Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Consumer Theory Burkey Academy
Uploaded by
mazamniaziCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Consumer Theory Burkey Academy
Uploaded by
mazamniaziCopyright:
Available Formats
Overview Video: https://youtu.
be/T-q_ZXmfiLI
Consumer Theory with BurkeyAcademy www.burkeyacademy.com © Mark L. Burkey
Hicksian (Compensated) Demand
Marshallian Demand
Min B ≡ (Pxx+Pyy) s.t. ̅
U(x,y)=𝑈 (or =Uo)
Max U(x,y) s.t. Pxx+Pyy=𝐵̅ (or 𝐼 ̅ , 𝑚
̅)
̅
Example: Min Pxx+Pyy s.t. x.3y.7 =𝑈
Example: Max U=x y s.t. Pxx+Pyy =𝐵̅ e.g., 𝑩
.3 .7 ̅ =$100
Solve using calculus ̅ For example, x.3y.7 =10
or solve MRSxy= Px/Py, U(x,y)=𝑈
Solve using calculus, or Solve MRSxy= Px/Py , PxX+PyY=𝐵̅
𝜕𝑈
MRSxy=MUx/MUy , MUx= Plug Expenditure in for B in
𝜕𝑥
̅
Hicksian (Compensated) Demand How much x and y should I buy to get 𝑼
Marshallians, get Hicksians!
Marshallian Demands for x & y How much x and y the cheapest way?
should I buy seeing these prices with this budget to max U? ̅) , yc (Px,Py,𝑈
xc (Px,Py,𝑈 ̅) ̅))
(or x*=H(Px,Py,𝑈
x*( Px,Py,𝐵̅ ) , y*( Px,Py,𝐵̅) Plug Indirect in for U in .7 .3
Hicksians, get Marshallians!
̅ (3𝑃𝑦 ) , yc = 𝑈
Example: xc =𝑈 ̅ (7𝑃𝑥 )
Example: x*= .3𝐵̅/Px y*=.7𝐵̅/Py 7𝑃 𝑥 3𝑃 𝑦
Substitute x* and y* Roy’s Identity Substitute xc and yc Shephard’s Lemma
−𝜕𝑈 ∗ 𝜕𝑈 ∗ 𝜕𝐸
into the utility function / = x* similar for y*, use Py into the Budget equation = xc similar for yc, use Py
𝜕𝑃𝑥 𝜕𝐵 𝜕𝑃𝑥
Indirect Utility Function: Direct utility converts x and y into ̅ in the cheapest way
Expenditure Function How much does it cost to get 𝑼
Solve Indirect for B
happiness. Indirect uses prices and budget to do this, indirectly. given Px & Py?
(Invert)
̅) = Pxxc + Pyyc
E(Px,Py,𝑈
𝐵 .3 𝐵 .7
Utility*= V(Px, Py, 𝐵̅) Example: U = .5423*
( ) ( ) .7 .3 .7 .3
𝑃𝑥 𝑃𝑦
Solve Expenditure for U ̅ (3𝑃𝑦 ) + Py 𝑈
Example: Px 𝑈 ̅ (𝑝𝑦 ) (𝑝𝑥 )
̅ (7𝑃𝑥 ) = 10𝑈
7𝑃 𝑥 3𝑃 𝑦 7 3
(Invert)
Indirect Money Metric Utility Function: Take the Indirect Utility function and put Money Metric Utility Function: Plug the original utility function into the
bars on 𝑃̅𝑥 , 𝑃̅𝑦 , 𝐵̅. Substitute this fn. into the expenditure function for 𝑈
̅. This will
Expenditure function. This tells you “The mimimum $ needed to get the same
tell you how much $ you need to get the same utility you were getting at 𝑃̅𝑥 , 𝑃̅𝑦 , utility as I get from xo and yo. Example: MM=1.842𝑦𝑜.7 𝑥𝑜.3 𝑝𝑦.7 𝑝𝑥.3
𝑝𝑥 𝑝𝑦 𝐵 .3 .7 ̅
𝐵̅ under new prices Px & Py. Example: IMM= .3 .7
𝑝̅𝑥 𝑝̅𝑦
Legend: Green indicates various common symbols others might use for the same thing.
B, I, m: Budget, Income, money: If they are a free variable, or the outcome.
𝐵̅ or (𝐼 ,̅ 𝑚
̅ , 𝑜𝑟 𝐵𝑜 ):The bar or subscript, e.g. Bo (read “B nought”) means fixed level of income- the main constraint. Should think of as usually fixed.
U: Utility, happiness, satisfaction. 𝑈 ̅ or Uo : A fixed level of Utility that we want to achieve. U*: The optimal level of utility possible
x and y: Two goods we are consuming to produce Utility
x* and y* : Optimal levels of x and y that maximize utility; demand for x and y.
xc , yc : Hicksian demands for x and y; optimal levels of x and y that attain 𝑈 ̅ the cheapest way
Px and Py : Prices of the goods x and y.
You might also like
- Solution 1Document10 pagesSolution 1rajan20202000No ratings yet
- Welfare TheoremsDocument8 pagesWelfare TheoremsJesús M. VilleroNo ratings yet
- ECN 2215 - Topic - 2 PDFDocument54 pagesECN 2215 - Topic - 2 PDFKalenga AlexNo ratings yet
- Dsge AllDocument74 pagesDsge AllBùi Quang HiểnNo ratings yet
- Public EconomicsDocument19 pagesPublic EconomicsSumitava MajiNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply: Lipsey & Chrystal Economics 13EDocument47 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply: Lipsey & Chrystal Economics 13EJudhaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Notes (Advanced)Document98 pagesMicroeconomics Notes (Advanced)rafay010100% (1)
- Econometrics CheatDocument3 pagesEconometrics CheatLaurence TyrrellNo ratings yet
- Pset6 Solutions HandoutDocument10 pagesPset6 Solutions HandoutthemiykNo ratings yet
- Favero Applied MacroeconometricsDocument292 pagesFavero Applied MacroeconometricsMithilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document44 pagesLecture 7Tiffany TsangNo ratings yet
- The Linear Regression Model: An Overview: Damodar GujaratiDocument17 pagesThe Linear Regression Model: An Overview: Damodar GujaratisampritcNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Tortillas With AnswersDocument6 pagesCase Study On Tortillas With AnswersTran Nhat Thang50% (2)
- Handbook of Mathematical Economics VOL IDocument381 pagesHandbook of Mathematical Economics VOL IDiego EstebsnNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONs Introduction Dynamic Macroeconomic TheoryDocument9 pagesSOLUTIONs Introduction Dynamic Macroeconomic TheoryAdelaido García AndrésNo ratings yet
- AutocorrelationDocument172 pagesAutocorrelationJenab Peteburoh100% (1)
- Exercise 1 Multiple Regression ModelDocument6 pagesExercise 1 Multiple Regression ModelCarlos Villa AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument32 pagesFinancial MarketsArief Kurniawan100% (1)
- Advanced Panel Data Econometrics Sample Test PDFDocument8 pagesAdvanced Panel Data Econometrics Sample Test PDFQin FiFiNo ratings yet
- Sheetcheat EconometricsDocument1 pageSheetcheat EconometricsromainNo ratings yet
- Alpha Chiang Chapter 19Document10 pagesAlpha Chiang Chapter 19ansarabbasNo ratings yet
- Harvard Economics 2020a Problem Set 3Document2 pagesHarvard Economics 2020a Problem Set 3JNo ratings yet
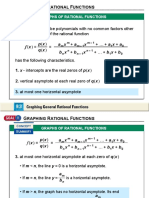
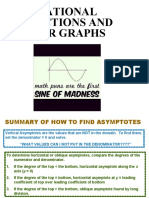
- Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument7 pagesGraphing Rational Functionsgtan@icacademy.orgNo ratings yet
- ACT-671 Introduction Econometrics-2012Document29 pagesACT-671 Introduction Econometrics-2012Zaheer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (The Capitalist Revolution)Document12 pagesUnit 1 (The Capitalist Revolution)jeannedreyer100% (1)
- 01 Econometrics - OverviewDocument41 pages01 Econometrics - OverviewTaufiq LuthfiNo ratings yet
- Basic Econometrics Old Exam Questions WiDocument9 pagesBasic Econometrics Old Exam Questions WiGulizaNo ratings yet
- CES Production FunctionDocument4 pagesCES Production Functionsaif09876No ratings yet
- Answers To Some Selected Exercises To Consumer Theory: R Finger Advanced Microeconomics ECH-32306 September 2012Document8 pagesAnswers To Some Selected Exercises To Consumer Theory: R Finger Advanced Microeconomics ECH-32306 September 2012Irina AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Advanced MicroeconomicsDocument605 pagesAdvanced MicroeconomicsNyakweba Denis100% (1)
- MWG Microeconomic Theory NotesDocument102 pagesMWG Microeconomic Theory Notes胡卉然No ratings yet
- Keynesian vs. Classical Income ModelDocument57 pagesKeynesian vs. Classical Income ModelTanujGuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Rational FunctionsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Rational FunctionsdennisNo ratings yet
- Homework EconometricsDocument7 pagesHomework EconometricstnthuyoanhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On MicroeconomicsDocument187 pagesLecture Notes On MicroeconomicsppapanatasNo ratings yet
- 3 - 1 Exponential Functions and Their GraphsDocument17 pages3 - 1 Exponential Functions and Their GraphsMar ChahinNo ratings yet
- 8 3 PowerPointDocument32 pages8 3 PowerPointGinoong CAPILI100% (1)
- Lagrange Multiplier PDFDocument10 pagesLagrange Multiplier PDFQarsam IlyasNo ratings yet
- Limits of Algebraic Functions: Basic CalculusDocument40 pagesLimits of Algebraic Functions: Basic CalculusLucky Canda Gojetia100% (1)
- s1 Past Paper QuestionsDocument377 pagess1 Past Paper QuestionsKavay KapoorNo ratings yet
- Advanced MicroeconomicDocument70 pagesAdvanced Microeconomicalbi_12291214100% (1)
- Chapter 12H - Behind The Supply Curve - Inputs and CostsDocument15 pagesChapter 12H - Behind The Supply Curve - Inputs and CostsAthief VeteranNo ratings yet
- Studenmund Ch14 v2Document48 pagesStudenmund Ch14 v2Hasanul BannaNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Exam.Document4 pagesEconometrics Exam.Shayan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Econometricstutorials Exam QuestionsSelectedAnswersDocument11 pagesEconometricstutorials Exam QuestionsSelectedAnswersFiliz Ertekin100% (1)
- MidtermODE (2013)Document8 pagesMidtermODE (2013)osw2002No ratings yet
- Ps 1Document2 pagesPs 1boja-bojaNo ratings yet
- A First Course in Optimization TheoryDocument8 pagesA First Course in Optimization TheoryAnanya ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- 20201221203332YWLEE003Perfect Compyp SolutionDocument19 pages20201221203332YWLEE003Perfect Compyp SolutionDương DươngNo ratings yet
- Endogenous Growth ModelDocument14 pagesEndogenous Growth Modelsuraj ghimireNo ratings yet
- Econ11 09 Lecture3 PDFDocument34 pagesEcon11 09 Lecture3 PDFJoe23232232No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Practice Quiz: U (X, Y) 4x + 2yDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Practice Quiz: U (X, Y) 4x + 2yKyleNo ratings yet
- Math For Econ (MIT)Document8 pagesMath For Econ (MIT)BorisTurkinNo ratings yet
- Bell Work: What Are These Substances?: © Boardworks LTD 2008Document13 pagesBell Work: What Are These Substances?: © Boardworks LTD 2008Janseen Datuin JunioNo ratings yet
- 03-Manufacturing and MiningDocument12 pages03-Manufacturing and MiningJahanzaib JavaidNo ratings yet
- Trade and PaymentsDocument17 pagesTrade and PaymentsmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- 02-Agriculture Pak Econ SurveyDocument17 pages02-Agriculture Pak Econ SurveyMir Zain Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Survey 1Document13 pagesSurvey 1scorpionkingpkNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Economic Survey Ch01-Growth and InvestmentDocument15 pagesPakistan Economic Survey Ch01-Growth and Investmentmmubashirm504No ratings yet
- Economic SurveryDocument11 pagesEconomic SurveryAhmed MustafaNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmemazamniaziNo ratings yet
- The Looming Trade War Over Plant Biotechnology, Cato Trade Policy Analysis No. 18Document20 pagesThe Looming Trade War Over Plant Biotechnology, Cato Trade Policy Analysis No. 18Cato InstituteNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Economic Survey Ch01-Growth and InvestmentDocument15 pagesPakistan Economic Survey Ch01-Growth and Investmentmmubashirm504No ratings yet
- The Looming Trade War Over Plant Biotechnology, Cato Trade Policy Analysis No. 18Document20 pagesThe Looming Trade War Over Plant Biotechnology, Cato Trade Policy Analysis No. 18Cato InstituteNo ratings yet
- Pakistan's Food and Agri Sysem PDFDocument138 pagesPakistan's Food and Agri Sysem PDFMudassir Ali QazalbashNo ratings yet
- Poultry Role RurDocument8 pagesPoultry Role RurmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- 01-Growth and InvestmentDocument14 pages01-Growth and InvestmentAmanullah Bashir GilalNo ratings yet
- Baked Snacks in Biscuit LineDocument2 pagesBaked Snacks in Biscuit LinemazamniaziNo ratings yet
- PriceIndices ISDA PDFDocument23 pagesPriceIndices ISDA PDFmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- ARDL GoodSlides PDFDocument44 pagesARDL GoodSlides PDFmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Rakaposhi Menu - Islamabad Serena Hotel PDFDocument9 pagesRakaposhi Menu - Islamabad Serena Hotel PDFMahparah RizwanNo ratings yet
- Lecture / Discussion Simultaneous Equations: Regression Analysis TutorialDocument20 pagesLecture / Discussion Simultaneous Equations: Regression Analysis TutorialmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Basmati Value Chain PunjabDocument19 pagesBasmati Value Chain PunjabmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Flood PDFDocument12 pagesPakistan Flood PDFmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Detailed Answer:: MP W MP RDocument3 pagesDetailed Answer:: MP W MP RmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- 59 - National Nutrition Survey-2011Document113 pages59 - National Nutrition Survey-2011mazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Flood PDFDocument12 pagesPakistan Flood PDFmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Pakistan FloodDocument11 pagesPakistan FloodmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Phutti Oct15Document18 pagesPhutti Oct15mazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Ridge Regression (Section 10.2) : - X X X, X, X N (µ, Σ) µ - -Document4 pagesRidge Regression (Section 10.2) : - X X X, X, X N (µ, Σ) µ - -mazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Geneve Chapitre0Document37 pagesGeneve Chapitre0Naseer ShahzadaNo ratings yet
- Functional Form and Dynamic ModelsDocument27 pagesFunctional Form and Dynamic ModelsmazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Economics of Information (ECON3016) : Review of Decision Theory Under UncertaintyDocument40 pagesEconomics of Information (ECON3016) : Review of Decision Theory Under UncertaintymazamniaziNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky EssayDocument3 pagesVygotsky Essayapi-526165635No ratings yet
- LEMBAR JAWABAN CH.10 (Capital Budgeting Techniques)Document4 pagesLEMBAR JAWABAN CH.10 (Capital Budgeting Techniques)Cindy PNo ratings yet
- Alphabetic KnowledgeDocument8 pagesAlphabetic KnowledgejsdgjdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Q3 Figure Life DrawingDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Q3 Figure Life DrawingCAHAPNo ratings yet
- Openvpn ReadmeDocument7 pagesOpenvpn Readmefzfzfz2014No ratings yet
- Duo Interpretation Class PresentationDocument31 pagesDuo Interpretation Class PresentationPlanetSparkNo ratings yet
- CUBE Dealer Book 2009Document280 pagesCUBE Dealer Book 2009maikruetzNo ratings yet
- Oceanarium: Welcome To The Museum Press ReleaseDocument2 pagesOceanarium: Welcome To The Museum Press ReleaseCandlewick PressNo ratings yet
- Cultural Sensitivity BPIDocument25 pagesCultural Sensitivity BPIEmmel Solaiman AkmadNo ratings yet
- Accounting Students' Perceptions On Employment OpportunitiesDocument7 pagesAccounting Students' Perceptions On Employment OpportunitiesAquila Kate ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cpar Characteristics and Functions Week 3Document128 pagesCpar Characteristics and Functions Week 3christianwood0117No ratings yet
- Verniers Micrometers and Measurement Uncertainty and Digital2Document30 pagesVerniers Micrometers and Measurement Uncertainty and Digital2Raymond ScottNo ratings yet
- MCQ Floyd ElexDocument87 pagesMCQ Floyd ElexnicoleNo ratings yet
- Caradol sc48 08Document2 pagesCaradol sc48 08GİZEM DEMİRNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Composition: Parts of An EggDocument22 pagesLesson 1: Composition: Parts of An Eggjohn michael pagalaNo ratings yet
- Reflection On The PoorDocument5 pagesReflection On The Poorapi-347831792No ratings yet
- June 2017 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument16 pagesJune 2017 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelNyraStardollNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Speech 2016 - Whole Person ParadigmDocument4 pagesPersuasive Speech 2016 - Whole Person Paradigmapi-311375616No ratings yet
- Quanta To QuarksDocument32 pagesQuanta To QuarksDaniel Bu100% (5)
- Fire Prevention Plan Template - FINAL 5-30-08Document5 pagesFire Prevention Plan Template - FINAL 5-30-08Peter GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Principles of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions Manualoutlying.pedantry.85yc100% (28)
- Song LyricsDocument13 pagesSong LyricsCyh RusNo ratings yet
- Toshiba MotorsDocument16 pagesToshiba MotorsSergio Cabrera100% (1)
- SDN Van NotesDocument26 pagesSDN Van Notesmjsmith11No ratings yet
- Cosmopolitanism in Hard Times Edited by Vincenzo Cicchelli and Sylvie MesureDocument433 pagesCosmopolitanism in Hard Times Edited by Vincenzo Cicchelli and Sylvie MesureRev. Johana VangchhiaNo ratings yet
- The Rock Reliefs of Ancient IranAuthor (Document34 pagesThe Rock Reliefs of Ancient IranAuthor (mark_schwartz_41No ratings yet
- How To Add Attachment Using JAVA MappingDocument4 pagesHow To Add Attachment Using JAVA MappingmvrooyenNo ratings yet
- Resistance & Resistivity: Question Paper 1Document15 pagesResistance & Resistivity: Question Paper 1leon19730% (1)
- 2022 Tony Elumelu EntrepreneursDocument10 pages2022 Tony Elumelu EntrepreneursOladosu EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Sheltered 2 Item Recycle ListDocument5 pagesSheltered 2 Item Recycle ListRachel GNo ratings yet