Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
Uploaded by
Elbert Vierneza100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
5K views4 pagesActivity intolerance occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. The heart rate increases as a compensatory mechanism to increase cardiac output, and vasoconstriction occurs to try to maintain blood pressure. A saturation of greater than 90mmHg recommended. Lower values require supplemental oxygen during activity and slower activity progression.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentActivity intolerance occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. The heart rate increases as a compensatory mechanism to increase cardiac output, and vasoconstriction occurs to try to maintain blood pressure. A saturation of greater than 90mmHg recommended. Lower values require supplemental oxygen during activity and slower activity progression.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
5K views4 pagesNCP
Uploaded by
Elbert ViernezaActivity intolerance occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. The heart rate increases as a compensatory mechanism to increase cardiac output, and vasoconstriction occurs to try to maintain blood pressure. A saturation of greater than 90mmHg recommended. Lower values require supplemental oxygen during activity and slower activity progression.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
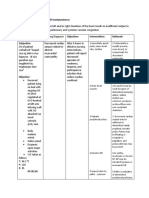
Name of Patient: M.
E
Age: 28
Medical Diagnosis: CHF
Nursing Diagnosis: Activity intolerance r/t reduced cardiac output
Short Term Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient will verbalize confidence with progressive activity.
Long Term Goal: After the period of hospitalization, the patient will continue to verbalize confidence with progressive activity at home.
CUES PROBLEM SCIENTIFIC REASON NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
INTERVENTIONS
Subjective: Activity Heart failure, also called Independent:
intolerance congestive heart failure - Assess patients readiness to - Older patients with CHF can GOAL MET. The
Ø , occurs when cardiac output increase activity be quite fearful of overexerting patient verbalized
is inadequate to meet the their hearts or causing confidence with
Objective: metabolic demands of the discomfort. progressive activity.
body. The heart rate - For in patients monitor - A saturation of greater than
- Pallor increases as a compensatory oxygen saturation 90mmHg recommended.
- Weak looking mechanism to increase Lower values require
- V/S taken: cardiac output, and supplemental oxygen during
BP: 90/70 vasoconstriction occurs to try activity and slower activity
PR: 42 to maintain blood pressure. progression.
Eventually, the chronic - Encourage verbalization of - An honest relationship
increase in preload and feelings regarding exercise facilitates problem solving and
afterload contribute to or need to increase activity successful coping.
chamber dilation and
hyperthrophy, worsening - Inform patient about health - Activity prevents
heart failure. Underlying benefits and physical effects complications related to
causes of heart failure of activity or exercise immobilization, improves
include congenital heart feelings of well being and may
disease, rheumatic heart improve mortality(w/ long
disease, endocarditis, term exercise)
myocarditis, and - Instruct patient regarding - Information enables patient
noncardiovascular causes whom to call if any abnormal to take control of situation.
such as, chronic pulmonary response to exercise is noted
disease, various metabolic
diseases, and anemia. - Teach patient to self - HR is a guide for monitoring
Complications of heart monitor their pulse rate if intensity or duration of
failure include pneumonia, appropriate exercise.
pulmonary edema,
pulmonary emboli, refractory
heart failure, and myocardial
failure.
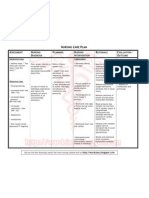
Name of Patient: M.E
Age: 28
Medical Diagnosis: CHF
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired gas exchange r/t altered oxygen-carrying capacity of blood
Short Term Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient will maintain optimal gas exchange as evidenced by normal rate, pattern, depth, and breathing effort
Long Term Goal: After the period of hospitalization, the patient will continue to maintain optimal gas exchange as evidenced by normal rate, pattern, depth, and breathing
effort
CUES PROBLEM SCIENTIFIC REASON NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
INTERVENTIONS
Subjective: Heart failure, also called Independent:
Impaired Gas congestive heart failure - Position with proper body - This promotes lung GOAL MET. The
Ø Exchange , occurs when cardiac output alignment for optimal expansion and improves air patient slightly
is inadequate to meet the respiratory excursion exchange maintain optimal gas
Objective: metabolic demands of the exchange as evidenced
body. The heart rate - Routinely check the - This would cause the by normal rate,
- Pallor increases as a compensatory patient’s position so that he abdomen to compress the pattern, depth, and
- Difficulty of mechanism to increase or she does not slide down in diaphragm, which would cause breathing effort
breathing cardiac output, and bed respiratory embarrassment
- Weak looking vasoconstriction occurs to try
- V/S taken: to maintain blood pressure. - Pace activities and schedule - Even simple activities such as
BP: 90/70 Eventually, the chronic rest periods to prevent bathing during bed rest can
RR: 35 increase in preload and fatigue cause fatigue and increase
afterload contribute to oxygen consumption
chamber dilation and
hyperthrophy, worsening - Change patient’s position - This facilitates secretion
heart failure. Underlying every 2 hours movement and drainage
causes of heart failure
include congenital heart - Encourage deep breathing - This reduces alveolar
disease, rheumatic heart exercises collapse
disease, endocarditis,
myocarditis, and
noncardiovascular causes
such as, chronic pulmonary Dependent:
disease, various metabolic - Maintain oxygen - This provides for adequate
diseases, and anemia. administration device as oxygenation
Complications of heart ordered, attempting to
failure include pneumonia, maintain oxygen saturation
pulmonary edema, at 90% or greater
pulmonary emboli, refractory
heart failure, and myocardial - Administer medications as - To relieve uneasy feeling of
failure. prescribed the patient
You might also like
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument10 pagesPulmonary HypertensionqingwenNo ratings yet
- CHF NCPDocument8 pagesCHF NCPZy Hallasgo100% (1)
- NCP For AnginaDocument5 pagesNCP For Anginacarizza_bernas100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesNo ratings yet
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- NCP For Mi PainDocument2 pagesNCP For Mi PainKahMallariNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP - Impaired Gas Exchangejanelee2824No ratings yet
- NCP For CHFDocument2 pagesNCP For CHFMayet De Castro Lejano100% (1)
- SAMPLE NCP For Angina PectorisDocument3 pagesSAMPLE NCP For Angina Pectorisseanne_may100% (4)
- NCP For Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument3 pagesNCP For Acute Coronary Syndromesarahtot75% (4)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP Myocardial InfarctionDocument1 pageNCP Myocardial InfarctionjamieboyRN88% (8)
- NCP AidsDocument16 pagesNCP AidstferdianingsihNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- NCP MiDocument4 pagesNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyDocument7 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyKym RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyDocument3 pagesNCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyKyle Stephen TancioNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimNo ratings yet
- Stroke Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageStroke Nursing Care PlanTracy PearlNo ratings yet
- Myocarditis NCP 2Document8 pagesMyocarditis NCP 2astro_aaron117375% (4)
- TB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsDocument1 pageTB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsnikkilyceeNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocument1 pageActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 pagesConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputTiffany Mathis100% (1)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- CRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 pagesCRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPchubbielitaNo ratings yet
- NCP AnginaDocument3 pagesNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceMaze Reyes40% (5)
- NCP For SVTDocument6 pagesNCP For SVTRen VillenaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismneuronurseNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of NephrosclerosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- NCP - Difficulty of BreathingDocument2 pagesNCP - Difficulty of BreathingTarquin Tomada33% (3)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternruguNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For ESRDDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For ESRDChester Manalo94% (17)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitFrances Anne Pasiliao100% (3)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- NCP For OxygenationDocument6 pagesNCP For OxygenationChriz LechNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisRachel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Care Plan ExampleDocument2 pagesCare Plan Exampleincess27100% (1)
- NCP: DysrhythmiasDocument12 pagesNCP: DysrhythmiasJavie100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressLeticia ElricNo ratings yet
- Seminar - Heart FailuerDocument19 pagesSeminar - Heart Failuermustafalotfy01No ratings yet
- Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Margaret Macasaet0% (1)
- NCP 3Document2 pagesNCP 3ABIL ABU BAKARNo ratings yet
- 1-!nursing Diagnosis:: Myocardial Infarction As Evidenced by Reports of Chest Pain With Radiation in Bilateral ArmDocument3 pages1-!nursing Diagnosis:: Myocardial Infarction As Evidenced by Reports of Chest Pain With Radiation in Bilateral Armون توNo ratings yet
- Tabije, Arvie Jayselle PDocument6 pagesTabije, Arvie Jayselle PJayselle ArvieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Doppler Scan and Stress TestingDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For Doppler Scan and Stress TestingAmy Rose AbuevaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document4 pagesNCP 1Jezrale FameNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPeter Emmil GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGDocument11 pagesAssessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- B. Inggris PPT NCP Kel. 6Document9 pagesB. Inggris PPT NCP Kel. 6Emi LestariNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: SubjectiveDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: SubjectiveAlimansor M. DarpingNo ratings yet
- Clinical States of Cirrhosis and Competing RisksDocument14 pagesClinical States of Cirrhosis and Competing RisksmaryNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Committee Report 1996Document267 pagesBajaj Committee Report 1996lalit823187No ratings yet
- Common Mental Health Disorders in Primary Care Common Mental Health Disorders in Primary Care OverviewDocument7 pagesCommon Mental Health Disorders in Primary Care Common Mental Health Disorders in Primary Care OverviewRichi BustosNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For Cardiopumonary DisordersDocument101 pagesPhysical Therapy For Cardiopumonary Disorderssunita_h100% (5)
- Residents Self Assessment FormDocument5 pagesResidents Self Assessment Formapi-245673459No ratings yet
- 1 - Common Disorders of The Ear Nose and ThroatDocument7 pages1 - Common Disorders of The Ear Nose and ThroatDina DestrianaNo ratings yet
- Liver MCQDocument14 pagesLiver MCQMohammad Ra'fat Rostom86% (7)
- WWW - Reliancegeneral.co - In: Important Note: This Is An Electronically Generated Document and Requires No Seal / StampDocument1 pageWWW - Reliancegeneral.co - In: Important Note: This Is An Electronically Generated Document and Requires No Seal / StampdhanishlNo ratings yet
- Hiperkolesterolemia, PPT Webinar 28 MeiDocument74 pagesHiperkolesterolemia, PPT Webinar 28 MeiAprianti Hardi100% (1)
- Paramedical E-BrochureDocument4 pagesParamedical E-BrochureMohil DaveraNo ratings yet
- 6 Domains of Resilience PDFDocument4 pages6 Domains of Resilience PDFRonna Panganiban DipasupilNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Brain TumorDocument24 pagesIntracranial Brain TumorheruNo ratings yet
- 2017-New Insights Into Burnout and Health Care Strategies For Improving Civility and Alleviating BurnoutDocument5 pages2017-New Insights Into Burnout and Health Care Strategies For Improving Civility and Alleviating Burnoutxi LuNo ratings yet
- John Keith Krebs 1 SubstanceAbuse UnjustifiedPrescriptions PDFDocument30 pagesJohn Keith Krebs 1 SubstanceAbuse UnjustifiedPrescriptions PDFWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- Philosophy: I.Meaning of PhilosophyDocument12 pagesPhilosophy: I.Meaning of Philosophysivagiri.pNo ratings yet
- MCQ of NeurologyDocument45 pagesMCQ of Neurologyeffe26100% (7)
- Quiz TraumaDocument1 pageQuiz Traumaaqsa rehmanNo ratings yet
- Adult Obesity ResearchDocument19 pagesAdult Obesity Researchchoraz100% (1)
- Approach To Common Respiratory DiseaseDocument57 pagesApproach To Common Respiratory DiseaseRajhmuniran KandasamyNo ratings yet
- TAYLOR 1984 AnaesthesiaDocument3 pagesTAYLOR 1984 Anaesthesiapolly91No ratings yet
- The Zodiac and The Salts of SalvationDocument32 pagesThe Zodiac and The Salts of Salvationrogerfpa100% (1)
- IepDocument26 pagesIepapi-326610254No ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Nursing Management of DementiaDocument4 pagesChapter 10: Nursing Management of DementiaJoanne FojaNo ratings yet
- Research MCNPDocument57 pagesResearch MCNPmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan MiloDocument20 pagesMarketing Plan MiloSpear HenryNo ratings yet
- Коспект лекційDocument51 pagesКоспект лекційМарія МайорчакNo ratings yet
- Prescription Pain MedicationDocument9 pagesPrescription Pain Medicationapi-409112773No ratings yet
- Levetiracetam (Keppra®) in SarcinaDocument2 pagesLevetiracetam (Keppra®) in SarcinaI.m. DanielNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario/Situation Answer/Explanation: NCM 101 RLE - Health AssessmentDocument2 pagesCase Scenario/Situation Answer/Explanation: NCM 101 RLE - Health AssessmentmaryNo ratings yet
- Medical AspectsofBiologicalWarfareDocument633 pagesMedical AspectsofBiologicalWarfaredennyreno100% (2)