Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Car Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have Four
Uploaded by
Derrick BaltimoreOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Car Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have Four
Uploaded by
Derrick BaltimoreCopyright:
Available Formats
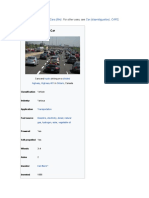
A car (or automobile) is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transportation.
Most definitions of
car say they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four tires, and mainly
transport people rather than goods.[2][3] Cars came into global use during the 20th century, and
developed economies depend on them. The year 1886 is regarded as the birth year of the
modern car when German inventor Karl Benz built his Benz Patent-Motorwagen. Cars
became widely available in the early 20th century. One of the first cars that were accessible
to the masses was the 1908 Model T, an American car manufactured by the Ford Motor
Company. Cars were rapidly adopted in the US, where they replaced animal-drawn carriages
and carts, but took much longer to be accepted in Western Europe and other parts of the
world.
Cars have controls for driving, parking, passenger comfort and safety, and controlling a
variety of lights. Over the decades, additional features and controls have been added to
vehicles, making them progressively more complex. Examples include rear reversing
cameras, air conditioning, navigation systems, and in car entertainment. Most cars in use in
the 2010s are propelled by an internal combustion engine, fueled by the combustion of fossil
fuels. This causes air pollution and also contributes to climate change and global warming.[4]
Vehicles using alternative fuels such as ethanol flexible-fuel vehicles and natural gas vehicles
are also gaining popularity in some countries. Electric cars, which were invented early in the
history of the car, began to become commercially available in 2008.
There are costs and benefits to car use. The costs include acquiring the vehicle, interest
payments (if the car is financed), repairs and maintenance, fuel, depreciation, driving time,
parking fees, taxes, and insurance.[5] The costs to society include maintaining roads, land use,
road congestion, air pollution, public health, health care, and disposing of the vehicle at the
end of its life. Road traffic accidents are the largest cause of injury-related deaths
worldwide.[6]
The benefits include on-demand transportation, mobility, independence, and convenience.[7]
The societal benefits include economic benefits, such as job and wealth creation from the
automotive industry, transportation provision, societal well-being from leisure and travel
opportunities, and revenue generation from the taxes. The ability for people to move flexibly
from place to place has far-reaching implications for the nature of societies.[8] It was
estimated in 2014 that the number of cars was over 1.25 billion vehicles,[9] up from the 500
million of 1986.[10] The numbers are increasing rapidly, especially in China, India and other
newly industrialized countries.[11]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Car
You might also like
- CarDocument2 pagesCarSimran Singh KotlaNo ratings yet
- Ethanol Flexible-Fuel VehiclesDocument1 pageEthanol Flexible-Fuel VehicleslatchanyananaNo ratings yet
- Citation NeededDocument1 pageCitation NeededDexterNo ratings yet
- Cars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiesDocument5 pagesCars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiestjasaNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarinbawNo ratings yet
- Recarch CarDocument1 pageRecarch CarBhupender AswalNo ratings yet
- Rise of Motorized VehiclesDocument2 pagesRise of Motorized VehiclesMauyrNo ratings yet
- მანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობDocument1 pageმანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობdachi apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- WkiDocument1 pageWkiAle IlovanNo ratings yet
- Modern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntarioDocument2 pagesModern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntariosudinorangeNo ratings yet
- Car Doc: History of Cars from 1886 Model T to 1B Vehicles TodayDocument5 pagesCar Doc: History of Cars from 1886 Model T to 1B Vehicles Todaybluesparkles013No ratings yet
- Reference:WikipediaDocument1 pageReference:Wikipediagnoble30No ratings yet
- Cars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument3 pagesCars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orAndrei SlabakovNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarSuryansh RajputNo ratings yet
- FDFXDocument1 pageFDFXMahmoud Al NuaimiNo ratings yet
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument2 pagesJump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orFrances camille TumbagaNo ratings yet
- CARSDocument8 pagesCARSRajbir SinghNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- AutomobileDocument1 pageAutomobileschoolemail bellaNo ratings yet
- Accident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportDocument40 pagesAccident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportAlmubeenNo ratings yet
- A Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsDocument2 pagesA Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsAlin VoicuNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument2 pagesCarssaleha3695No ratings yet
- Safari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Document1 pageSafari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Santosh J Yadav's FriendNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of CarsDocument1 pageThe Evolution of CarsmikkelNo ratings yet
- All About CarsDocument16 pagesAll About Carsapi-255581071No ratings yet
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For The Country, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument30 pagesJump To Navigation Jump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For The Country, See - For Other Uses, See,, orLeonard IonutNo ratings yet
- For Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andDocument4 pagesFor Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andewbNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesDocument88 pagesTata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesParth AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Car HistoryDocument15 pagesCar HistoryprakashNo ratings yet
- Title The Automobile Revolution A JDocument2 pagesTitle The Automobile Revolution A JromohacNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Source - WikipediaDocument3 pagesEtymology: Source - WikipediaWolfMensch1216No ratings yet
- POM SC045 Study ReportDocument6 pagesPOM SC045 Study ReportRushikesh PatilNo ratings yet
- History of CarsDocument21 pagesHistory of CarsGayle OmisolNo ratings yet
- Car ReviewDocument3 pagesCar Reviewerwand21No ratings yet
- Cars Say That They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDocument9 pagesCars Say That They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourShrinivas_shprNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About CarsDocument5 pagesEverything You Need to Know About CarsPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Automotive Industry Analysis of Top CompaniesDocument31 pagesAutomotive Industry Analysis of Top CompaniesSaif Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of AutomobilesDocument2 pagesThe Evolution of Automobilesrjn46189nezidcomNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument56 pagesINTRODUCTIONkoolvansh692No ratings yet
- Promoting Lucas-TVS Filters: Understanding Decreasing SalesDocument58 pagesPromoting Lucas-TVS Filters: Understanding Decreasing SalesSourav Roy0% (1)
- Natural SciencesDocument13 pagesNatural Sciencesxxmahnoor21No ratings yet
- Global Car Industry: A Brief HistoryDocument3 pagesGlobal Car Industry: A Brief HistoryLillian KobusingyeNo ratings yet
- Cars StudyDocument2 pagesCars StudyFfkfj djdjfjNo ratings yet
- Wiki Loves Food - Wikipedia Photo Contest. Upload Pictures of Indian Food and Win PrizesDocument24 pagesWiki Loves Food - Wikipedia Photo Contest. Upload Pictures of Indian Food and Win PrizesgadmaleNo ratings yet
- The World of AutomobilesDocument3 pagesThe World of AutomobilesAmogus MogusNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument12 pagesSwot Analysispoonamy09No ratings yet
- How To Get Spanish Driving License EasilyDocument3 pagesHow To Get Spanish Driving License EasilyDeangelo ParkhursterNo ratings yet
- Scientific PaperDocument9 pagesScientific Paperapi-317125318No ratings yet
- Evolution of Cars Over 100 YearsDocument1 pageEvolution of Cars Over 100 YearsdiogoNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesLiterature ReviewMuhammad Irfan Dogar100% (1)
- CarsDocument2 pagesCarsda. f1tnessNo ratings yet
- Nama: Raina Fishecella Nim: C100220187: Transportation (Car)Document1 pageNama: Raina Fishecella Nim: C100220187: Transportation (Car)Farid AzisNo ratings yet
- Cars and Trucks Driving On A Divided Highway, Highway 401 in Ontario, CanadaDocument24 pagesCars and Trucks Driving On A Divided Highway, Highway 401 in Ontario, CanadaToday NewsNo ratings yet
- Project Report OnDocument61 pagesProject Report OnVinayKumarNo ratings yet
- My Research On CarsDocument1 pageMy Research On Carsjohn williamsNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Muscle CarsDocument15 pagesThe Evolution of Muscle Carsvishal HarshNo ratings yet
- Page SemiDocument39 pagesPage SemiBallon DopeNo ratings yet
- Automobile Industry: Idustry HistoryDocument2 pagesAutomobile Industry: Idustry HistoryFatma MusallamNo ratings yet
- U-UTP - CAT6A Cable PDFDocument4 pagesU-UTP - CAT6A Cable PDFkoen verhoevenNo ratings yet
- A320mh 220712 (En+ru+cn)Document82 pagesA320mh 220712 (En+ru+cn)apolakan65No ratings yet
- Basic Circuits, Laws, and Measurements: Chapter ObjectivesDocument20 pagesBasic Circuits, Laws, and Measurements: Chapter ObjectivesSneha PavithranNo ratings yet
- Veritas Shooting Board C 03 eDocument4 pagesVeritas Shooting Board C 03 eMichael McKennaNo ratings yet
- GMK Manitowoc Training Catalog 2020Document32 pagesGMK Manitowoc Training Catalog 2020aleksandr100% (1)
- Road Wheels & Tires: SectionDocument25 pagesRoad Wheels & Tires: SectionascguateNo ratings yet
- Database-Mm2100 Company Name ListDocument15 pagesDatabase-Mm2100 Company Name ListRina RachmanNo ratings yet
- Easy Touch Pro Datasheet 2023 4 1Document2 pagesEasy Touch Pro Datasheet 2023 4 1Moisés Antonio Gamboa MartínezNo ratings yet
- All About Op Amplifier-CollectionDocument105 pagesAll About Op Amplifier-CollectionAnonymous DjWqKpZ1No ratings yet
- TA7291ASDocument14 pagesTA7291ASGustavo GarciaNo ratings yet
- RAM 5.7 2020 EcmDocument7 pagesRAM 5.7 2020 Ecmjesus mtzNo ratings yet
- Book Parts E-WE 1204-55 INGDocument138 pagesBook Parts E-WE 1204-55 INGricardo assaf marchetiNo ratings yet
- TDK CD70 B2GA101KYGS Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesTDK CD70 B2GA101KYGS Datasheet PDFSebastian ChaileNo ratings yet
- Catalogue PDFDocument45 pagesCatalogue PDFAbhinavDixit100% (1)
- IC A200 BrochureDocument2 pagesIC A200 BrochureelsaaddyNo ratings yet
- F9540n Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageF9540n Datasheet PDFDanielNo ratings yet
- Moog G122-829-001 - Catalog1Document2 pagesMoog G122-829-001 - Catalog1Jean-Roch JacquesNo ratings yet
- Quantity Take-Off Septic Vault:1 Lot Items Qty UnitDocument24 pagesQuantity Take-Off Septic Vault:1 Lot Items Qty UnitnathanieldagsaNo ratings yet
- Practical Programs For Construction Blasting PatternsDocument10 pagesPractical Programs For Construction Blasting PatternsDinoYancachajllaNo ratings yet
- SERVO CONTROLLED VOLTAGE STABILIZERDocument4 pagesSERVO CONTROLLED VOLTAGE STABILIZERYOUTH FUTURENo ratings yet
- Motor Selection - Three-Phase MotorsDocument6 pagesMotor Selection - Three-Phase MotorsRich_78No ratings yet
- Aten KVM Switch ManualDocument86 pagesAten KVM Switch ManualDiNo ratings yet
- BobcatDocument3 pagesBobcatJorge CabreraNo ratings yet
- Green-Mode PWM Controller Reduces Audio NoiseDocument18 pagesGreen-Mode PWM Controller Reduces Audio NoisePaulo Roberto s freireNo ratings yet
- Frame Stretching BasicsDocument2 pagesFrame Stretching BasicsMassey FergusonNo ratings yet
- DB String Monitoring Unit 2422 enDocument2 pagesDB String Monitoring Unit 2422 enrisqi rotbiNo ratings yet
- SKI-DOO Engine Leak Test (SUMMIT X) - Shop Manual - 04cciLAAQ - SM11Y015S01 - enDocument5 pagesSKI-DOO Engine Leak Test (SUMMIT X) - Shop Manual - 04cciLAAQ - SM11Y015S01 - enHannu LeinonenNo ratings yet
- 2SA1568Document13 pages2SA1568raquelNo ratings yet
- CT PartsDocument13 pagesCT PartsJose Aldrin Climacosa SerranoNo ratings yet