Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classroom Observation Guidelines
Uploaded by
Puskar Bist0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views5 pagesThis document provides guidelines for classroom observations, including items to qualitatively describe such as the development of learning objectives, selection and use of instructional materials, educational climate, variety of instructional activities, preparation for class, instructional methods, opportunity for student participation, individualization of instruction, responsiveness to student feedback, and learning difficulties. The observer is asked to provide thick descriptions for each item. At the end, the observer lists competencies learned from the class and signs the document.
Original Description:
Classroom Observation Guidelines...
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidelines for classroom observations, including items to qualitatively describe such as the development of learning objectives, selection and use of instructional materials, educational climate, variety of instructional activities, preparation for class, instructional methods, opportunity for student participation, individualization of instruction, responsiveness to student feedback, and learning difficulties. The observer is asked to provide thick descriptions for each item. At the end, the observer lists competencies learned from the class and signs the document.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views5 pagesClassroom Observation Guidelines
Uploaded by
Puskar BistThis document provides guidelines for classroom observations, including items to qualitatively describe such as the development of learning objectives, selection and use of instructional materials, educational climate, variety of instructional activities, preparation for class, instructional methods, opportunity for student participation, individualization of instruction, responsiveness to student feedback, and learning difficulties. The observer is asked to provide thick descriptions for each item. At the end, the observer lists competencies learned from the class and signs the document.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Classroom Observation Guidelines
Name of Teacher: ………………….. Date of Observation: ……………………………………….. Observed Time: ……………………………
Level of Observed Class: …………………… Name of Observed Campus/School: ……………………………………………………………..
Items Qualitative Information (Thick Description)
Development of Learning Objectives
Objectives for the class are given (verbally,
written, or not at all)
Objectives only discussed at the end of class
Objectives communicate only higher order
thinking and deeper understanding skills
Objectives confer only necessary skills
Selection and Use of Instructional Materials
Text books are only materials provided to
students
Films, websites, and other audiovisual materials
have a clear purpose
Handouts are provided appropriately
Since the text may be pre-selected, thus the
teacher provides support with reading or using the
text, if necessary
Educational Climate for Learning
Students and the teacher are interested and
enthusiastic
The teacher uses students names in the class
Humor is used appropriately
Teacher does not embarrass or belittle students in
any way
The atmosphere of the class is participative
The teacher had eye contact with students
Teacher incorporate collaborative structures,
working in pair, triads, and quads on task aligned
with the standards during guided practice
Variety of Instructional Activities
Timing of classroom activities considers attention
spans
Teacher involves students in deciding what issues
to discuss
The teacher provides a chance to students in order
to solve problems as independent critical inquirer
Students help each other with procedures as well
as content
Preparation for Class Session
The teacher provides examples that show
preparation
Students know what preparation (reading or other
assignments ) they should have completed prior to
class
Students are presented with a real world, ill
structured, or complex problems as motivational
strategy
Students demonstrate intrinsic motivation
The teacher caters for problems to engage
students in order to develop their three level of
criticality
Instructional Methods
The opening gained the class’s attention
It established rapport
The opening outlined the topic and purpose of the
lecture
The delivery is paced to students’ needs
The teacher introduces topic and state goals
The teacher presents the material or activity
effectively
The teacher summarizes the lesson and gives the
assignment
The teacher suggests an idea to consider before
the next class
The teacher could be seen and heard
Key points were emphasized
Explanations were clear to students
Examples, metaphors, and analogies were
appropriate
The lecture was stimulating and thought
provoking
The teacher focuses small group
The teacher focuses only whole class discussion
The teacher evaluates the class such that the
students would know his/her presentation
The teacher provides students chance to prepare
their own notes rather than copied lecture
The teacher groups the students according to their
learning ability during class
The teacher construes the students’ ownership as
in critical understanding
Most students included in discussion or in
problem solving
Opportunity for Students Participation
The teacher encourages students to summarize
and add to others’ summaries
The teacher helps quieter students to interact with
others
Students have internalized the value of hard work
The teacher encourages students to make real
world connections
Students are engaging in the new knowledge
learned practice.
The teacher encourages students to respond
frequently
Individualization of Instruction
The emotional, physical, and intellectual needs of
students are met
The teacher solves the problem raised by
individual student in the class
The teacher prompts awareness of students’ prior
learning and experiences
The teacher offers “real world” application
The teacher is available before or after class
The teacher relates class to course goals, students’
personal goals, or societal concerns
The teacher provides conversation among
students of different ability
The teacher uses an individual’s past and current
state of knowledge for solving problems
The teacher identifies appropriate types of
knowledge for skill development
Responsiveness to Students Feedback
The teacher is paying attention to cues of
boredom and confusion
The teacher encourages students’ questions
The teacher provides students opportunity to
mention problems/concerns with the class, either
verbally or in writing
The teacher uses feedback as interwoven process
with instruction
Learning Difficulties
Students need assistance
One or more students are not motivated or unable
to follow the class
Students are able to see visual aids
One group dominates discussion and hinder
others’ participation
Students need ICT for demystifying the
contingency questions
Only few students engage in accountable talks to
show and reasoning during modeled instructions
List the competencies that you leant from the class observation
…………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………….....
Observed By: ……………………..
You might also like
- Bed 150 Observation List PrimaryDocument12 pagesBed 150 Observation List Primaryapi-330260924No ratings yet
- Kindergarten Reading: PhonicsDocument38 pagesKindergarten Reading: PhonicsSuzanne MorgeraNo ratings yet
- Career Guidance Program S.Y. 2016 - 2017 Objectives Program/Activities Target Persons Venue Resources/Budget Time FrameDocument3 pagesCareer Guidance Program S.Y. 2016 - 2017 Objectives Program/Activities Target Persons Venue Resources/Budget Time FrameKarissa100% (1)
- Trends and Issues On Special EducationDocument7 pagesTrends and Issues On Special Education明 志No ratings yet
- Annual Accomplishment 2018-2020: Sto. Rosario Elementary SchoolDocument19 pagesAnnual Accomplishment 2018-2020: Sto. Rosario Elementary SchoolJoe Ralph Cabasag MabborangNo ratings yet
- San Andres Elementary School Intervention ProgramDocument9 pagesSan Andres Elementary School Intervention ProgramMarites Bandong EliangNo ratings yet
- Post Observation - Teacher Self-Evaluation v2015.1 (Oct 2015)Document2 pagesPost Observation - Teacher Self-Evaluation v2015.1 (Oct 2015)Dale Joseph KiehlNo ratings yet
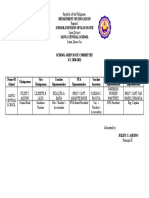
- School Grievance CommitteeDocument1 pageSchool Grievance CommitteeJoel Bagoyo100% (1)
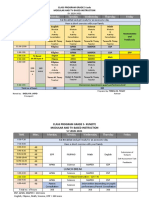
- Proposed - CLASS PROGRAM GRADE 5 EditedDocument3 pagesProposed - CLASS PROGRAM GRADE 5 EditedTeresa Medina TicsayNo ratings yet
- Sample Curriculum Review Form PDFDocument3 pagesSample Curriculum Review Form PDFallan.manaloto23No ratings yet
- Assessing Learners' Performances in Physical Education in The New Normal: Teachers' ExperiencesDocument7 pagesAssessing Learners' Performances in Physical Education in The New Normal: Teachers' ExperiencesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Observation 2Document3 pagesObservation 2api-276753096No ratings yet
- Narrative Report OrientationDocument5 pagesNarrative Report OrientationSHAINA ELOISA CAUNINNo ratings yet
- Arpan Survey InstrumentDocument4 pagesArpan Survey InstrumentJessete YaralNo ratings yet
- Teacher Training Workshop Evaluation Form PDFDocument2 pagesTeacher Training Workshop Evaluation Form PDFSreyneath ChorNo ratings yet
- Teacher Professional Growth PlanDocument4 pagesTeacher Professional Growth Planapi-250249278No ratings yet
- Workplan in ReadingDocument2 pagesWorkplan in ReadingJhe VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- What Is Instructional Supervision-OlarteDocument3 pagesWhat Is Instructional Supervision-OlarteLeu Gim Habana PanuganNo ratings yet
- School Reading Profile: Del Monte National High SchoolDocument5 pagesSchool Reading Profile: Del Monte National High SchoolShirleyNo ratings yet
- Seminar Workshop On SBMDocument37 pagesSeminar Workshop On SBMMary Chris Saldon Balladares100% (1)
- Edu232 Lea Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesEdu232 Lea Lesson Planapi-356636502No ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report Kinder 2020 2021 2ND QDocument4 pagesAccomplishment Report Kinder 2020 2021 2ND QRhell FhebNo ratings yet
- 20 Unit 2 Planning For InstructionDocument52 pages20 Unit 2 Planning For InstructionHazeena SidhikNo ratings yet
- Guide To Formative Assessment Rubric SDocument33 pagesGuide To Formative Assessment Rubric SReygie Fabriga100% (1)
- Employing Vocabulary Instruction For Effective Word Structure and Meaning RecognitionDocument21 pagesEmploying Vocabulary Instruction For Effective Word Structure and Meaning RecognitionWena Fernando Ildefonso100% (1)
- School Learning Continuity Plan - BUYOGAN ES PDFDocument5 pagesSchool Learning Continuity Plan - BUYOGAN ES PDFmark gelNo ratings yet
- Midyear-Performance-Review-In-Service-Training-For-Teachers PresentationDocument22 pagesMidyear-Performance-Review-In-Service-Training-For-Teachers PresentationDIANA ROSE CANON100% (1)
- MATATAGDocument9 pagesMATATAGAce BanggoyNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Monitoring Tool For The Reading Level of Grs. 1 - 3 PupilsDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Monitoring Tool For The Reading Level of Grs. 1 - 3 PupilsXhie Ramos100% (1)
- SHDP Foundation Course Application Project PlanDocument5 pagesSHDP Foundation Course Application Project PlanDenward Pacia100% (2)
- Classroom Observation ReportDocument2 pagesClassroom Observation ReportIzzah Kamilah0% (1)
- Prepare For Principal Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesPrepare For Principal Interview QuestionsRhea Anne NiervesNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation FormDocument2 pagesClassroom Observation FormHeri Zo0% (1)
- LCPDocument18 pagesLCPRydan MinorNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Annex 2: Homeroom Guidance School Implementation Tool (School Level)Document3 pagesDepartment of Education: Annex 2: Homeroom Guidance School Implementation Tool (School Level)prima angelita caneteNo ratings yet
- Learning Process: Wilma R. CamiñaDocument51 pagesLearning Process: Wilma R. CamiñaJohn Joseph Enriquez100% (1)
- Preparation, Submission, & Checking of School Forms For SY 2020-2021Document60 pagesPreparation, Submission, & Checking of School Forms For SY 2020-2021jpfriasNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Reading Assessment1Document67 pagesGuidelines On Reading Assessment1Zybyl ZybylNo ratings yet
- School Readiness Form (December 5, 2017)Document1 pageSchool Readiness Form (December 5, 2017)Joyce PerezNo ratings yet
- Azenith and JoveroseDocument100 pagesAzenith and JoveroseJhongNo ratings yet
- Teacher Behavior Ed IsDocument8 pagesTeacher Behavior Ed IsWidya Kristina ManaluNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Written Assignment - Claros With PicDocument12 pagesModule 11 Written Assignment - Claros With PicLeoniel L. Ronsable100% (1)
- Classroom Observation Form 1Document4 pagesClassroom Observation Form 1api-284530980No ratings yet
- Adm - Night High SchoolDocument35 pagesAdm - Night High SchoolSONNY PEREZ100% (1)
- Lesson Observation Form With Ofsted IndicatorsDocument1 pageLesson Observation Form With Ofsted IndicatorsBenj AlejoNo ratings yet
- Brigada SlipDocument1 pageBrigada SlipVincent Paul SuarezNo ratings yet
- Explicit TeachingDocument7 pagesExplicit TeachingPeter O. GoyenaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Student LearningDocument40 pagesAssessing Student LearningBatutoy925No ratings yet
- DepEd Form 137 E 1Document8 pagesDepEd Form 137 E 1Dennis Millares YapeNo ratings yet
- Elln Assignment Lesson 1 16Document20 pagesElln Assignment Lesson 1 16Venna Mae Jagonio100% (1)
- Post Conference Questions Observation 1Document2 pagesPost Conference Questions Observation 1api-658998541No ratings yet
- Rachel Cummins lp4 Reflection 11-6-17Document2 pagesRachel Cummins lp4 Reflection 11-6-17api-355496659No ratings yet
- ESP Monitoring DLPDocument4 pagesESP Monitoring DLPAileen Sarte JavierNo ratings yet
- Template For Peer Observation 4 Yasmin IbrahimDocument4 pagesTemplate For Peer Observation 4 Yasmin Ibrahimapi-286718309No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Early Grade Reading Assessment Toolkit English 1Document18 pagesDepartment of Education: Early Grade Reading Assessment Toolkit English 1Taegyu100% (1)
- Output Checklist Quality Assessment Criteria Available 1 Yes 0 No Reviewer Comments (What Needs Improvement? or Total Revision?)Document9 pagesOutput Checklist Quality Assessment Criteria Available 1 Yes 0 No Reviewer Comments (What Needs Improvement? or Total Revision?)Guitnang bayan es 109487No ratings yet
- Teacher Performance Observation Guide: Appendix CDocument6 pagesTeacher Performance Observation Guide: Appendix Cmarylen trapalNo ratings yet
- SIP DraftDocument59 pagesSIP DraftLiezl SabadoNo ratings yet
- Sped Director Letter of Intent 2014Document2 pagesSped Director Letter of Intent 2014api-235279180No ratings yet
- Progressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumFrom EverandProgressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumNo ratings yet
- 9 - Compliance Monitoring & LISA in LGsDocument3 pages9 - Compliance Monitoring & LISA in LGsPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- शिक्षा ऐन २०७५ PDFDocument40 pagesशिक्षा ऐन २०७५ PDFPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Pesha QuestionDocument8 pagesPesha QuestionPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- (Paper II) : General Technical Subject Section (A) - 30 MarksDocument4 pages(Paper II) : General Technical Subject Section (A) - 30 MarksPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- 3 All - Non-tech-Officer 6 Level 076-2-9-FinalDocument19 pages3 All - Non-tech-Officer 6 Level 076-2-9-FinalPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Hunger Index of NepalDocument44 pagesHunger Index of NepalPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Hofldtl L WF /) VF / JQM /) VF P2) Zo Fdfu - L Ls - OfsnfkDocument2 pagesHofldtl L WF /) VF / JQM /) VF P2) Zo Fdfu - L Ls - OfsnfkPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Consequence of WarDocument2 pagesConsequence of WarPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Crossing Borders: More InformationDocument10 pagesCrossing Borders: More InformationPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Senior Officer 7 LevelDocument5 pagesSenior Officer 7 LevelPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- What We Do: ForestDocument4 pagesWhat We Do: ForestPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- The Status of Nepal's Mammals - Red ListDocument276 pagesThe Status of Nepal's Mammals - Red ListPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Useful Notes For PSC First PaperDocument2 pagesUseful Notes For PSC First PaperPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Moberly Area Community College: Common Syllabus PSC 150: International RelationsDocument3 pagesMoberly Area Community College: Common Syllabus PSC 150: International RelationsPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Sources of ConflictDocument2 pagesSources of ConflictPuskar BistNo ratings yet
- Teacher Professional Growth PlanDocument3 pagesTeacher Professional Growth Planapi-238881083No ratings yet
- My Mama Had A Dancing HeartDocument3 pagesMy Mama Had A Dancing Heartapi-296427690No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log in MTBDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Log in MTBJayvee UnajanNo ratings yet
- Weebly Lesson Plan-MathDocument3 pagesWeebly Lesson Plan-Mathapi-272273885No ratings yet
- Pecha Kucha Presentation: Classroom Practices To Enable Student ReflectionsDocument6 pagesPecha Kucha Presentation: Classroom Practices To Enable Student ReflectionsraginiNo ratings yet
- INTERDICIPLINARYDocument3 pagesINTERDICIPLINARYEMMANUEL BERNARDINONo ratings yet
- Claire Ross Integrating Skills FinalDocument17 pagesClaire Ross Integrating Skills FinalMilaNo ratings yet
- CICB - NCCCO Preparatory Mobile Crane SeminarDocument3 pagesCICB - NCCCO Preparatory Mobile Crane SeminarAmauri MarrugoNo ratings yet
- DLP For Opening of The ClassDocument2 pagesDLP For Opening of The ClassRey Lacdan GlendroNo ratings yet
- Special Interest Group HandoutDocument2 pagesSpecial Interest Group Handoutapi-241949549No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan RPH English Transition Week Year 1 2021Document5 pagesLesson Plan RPH English Transition Week Year 1 2021Norlizza IsmailNo ratings yet
- New Teacher Orientation Day Classroom ManagementDocument3 pagesNew Teacher Orientation Day Classroom Managementapi-248910805No ratings yet
- Paragraph HamburgerDocument1 pageParagraph HamburgerClaire0% (1)
- 4h Lesson Plan Caitlin Hanson and Emily ADocument3 pages4h Lesson Plan Caitlin Hanson and Emily Aapi-518483960No ratings yet
- Reading Program FormatDocument19 pagesReading Program FormatHenson MadambaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report LAC SessionDocument5 pagesNarrative Report LAC SessionMA. IRISH ACE MAGATAONo ratings yet
- EJ1255862Document5 pagesEJ1255862Ahmad HumaidiNo ratings yet
- PSL I & PSL II Early Childhood Education Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesPSL I & PSL II Early Childhood Education Lesson Planapi-443493732No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan VBDocument4 pagesLesson Plan VBAna MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Tpack Lesson Plan Sample 1Document3 pagesTpack Lesson Plan Sample 1api-534313175100% (2)
- Differentiated InstructionDocument6 pagesDifferentiated InstructionvebibollNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Project 12 Philosophy of EducationDocument3 pagesPortfolio Project 12 Philosophy of Educationapi-516711376No ratings yet
- Criteria For Selecting Childrens LiteratureDocument2 pagesCriteria For Selecting Childrens LiteratureDalynai100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in SCIENCE III-CO2Document8 pagesLesson Plan in SCIENCE III-CO2Ailljim Remolleno Comille100% (1)
- Texas History Lesson Plan28129 WeeblyDocument2 pagesTexas History Lesson Plan28129 Weeblyapi-248692833No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Role PlayDocument9 pagesLesson Plan On Role PlayPriya100% (2)
- Mathematics Assignment 1Document6 pagesMathematics Assignment 1Dexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- Task 2 - My Wonderful DreamsDocument4 pagesTask 2 - My Wonderful DreamsKary Julieth Estrada PeralesNo ratings yet
- Business Description: The Gingerbread House Is A Local Bakery Situated at BormillDocument3 pagesBusiness Description: The Gingerbread House Is A Local Bakery Situated at BormillLokaNo ratings yet
- Materi PPG 2021Document15 pagesMateri PPG 2021herkamayaNo ratings yet