Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Healthcare System of Pakistan
Uploaded by
IJARP PublicationsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Healthcare System of Pakistan
Uploaded by
IJARP PublicationsCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Advanced Research and Publications
ISSN: 2456-9992
Healthcare System Of Pakistan
Dr. Ahmad Hassan, Dr. Khalid Mahmood, Dr. Hudebia Allah Bukhsh
College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan, Lahore, Pakistan, PH- +92 3007452269
dr.ahmadmalik@yahoo.com
College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan, Hyderabad, Pakistan, PH- +92 3359098877
khalid281f@yahoo.com
College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan, Karachi, Pakistan
hudebia@yahoo.com
Abstract: Paper is about healthcare delivery system, multiple challenges, weaknesses in health policies and recommendations to improve
Healthcare System of Pakistan. Healthcare sector is very important for any country which directly affects the economy of country. If there
would be healthy manpower there would be increase in the productivity and as a result the economy of the country will also see an increase
that leads to human welfare. Pakistan inherited totally inadequate Healthcare delivery system that was a heritage of grand British period.
Healthcare system in Pakistan is practically vertical and in part, horizontal. Healthcare system of Pakistan consists of private and public
sector. The private sector serves nearly 70% of population and 30% by public sector (1). Pakistan is a low income country and according to
Human Poverty Index (HPI), it ranks 65th among 102 developing countries (2). Only 27% of the population benefited from full healthcare
coverage which includes mostly government employees and members of armed forces, and remaining 73% depends on out of pocket
payments (3). In Pakistan public sector health expenditure is 0.919% of GDP as per World Bank data 2014 (4). As per Pakistan constitution
provision of health is responsibility of provincial governments except in federally administered areas. State Healthcare Service delivery is
being organized through a three-tiered Healthcare delivery system. The former includes Basic Health Units (BHUs) and Rural Health
Centers (RHCs) forming core of primary Healthcare structure. Tehsil Head Quarters (THQs) and District Head Quarters (DHQs) for
secondary care including first and second referral facilities which are supported by Tertiary care from teaching hospitals (3).
Keywords: Healthcare System, health policies, healthcare delivery system, regional countries health index, health challenges & health
programs in Pakistan.
2. Secondary Healthcare
Healthcare Regulatory authorities It is an intermediate level of Healthcare that is concerned
Pakistan Medical & Dental Council, Pakistan Council of with provision of technical, therapeutic and diagnostic
Homeopathy, Pakistan Nursing Council, Council of Tibb and services. It is first referral level serving at district and tehsil.
Ministry of National Health Services, Regulation & Specialist consultation and hospital admissions fall into this
Coordination. Under 18th amendment Ministry of Health category.
was devolved to the provinces by Federal Government on
June 30, 2011. Although re-installed again in April 2013, but 2.1 Tehsil Head Quarters & District Head Quarters
most of the programs and responsibilities of Health Ministry Tehsil Head Quarters (THQs) serve a population of 0.5 to 1
are transferred to provincial health departments (5). Pakistan Million peoples. Most of THQs have 40-60 beds. THQs are
Medical & Dental Council (PM&DC) is a regulatory supposed to provide basic and comprehensive Emergency,
authority established under (PM&DC) ordinance 1962 as a Obstetrics and newborn care. Provide referral care to those
body corporate. Aim is to provide quality Healthcare referred by RHCs, BHU and Lady Health Workers (7).
Services to the people of Pakistan (6). District Head Quarters (DHQs) are located at district level
and serves 1-3 million population. DHQs provide promotive,
Healthcare delivery system of Pakistan preventive, curative, diagnostics, inpatient and referral
services. All DHQs provide referral care to patients referred
1. Primary Healthcare by BHUs, RHCs and Tehsil Head Quarters (7).
This is first level of Healthcare, where patients have their
initial interaction with system and it provides curative and 3. Tertiary Healthcare
preventive Healthcare Services. Tertiary Healthcare hospitals are for more specialized
inpatient care. Specialized Healthcare services usually for
1.1 Basic Health Units & Rural Health Centers inpatients and on referrals from primary or secondary health
Basic Health Units (BHUs) are located at Union Council professionals (7).
level and serves catchment population of up to 25,000.
Preventive curative and referral services are provided.
Maternal and child health (MCH) services are also part of
services packages provided at Basic Health Units. BHUs
also provide clinical, logistical and managerial support to
Lady Health Workers (LHWs) (7). Rural Health Centers
(RHCs) serve catchment population of up to 100,000 people.
Here provided promotive, preventive, curative, diagnostics
and referrals along with inpatient services. Also provide
clinical, logistical and managerial support to BHUs, LHWs
and MCH Centers (7).
Volume 1 Issue 4, Oct 2017 170
www.ijarp.org
International Journal of Advanced Research and Publications
ISSN: 2456-9992
Health Indicators comparison Regional countries Human Healthcare System in Pakistan has been confronted with
Development Indicator (HDI) problems of scarcity of resources, inequity, insufficient and
untrained human resources, structural mismanagement and
gender insensitivity. Health system has been designed by
politicians while implemented by the health professionals on
the ground (9). Accessibility and affordability for health
services especially for rural population of the country is a big
issue because of severe shortage of healthcare professionals
and inadequate allocation of funds for Primary Healthcare
sector (3). Reliable Health Information Management system
is not available at Primary and Secondary level to evaluate
and improve the services. Lack of medical research and
technology at national level is one of reason to deliver sub-
standard services (9). Health Policies developed are unhealthy
and their weak implementation. There are certain reasons
Pakistan has highest population growth rate of 1.92% behind, such as insufficient healthcare financing in public
followed by Philippines 1.73% in 2013 (8). MMR in Pakistan sector, corruption, political interference and lack of
is 170/10000 which is 4th largest after Philippines, India and accountability for low performance (3). There are some other
Nepal 190/10000 in 2013 (8). Pakistan is at top of the ranking key challenges in the way to provide quality healthcare
in the region Under 5 mortality rate per 1000 is 85.5 service in Pakistan. These are; double burden of disease,
followed by India 52.7 in 2013 (8). IMR is 69/1000; also first vertical service delivery structure, and development of
place in regional ranking followed by India 41.4 in 2013 (8). inadequate human resource in health sector, population
Life expectancy, only India is below to Pakistan with the explosion, poverty, and illiteracy, lack of health education in
difference of 0.1 in 2013 (8). community, poor sanitation and sewerage.
Regional countries health expenditure, public (% of Health Policies of Pakistan
GDP) First formal National Health Policy was announced in 1990
in Pakistan. In first National Health policy declared high
commitment to health by increasing health expenditures up
to 5% of GNI. Attention was given to clean water and family
planning to improve health (10). Second National Health
Policy was formulated in 1997. It was based on the concept
of health for all (HFA). Attention was given to HIV/AIDS,
road traffic accidents, violence, tuberculosis, cancer, diabetes
and mental health (10). Third National Health Policy (2001)
is again based on health for all approach. Ten key areas
identified reducing communicable disease, addressing
inadequacies in primary/secondary healthcare, promoting
gender equity, correcting rural/urban discrepancy in health
sector and improvements in drug sector etc. (10). Only draft
policy was developed in 2010 but not approved due to
As per World Bank reports for the regional countries, ongoing process of devolution. Federal and Provincial
Pakistan has 2nd lowest health expenditures (% of GDP) Governments agreed on common Nation Health Vision
which is 0.919 in 2014 after Bangladesh of 0.787 in the same (2016-2025). Vision statement is to improve health of all
year (4). Highest among the region is by Thailand which is Pakistanis particularly women and children through
5.615 (% of GDP) in 2014. affordable universal access to quality Healthcare Services,
delivered through responsive health system (11).
Healthcare Facilities in Pakistan 2011-2015
Health interventions/programs in Pakistan
Pakistan is a struggling economy with poor health indicators
in the region. However there are some programs
/interventions to ensure timely preventive and curative
services to the public. National Program for Family Planning
& Primary Healthcare was launched in 1994. This provides
Primary Healthcare Services to about 80 million peoples,
most of which is from rural and poor (12). Extended program
on immunization (EPI) started in Pakistan in 1978 and still
continuing. Objective of the EPI program is to reduce
mortality and morbidity by offering timely immunization
services (13). National TB Control Program stands out as one
of the Public Health Programs towards achievement of
Millennium Developmental Goal targets in 2015. Objective
of the program is to reduce the prevalence of MDR-TB
Challenges in Health System of Pakistan among the patients who have never received any tuberculosis
Volume 1 Issue 4, Oct 2017 171
www.ijarp.org
International Journal of Advanced Research and Publications
ISSN: 2456-9992
treatment by at least 5% per year by 2020 (14). National 1. It would be better to move away from curative biomedical
AIDS Control Program (NACP) in collaboration with model towards more extensive and holistic approach. Other
provincial programs developed its first National Strategy factors such as environment, social and cultural aspects need
Framework in 2001. This followed by 2nd National Strategy to be concurrently addressed to improve the health of people
(18)
Framework and then 3rd Framework that focused on the .
quality HIV treatment and services (15). Malaria Control 2. It would be highly beneficial, if policy making is
Programs are on ground since 1950s. Malaria control decentralized and delegated to districts, because they can
activities were integrated with communicable disease control adopt better and realistic approach for the problems they
selection by the provinces in 1977. In July 2011 again encounter on daily basis (18).
revived under administrative control of Ministry of Inter 3. More resources should be kept into capacity building of
Provincial Coordination (16). Drug Abuse Control Program the administrators at district level to understand
by Ministry of Narcotics Control in 2010-14. Objective of contemporary health issues, because the root causes of
the program is drug free Pakistan (17). There are numerous problems are not addressed while formulating policies, due
other programs at the national level such as; National to lack of knowledge about concerned place and population
(18)
Program for the Prevention and Control of Blindness, Cancer .
Treatment Program, Tobacco Control Cell, National 4. All stakeholders should be involved in planning, decision
Nutrition Program and National Maternal, Newborn and and implementation of programs at all levels to ensure
Child Health Program. efficiency and sustainability of programs (19).
5. Better monitoring and evaluation tools should be
Weaknesses in Health Policies of Pakistan constructed to get valuable and unbiased feedback to policy
Health Policies mainly focus on curative Healthcare such as makers and implementers (18).
increasing number of health facilities, laboratories, 6. Other key measures can be taken to improve Healthcare
ambulances and modern equipment’s without assessment of sector of Pakistan; control population growth, increase
how health professionals will use them, who are not trained literacy rate, increase health budget, control corruption in
for modern technology (18). While formulating the policies, public health projects, regionalization of Healthcare services,
insight is taken from success stories of developed countries and promote health education, proper check on quackery and
without considering ground realities, religious, cultural exchange of human resource and knowledge with developed
values, social dimension and paying less attention to countries.
economic differences (18). Contents of Health policies shows
same traditional biomedical model dealing with the References
treatment of disease rather than covering cultural and [1] @. (2015, March 23). Health Care System In Pakistan
environmental determinants to prevent disease (18). All Health And Social Care Essay. Retrieved October 25,
vertical programs are implemented at primary Healthcare 2016, from https://www.ukessays.com/essays/health-
facilities but are administered and run by Federal and-social-care/health-care-system-in-pakistan-health-
Government. This creates disharmony at BHU and district and-social-care-essay.php
level because they are not involved in planning of programs.
Monitoring and evaluation is another gap in health policies. [2] Health System Profile - Pakistan. (2007). Retrieved
No system to compile, evaluate and use data for assessment October 25, 2016, from
and policy reforms at district level. As a result data is not http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js17305e/
presented to Federal Ministry for feedback and evaluation of
vertical programs (18). [3] Analysis of Healthcare Delivery system: Pakistan vs
United States. (2014, June 01). Retrieved October 25,
Conclusion 2016, from http://aeirc-edu.com/wp-
Healthcare system of Pakistan especially primary Healthcare content/uploads/11download-full-paper.pdf
is facing numerous problems. Decentralization presents an
opportunity to bring in fundamental changes in Primary [4] Health expenditure, public (% of GDP). (n.d.).
Healthcare to make it more efficient and effective to the Retrieved October 25, 2016, from
masses. A goal of reforms in Primary Healthcare sector is to http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.XPD.PUBL.ZS?l
restructure the non-efficient system by devolving from ocations=PK
Federal to district level. Healthcare system includes building
blocks such as leadership, service delivery, technology, [5] Ministry of National Health Services Regulation and
health workforce, healthcare finance and research. To Coordination.(n.d.). Retrieved October
achieve access coverage and quality services monitoring and 25,2016,fromhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ministry_of_
evaluation plays important role (03, 18 and 20). National_Health_Services_Regulation_Coordination
Recommendations [6] Pakistan Medical & Dental Council. (2006). Retrieved
A healthy and functioning healthcare delivery system October 26, 2016, from
mandates mutually supportive and symbiotic relationship http://www.pmdc.org.pk/Home/tabid/36/Default.aspx
and integrates primary, secondary and tertiary care. Such
integration and several strategies could be planned and [7] Primary & Secondary Health Care Department. (n.d.).
implemented to improve healthcare delivery system of Retrieved October 26, 2016, from
Pakistan. Following are the key recommendations to http://www.pshealth.punjab.gov.pk/Services.aspx
improve Healthcare sector of Pakistan (3).
Volume 1 Issue 4, Oct 2017 172
www.ijarp.org
International Journal of Advanced Research and Publications
ISSN: 2456-9992
[8] Health and Nutrition - | Ministry of Finance. (2014- Author 1 received M.D degree in the profession of General
2015). Retrieved October 26, 2016, from Medicine from International Higher School of Medicine
http://www.finance.gov.pk/survey/chapters_15/11_Healt (International University of Kyrgyzstan) in 2013. He joined
h.pdf two years program called Membership of College of
Physicians and Surgeons in Healthcare System Management
[9] Sheikh, B. T. (n.d.). The district health system: A (MCPS-HCSM) at College of Physicians
challenge that remains (PDF ... Retrieved and Surgeons Pakistan in 2016 and now
October26,2016,fromhttps://www.researchgate.net/publi working on thesis to accomplish the MCPS-
cation/7562976_The_district_health_system_A_Challen HCSM degree.
ge_that_remains
[10] Health Policy: What does it mean in Pakistan? (n.d.).
Retrieved October 27, 2016, from
http://www.phmed.umu.se/digitalAssets/76/76123_inlag
a---halema-masoud.pdf
[11] National Health Vision Pakistan 2016-2025. (2016).
Retrieved October 27, 2016, from
http://202.83.164.28/new/userfiles/file/2016
nhsrc/National Health Vision 2016-25_30-08-2016.pdf
[12] Wazir, M. S., Shaikh, B. T., & Ahmed, A. (2013).
National program for family planning and primary
health care Pakistan: A SWOT analysis. Retrieved
October 28, 2016, from
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC384279
7/
[13] Extended Program on Immunization (EPI). (n.d.).
Retrieved October 28, 2016, from
http://health.punjab.gov.pk/epi
[14] Welcome To NTP Pakistan. (n.d.). Retrieved October
29, 2016, from http://www.ntp.gov.pk/
[15] Message from NPM - National AIDS Control Program.
(n.d.). Retrieved October 30, 2016, from
http://www.nacp.gov.pk/howwework/message-npm.html
[16] Malariar7. (n.d.). Retrieved October 30, 2016, from
http://www.dmc.gov.pk/
[17] Drug Abuse Control Master Plan 2010-14. (n.d.).
Retrieved October 30, 2016, from
http://anf.gov.pk/Library ANF/mstrplan.pdf
[18] Health Policy in Pakistan. (2012, May 18). Retrieved
October 30, 2016, from
http://healthpolicypak.blogspot.ae/2012/05/failure-
analysis-of-health-policy-of.html
[19] Analysis of Health Care Delivery System in Pakistan
and Singapore. (n.d.). Retrieved
October30,2016,fromhttps://www.researchgate.net/publi
cation/301561521_Analysis_of_Health_Care_Delivery_
system_in_Pakistan_and_Singapore
[20] Ghaffar, A. (n.d.). An overview of healthcare system in
Pakistan. Retrieved October 30, 2016, from
http://jpubhealth.oxfordjournals.org/content/22/1/38.full.
Author Profile
Volume 1 Issue 4, Oct 2017 173
www.ijarp.org
You might also like
- Health Care Conditions in PakistanDocument35 pagesHealth Care Conditions in PakistanAamir Shehzad93% (14)
- Health Policy Analysis-PakistanDocument138 pagesHealth Policy Analysis-PakistanOurfamily AvinNo ratings yet
- Democracy in Pakistan Hopes and HurdlesDocument10 pagesDemocracy in Pakistan Hopes and HurdlesFarwa HussainNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Health SolutionsDocument43 pagesPakistan Health SolutionsShayan Abbas100% (1)
- Health Sector Reform PDFDocument54 pagesHealth Sector Reform PDFCherry Mae L. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Health Sector in Pakistan by Aamir Mughal and Pakistan Medical AssociationDocument81 pagesHealth Sector in Pakistan by Aamir Mughal and Pakistan Medical AssociationAamir Mughal100% (1)
- Informal EducationDocument4 pagesInformal Educationiqra0% (1)
- Panchayat RajDocument33 pagesPanchayat RajSurabhi Sadavat100% (1)
- Failure Analysis 6-28-09Document41 pagesFailure Analysis 6-28-09farah goharNo ratings yet
- BSC Nursing ProspectusDocument43 pagesBSC Nursing ProspectusMohamed Aarthif JanaNo ratings yet
- Major Stakeholders in Healthcare SystemDocument7 pagesMajor Stakeholders in Healthcare SystemsurajNo ratings yet
- Socio Economic Problems of PakistanDocument12 pagesSocio Economic Problems of PakistanSyed Mustafa NajeebNo ratings yet
- Five Year PlanDocument11 pagesFive Year Plananjali ahuklaNo ratings yet
- Health and SanitationDocument10 pagesHealth and SanitationMuhammad Sadiq NaseerNo ratings yet
- Women Workers in NREGA: Literature ReviewDocument28 pagesWomen Workers in NREGA: Literature ReviewIISaireneII50% (2)
- POSHAN Abhiyaan PDFDocument2 pagesPOSHAN Abhiyaan PDFVishal Pal Vishal PalNo ratings yet
- Over Population in PakistanDocument3 pagesOver Population in PakistanTubi NazNo ratings yet
- Poverty in PakistanDocument23 pagesPoverty in PakistanmubeenbuttNo ratings yet
- Health System Delivery in BangladeshDocument50 pagesHealth System Delivery in BangladeshDip Ayan MNo ratings yet
- Destiny of A Nation Is Shaped in Its ClassroomDocument8 pagesDestiny of A Nation Is Shaped in Its Classroomsabir17No ratings yet
- Health Care DeliveryDocument55 pagesHealth Care Deliveryavinash dhameriyaNo ratings yet
- Read The Presidential Health Summit ReportDocument35 pagesRead The Presidential Health Summit ReportBhekisisa Health100% (1)
- Community Based RehabilitationDocument34 pagesCommunity Based RehabilitationAshwathiNo ratings yet
- Primary Health CareDocument30 pagesPrimary Health CareSan SiddzNo ratings yet
- Major Environmental Issues of Pakistan Prevention and SolutionsDocument29 pagesMajor Environmental Issues of Pakistan Prevention and SolutionssaadNo ratings yet
- Css NotesDocument90 pagesCss NotesWaqas AmjadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 2Shini SimonNo ratings yet
- Education System of Pakistan Problems, Issues and Its Solution (Gul Muhammad Education Planning and Management Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad)Document8 pagesEducation System of Pakistan Problems, Issues and Its Solution (Gul Muhammad Education Planning and Management Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad)Gul Muhammad100% (1)
- Unit I Introduction To HealthDocument11 pagesUnit I Introduction To Healthishir babu sharmaNo ratings yet
- Problems Faced by Elderly in IndiaDocument3 pagesProblems Faced by Elderly in IndiaDevi Nair100% (1)
- Problems of Youth in The Present ScenarioDocument3 pagesProblems of Youth in The Present ScenarioMalik KhanNo ratings yet
- PMS INterviewDocument24 pagesPMS INterviewRead To LeadNo ratings yet
- Health Care System in PakistanDocument20 pagesHealth Care System in PakistanSobia50% (2)
- Democracy and Governance in PakistanDocument207 pagesDemocracy and Governance in Pakistancooll7553950No ratings yet
- Women EmpowermentDocument14 pagesWomen Empowermentjohnmail9830No ratings yet
- Reasons For The Low Literacy Rate in PakistanDocument4 pagesReasons For The Low Literacy Rate in PakistanHaris AliNo ratings yet
- Pakistan's Foreign PolicyDocument107 pagesPakistan's Foreign PolicyFarooq ShahNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Private Sector in Achieving Universal Healthcare in IndiaDocument7 pagesThe Role of The Private Sector in Achieving Universal Healthcare in IndiaEmerging Markets Health NetworkNo ratings yet
- IlliteracyDocument9 pagesIlliteracyAbdullah SheikhNo ratings yet
- Issues in Health Sector India: Dr. P. P. DokeDocument60 pagesIssues in Health Sector India: Dr. P. P. DokeAmrita RoyNo ratings yet
- Patterns in Maternal Mortality Following The Implementation of A Free Maternal Health Care Policy in Kenyan Public Health FacilitiesDocument12 pagesPatterns in Maternal Mortality Following The Implementation of A Free Maternal Health Care Policy in Kenyan Public Health FacilitiesCosmas MugambiNo ratings yet
- Primary Health Care in IndiaDocument37 pagesPrimary Health Care in Indiadrsanjeev15No ratings yet
- Education CSS EssayDocument7 pagesEducation CSS EssayAsif Khan100% (1)
- Right To Information Act by Abdul MatinDocument16 pagesRight To Information Act by Abdul Matinibrahim khanNo ratings yet
- Gender Mainstreaming in India - FDocument187 pagesGender Mainstreaming in India - Fbrsiwal1475100% (5)
- Educational Problems in PakistanDocument14 pagesEducational Problems in PakistanABM2014No ratings yet
- Major Social Problems of PakistanDocument11 pagesMajor Social Problems of Pakistannimra rafiNo ratings yet
- "It Is Health That Is Real Wealth and Not Pieces of Gold and Silver" Mahatma GandhiDocument8 pages"It Is Health That Is Real Wealth and Not Pieces of Gold and Silver" Mahatma GandhishivamNo ratings yet
- Education System of PakistanDocument4 pagesEducation System of PakistanWaris Arslan0% (1)
- Privatization in PakistanDocument4 pagesPrivatization in PakistanArshgeeNo ratings yet
- Decentralization Reforms in PakistanDocument11 pagesDecentralization Reforms in PakistanZulkifl HaiderNo ratings yet
- Freedom of Media in Pakistan Blessing or BaneDocument20 pagesFreedom of Media in Pakistan Blessing or BaneIkra Malik100% (1)
- Socio Economic Problems of PakistanDocument5 pagesSocio Economic Problems of PakistanHassan RazaNo ratings yet
- Social Issues of Pakistan: Dated: 23 April 2019Document23 pagesSocial Issues of Pakistan: Dated: 23 April 2019Muhammad Ahmed SaleemNo ratings yet
- Healthcare System of Pakistan PDFDocument4 pagesHealthcare System of Pakistan PDFMOIZ ZUBAIRNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Systems Its Challenges in PakistanDocument7 pagesHealthcare Systems Its Challenges in PakistanYusra NazNo ratings yet
- Healthcare System of PakistanDocument7 pagesHealthcare System of PakistanHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Review-Health Systems in India PDFDocument4 pagesReview-Health Systems in India PDFTehMarianNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Health Care Services Under Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana AB (PM-JAY) - A Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesIntroduction of Health Care Services Under Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana AB (PM-JAY) - A Literature ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- CC-5 ACCESS TO RURAL HEALTHCARE-minDocument12 pagesCC-5 ACCESS TO RURAL HEALTHCARE-minsmsunil12345No ratings yet
- Coronary Diseases Modeling of Some Risk Factors Using Artificial Intelligence TechniquesDocument5 pagesCoronary Diseases Modeling of Some Risk Factors Using Artificial Intelligence TechniquesIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Clotting and Gel Separator Property of Extract From The Roots of Damong Maria Artemisia Vulgaris With Oryza SativaDocument9 pagesClotting and Gel Separator Property of Extract From The Roots of Damong Maria Artemisia Vulgaris With Oryza SativaIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Construction of Incomplete Counterbalancing For Immediate Sequential Effects Crossover DesignDocument3 pagesConstruction of Incomplete Counterbalancing For Immediate Sequential Effects Crossover DesignIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Deforestation Forest Scarcity and Adaptation Stategy in Sapele Delta State NigeriaDocument9 pagesDeforestation Forest Scarcity and Adaptation Stategy in Sapele Delta State NigeriaIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Effectiveness of Modelling Technology of Instructional Media On The Junior Secondary Students Creative Arts in Abuja NigeriaDocument6 pagesComparative Effectiveness of Modelling Technology of Instructional Media On The Junior Secondary Students Creative Arts in Abuja NigeriaIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Moveable Solar Energy Street Light For Use in Nigerian Institute of Leather and Science TechnologyDocument3 pagesDesign and Construction of Moveable Solar Energy Street Light For Use in Nigerian Institute of Leather and Science TechnologyIJARP Publications100% (1)
- Teachers Career Performance in Secondary Education Case Study of Teachers Psychology Ethics Moral and Values in Dodoma M TanzaniaDocument8 pagesTeachers Career Performance in Secondary Education Case Study of Teachers Psychology Ethics Moral and Values in Dodoma M TanzaniaIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Variation in Topsoil Electrcial Resistivity With Chromium ConcentrationDocument5 pagesVariation in Topsoil Electrcial Resistivity With Chromium ConcentrationIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Control of Weed Threshold Using Artificial Neural NetworksDocument4 pagesControl of Weed Threshold Using Artificial Neural NetworksIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Training Needs Assessment of Health Personnel On The Management of Diabetes Mellitus in The West Region of CameroonDocument6 pagesTraining Needs Assessment of Health Personnel On The Management of Diabetes Mellitus in The West Region of CameroonIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Fitness Levels Among Undergraduate Students of A Nigerian University Using Coopers 12 Minute Walk TestDocument3 pagesAerobic Fitness Levels Among Undergraduate Students of A Nigerian University Using Coopers 12 Minute Walk TestIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Proximate Chemical Components Nutritional Value Antinutritional and Antioxidant Properties in Yellow Mustard SeedsDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Proximate Chemical Components Nutritional Value Antinutritional and Antioxidant Properties in Yellow Mustard SeedsIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis On The Factors Affecting Employee Turnover Between Supervisors and Frontline Employees in The Bpo IndustryDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis On The Factors Affecting Employee Turnover Between Supervisors and Frontline Employees in The Bpo IndustryIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of Instagram Buzzer Accounts For Maximizing Promotional ActivityDocument6 pagesThe Analysis of Instagram Buzzer Accounts For Maximizing Promotional ActivityIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Reclamation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil by Using Biochar As Soil ConditionerDocument5 pagesReclamation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil by Using Biochar As Soil ConditionerIJARP Publications100% (1)
- The Entry Level Nursing Competencies and The Gaps Between Nursing Education and PracticeDocument6 pagesThe Entry Level Nursing Competencies and The Gaps Between Nursing Education and PracticeIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Zeolite Membrane and Modeling Dehydration of Organic Compounds On The Pilot Scale With The Help of Artificial Neural NetworkDocument7 pagesPreparation of Zeolite Membrane and Modeling Dehydration of Organic Compounds On The Pilot Scale With The Help of Artificial Neural NetworkIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Adsorption Process in Wastewater Treatment Using Artificial Neural NetworkDocument5 pagesModeling of Adsorption Process in Wastewater Treatment Using Artificial Neural NetworkIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Investment in Bursa Malaysia Between Returns and RisksDocument8 pagesInvestment in Bursa Malaysia Between Returns and RisksIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- The Vat and The Importance of Its Application in IraqDocument4 pagesThe Vat and The Importance of Its Application in IraqIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Peacekeeping Action Team in Crime Prevention of Selected Villages in Cebu City PhilippinesDocument9 pagesPeacekeeping Action Team in Crime Prevention of Selected Villages in Cebu City PhilippinesIJARP Publications100% (1)
- Optimality Boundary Conditions For Stochastic Elliptic System Involving Higher Order OperatorDocument4 pagesOptimality Boundary Conditions For Stochastic Elliptic System Involving Higher Order OperatorIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Heavy Traffic Vehicular Exhausts Roads Side Polluted Guinea Grass Paniaum Maximum On Health Performance and Pathological Responses of Guinea Pigs in Humans As The Consumer of Its MeatDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Heavy Traffic Vehicular Exhausts Roads Side Polluted Guinea Grass Paniaum Maximum On Health Performance and Pathological Responses of Guinea Pigs in Humans As The Consumer of Its MeatIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Print Media and The Challenges of Social MediaDocument6 pagesPrint Media and The Challenges of Social MediaIJARP Publications100% (1)
- Prevalence of Nematode Contracaecum and Cestode Ligula Intestinalis Parasites Infection in Two Fish Species at Lake TanaDocument8 pagesPrevalence of Nematode Contracaecum and Cestode Ligula Intestinalis Parasites Infection in Two Fish Species at Lake TanaIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Resource Supply Thresholds That Trigger Livestock Movement Leading To Grazing Conflicts in Northern KenyaDocument6 pagesEvaluating The Resource Supply Thresholds That Trigger Livestock Movement Leading To Grazing Conflicts in Northern KenyaIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Hivaids Related Knowledge Attitude Risk Perception and Sexual BehaviorDocument5 pagesHivaids Related Knowledge Attitude Risk Perception and Sexual BehaviorIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of Proportional Allocation Procedure Over Other Allocation Procedures in Stratified Random SamplingDocument3 pagesEfficiency of Proportional Allocation Procedure Over Other Allocation Procedures in Stratified Random SamplingIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Factors Related To The Maritime Pre Apprenticeship Phase of A UniversityDocument7 pagesFactors Related To The Maritime Pre Apprenticeship Phase of A UniversityIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Recombinant Inbred Lines Derived From Bulk Population Method of Selection in Rice Oryza Sativa LDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Recombinant Inbred Lines Derived From Bulk Population Method of Selection in Rice Oryza Sativa LIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- PFA Vs PTFE in InstrumentationDocument5 pagesPFA Vs PTFE in InstrumentationArif HakimNo ratings yet
- Handover Paper Final 22 3 16 BJNDocument13 pagesHandover Paper Final 22 3 16 BJNsisaraaah12No ratings yet
- Paracetamol DegradationDocument9 pagesParacetamol DegradationTruyền Phạm MinhNo ratings yet
- Trophic Levels - 10% RuleDocument5 pagesTrophic Levels - 10% RulerebbiegNo ratings yet
- Bad Effects of Festivals On The EnvironmentDocument10 pagesBad Effects of Festivals On The EnvironmentSahil Bohra85% (52)
- Dental Hygienist Learning Outcomes Form v1.2Document32 pagesDental Hygienist Learning Outcomes Form v1.2Karman Deep Singh100% (1)
- Comprehensive Soup ProjectDocument98 pagesComprehensive Soup ProjectSachin Soni63% (8)
- 2mw Biomass Gasification Gas Power Plant ProposalDocument9 pages2mw Biomass Gasification Gas Power Plant ProposalsabrahimaNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy: Treatment For Grade 11 Stem Students Who Suffer Stress From Basic CalculusDocument12 pagesMusic Therapy: Treatment For Grade 11 Stem Students Who Suffer Stress From Basic CalculusArvinel L. VileganoNo ratings yet
- Shelf Life ControlDocument7 pagesShelf Life ControlRushikesh Deshpande100% (1)
- ASNT QuestionsDocument3 pagesASNT Questionsshabbir626100% (1)
- APPLE FRITTER CAKE Cook Heavenly RecipesDocument4 pagesAPPLE FRITTER CAKE Cook Heavenly Recipes1940LaSalleNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis DissertationDocument8 pagesOsteoarthritis DissertationPaperHelpJackson100% (1)
- LabExercise2 PoriferaDocument13 pagesLabExercise2 PoriferaMarvin I. Delos SantosNo ratings yet
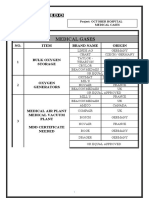
- Medical Gases: NO. Item Brand Name OriginDocument4 pagesMedical Gases: NO. Item Brand Name OriginMahmoud AnwerNo ratings yet
- Manual Jib 25 10 02Document256 pagesManual Jib 25 10 02Luis Jose LlobanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Financial Statements of Company, Oil and Gas.Document105 pagesComparative Study of Financial Statements of Company, Oil and Gas.Ray Brijesh AjayNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Shock (Anestesi)Document44 pagesHemorrhagic Shock (Anestesi)Dwi Meutia IndriatiNo ratings yet
- Envirotainer RKN E1 Operations ManualDocument46 pagesEnvirotainer RKN E1 Operations ManualJorge de oliveiraNo ratings yet
- School Administration and Supervision MAED 605Document24 pagesSchool Administration and Supervision MAED 605Jaynie Ann TapdasanNo ratings yet
- All About Ocean Life-Rachel BladonDocument6 pagesAll About Ocean Life-Rachel BladonRichard TekulaNo ratings yet
- Allnex Powder BrochureDocument28 pagesAllnex Powder BrochureandreathomeNo ratings yet
- SubstationsDocument39 pagesSubstationspNo ratings yet
- Bandura Social Cognitive TheoryDocument93 pagesBandura Social Cognitive TheoryВикторияNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQJagdishVankar100% (1)
- Location: Map of Naga CityDocument2 pagesLocation: Map of Naga Citycatherine boragayNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument3 pagesControllingGenesis_Y_Gall_6808No ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Family With An InfantDocument26 pagesNursing Care of A Family With An InfantJc GarciaNo ratings yet
- Facebow Tech Spec Gen LRDocument1 pageFacebow Tech Spec Gen LRrojNo ratings yet
- SM Electrical Guidelines: General Notes:: Site HereDocument1 pageSM Electrical Guidelines: General Notes:: Site HereNathaniel DreuNo ratings yet