Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Management of Normal Labour Chart
Uploaded by
wedishaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Management of Normal Labour Chart
Uploaded by
wedishaCopyright:
Available Formats
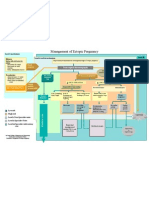
Management of Uncomplicated labour
• Painful contractions Not in labour Observe in antenatal ward
• Show
• Effacement & progressive Uncertain Review after 2 hours
dilatation of cervix
Established labour
Transfer to the labour suite Admission CTG to be
Identify risk factors by, done in all three groups
Episiotomy
o Review antenatal records. o Avoiding faecal soiling and interpreted before
- Medio-lateral Episiotomy o Shaving of perineal hair decision is made (Y)
o Detailed clinical history
2.Cord clamp At the time of crowning o Oral fluids
o Examination
Urine for protein o IV access
o Left Lateral recombinant
position
Monitoring by Partogram
Maintain Partogram*(X)
Progress of labour
o Cervical dilatation
o Decent of the presenting part
o Uterine contractions
Routine
All steps in the management of labour should be carried out under aseptic conditions
care in
All steps in the management of labour should be documented in the bed head ticket
Maternal condition
labour suit Pain relief
o Pulse, BP, Temperature & hydration.
o Evaluation of drugs(oxytocin, antibiotics, Opioid -Pethidine
Anti hypertensives, Analgesics Regional analgesia-Epidural
o Undistended bladder-catheterize if Other-spinal analgesia
indicated Combined spinal-epidural analgesia
Fetal condition Inhalational analgesia-Entonox
o Intermittent auscultation of fetal heart Pudendal block for
o Liquor volume episiotomy/forceps/vacuum
o Meconeum in liquor
Positioning
Most comfortable Second stage
position Diagnosis
Second stage of labour
Supine position-avoided 9 Vaginal examination
Descent phase- for full dilatation
-Not to bear down 9 Perineal distention
-Fetal heart assessed 9 Anal dilatation
every 15 mints
Expulsive phase-
-Encourage to bear down
-Fetal heart assessed after
each contraction Episiotomy
- Medio-lateral
Episiotomy
At the time of
Delivery Delivery crowning
Third stage of labour
1.Oxytocics Third stage 3.Controlled
cord traction
Active
management
2.Cord clamp 4.Examine the
placenta
5. Observation for signs of
o Haemorrhage
o Utrine fundal level
o Evidence of collapse
o Respiratory difficulty
o Unusual behaviouror
o Abdominal pain
Monitoring
Mother should be
Post-partum
closely monitored in
the labour room for
at least two hours
Sri Lanka College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Health sector development Project
Guidelines- Management of Uncomplicated labour
You might also like
- Vaginal Birth After Cesarean Section (VBAC) (Trial of Scar) : InternationalDocument12 pagesVaginal Birth After Cesarean Section (VBAC) (Trial of Scar) : InternationalZaenal ArifNo ratings yet
- WaterbirthDocument2 pagesWaterbirthapi-405873549No ratings yet
- Primitive Reflex in Preterm BabiesDocument5 pagesPrimitive Reflex in Preterm BabiesAmirul Zakri IsmailNo ratings yet
- Drug Use in Labour RoomDocument22 pagesDrug Use in Labour RoomManoj Dongarwar100% (1)
- Fetal PositionDocument44 pagesFetal Positionjean therese100% (1)
- Iycf Who PDFDocument157 pagesIycf Who PDFMarilyn RealistaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Birth After Caesarean (Vbac) : Max Brinsmead MB Bs PHD December 2015Document36 pagesVaginal Birth After Caesarean (Vbac) : Max Brinsmead MB Bs PHD December 2015kikyNo ratings yet
- Up Dated Respectiful Maternity Care (RMC)Document21 pagesUp Dated Respectiful Maternity Care (RMC)nyangaraNo ratings yet
- Appearance of A NewbornDocument33 pagesAppearance of A NewbornGeguirra, Michiko SarahNo ratings yet
- Baby Bullet: User Manual and CookbookDocument61 pagesBaby Bullet: User Manual and CookbookJennyNo ratings yet
- Sem2 Case7 CPDocument10 pagesSem2 Case7 CPJemie JaleaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Vital Signs FormDocument2 pagesNeuro Vital Signs FormAbegail TabuniagNo ratings yet
- Need of New Born and Parenting ProcessDocument13 pagesNeed of New Born and Parenting ProcessKrini TandelNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practices in ObstetricsDocument46 pagesEvidence Based Practices in Obstetricsvikas takNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument34 pagesAmniotic Fluid EmbolismReygie MataNo ratings yet
- What Reflexes Should Be Present in A Newborn?Document4 pagesWhat Reflexes Should Be Present in A Newborn?Nicole OrtizNo ratings yet
- Technique OF Assessment OF GrowthDocument42 pagesTechnique OF Assessment OF GrowthnNo ratings yet
- Newborn Assessment, Apgar & Ballard Scoring NotesDocument3 pagesNewborn Assessment, Apgar & Ballard Scoring NotesAshitakaNo ratings yet
- QP Code:111010 Reg. No: ........................ First Year B.SC Nursing Degree Examinations October 2017 Anatomy (2016 Scheme) Model Question PaperDocument6 pagesQP Code:111010 Reg. No: ........................ First Year B.SC Nursing Degree Examinations October 2017 Anatomy (2016 Scheme) Model Question PaperdrsNo ratings yet
- Needs of New-Born CareDocument27 pagesNeeds of New-Born CarePruthviNo ratings yet
- Physiology of SleepDocument36 pagesPhysiology of SleepTanisha DiwanNo ratings yet
- Fetal Malpresentations: Abundo, Esther Ellise Espinol, Hazel AnnDocument21 pagesFetal Malpresentations: Abundo, Esther Ellise Espinol, Hazel AnnEsther Ellise Abundo100% (1)
- Fetal Biophysical Profile PDFDocument2 pagesFetal Biophysical Profile PDFVickiNo ratings yet
- Unang YakapDocument7 pagesUnang YakapApol AstigNo ratings yet
- Normal Sponatneous Vaginal DeliveryDocument6 pagesNormal Sponatneous Vaginal DeliveryT helper CellsNo ratings yet
- Obstetrical Emergency & ManagementDocument38 pagesObstetrical Emergency & ManagementDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Fetal MalpresentationDocument33 pagesFetal MalpresentationMichael Angelo Seña100% (1)
- New Born Care: Catheter SuctioningDocument17 pagesNew Born Care: Catheter SuctioningRaffy100% (1)
- Therapeutic PlayDocument9 pagesTherapeutic PlayVivek PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Active Management of LabourDocument4 pagesActive Management of LabourHytham AtiaNo ratings yet
- Assessing For Violence (Case Study) Health AssessmentDocument4 pagesAssessing For Violence (Case Study) Health AssessmentJeahannNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Challenges and The Preterm Mother-Infant Dyad A Conceptual ModelDocument10 pagesBreastfeeding Challenges and The Preterm Mother-Infant Dyad A Conceptual Modelunisa magisterNo ratings yet
- Occipito-Posterior Position of The Fetal HeadDocument8 pagesOccipito-Posterior Position of The Fetal HeaduouoNo ratings yet
- Benson Relaxation Technique in Reducing Pain Intensity in Women After Cesarean SectionDocument5 pagesBenson Relaxation Technique in Reducing Pain Intensity in Women After Cesarean SectionMarinaNo ratings yet
- FC Insertion and RemovalDocument30 pagesFC Insertion and RemovalAngel Alexa Del MundoNo ratings yet
- 19 - Vaginal DeliveryDocument16 pages19 - Vaginal DeliveryGen XNo ratings yet
- Ed-Child Febrile FitDocument2 pagesEd-Child Febrile Fitmanish708345No ratings yet
- Vaccum Assisted BirthDocument1 pageVaccum Assisted BirthjhaymajuiyNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 & 102 ReviewerDocument14 pagesNCM 101 & 102 ReviewerBing58No ratings yet
- What Is Cerebral PalsyDocument6 pagesWhat Is Cerebral PalsyAriel BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics - Febrile Convulsions Assessment, Treatment and Education PDFDocument12 pagesPaediatrics - Febrile Convulsions Assessment, Treatment and Education PDFPalash NagdeoteNo ratings yet
- Induction of Labour Techniq SADocument18 pagesInduction of Labour Techniq SAPujanaWiaktaNo ratings yet
- Pregestational Diabetes Mellitus: Group 2Document24 pagesPregestational Diabetes Mellitus: Group 2Jellie An TalattagNo ratings yet
- Adaptation For Life After Birth A Review of Neonatal PhysiologyDocument9 pagesAdaptation For Life After Birth A Review of Neonatal PhysiologyGrifanda HumairahNo ratings yet
- Psychological Disorders During PuerperiumDocument29 pagesPsychological Disorders During PuerperiumKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- LabouranalgesiaDocument45 pagesLabouranalgesiaA.H.ANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PelvisDocument15 pagesAnatomy of PelvisJonnah Mae Belmonte100% (1)
- Optimizing Postpartum CareDocument11 pagesOptimizing Postpartum Carengga.makasihNo ratings yet
- Inner ChildDocument1 pageInner ChildSubconscious HealingNo ratings yet
- Week 11Document11 pagesWeek 11Sal MiahNo ratings yet
- 1a Pediatrics Basic Concepts11-2010rhDocument299 pages1a Pediatrics Basic Concepts11-2010rhreecoleNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Manuever Final 21aDocument27 pagesLeopolds Manuever Final 21aArun Roa DanielNo ratings yet
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care 1Document5 pagesEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care 1Genierose YantoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Pain Assessment and ManagementDocument24 pagesUnit 8: Pain Assessment and ManagementMatthew RyanNo ratings yet
- Navjaat Shishu Suraksha Karyakram 2020 Flip Chart: Resuscitation and Essential Newborn CareDocument54 pagesNavjaat Shishu Suraksha Karyakram 2020 Flip Chart: Resuscitation and Essential Newborn CarePawan MishraNo ratings yet
- Abortion Nursing Care Planning and ManagementDocument11 pagesAbortion Nursing Care Planning and ManagementSyamsiah ChandrawatiNo ratings yet
- PromDocument1 pagePromwedishaNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Module 3mDocument25 pagesNCM 109 Module 3mKyle ChuaNo ratings yet
- 15 NG - PPH Algorithm-Aug08Document2 pages15 NG - PPH Algorithm-Aug08abdelhamed aliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DinoprostoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study DinoprostoneMva AgueroNo ratings yet
- Scarred UterusDocument1 pageScarred UteruswedishaNo ratings yet
- RhesusDocument1 pageRhesuswedishaNo ratings yet
- Puerperal SepsisDocument1 pagePuerperal Sepsiswedisha100% (1)
- PromDocument1 pagePromwedishaNo ratings yet
- IUDDocument1 pageIUDwedishaNo ratings yet
- EctopicpregnancyDocument1 pageEctopicpregnancywedisha100% (1)
- CINDocument1 pageCINwedishaNo ratings yet
- Management of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Peripheral Unit: Female Presenting To A With AUBDocument1 pageManagement of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Peripheral Unit: Female Presenting To A With AUBwedishaNo ratings yet
- APHDocument1 pageAPHwedishaNo ratings yet
- BreechDocument1 pageBreechAraceli Ecot CalunodNo ratings yet
- Ec/irbDocument28 pagesEc/irbRachana ShettyNo ratings yet
- Whats Wrong With Me - Priya MekalaDocument11 pagesWhats Wrong With Me - Priya Mekalaapi-283410724No ratings yet
- Wa0008.Document2 pagesWa0008.Mmangaliso KhumaloNo ratings yet
- Abstract Vetigel (Reparation)Document2 pagesAbstract Vetigel (Reparation)bayuNo ratings yet
- Varicocele and Testicular PainDocument7 pagesVaricocele and Testicular PainseptaayuNo ratings yet
- 100 MCQs-3Document19 pages100 MCQs-3hassan qureshiNo ratings yet
- Pharma Topic 3 NotesDocument3 pagesPharma Topic 3 NotesAshley Franceska CansanayNo ratings yet
- Procedural Outcomes of Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocument9 pagesProcedural Outcomes of Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary InterventionsarahNo ratings yet
- What S in A Case Formulation PDFDocument10 pagesWhat S in A Case Formulation PDFNicole Flores MuñozNo ratings yet
- DVLA and Medical ConditionsDocument6 pagesDVLA and Medical ConditionsFourth YearNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument172 pagesSampleSwisskelly1No ratings yet
- Case Study Part 2 Patient With Uti (Bag-O)Document48 pagesCase Study Part 2 Patient With Uti (Bag-O)Eaht Quirong0% (1)
- Assessment 4 (BE)Document9 pagesAssessment 4 (BE)Aryan Judith DoloresNo ratings yet
- IV Manual 7th Edition July 2020Document175 pagesIV Manual 7th Edition July 2020Deena AlJawamisNo ratings yet
- Case Study On AnaemiaDocument16 pagesCase Study On AnaemiaLavie Gangwar100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: RationaleDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: RationalechelseyNo ratings yet
- NPO GuidelinesDocument2 pagesNPO GuidelinesDan HoNo ratings yet
- Adult Hip (2nd Edition)Document1,693 pagesAdult Hip (2nd Edition)Jocelyne SturridgeNo ratings yet
- Surgical Site InfectionsDocument5 pagesSurgical Site Infectionsapi-320469090No ratings yet
- Cleveland Clinic Facts and FiguresDocument2 pagesCleveland Clinic Facts and FiguresUzair Ul GhaniNo ratings yet
- KAD Pada DM Tipe 1Document56 pagesKAD Pada DM Tipe 1hilmiana putriNo ratings yet
- Project On AidsDocument7 pagesProject On AidsRoshanGS20% (5)
- Cashless Authorisation Requisition FormDocument1 pageCashless Authorisation Requisition FormPandurangaNo ratings yet
- Uses of External Applications in Homoeopathy - JustifyDocument5 pagesUses of External Applications in Homoeopathy - JustifyHomoeopathic PulseNo ratings yet
- Case Study OsteomyelitisDocument3 pagesCase Study OsteomyelitisFirsandiPrasastyaFikryGozaliNo ratings yet
- Algoritmo de La Gasometría ArterialDocument15 pagesAlgoritmo de La Gasometría ArterialJhonatan Efraín López CarbajalNo ratings yet
- The Perfusion Crisis ManualDocument3 pagesThe Perfusion Crisis Manualghg sddNo ratings yet
- SMT Ebook ManualDocument95 pagesSMT Ebook ManualLuis Andrade100% (1)
- Clinical Guidelines (Nursing) - Oxygen DeliveryDocument16 pagesClinical Guidelines (Nursing) - Oxygen DeliveryPhan0% (1)
- Medical Termination of PregnancyDocument8 pagesMedical Termination of PregnancyNikhil BijuNo ratings yet