleccespirituHeart failure, also called congestive heart failure, occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. Causes of heart failure include congenital heart disease, rheumatic heartdisease, endocarditis. Pulmonary edema, pulmonary emboli, refractory heart failure, and myocardial failure. After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient was able to display vital signs within acceptable limits, dysrhythmias controlled and no symptoms of failure
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Far Eastern University
Institute of Nursing
Nursing Care Plan
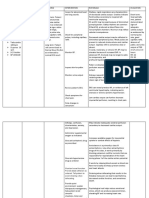
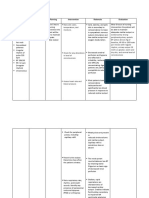
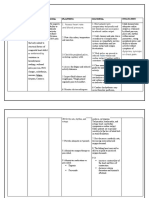
Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Objectives
Decreased cardiac Heart failure, After 8 hours of After the
output related to also called Nursing nursing
altered myocardial congestive intervention the intervention
contractility heart failure, patient will the patient
/inotropic changes occurs when display vital signs was able to
as manifested by cardiac output is within acceptable display vital
tachycardia/dysrhy inadequate to limits, signs within
thmias. meet the dysrhythmias acceptable
metabolic controlled and no limits,
SUBJECTIVE: demands of the symptoms of dysrhythmia
body. The heart failure. s controlled
The client verbalized rate increases and no
that “minsan as a Objectives: symptoms of
nahihirapan ako compensatory After the nursing Auscultate Tachycardia failure. The
huminga at mabilis mechanism to intervention, the apical is usually goal was
ako mapagod”. increase cardiac client will be able: pulse; present even met.
output, and assess at rest to
“Minsan ay sumasakit vasoconstriction a. To display heart rate, compensate
din ang ulo ko at occurs to try to hemodynami and for decreased
nahihilo”. maintain blood c stability. rhythm. ventricular
pressure. contractility.
OBJECTIVE: Eventually, the
chronic increase Pallor is an
Cool, clammy in preload and Inspect skin indicative of
skin after load for pallor, diminished
(+) Fatigue contributes to cyanosis. peripheral
(+) Shortness chamber dilation perfusion
of breath and secondary to
hyperthrophy, inadequate
Measurement: worsening heart cardiac
failure. output,
Underlying
RR = 26cpm causes of heart vasoconstricti
CR = 112bpm failure include on, and
TEMP = 36.2°C congenital heart anemia.
BP = 140/80mmHg disease, Cyanosis may
rheumatic develop in
heartdisease, refractory
endocarditis, heart failure.
myocarditis, and Dependent
non areas are
cardiovascular often blue or
causes such as, mottled as
chronic venous
pulmonary congestion
disease, various Monitor increases.
metabolic urine
diseases, and output, Urine output
anemia. noting is usually
Complications of decreasing decreased
heart failure output and during the
include dark or day because
pneumonia, concentrate of fluid shifts
pulmonary d urine. into tissues
edema, but may be
pulmonary increased at
emboli, night because
refractory heart fluid returns
failure, and to circulation
myocardial b. Demonstrate when patient
failure. an increase Note is recumbent.
in activity changes in
tolerance. sensorium. May indicate
inadequate
cerebral
perfusion
secondary to
decreased
cardiac
Provide output.
quiet
environmen Psychological
t. rest help
reduce
emotional
stress, which
c. Participate in can produce
activities that vasoconstricti
reduce the on, elevating
workload of BP and
the heart. increasing
Administer heart rate or
supplement work.
al oxygen
as Increases
indicated. available
oxygen for
myocardial
uptake to
combat
Administer effects of
diuretics as hypoxia or
prescribed. ischemia.
Diuretics, in
conjunction
with
restriction of
dietary
sodium and
fluids, often
lead to
clinical
improvement
in patients
with heart
failure.
You might also like
- Complaint at Law FILEDDocument12 pagesComplaint at Law FILEDRobert GarciaNo ratings yet
- Akt Notes VtsDocument50 pagesAkt Notes VtsMin Maw100% (1)
- Internal Medicine NotesDocument54 pagesInternal Medicine NotesHayley Welsh75% (4)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MCQs in Intensive Care MedicineDocument288 pagesMCQs in Intensive Care MedicineHiago Sousa90% (10)
- Afib NCPDocument3 pagesAfib NCPGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionJessy MalloNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument11 pagesCardiac Study Guidejenwiley318096% (73)
- Organo-Therapy Handbook 2Document5 pagesOrgano-Therapy Handbook 2kaswalder100% (1)
- Nursingcrib Com Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure PDFnadzwa velascoNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Atherosclerosis 1. Risk Factors of AtherosclerosisDocument5 pagesCase Study of Atherosclerosis 1. Risk Factors of AtherosclerosisCarly Beth Caparida LangerasNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DisorderDocument4 pagesCongenital Heart DisorderElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure BloodDocument27 pagesCongestive Heart Failure BloodmarvinawatiNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure in Dogs: 6 Practical Tips From CardiologistsDocument6 pagesHeart Failure in Dogs: 6 Practical Tips From CardiologistsJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) : Causes DiagnosisDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) : Causes DiagnosisSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Nursing Care Plans - 15 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsDocument13 pagesHeart Failure Nursing Care Plans - 15 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsJOSHUA DICHOSONo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot NCPDocument6 pagesTetralogy of Fallot NCPHarlene Joyce ReyNo ratings yet
- Blood: Heart Failure (HF) or (CHF) Is A PhysiologicDocument11 pagesBlood: Heart Failure (HF) or (CHF) Is A PhysiologicSeptika LestariNo ratings yet
- Chronic Heart Failure: I. Brief Definition Iv. Disease ProcessDocument12 pagesChronic Heart Failure: I. Brief Definition Iv. Disease ProcessJennifer BeguinwaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPMae Denn LabordoNo ratings yet
- Jas AssignmentDocument3 pagesJas AssignmentjasperNo ratings yet
- 7MB, Ac, 1PCSDocument1 page7MB, Ac, 1PCSRicko CiadyNo ratings yet
- Jas AssignmentDocument3 pagesJas AssignmentjasperNo ratings yet
- Trans Cardio ComplicationsDocument4 pagesTrans Cardio ComplicationsNishina Aicy ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document4 pagesActivity 5AngieNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFdubsNo ratings yet
- B. Create Your Concept Map of The Disorder. Use A Separate Paper For This. Use Short Coupon Bond and Draw Your Concept Map Using This FormatDocument5 pagesB. Create Your Concept Map of The Disorder. Use A Separate Paper For This. Use Short Coupon Bond and Draw Your Concept Map Using This FormatPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- NCP CHF Er SettingDocument9 pagesNCP CHF Er SettingroseasNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Hypotension Is The Result of AnDocument4 pagesDialysis Hypotension Is The Result of AnCathy ManicadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AnswerDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Answercoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure & Cardiac Arrest: Rony YuliwansyahDocument92 pagesHeart Failure & Cardiac Arrest: Rony YuliwansyahSasha ManoNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine NotesDocument54 pagesInternal Medicine NotesKiara Govender100% (1)
- (Clonidine) : Drug Class: Ates Alpha-Adrenoceptors in The Brain Stem. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate Frequent LyDocument3 pages(Clonidine) : Drug Class: Ates Alpha-Adrenoceptors in The Brain Stem. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate Frequent LyKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Increased Size of Legs. Achy LegsDocument8 pagesIncreased Size of Legs. Achy LegsMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageRationale EvaluationAshraf DalumaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGDocument11 pagesAssessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument11 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PDFpriyanka bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputRae AnnNo ratings yet
- LT ShockDocument26 pagesLT ShockLong LieNo ratings yet
- Actual Nursing Care Plan #1: Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument7 pagesActual Nursing Care Plan #1: Deficient Fluid VolumeAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Objective DataDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Objective DataMoonNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureDocument5 pages2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureLovely CacapitNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Heart FailureDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Heart FailureLynx Kee Bayating100% (1)
- HandoutDocument1 pageHandoutKat AñosaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing - Responses To Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument23 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - Responses To Altered Tissue PerfusionLouise NicoleNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy PathogenesisDocument3 pagesCardiomyopathy PathogenesisThrift AdvisoryNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- P 3a Gagal JTGDocument35 pagesP 3a Gagal JTGAnaMariyaMaNo ratings yet
- 109 FullDocument8 pages109 FullBinod KumarNo ratings yet
- In Premature Ventricular Complex, An Impulse That Starts in A Ventricle and Is Conducted Through The Ventricles Before The Next Normal SinusDocument7 pagesIn Premature Ventricular Complex, An Impulse That Starts in A Ventricle and Is Conducted Through The Ventricles Before The Next Normal SinushelloaNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Learning Cardiovascular System: 2nd GroupDocument47 pagesProblem Based Learning Cardiovascular System: 2nd GroupClaudia Narinda R. PNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade 2Document8 pagesCardiac Tamponade 2jelenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNo ratings yet
- Handout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Document7 pagesHandout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Orlyn Joy TanaweNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCDocument25 pagesCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCYUSRIL ZUMADINSYAHNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document2 pagesNCP 1Momshie SyNo ratings yet
- Icu 4Document7 pagesIcu 4GemilleDaphneAndradaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Pharmacology s2t2 HeartfailureDocument6 pages2022 Pharmacology s2t2 Heartfailurejed larsen capulong gavinoNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- '07 Sullivan CDocument32 pages'07 Sullivan CGeo NavarroNo ratings yet
- A Patient With Oedema PresentationDocument35 pagesA Patient With Oedema PresentationWasswaNo ratings yet
- Acute Hypertension-Hypertensive Urgency and Hypertensive EmergencyDocument13 pagesAcute Hypertension-Hypertensive Urgency and Hypertensive EmergencyAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Child With Red UrineDocument4 pagesChild With Red UrineZul Hisyam FikriNo ratings yet
- Atenolol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAtenolol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Pulmonary and Critical Care MnemonicsDocument10 pagesPulmonary and Critical Care MnemonicsnmahpbooksNo ratings yet
- Thyroid StormDocument7 pagesThyroid StormTrisha Anne SelvarajNo ratings yet
- New DOCX DocumentDocument2 pagesNew DOCX DocumentPunjabi FootballNo ratings yet
- 1047Document1,149 pages1047MANG82% (11)
- Postpartum Maternal BradycardiaDocument27 pagesPostpartum Maternal BradycardiaVero GlzNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Heart DiseaseDocument18 pagesHypertensive Heart DiseaseKaye ViolaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiac AnamnesisDocument3 pagesPediatric Cardiac Anamnesissofia butron friasNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Congestive Heart FailureDocument7 pagesCase Study: Congestive Heart FailureXI-E / 21 / MARY TRIANANo ratings yet
- History Taking and Ce of Cardiac PatientsDocument89 pagesHistory Taking and Ce of Cardiac Patientsapi-3858544100% (1)
- Review Jurnal ProcainamidDocument9 pagesReview Jurnal ProcainamidEko FebryandiNo ratings yet
- Type A Choice Questions (Only One Answer Is Correct) : A. B. C. D. EDocument10 pagesType A Choice Questions (Only One Answer Is Correct) : A. B. C. D. ERAED GhunaimNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: S.PavithraDocument20 pagesObstructive Sleep Apnoea: S.PavithraSyed Mujtaba Hussain RazviNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic FeverDocument87 pagesRheumatic FeverFarida Mawaddah Husna100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Disorders LectureDocument18 pagesCardiovascular Disorders LectureCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- Krok 19 20 21 - CompressedDocument148 pagesKrok 19 20 21 - CompressedPaulNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea On Exertion - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesDyspnea On Exertion - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfyohanNo ratings yet
- CCRN CardiacDocument39 pagesCCRN CardiacMike100% (5)
- Resident Survival Guide: (Include Ranges of Any Abnormal Vital Signs But Also Include The Current Value For All Vitals.)Document104 pagesResident Survival Guide: (Include Ranges of Any Abnormal Vital Signs But Also Include The Current Value For All Vitals.)scalixto100% (1)
- Peny Jantung PDFDocument18 pagesPeny Jantung PDFErna Jovem GluberryNo ratings yet
- SemaglitidDocument5 pagesSemaglitidNguyên PhươngNo ratings yet