Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cranial Nerves Function
Uploaded by
inagasi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views1 pageCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views1 pageCranial Nerves Function
Uploaded by
inagasiCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
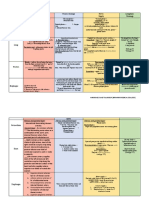
Cranial nerve zero (CN0 is not traditionally New research indicates CN0 may play a role in the detection
on of pheromones [2][3] Linked to olfactory system in
recognized.) human embryos[4
Olfactory nerve Transmits the sense of smell; Located in olfactory foramina in the Cribriform plate of ethmoid
Optic nerve Transmits visual information to the brain; Located in optic canal
Oculomotor nerve Innervates levator palpebrae superioris, superior rectus, medial rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique,
which collectively perform most eye movements; Also innervates m. sphincter pupillae. Located in superior
orbital fissure
Trochlear nerve Innervates the superior oblique muscle, which depresses, rotates laterally (around the optic axis), and intorts
the eyeball; Located in superior orbital fissure
Trigeminal nerve Receives sensation from the face and innervates the muscles of mastication; Located in superior orbital fissure
(ophthalmic nerve - V1), foramen rotundum (maxillary nerve - V2), and foramen ovale (mandibular nerve - V3)
Abducens nerve Innervates the lateral rectus, which abducts the eye; Located in superior orbital fissure
Facial nerve Provides motor innervation to the muscles of facial expression, posterior belly of the digastric muscle, and
stapedius muscle, receives the special sense of taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue, and provides
secretomotor innervation to the salivary glands (except parotid) and the lacrimal gland; Located and runs
through internal acoustic canal to facial canal and exits at stylomastoid foramen
Vestibulocochlear nerve (or auditory- Senses sound, rotation and gravity (essential for balance & movement). More specifically. the vestibular
vestibular nerve or statoacoustic nerve) branch carries impulses for equilibrium and the cochlear branch carries impulses for hearing.; Located in
internal acoustic canal
Glossopharyngeal nerve Receives taste from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue, provides secretomotor innervation to the parotid gland,
and provides motor innervation to the stylopharyngeus. Some sensation is also relayed to the brain from the
palatine tonsils. Sensation is relayed to opposite thalamus and some hypothalamic nuclei. Located in jugular
foramen
Vagus nerve Supplies branchiomotor innervation to most laryngeal and all pharyngeal muscles (except the
stylopharyngeus, which is innervated by the glossopharyngeal); provides parasympathetic fibers to nearly all
thoracic and abdominal viscera down to the splenic flexure; and receives the special sense of taste from the
epiglottis. A major function: controls muscles for voice and resonance and the soft palate. Symptoms of
damage: dysphagia (swallowing problems), velopharyngeal insufficiency. Located in jugular foramen
Accessory nerve (or cranial accessory nerve Controls sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, overlaps with functions of the vagus. Examples of
or spinal accessory nerve) symptoms of damage: inability to shrug, weak head movement; Located in jugular foramen
Hypoglossal nerve Provides motor innervation to the muscles of the tongue (except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by
the vagus) and other glossal muscles. Important for swallowing (bolus formation) and speech articulation.
Located in hypoglossal canal
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Innervation of The Soft Palate MusclesDocument7 pagesThe Innervation of The Soft Palate MusclesjmccoyNo ratings yet
- The Detailed Neurologic Examination in AdultsDocument21 pagesThe Detailed Neurologic Examination in AdultsLuisa FernandaNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument67 pagesCranial NervesBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Glossopharyngeal Nerve Injury Following Tonsillectomy 5542Document4 pagesGlossopharyngeal Nerve Injury Following Tonsillectomy 5542Kenza SeddikNo ratings yet
- Brainstem NucleiDocument9 pagesBrainstem Nucleiankur_1No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Trigeminal NerveDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Trigeminal NerveBharath Kumar Uppuluri100% (1)
- Fracture Closed Complete Displaced Middle Third Femur Right Secondary To FallDocument102 pagesFracture Closed Complete Displaced Middle Third Femur Right Secondary To FallRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument90 pagesCranial NervesGaVee AgranNo ratings yet
- Kumar PDFDocument79 pagesKumar PDFLina LinuxNo ratings yet
- Sensory and Motor Cranial NervesDocument13 pagesSensory and Motor Cranial NervesAnn HeerahNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System AssessmentDocument22 pagesNeurologic System Assessmentroy_linaoNo ratings yet
- NBDE Part 1 - 2010 Remembered QuestionsDocument1 pageNBDE Part 1 - 2010 Remembered QuestionsGEORGWHTNo ratings yet
- Ha Lec 16 - Neurological ExaminationDocument20 pagesHa Lec 16 - Neurological ExaminationGian SolimanNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Exam and Cranial NervesDocument78 pagesMental Status Exam and Cranial Nervessarguss14100% (2)
- Mcqs Babu S ParmerDocument320 pagesMcqs Babu S Parmershoaibiidc8No ratings yet
- Neuro Part 2Document6 pagesNeuro Part 2vetthamilNo ratings yet
- The Far-Lateral Approach and Its Transcondylar, Supracondylar, and Paracondylar ExtensionsDocument15 pagesThe Far-Lateral Approach and Its Transcondylar, Supracondylar, and Paracondylar Extensionsbodeadumitru9261No ratings yet
- Cranial Fossa Foramina Vessels Nerves BoneDocument4 pagesCranial Fossa Foramina Vessels Nerves BoneYongNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia CarolMcKee (1) DPNS StudyDocument23 pagesTreatment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia CarolMcKee (1) DPNS Studyconstantineelia100% (1)
- Lecture PharynxDocument28 pagesLecture PharynxHoor AlnabhaniNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssesmentDocument78 pagesNeurological AssesmentSafiyamohammadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Anatomical Organization of Cranial Nerves 2009 Manual Therapy For The Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Anatomical Organization of Cranial Nerves 2009 Manual Therapy For The Cranial NervesDaniela Bustos PéndolaNo ratings yet
- Artery Supply Venous Drainage Nerve Supply Lymphatic DrainageDocument9 pagesArtery Supply Venous Drainage Nerve Supply Lymphatic DrainageTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve: Dr. Dian Prasetyo Wibisono, M.SCDocument49 pagesCranial Nerve: Dr. Dian Prasetyo Wibisono, M.SCgeneNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Taste and Smell ImageDocument10 pagesDisorders of Taste and Smell Imageडा. सत्यदेव त्यागी आर्यNo ratings yet
- 2615Document118 pages2615ReekBhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Jean-Pierre Barral and Alain Croibier (Auth.) - Manual Therapy For The Cranial Nerves (2009)Document271 pagesJean-Pierre Barral and Alain Croibier (Auth.) - Manual Therapy For The Cranial Nerves (2009)Bruno Gonçalves100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Salivary Gland ShivaniDocument43 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Salivary Gland ShivaniDeepika LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Cranial NerveDocument3 pagesCranial NerveMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- 12 Cranial Nerves: By: Dr. Pamela Josefina T. FabieDocument48 pages12 Cranial Nerves: By: Dr. Pamela Josefina T. FabieAbdullah Saleem100% (3)