Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manual
Uploaded by
TarunPatraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manual
Uploaded by
TarunPatraCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION:
Vertical Turbine Pumps are designed to operate in a vertical configuration with the main
pumping element, The Bowl assembly, submerged deep into water. The main advantages of
a Vertical Pump over a Horizontal Pump are, lesser floor space requirement, uniform
distribution of radial forces because of 360ᵒ diffusion; absence of radial loads on shaft
bearings due to vertically suspended configuration, hanging from the top. The Impeller
design ranges from Francis, Mixed Flow, Semi-axial and axial flow type based on different
head and capacity requirements. These pumps can be in single stage or multi stage
construction for varying discharge head requirements. Owing to simplicity of operation and
minimal mechanical friction, these pumps normally operate at high level of hydraulic
efficiency.
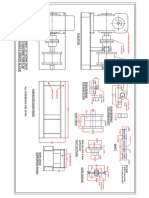
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF VERTICAL TURBINE PUMPS:
A Vertical Turbine Pump consists of five basic elements, namely,
1. Pump Bowl Assembly
2. Column Pipe Assembly
3. Line Shafting
4. Discharge Head Assembly and
5. Driver (Prime Mover)
1. PUMP BOWL ASSEMBLY :
Bowl assembly of a vertical turbine pump is the main pumping element. The number of
stages of pump bowls in an assembly is determined by the head requirements of individual
installation. A typical single stage pump bowl assembly is made up of a suction case or bell,
an impeller (enclosed or semi-open type), a top intermediate bowl and a discharge case
with guide vanes. Impellers are connected to the pump shaft by split cone shaped impeller
lock collets or by key. The suction case/ bell serves as the intake of pump bowl assembly for
smooth inflow of water with minimum losses. Liquid is moved by the impeller through the
pump bowls. The top inter bowl acts as a diffuser and guides the flow into the discharge
case which, in turn, gets delivered into the column pipe. Pump shaft bearings are located in
the Suction bell, top inter bowl/ discharge case, and in each inter bowl (for multi stage
pumps) between stage impellers. Basic design features of a bowl assembly differ for
different types of shaft lubrication arrangement, i.e., self water lubrication or external clear
water lubrication or oil lubrication with enclosed line shaft.
2. COLUMN PIPE ASSEMBLY :
It either cast or fabricated, it houses line shaft bearings and directs water from bowl
assembly to discharge head/elbow. Column pipe may either be threaded or flanged,
depending upon pump figure, size or site requirements. Flanged column pipes have male
and female spigots to ensure proper alignment of the two adjacent lengths of column pipes.
The flanged column pipes are bolted together with a gasket / ‘O’ ring between the flanges
so that any possibility of leakage is eliminated.
3. LINE SHAFT ASSEMBLY :
A vertical turbine pump’s line shaft assembly rotates inside the column pipe and transmits
torque from the pump driver to the pump bowl assembly. Both ends are precision machined
and two adjacent lengths are secured together with threaded couplings or muff couplings
with split ring. This shafting is supported by bearings at specific intervals. The types of
bearings used and how they are lubricated are described below:
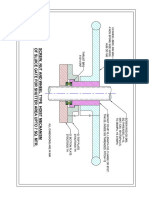
3.1. OPEN LINE SHAFT- RUBBER BEARING:
The open line shaft design is such that the line shaft and bearings are exposed to the liquid
being pumped. The line shaft is supported at intervals of not more than 3m by cutless
rubber bearings of natural / synthetic rubber / Elastomeric with outer shell of brass or
suitable material and theserubber bearings run on Stainless Steel shaft sleeves and get
lubricated by the water being pumped. Provision of shaft sleeves protects the shaft from
undue damage. Support for these bearings is supplied by bearing retainers. The outer hub of
the retainer is seated between the two column pipe ends.
3.2. ENCLOSED LINE SHAFT- RUBBER BEARING:
In the enclosed line shaft design the shaft is surrounded by tubing. This tubing protects both
the shaft and shaft bearings form the pumped liquid and provides a channel for lubricating
the shaft bearings. The rubber bearing is lubricated by external clear water.
3.3. ENCLOSED LINE SHAFT- BRONZE BEARINGS:
The bearings in this design are of bronze with grooves on the inside diameter to allow
lubricating oil to flow from one bearing to the next. These bearings are also threaded on the
outside diameter and are used to connect the enclosing tube sections. Lubrication for this
style is normally oil and is supplied by a solenoid oiler mounted on the Surface Discharge
head. Intermediate tubes are supported by rubber spiders to reduce the risk of vibrations.
4. DISCHARGE HEAD ASSEMBLY :
Discharge heads perform multiple functions. Firstly, they provide a base from which the
pump is suspended. Secondly, it directs flow from column pipe to discharge pipe located
above or below ground level.
5. DRIVER (PRIME MOVER) :
A three phase induction motor is the most extensively used driver for vertical pumps. They
are available in the following two designs:
5.1. HOLLOW SHAFT DESIGN :
In this design the drive shaft of the motor is a hollow cylindrical shaft through which the
pump top shaft passes right upto the top of motor. The driver and driven shafts are coupled
together through a gib key. The drive motor is provided with a thrust bearing of ample
capacity to cater to its own thrust load together with the thrust generated by the pump.
Impeller adjusting nut sits on top of the motor coupling bush.
5.2. SOLID SHAFT DESIGN
Unlike the above design, the drive shaft of the motor is made of solid round bar. The shaft
projects below the driver’s mounting base and is coupled to the pump top shaft through a
flexible coupling. In addition, a separate thrust bearing has to be provided in the pump
design to absorb the thrust generated by the pump during normal operation. The impeller
adjusting nut is positioned between the two flanges of flexible coupling.
You might also like
- SKF Latest Price List 2021Document148 pagesSKF Latest Price List 2021nitesh mulhallNo ratings yet
- Irjet V2i822 PDFDocument6 pagesIrjet V2i822 PDFTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Memo requests room booking at Purulia irrigation bungalowDocument1 pageMemo requests room booking at Purulia irrigation bungalowTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Schedule-II SAR InstructionsDocument4 pagesSchedule-II SAR InstructionsTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Document From JohannDocument48 pagesDocument From JohannTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Estimate For 2500 Cusec BagjolaDocument12 pagesEstimate For 2500 Cusec BagjolaTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Overhauling of pumps, pipes and valves at Ranichak pumping stationDocument40 pagesOverhauling of pumps, pipes and valves at Ranichak pumping stationTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- FS - Vol 3 - TECH - SPECDocument31 pagesFS - Vol 3 - TECH - SPECTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar DesignDocument5 pagesBus Bar DesignRamadhar Sharma100% (1)
- 06 - Pert CPMDocument24 pages06 - Pert CPMManinee Bhojraj DholeNo ratings yet
- Rtu Panel With 2.2 KW X 5 VFD NewDocument29 pagesRtu Panel With 2.2 KW X 5 VFD NewTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Axial Flow or Propeller PumpDocument4 pagesAxial Flow or Propeller PumpTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Trash Rack at Forebay BridgeDocument1 pageTrash Rack at Forebay BridgeTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- System Head Ranichak P SDocument8 pagesSystem Head Ranichak P STarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Incone TechnologiesDocument6 pagesIncone TechnologiesTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Unbrako Fasteners Price List 2Document70 pagesUnbrako Fasteners Price List 2TarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Dam Automation Case StudyDocument6 pagesDam Automation Case StudyTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- D - 20 and 16 Vent Sluce at Ghusighata - Draw Shutter 20 and 16 Vent - Pedestal Stool Model (1Document1 pageD - 20 and 16 Vent Sluce at Ghusighata - Draw Shutter 20 and 16 Vent - Pedestal Stool Model (1TarunPatraNo ratings yet
- L&T Panel Accessories Price List 01JUL2017Document44 pagesL&T Panel Accessories Price List 01JUL2017TarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Drawing - Pumphouse Pinjarapole Khal HWHDocument1 pageDrawing - Pumphouse Pinjarapole Khal HWHTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- D - Drawing - Foundation Details 2nd Ups Model (1Document1 pageD - Drawing - Foundation Details 2nd Ups Model (1TarunPatraNo ratings yet
- The Illustration Is That of A "Power Unit" Which Includes The ReservoirDocument30 pagesThe Illustration Is That of A "Power Unit" Which Includes The ReservoirTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- D - Est. For Satpukuria Lifting Winch - Worm Gear Drive Lifting Winch MC Model (1Document1 pageD - Est. For Satpukuria Lifting Winch - Worm Gear Drive Lifting Winch MC Model (1TarunPatraNo ratings yet
- K Lite Products Portfolio 2016 V 0Document56 pagesK Lite Products Portfolio 2016 V 0TarunPatra100% (2)
- Canal System L.D.I. Old A3Document1 pageCanal System L.D.I. Old A3TarunPatraNo ratings yet
- SKF Industrial PricelistApril2017 Edition2Document140 pagesSKF Industrial PricelistApril2017 Edition2shekar_991985346No ratings yet
- Schedule of Rates Building Works Vol I 2017Document407 pagesSchedule of Rates Building Works Vol I 2017TarunPatra0% (1)
- D - Drawing - Screw Nut Wheel Type Hoist 650mm ScrewDocument1 pageD - Drawing - Screw Nut Wheel Type Hoist 650mm ScrewTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Technical Specifications For Hydro Mechanical WorksDocument62 pages2.5 Technical Specifications For Hydro Mechanical WorksAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 1001 Positive Pressure ChillersDocument4 pages1001 Positive Pressure ChillersNiwej YasoongnoenNo ratings yet
- US10450060Document13 pagesUS10450060雷黎明No ratings yet
- Butterfly ValveDocument24 pagesButterfly ValveJoy Arief JanuarNo ratings yet
- K Series 20 31 - CatalogueDocument19 pagesK Series 20 31 - CatalogueFilip StenströmNo ratings yet
- H Series Right Angle Gear Box Catalog - 20230201Document11 pagesH Series Right Angle Gear Box Catalog - 20230201Nour Nour El IslamNo ratings yet
- Porsgrunn Steering GearDocument4 pagesPorsgrunn Steering GearPedro EscarráNo ratings yet
- Borets Artificial Lift CatalogDocument150 pagesBorets Artificial Lift CatalogElena AlexandrovaNo ratings yet
- Carter Auto Water Pump Components 072420Document2 pagesCarter Auto Water Pump Components 072420geniusNo ratings yet
- Bomag Single Drum Rollers 40Document12 pagesBomag Single Drum Rollers 40Alex TanNo ratings yet
- Installation & Operation Manual: Rev. 2A SEPT 07 P/N 77740213Document17 pagesInstallation & Operation Manual: Rev. 2A SEPT 07 P/N 77740213Anonymous alQXB11EgQNo ratings yet
- Plummer Block Housings - SNS3134-H-D + 23134..-K + H3134 (-HG) + 2 NFR280 - 10 + NTS34 + NDK34Document2 pagesPlummer Block Housings - SNS3134-H-D + 23134..-K + H3134 (-HG) + 2 NFR280 - 10 + NTS34 + NDK34ZiaNo ratings yet
- Fan VibrationDocument8 pagesFan Vibrationlafondejs100% (1)
- 330C L Excavator - 9 Engine PDFDocument26 pages330C L Excavator - 9 Engine PDFRICHARDNo ratings yet
- Sliding Contact Bearing AssignmentsDocument3 pagesSliding Contact Bearing AssignmentsRakesh Kumar Shukla KEC0% (1)
- Service Manual Transmission 1992-1993Document276 pagesService Manual Transmission 1992-1993Jose Chong Loo Gonzalez100% (2)
- Double Suction Horizontal Split Case Centrifugal Pumps BSC/BSCM SeriesDocument56 pagesDouble Suction Horizontal Split Case Centrifugal Pumps BSC/BSCM SeriestdccmpnNo ratings yet
- MK 6 Oil Mist DetectorDocument132 pagesMK 6 Oil Mist DetectorJahid IslamNo ratings yet
- Transfer D22Document38 pagesTransfer D22Jose FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Gear Box DesignDocument8 pagesGear Box Designandiksribd100% (1)
- Astm F2162-01 (2016)Document5 pagesAstm F2162-01 (2016)arcadioscoNo ratings yet
- Meritor Axle MT 40 143MA NDocument55 pagesMeritor Axle MT 40 143MA Nford62bNo ratings yet
- General Catalogue en 2011Document96 pagesGeneral Catalogue en 2011anupthattaNo ratings yet
- Erhard Double-Eccentric Butterfly ValveDocument36 pagesErhard Double-Eccentric Butterfly ValveMohammad FouladiNo ratings yet
- Motor 60Z02152 - 03 (1) CAT3306 CrankshaftDocument5 pagesMotor 60Z02152 - 03 (1) CAT3306 CrankshaftIsmael De Jesus AndradeNo ratings yet
- RHP - Catálogo de Rodamientos de Super Precisión PDFDocument24 pagesRHP - Catálogo de Rodamientos de Super Precisión PDFljcmexNo ratings yet
- Gear MotorDocument45 pagesGear Motorb3ltaNo ratings yet
- Names of Companies in Power IndustryDocument14 pagesNames of Companies in Power IndustrygulmuhrNo ratings yet
- Generator Bearing ServiceDocument10 pagesGenerator Bearing ServiceMustafa A.W100% (1)
- Bridge BearingsDocument13 pagesBridge BearingsBenard OmondiNo ratings yet
- 2024 Vivid Service ManualDocument113 pages2024 Vivid Service ManualZbyněk SyptákNo ratings yet