Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DHFXSRT
Uploaded by
adninhanafiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DHFXSRT
Uploaded by
adninhanafiCopyright:
Available Formats
By definition TB is a contagious disease that is transmitted from person to person through coughing and
breathing in airborne droplets that contain bacteria. TB primarily affects the lungs, but can affect any part
of the body. As one of the most common infections in the world, TB remains a major problem in many
countries and among vulnerable populations
TB is caused by slow-growing bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. When these bacteria enter
the lungs, they are usually walled off into harmless capsules (granulomas) in the lung, causing infection
but not disease. These capsules may later wake up weeks, months or decades later causing active TB
disease
People who are more likely to acquire TB infection are the following: (1) People recently exposed to
someone who has symptomatic TB disease; (2) People who live in congregate settings with high risk
persons; (3) People who live or have lived in countries where TB is common; or (4) People who are health
care workers who are in contact with TB patients when proper infection control procedures are not followed.
Many people who acquire TB infection do not have symptoms and may never develop TB disease. These
people have latent TB infections (LTBI). However, people with TB infection who have weaker immune
systems due to diabetes, HIV infection, kidney failure, or take certain immunosuppressive medications such
as TNF-alpha blockers may be more likely to develop active TB disease with symptoms
Symptoms are usually mild and tend to present over a period of weeks, months, or sometimes years. TB
disease symptoms are often initially mistaken for a smoker’s cough, allergies, or chronic bronchitis from a
lingering cold or flu infection. TB infection most often affects the lungs but can cause problems in other
parts of the body. The classic symptoms of TB in the lungs include:
Cough lasting more than three weeks
Chest pain, or pain with breathing or coughing
Unexplained weight loss
Prolonged Low-grade fever
Night sweats without any physical activity
Loss of appetite
If you have these symptoms, you should check with your health care provider.
TB is spread by tiny airborne droplets created by coughing. It is not spread by sharing food, utensils, drinks,
touching, or having sex. Covering the mouth and nose when coughing is an important way to stop the spread
of TB and other airborne diseases. If you have TB disease and are coughing, it is important to wear a mask
and limit contact with others until your health care provider tells you that you are no longer contagious
while on treatment. Seeking care right away and fnding out you have TB is the best way to stop its spread
since treatment of disease helps you not be contagious, decreasing transmission. Houses should be
adequately ventilated and taking a single dose of BCG should be given to all infants as soon as possible
after birth.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- WNKSNKBSBDocument3 pagesWNKSNKBSBadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Among Fishermen 16 2017Document23 pagesPost Traumatic Stress Disorder and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Among Fishermen 16 2017adninhanafiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Untitled DojdbdcumentDocument1 pageUntitled DojdbdcumentadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Presentation 1Document8 pagesPresentation 1adninhanafiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Cederholm, T., Bosaeus, I., Barazzoni, R., & Bauer, J. (2015) - Diagnostic Criteria For Malnutrition - AnDocument1 pageCederholm, T., Bosaeus, I., Barazzoni, R., & Bauer, J. (2015) - Diagnostic Criteria For Malnutrition - AnadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Search DownloadsearchresultaspdfDocument4 pagesSearch DownloadsearchresultaspdfadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Search DownloadsearchresultaspdfDocument4 pagesSearch DownloadsearchresultaspdfadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Daftar PustakaDocument1 pageDaftar PustakaadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Practice Immunology SystemDocument20 pagesPractice Immunology SystemadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- VJGKGDocument1 pageVJGKGadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Dyspnoea: Pathophysiology and A Clinical Approach: ArticleDocument5 pagesDyspnoea: Pathophysiology and A Clinical Approach: ArticleadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- CBCGNCGDocument2 pagesCBCGNCGadninhanafiNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Chemotherapy PDFDocument27 pagesChemotherapy PDFimam trisutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Hyd Pharm CompaniesDocument5 pagesHyd Pharm CompaniesValluru RaviNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Wells Fargo MemoDocument5 pagesWells Fargo MemoLucas ManfrediNo ratings yet
- Maklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsDocument2 pagesMaklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsMohd Faizal Bin Omar HathabNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- First Aid: Dog BitesDocument35 pagesFirst Aid: Dog BitesHairul MaisarNo ratings yet
- Environmental & Pharmaceutical MicrobiologyDocument141 pagesEnvironmental & Pharmaceutical MicrobiologyShanthi_KV100% (4)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- News, Sport and Opinion From The Guardian's Global Edition The GuardianDocument1 pageNews, Sport and Opinion From The Guardian's Global Edition The GuardianCatalina Florentina PricopeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology ExamDocument10 pagesMicrobiology ExamRustom Jose RojoNo ratings yet
- Book Club Pack: Angel of Death: The Story of Smallpox by Gareth WilliamsDocument2 pagesBook Club Pack: Angel of Death: The Story of Smallpox by Gareth WilliamsWellcome TrustNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Enfermedades de Transmision SexualDocument45 pagesEnfermedades de Transmision SexualGerardo LermaNo ratings yet
- Hadith About The FlyDocument4 pagesHadith About The FlyomeganeuNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Model Paper - 1 (Sscstudy - Com)Document13 pagesSSC CGL Model Paper - 1 (Sscstudy - Com)Anand PrakashNo ratings yet
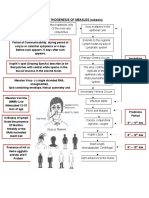
- Measles PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMeasles PathophysiologyAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal SampleDocument3 pagesProject Proposal SamplePhillippe Vikxen Layco Ermino69% (13)
- Edt WordDocument6 pagesEdt Wordapi-285467610No ratings yet
- MCPC Agar (Vibrio) PDFDocument2 pagesMCPC Agar (Vibrio) PDFpollux23No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- L.loaf - The Truth About Vaccination and Immunization (1951)Document35 pagesL.loaf - The Truth About Vaccination and Immunization (1951)BobNo ratings yet
- Sanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 5 BedwettingDocument1 pageSanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 5 BedwettingEduardoNo ratings yet
- 7) Preventive Health and EPIDocument51 pages7) Preventive Health and EPIDr. Zirwa AsimNo ratings yet
- Disease and Immunity P1Document8 pagesDisease and Immunity P1Soliman MNo ratings yet
- IMP SREQ RequirementsDocument2 pagesIMP SREQ RequirementsAlexandreau del FierroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Rivision QuestionsDocument38 pagesNursing Rivision Questionssosokhideer100% (1)
- Gulf Times PDFDocument12 pagesGulf Times PDFAshif IqubalNo ratings yet
- SCIAM February 2014Document92 pagesSCIAM February 2014Bruno MoreiraNo ratings yet
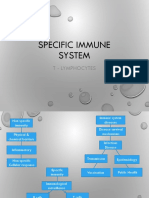
- Specific Immune System: T - LymphocytesDocument18 pagesSpecific Immune System: T - Lymphocytesarun231187No ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument14 pagesPoliomyelitisEzekiel Reyes100% (1)
- Plant Derived Edible Vaccine Through Transgenics PowerpointDocument23 pagesPlant Derived Edible Vaccine Through Transgenics PowerpointHelein Marina Joseph100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Protozoan DiseasesDocument26 pagesProtozoan DiseasesMykki Gigi NateNo ratings yet
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocument1 pageCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsCTM MURUGANNo ratings yet
- From Fear To HopeDocument3 pagesFrom Fear To Hopeapi-543565116No ratings yet