Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pat20100093391 PDF
Uploaded by
Buk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views18 pagesOriginal Title
pat20100093391.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views18 pagesPat20100093391 PDF
Uploaded by
BukCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
a9)
‘US 2010009:
United States
SIAL
«2 Patent Application Publication co) Pub. No.: US 2010/0093391 AL
Saban et al.
(43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010
(54) MULTIPLE DATA SERVICES OVER A (22) us.e1 455/552.1;455/562.1
DISTRIBUTED ANTENNA SYSTEM aa ae
(96) Imveors: Ofer Saban, Alexandria, VA (US); The invention sdected toa method and system for support
Teaue Shapira, Peta Tikva (Cig mle time division duplexed (IDD) based wireless
service o roquency division duplexed (FDD) icles se
eee ‘ices on # Dstibuted Amen System (DAS). A DAS ean
Gomespondence Adres Support a many’ wireless services, inelding voice and data
Dee ey Services ing the sme piysialegpment. TDD based se
Nizon Peabody LLP, 1005 ‘ows use a common clock sigal to synchronize the compe
Boston, MA 02110 (US) ents of the DAS for transmission aad reception of TDD
Signals. In accordance withthe invention, the DAS
(1) ApplNos — 121465,288 include s GPS receker which ean exit timing signs]
(Goch as 1 pps signal) ow 8 OPS signal and distbate the
(2) Filed May 13,2009 timing signal to any andl components ofthe DAS tenable
Synchronization of the components for trasmitting. nd
Related US. Application Data ‘eeeiving TDD signals The GPS receiver cat he pact of the
interlace that connects & TDD besed service tothe DAS or
(60) Provisional aplication No. 61/052,851, led on May Separate component of the DAS. In accordance with the
13, 2008 Jnvention, the DAS can distribute a reference elock signal to
all ofthe components ofthe DAS in order to misinain zero
on Frequency shift while manipalating wth the carrier frequen
Le cles of the various wireless services came by the DAS. In
GD mck fudition, and in avordance withthe invention, $60 analog
Huss 100 (2006.01) architectures for better integration between the services
Hosw 36112 (2009.01) Soutees (BIS) and the DAS are disclosed.
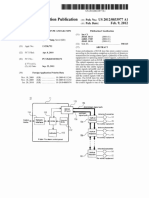
Mero/PeaFento 81920
cPu 165 Processor
oid 04 00
IP ltertace
04] | 51.0
To
Fhe
or8e] | cook
coq) [__ soe
I
os ‘eterna Uni 950
“anaiog Remte Radio Heed
Fi. Bein
To To
seta [| rtm,
62
Clock croc] 984 GPsor
ong Remote Gioset 910 322 seo | [_1PPs
t
922:
US 2010/0093391 AI
T Old
Apr. 15, 2010 Sheet 1 of 10
y seve ! j won9@s euuaruy ! 'S8OuNOS ssajaulM) |
1 ss 1 | puexeog | sid '
1 1
1 '
' ! i ' ‘9 s0unog
t
{ Tt a ! s]8s0|9 esol '
I t 1980 1980} 1
1 ia! i sj0Woy wen Chak)
INA A |
| 6s A veainog | !
I aa
Patent Application Publication
@ DIT
US 2010/0093391 AI
e €q s0unog 1
g ZQ e0unos UOMION dl
a
2
a Lg aounog OMEN di
: 1 — Goa Bulan 1
5 ue xe09,
I
| 9 se1nos
1
ye8019 198019 1
aj0woy wen T
1
| —t-Y| v eainog
g eounog
Patent Application Publication
US 2010/0093391 AI
Apr. 15, 2010 Sheet 3 of 10
Patent Application Publication
€ DIT
ore
ung 21q6
1
1
1
1
! fave
i 39019
T
! ee HA SdO HST
1
t ore L t
1 soeyow 444 | ee
1 ‘ua
! soinog
t
|
1
+ zie suun
1 uonebai66y
I 3801
i we
aren omy] ead
r
ove
US 2010/0093391 AI
Apr. 15, 2010 Sheet 4 of 10
Patent Application Publication
b OW
any
uonDeg euuejuy
¢ eounog + gzy
Z e0inos -}~ vay
| eounos +
“i
ue xe09 \
\
I
\
'
i ol 80% | ‘9 eoun0g
' i \
!
' 398010 98019 \
of t
| aoav i aaa een | a eaunog
' \
ao"v
ye [b—~L[yoanes
bia Lltooaee
349019 }-— vor
¥
oo»
US 2010/0093391 AI
Apr. 15, 2010 Sheet 5 of 10
Patent Application Publication
S$ DIA
pue xeog,
a
ee eee
\ 1a9a¥ |
€ s0inos, tky SdO | — oes
9¢S
Z scunog + ves
zos
_ | ea1nog +— 22g YN
1 \"(seaunog sserauia) |
| |
I os gos | + ‘9 a0unog, '
T
|
I 1
; 198019 398010 | 1
i joey wen! T—]_aeounes | |
|
1
+} vy squnog, :
oos
US 2010/0093391 AI
Apr. 15, 2010 Sheet 6 of 10
Patent Application Publication
9 ‘DIT
€ soinos 4— 979
oeg
Z BaINOS 4— ¥29
oso. ey Sd
an es: veonos
1 Vonsag euueiuy [1
pue xe09 \
I
07 we |_|_Toeamoe
T
\
\
328019 198010 I
1 srowes, uew T—]_ 9 90un0s
\
a4
a pHa
ee \ =
39019 09
Y
009
US 2010/0093391 AI
15, 2010 Sheet 7 of 10
Api
Patent Application Publication
£ DIT
ee oee
ze B0z
SOeL8IU| dl
207
ndo JOssa001q puegaseg
POL ‘$10)90S
49019) u-L
ai 44
I
20L
002
US 2010/0093391 AI
Apr. 15, 2010 Sheet 8 of 10
Patent Application Publication
8 ‘DIT
syup euuayuy || ung ayqe:y
ve
1 zee
it suun oD
i Bujulquicg [
! “oaiea
dona [=]
ove by
soeyauy aus | es
h ua
soinog
zie syun
uone6oiB6y
| e019
! 1 1 are
ee eretee + | 018 19801. ayoU9 ia
¥
oo8
US 2010/0093391 AI
Apr. 15, 2010 Sheet 9 of 10
Patent Application Publication
E86
t
Sddl 096 zoe 016 J2S0I9 a10Way
40S 996 O01
J+ 296
Ny baa u'laa
on oL
u"tag u"tdl
16
49019
peeH o1pey ejowey Bojeuy
086
0S6 W!UN euusjuy
{
206 P06
oo | [Be
ul
OL
u-taa | [p06
202 ye1UI dl
.
td 206 ere
s0sse001g 88 ao
026 1189 O18 4/0014/0191)
US 2010/0093391 AI
15, 2010 Sheet 10 of 10
Api
Patent Application Publication
Or DIT
Og0l
fesor OL0L 198010 e}oWeY
49019
| 42901
unbay uvpay [9108
OL OL
ub bad
0901
peeH o1pey eiowey Bojeuy
Osol yun euuaruy
feoor Saleh
unig 20. Sdd
OL
uvtaa | [oor
e0eHOIUI dl
.
7 feoor fevor
208880014 88 nao
0201 1189 0184/0914 ISO MOT
US 2010/0093391 AI
MULTIPLE DATA SERVICES OVER.
DISTRIBUTED ANTENNA SYSTEM.
(CROSS-REPERENCE TO RELATED
"APPLICATIONS,
10001] This application clsims any and all benefits as pro-
vided by law of U.S. Provisional Patent Application 61/052.
851 fled on May 13, 2008, whichis hereby incorporated by
reference in its enti.
10002] This application is related 10 the following US.
patent application Ser. Nos. 11/958,062 fled Dee. 17,2007,
12/016,459 filed Jan, 18, 2008, 121016,477 filed Jan. 18,
2008, 12/083,226 Filed Feb. 19, 2008 and 12/033.282 filed
Feb. 19,2008, which are hereby incorporated by reference in
their entity
‘STATEMENT REGARDING FEDERALLY
‘SPONSORED RESEARCH
10003] Not Applicable
REFERENCE TO MICROFICHE APPENDIX
{0008} Not Applicable
BACKGROUND
[0005] 1 Technical Field of the Invention
10006} The present invention is directed w Distributed
Antenna Systems (DASs) and more particulary, co methods
snd systems for supporting multiple wireless data services on
aDAS.
10007] Distributed Antenna Systems are used to provide or
‘enhance coverage for witeless services such as Public Safety,
(Cellular Telephony, Wireless LAN and Medical Telemetry
inside buildings and over campuses. The general architecture
‘of a DAS is depicted in FIG. 1.
10008] A single DAS can serve a single wireless service oF
‘combination of many wireless services operating over mul
tiple bands, With respect to each wircless service served hy
the DAS, the Aggregation Configuration ofthe wireless ser=
view canbe characterized as non-agregated or aguregated In
4 non-agaregated configuration, there is 2 1:1 relationship
between DAS antenaae and Base Transceiver Stations (BTS)
‘or Transmitter Receiver nits for that wireless service. In an
‘aggregated configuration, each BTS unit fora given wireless
service is associated with multiple DAS antennae through @
hierarchy of aggregation, For example, in FIG. 2, Services A,
BB, and C are aggregated and Services DI, D2, and D3 are
raguregated. Services sueh as D1, D2, and D3 ean be
ayaregated as well. The ability to aggregate services is typi-
‘ally 3 Tunetion of the remote wiring eloset equip. Typically,
‘wireless LAN services are arranged in #non-aggregated con-
figuration when using a DAS while cellular services are ypi-
cally arranged in an aggregated configuration.
10009] "One desited characteristic of amli-service DAS is
that it can use a single antenna to radiate aad receive the
signals forall servies and frequency bands supported by the
DAS, Such an antenna would need w eover (ie. have aecept-
able performance) in all fraqueney bands of intrest and is
‘commonly referee to a8 9 Broadband Antenna, An example
‘ofa supported frequency range for a DAS antenna would be
400 MElz-6 GHz. To provide MIMO based services, a MIMO.
fntenna which includes multiple antenna elements at a com-
‘moi locaton ean be used
Apr. 15, 2010
[010] In cefering tothe signal flows in DAS systems the
term Downlink signal refers tothe signal being trinsmited by
the source transmitter (eg, cellular base station) through an
‘antenna to the terminals and the term Uplink signal refers to
the signals being transmitted by the terminals which are
received by an antenna and lo 1 the source receiver. Many
Wireless serviees have both an uplink and a downlink, but
some have only a downlink (eg. mobile video broadcast
service)oronly an uplink e.g certain types of medical telem-
enn).
[0011] 2. Description ofthe Prior Ant
[0012] In addition to providing cellular and other wireless
services, these DAS can be used to provide Time Division
Duplexed (TDD) based services sueh as WiFi (EEE 802.11
‘and similar standards), ZigHice, Blue ‘Tooth, WiMAX,
Advanced Wireless Services (AWS) as well as Frequency
Division Duplex (FD) based services such as WiMAX,
Personal Communication Services (PCS) and AWS. When
DAS used to provide these services, either the Main wiring
closet orremote wiring closet equipment needsan interface
fonneet the service network tothe DAS, These souree inter
Taces are commonly referred 10 as a Macro/MienPica!
Femto BTS or Access Point (AP) etc For each additional
Wireless service that is connected to the DAS a separate,
dicated BTS is needed. Thus, tis difficult to support mul-
tiple service networks on a DAS because many expensive
BIS devices are need.
SUMMARY,
[0013] One of the benefits of a DAS is that it cam allow
‘many different wireless services to be provided over a com:
‘mon physical infastrctire (Wiring. wiring closet units
Anteuna units and other physical components). Thus, once the
physical infrastructure i installed, the same physical ini.
structure can be used to support akltonal wireless services
and avoids the expense of additional equipment and the
installation ofthat equipment. In adition, operational ben-
clits include lower energy costs and potenilly lower main-
[0014] Where DAS has been installed in a facility, itean
be desirable to ad other wireless services including TDD
based services such as WiFi, WiMAX, AWS, ZigBee, Blue
‘Tooth and FDD based services such es WiMAX, PCS and
AWS. For each service, an interface can he used to connect,
the service network tothe DAS. In addition, a GPS reociver
(or an envelop detector) can be connected to the DAS and
used to provide a 1 pulse per second (1 pps) signal to syn-
cchonize any anal fhe eomponcats ofthe DAS for trans-
ting and receiving the wireless signals, The 1 pps sigaal
can be distributed over the DAS to any or all of the wiring
closet units and wo the aatenna units to enable them to be
Synchronized for transmission and reception of the wireless
signal
[0015] In accordance with one embodiment of the inven-
‘ion, the DAS includes a B'TS coupled to one or more wiring
closet or combining units, each wiring closet unit being
coupled to one ormore antenna units fr providing a wireless
service, The antenna units can include passive or aetive
Antenna elements or combination of bath. The DAS ean be
‘sonple to first interface which is coupled oa frst wireless
‘network to enable the DAS to eamy the ist wireless network
signals over the DAS and the DAS can also be coupled to @
second interface which is coupled to a sconndl wireless net-
‘work to enable the DAS to carry the second wireless network
US 2010/0093391 AI
signals over the DAS, Al he active elements in the DAS ea
bbe monitored or configured by a point to meltpoint central-
‘zed management system, the management system can tas:
mit and receive point to mulipoia signals to and from any of
the addressed elements attached to the DAS, The DAS can
‘ako coupled to a global positioning system (GPS) receiver
‘andadapted to receive the | ppsclock signal fom one or more
GPS satellites and the DAS is adapted and configured to
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 2018 Used BMW X1 XDrive28i Sports Activity Vehicle at Motorwerks BMW Serving Bloomington, MN, IID 17353408Document7 pages2018 Used BMW X1 XDrive28i Sports Activity Vehicle at Motorwerks BMW Serving Bloomington, MN, IID 17353408BukNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub - No .: US 2017 / 0246207 A1Document17 pagesUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub - No .: US 2017 / 0246207 A1BukNo ratings yet
- CA2487806A1Document45 pagesCA2487806A1BukNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CA 2508460 CDocument51 pagesCA 2508460 CBukNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- JavascriptDocument9 pagesJavascriptBukNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Mount Tam Trail Run MapDocument1 pageMount Tam Trail Run MapBukNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- 142 Dinner 9.17-2Document4 pages142 Dinner 9.17-2BukNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Ion e Brochure BR 111353 enDocument8 pagesIon e Brochure BR 111353 enEngNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- iDTech Brochure2018Document27 pagesiDTech Brochure2018BukNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Neutral Host Model For Distributed Antenna Systems An 319347 AEDocument4 pagesNeutral Host Model For Distributed Antenna Systems An 319347 AEBukNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Alt As NytimesDocument2 pagesAlt As NytimesBukNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Command Line InterfaceDocument1 pageCommand Line InterfaceBukNo ratings yet
- Pat 20100093391Document18 pagesPat 20100093391BukNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Forerunner310XT OM EN PDFDocument56 pagesForerunner310XT OM EN PDFadrianftvNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- R H 1 (J5 12b: (19) United StatesDocument33 pagesR H 1 (J5 12b: (19) United StatesBukNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- United States Patent (10) Patent N6 US 8,206,244 B2: Honea Et A) - (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012Document34 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent N6 US 8,206,244 B2: Honea Et A) - (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012BukNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Trs-80 Lichello ProgramDocument3 pagesTrs-80 Lichello ProgramBukNo ratings yet
- Multiplexer/ 60 / S: (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.2 US 8,144,736 B2Document51 pagesMultiplexer/ 60 / S: (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.2 US 8,144,736 B2BukNo ratings yet
- Us6026304 PDFDocument25 pagesUs6026304 PDFBukNo ratings yet
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0184286 A1Document21 pagesUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0184286 A1BukNo ratings yet
- Us 20100290787Document17 pagesUs 20100290787BukNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- United States Patent: K K I I 4 (6Document13 pagesUnited States Patent: K K I I 4 (6BukNo ratings yet
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0148231 A1Document50 pagesUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0148231 A1BukNo ratings yet
- Us 6364892Document75 pagesUs 6364892BukNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- US6806791Document11 pagesUS6806791BukNo ratings yet
- US7205868Document83 pagesUS7205868BukNo ratings yet
- Pat 9171209Document18 pagesPat 9171209BukNo ratings yet
- Us 8971796Document86 pagesUs 8971796BukNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- United States Patent: AnneetalDocument25 pagesUnited States Patent: AnneetalBukNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)