Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Uploaded by
C Bala Diwakesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views6 pagesp & e
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentp & e
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryotes
Uploaded by
C Bala Diwakeshp & e
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
BIO205-CH4-Prok&Euka
BIO205 - Ch 4 - Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic
Cells - RioSalado - AZ
Question Answer
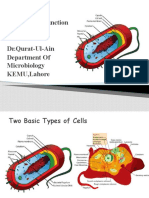
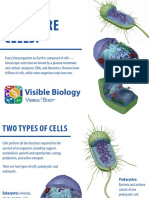
All living cells - what 2 catagories? Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes
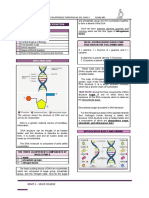
DNA in single, circular arranged chromosome
Structural characteristics of
w/o membrane - lack membrane - enclosed
prokaryotes.
organelles
Structural characteristics of Multiple chromosomes in membrane-enclosed
eukaryotes. nucleus.
Bacteria & Archaea are? Prokaryotes
Protozoa & fungi are? Eukaryotes
What main difference is there Structure of cell walls & membranes, & absence
between prokaryote & eukaryote? of organelles.
(1) No DNA membrane, (2) DNA w/no
5 distinguishing characteristics of histones, (3) lack membrane-enclosed
prokaryotes. organelles, (4) cell wall w/polysaccharide
peptidoglycan, & (5) binary fission.
DNA copied & cell splits into 2 - prokaryotes -
Binary fission
fewer processes than eukaryote cell division.
(1) DNA in nucleus w/membrane & multiple
5 distinguishing characteristics of chromosomes, (2) DNA associated w/histone,
eukaryotes. (3) membrane-enclosed organelles, (4) cell walls
chemically simple, (5) mitosis.
3 basic shapes of bacteria Coccus (berries), bacillus (rod-shaped), & spiral
Diplococci Cocci that remain in pairs after dividing.
Cocci that divide & are attached in chainlike
Streptococci
pattern.
Cocci that divide in 2 planes & remain in groups
Tetrads
of 4.
Cocci in 3 planes & remain in cubelike groups
Sarcinae
of 8.
Cocci in multiple plains & form grapelike
Staphylococci
clusters.
Why are there fewer groupings of
Because bacilli only divide across short axis
bacilli than cocci?
Diplobacilli Appear in pairs after division
Streptobacilli Appear in chains after division
Coccobacilli Oval bacilli that look like cocci.
Bacillus cells often form __. long, twisted chains of cells.
What is the difference between
One is bacterial shape & one is genus.
bacillus & Bacillus?
Vibrios Spiral bacteria that look like curved rod.
Spirilla Spiral bacteria that have helical shape
Spiral bacteria that have helical shape & are
Spirochetes
flexible - move by axial filaments.
Monomorphic Maintain a single shape
What prokaryotes are
Bacteria
monomorphic?
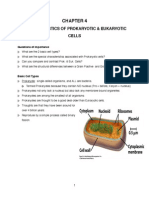
Structures external in prokayotic Glycocalyx, flagella, axial filaments, finbriae &
cell wall. pili.
"Sugar coat" - secreted on surface of
Glycocalyx prokaryotes - viscous - if firm, then called
capsule.
Firmly attached sugar coat around prokaryote
Capsule that can be determined by using negative
staining.
Loosely attached glycocalyx (sugar coat) around
Slime layer
prokaryote.
Capsules are important in
virulence - degree of disease causing ability.
contributing to bacterial __.
Capsules often protect pathogenic
From phagocytosis by cells of host.
bacteria __.
Glycocalyx made of sugars - enables bacteria to
Extracellular polysaccharide (EPS)
survive by attaching to various surfaces.
Atrichous Bacteria that lack flagella
Monotrichous Single polar flagellum
3 basic parts of flagellum Filament, hook, basal body
Protein that makes up flagellum
flagellin
filament.
Difference between prokaryote &
Most bacteria lack membrane/sheath covering it.
eukaryote flagella.
What anchors flagellum to cell wall Movement away from/toward a particular
& plasma membrane? stimulus.
How do spirochetes & spirilla Spirochetes move using axial
differ? filaments/endoflagella.
Axial filaments - bundles of fibrils that arise at
Endoflagella ends of cell beneath outer sheath & spiral
around cell.
Axial filaments propel spirochetes
in a spiral motion like a cork screw.
__.
Appendage on bacterial cell used to adhere to
fimbriae
surfaces - helps colonization.
Longer than fimbrae & join bacterial cells for
pili
transfer of DNA.
Process by which bacteria use pili to transfer
conjugation
DNA from one cell to another.
What is the function of fimbriae? to adhere to surfaces
Almost all prokaryotes have __. cell walls
Prevent rupture when water pressure in cell is
Major function of cell wall.
greater than outside.
What is used to differentiate major
The chemical composition of the cell wall.
types of bacteria?
Gram-positive cell walls contain? Many layers of peptidoglycan.
Gram-negative cell walls do not
teichoic acids
contain __.
Which is more susceptible to Gram negative because they only contain a
mechanical breakage? Gram - or +? small amount of peptidoglycan.
The outer membrane of gram-
Certain antibiotics & digestive enzymes.
negative provides barrier against?
Smallest known bacteria outside
Mycoplasmas - pass through most filters.
living host.
Archaea may lack cell walls but
Peptidoglycan - have pseudomurein instead.
definately lack __.
Acid-fast bacteria cell walls contain
Mycolic acid - resists dyes because it is waxy.
what lipid?
Why are prokaryote plasma
membranes less rigid than Because they lack sterols.
eukaryotes?
Infolding of plasma membrane where pigment
Chromatophores
located in photoautotrophic bacteria.
How does simple diffusion differ Both don't need ATP, but facilitated uses
from facilitated? transporter.
Net movement of solvent molecules across
What is osmosis? selectively permeable membrane from high to
low concentration of solvents.
In isotonic solution, movement is? No net movement of water
In hypotonic solution, movment is? Water moves into cell & may cause cell to burst.
In hypertonic solution, movment is? Water moves out of cell, causing shrinkage.
Osmotic lysis Water moving into a cell & it bursts.
Plasmolysis Water moving out of cell & it shrinks.
Pressure required to prevent movement of pure
Osmotic pressure
water into solution containing some solvents.
Most bacteria live in __ solutions. hypotonic
Only in prokaryotes - substance is chemically
Group translocation altered as it passes through plasma membrane &
can no longer leave - high energy PEP.
Difference between prokaryote &
The differences allow the cell to be killed by the
eukaryote ribosomes regarding
antibiotic, yet leave eukaryote host unaffected.
antibotic therapy.
Reserve deposits in prokaryote cytoplasm of
Inclusions
nutrients - good ID tag.
Volutin Reserve of inorganic phosphate for ATP.
Nuclear area of bacterial cell containing
Nucleoid
bacterial chromosome.
Circular DNA molecules that replicate
independent of chromosomal DNA - genetically
Plasmids
not crucial to bacterial survival except during
adverse conditions.
Highly durable dehydrated cells - almost seed-
Endospores
like
Under what conditions are When essential nutrients are depletes in certain
endospores formed by bacteria? gram-positive bacteria.
Sporogenesis/sporulation Process of endospore formation
When endospore returns to health later - water
Germination
enters.
What kingdoms contain eukaryote
Alge, protozoa, fungi, plants, & animals.
organisms.
What is antibiotic significance of Penicillins & cephalosporins act against
eukaryote cells not containing peptidoglycan & therefore don't affect eukaryote
peptidoglycan? cells.
How do plasma membranes differ
Prokaryote lack sterols and carbs.
between eukaryote and prokaryote.
cytosol refers to fluid portion of cytoplasm
Movement of cytoplasm in cell that helps
cytoplasmic streaming
distribute nutrients & move a cell over a surface.
Many enzymes found in
cytoplasmic fluid of prokaryote are Organelles
sequestered in __ of eukaryote.
Movement of substances between nucleus &
Nuclear pores control __.
cytoplasm.
Condensed regions of chromosomes where
Nucleoli/nucleolus
rRNA is being synthesized.
Cisterns Flattened membrane sacs of ER.
ER contains __ & synthesizes __. unique enzymes - phospholipids, fats & sterols.
What are the functions of golgi
Package substances in vesicles for transport.
complex?
Cristae Outer mitochondrial membrane
__ are organelles that can reproduce
mitochondria
more or less on their own.
Many of the metabolic steps
involved in cellular respiration are matrix of mitochondria
concentrated in __.
Organelle in algae & green plants that contain
Chloroplast
chlorophyll & enzymes
Chlorophyll is contained in what
thylakoids
sacs?
__ in plants can reproduce on own
chloroplasts
like mitochondria.
How are mitochondria similar to How they reproduce - increase in size - then
prokaryote cells? divide in two.
Contain enzymes that can oxidize various
peroxisomes
organic substances - aminoacids & fatty acids.
Peroxisomes protect other cell parts
H2O2 - hydrogen peroxide
from __.
Centrioles & pericentricular material - miotic
Centrosome
spindle organizing center.
Larger bacterial cell lost their cell walls &
Endosymbiotic theory engulfed smaller bacterial cells & so eukaryotes
formed.
Similar to bacterial cells, both
mitochondria & chloroplasts contain circular DNA & can reproduce on own.
__.
You might also like
- BMI1014: Chapter 2 - Bacteria-Morphology and ClassificationDocument6 pagesBMI1014: Chapter 2 - Bacteria-Morphology and ClassificationAkmal Adib FadzilNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MorphologyDocument75 pagesBacterial MorphologyJoan MelendresNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and TaxonomyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Taxonomyporkypig100% (11)
- Prokaryote PDF 2020Document49 pagesProkaryote PDF 2020พรนภา เจริญอายุวัฒNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Lecture Note (Bacteria) - 3Document9 pagesBio 102 Lecture Note (Bacteria) - 3Yin KuzNo ratings yet
- The Microbial World: Bacterial Cell Structure and FunctionDocument42 pagesThe Microbial World: Bacterial Cell Structure and Functionluthfiah adzaniNo ratings yet
- Sunarjati Sudigdoadi Dept. of Microbiology Medical Faculty Padjadjaran UniversityDocument27 pagesSunarjati Sudigdoadi Dept. of Microbiology Medical Faculty Padjadjaran UniversityKost Vila SakinahNo ratings yet
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument94 pagesComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- SGL 2 (Structure of Bacterial Cell)Document32 pagesSGL 2 (Structure of Bacterial Cell)rekanshwan5No ratings yet
- 2420 Procaryotic and Eucaryotic Cellular Structure 083110Document30 pages2420 Procaryotic and Eucaryotic Cellular Structure 083110wsarwar237No ratings yet
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Key DifferencesDocument38 pagesComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Key DifferencesFransiscaa HellenNo ratings yet
- Biol 1017-Cell Biology: Prokaryotes & MicrosDocument50 pagesBiol 1017-Cell Biology: Prokaryotes & MicrosJoshua HarveyNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Summaries 1-30 ReviewedDocument53 pagesMicrobiology Summaries 1-30 ReviewedyepNo ratings yet
- Procaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument64 pagesProcaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsNaufal QaweimNo ratings yet
- MicroPara 03 - Prokaryotic CellsDocument23 pagesMicroPara 03 - Prokaryotic CellsJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Morphology of BacteriaDocument44 pagesMorphology of BacteriaDr Harender SimarNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Structure 1) Capsule: Spirillum (Spiral) - Mycoplasmas Are BacteriaDocument4 pagesBacterial Cell Structure 1) Capsule: Spirillum (Spiral) - Mycoplasmas Are BacteriaTLCRNo ratings yet
- in Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Document21 pagesin Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Mica-Ella CasasolaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 ProkaryotesDocument33 pagesLECTURE 3 ProkaryotesNicole MandyNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsDocument17 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsApryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Unit I Module 2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument8 pagesUnit I Module 2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsMirunalini GobinathNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument15 pagesStructurefatimasanusimorikiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument29 pagesProkaryotic CellSeshime Thyrone DavidsonNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pages1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Morphology and StructureDocument31 pagesBacterial Morphology and StructureBlessy MartinNo ratings yet
- Eukariot Dan ProkariotDocument37 pagesEukariot Dan ProkariottidaniadevNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument55 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsRufaro SadindiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument80 pagesUnit 2 Cell Structure and FunctionNICOLE ANGELIQUE M. DINOYNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Wastewater Microbiology PDFDocument14 pagesA Guide To Wastewater Microbiology PDFmanifNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Structure Function LectureDocument39 pagesProkaryotic Cell Structure Function LectureMisbah ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab Guide: Prokaryotes CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Lab Guide: Prokaryotes CharacteristicsIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- L5 Pha204Document24 pagesL5 Pha204USAYATUN MAHERANo ratings yet
- QMS MicrobiologyDocument21 pagesQMS MicrobiologyDr-Shubhaneel NeogiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument17 pagesUnderstanding Prokaryotes and EukaryotesjasminedevesaNo ratings yet
- Morfology AND Citology of Bacteria: Sidarningsih, Drg.,mkesDocument47 pagesMorfology AND Citology of Bacteria: Sidarningsih, Drg.,mkesDaffa YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Morphology & StructureDocument33 pagesBacterial Morphology & Structureلو ترى100% (1)
- Yel's ReportDocument25 pagesYel's ReportMarc De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document14 pagesChapter 4EDLE FAITH ANDREA CATABIANNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Structure FunctionDocument35 pagesBacterial Cell Structure FunctionItzz MilzzNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument34 pagesProkaryotic CellRobelle Grace M. CulaNo ratings yet
- ProkaryotesDocument14 pagesProkaryotesHiede Naharine MagangcongNo ratings yet
- Q1 General Biology Rev L2Document5 pagesQ1 General Biology Rev L2Dwen Kirby VillamorNo ratings yet
- Bacteria y ArqueaDocument42 pagesBacteria y ArquealeztlyNo ratings yet
- Micro CH 2a StructureDocument155 pagesMicro CH 2a StructureBernadette Joyce PascualNo ratings yet
- This Is A Self-Explaining Powerpoint Presentation by DR Mouton (No Voice Narration)Document43 pagesThis Is A Self-Explaining Powerpoint Presentation by DR Mouton (No Voice Narration)mpaka felliNo ratings yet
- Archaebacteria and EubacteriaDocument3 pagesArchaebacteria and EubacteriaalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- BRUHDocument43 pagesBRUHZero EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Compare microbes in cells, shapes and reproductionDocument5 pagesCompare microbes in cells, shapes and reproductionJemima Kesia ApallaNo ratings yet
- Parker 2001Document6 pagesParker 2001Chinasa EkejiubaNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology Course Bacterial Cell StructureDocument5 pagesMedical Microbiology Course Bacterial Cell StructureariffdrNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diversity IDocument43 pagesMicrobial Diversity IHilmi IrsyadNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: PROKARYOTIC & EUKARYOTIC CELLSDocument10 pagesMicrobiology: PROKARYOTIC & EUKARYOTIC CELLSEmily RaeNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Cell ComparisonDocument10 pagesVisibleBody Cell ComparisonAnjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Micro para 1Document4 pagesMicro para 1Reselle EspirituNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument36 pagesProkaryotic CellPrecious Marie AgabeNo ratings yet
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byDocument11 pagesRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byKamlesh RatnamNo ratings yet
- Second Seat Allotment List MBBS - College - List - Phase2Document94 pagesSecond Seat Allotment List MBBS - College - List - Phase2C Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- DNB (Post Diploma) Emergency Medicine Indicative Seat Matrix Jan 2015Document3 pagesDNB (Post Diploma) Emergency Medicine Indicative Seat Matrix Jan 2015C Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- CrownsDocument6 pagesCrownsC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- NEET PG General Medicine - I ContentsDocument18 pagesNEET PG General Medicine - I ContentsC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- PG Revised Cut OffDocument2 pagesPG Revised Cut OffC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- DNB (Post MBBS) Indicative Seat Matrix Jan 2018 - 03.05.2018 PDFDocument140 pagesDNB (Post MBBS) Indicative Seat Matrix Jan 2018 - 03.05.2018 PDFSahid KapoorNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology 05Document6 pagesRheumatology 05C Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Elevation of Serum Creatinine Phosphokinase Level As A Marker For Severity in Acute OrganophosphorouDocument18 pagesElevation of Serum Creatinine Phosphokinase Level As A Marker For Severity in Acute OrganophosphorouC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart of Online Counseling PDFDocument2 pagesFlow Chart of Online Counseling PDFAnonymous 4gnjzsNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Renal DiseasesDocument14 pagesNutrition in Renal DiseasesC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- JIPMER MD/MS Prospectus 2017Document40 pagesJIPMER MD/MS Prospectus 2017C Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- How Rich Countries Became Rich and Why Poor Countries Remain Poor: It's The Economic Structure - . - Duh!Document55 pagesHow Rich Countries Became Rich and Why Poor Countries Remain Poor: It's The Economic Structure - . - Duh!C Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Cms 2017 Obc AnnexureDocument4 pagesCms 2017 Obc AnnexureC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- PG Counseling Scheme 17Document13 pagesPG Counseling Scheme 17Rohit BansalNo ratings yet
- For All India Quota/ Deemed/ Central Universities Online Counseling For Post-Graduate Medical/ Dental /diploma SeatsDocument15 pagesFor All India Quota/ Deemed/ Central Universities Online Counseling For Post-Graduate Medical/ Dental /diploma SeatsC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Biology Midterm ReviewDocument19 pagesBiology Midterm ReviewC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Eapar in SparrowDocument4 pagesInstructions For Eapar in SparrowC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument5 pagesGeneticsC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Azetecs EmpireDocument7 pagesAzetecs EmpireC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- MD R1Document555 pagesMD R1kashif zafarNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna TechnologyDocument5 pagesRecombinant Dna TechnologyC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Biology XII SET-A - Cbse GuessDocument8 pagesBiology XII SET-A - Cbse GuessC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- The Spontaneous Healing of Belief: Audio SummaryDocument1 pageThe Spontaneous Healing of Belief: Audio SummaryC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Marking System 12th Biology Sample Paper 1 PDFDocument26 pagesMarking System 12th Biology Sample Paper 1 PDFC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Fractal Time PDFDocument64 pagesFractal Time PDFSrdjan DrazovicNo ratings yet
- UserManual ApplicationForm v1.2Document5 pagesUserManual ApplicationForm v1.2C Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Image InstructionsDocument2 pagesImage InstructionsC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- DNB Cet June 2018Document3 pagesDNB Cet June 2018C Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Removal of Hardness 1Document35 pagesRemoval of Hardness 1KISHAN PATELNo ratings yet
- MCQ IjsoDocument20 pagesMCQ IjsommhabgNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Primer AnswersDocument13 pagesSpectroscopy Primer AnswersjayshreeNo ratings yet
- Magnaglo 14a Dry PowderDocument2 pagesMagnaglo 14a Dry Powdermlowe680No ratings yet
- Computational Models For Drug Design and DelivDocument235 pagesComputational Models For Drug Design and DelivIbrahim Al SharabiNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Lab Exercise on Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumDocument21 pagesGroup 4 Lab Exercise on Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumEUNICE JOI SARCONNo ratings yet
- TDS - Mastertop 1330Document2 pagesTDS - Mastertop 1330Venkata RaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To R.T.P.P: 1.1 GeneralDocument12 pagesIntroduction To R.T.P.P: 1.1 GeneralSairam Kumar ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Name of Elements Properties Use/S 1. ZinkDocument13 pagesName of Elements Properties Use/S 1. ZinkNora Alfaro BalsakiNo ratings yet
- 2 Basic Clinical Genetic - ppt-1Document24 pages2 Basic Clinical Genetic - ppt-1Najib M. NauvalNo ratings yet
- Urea MsdsDocument5 pagesUrea MsdsVinnyVidichiNo ratings yet
- Product and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesProduct and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetZirve PolimerNo ratings yet
- 109 Sodium ChlorideDocument6 pages109 Sodium Chlorideeng20072007No ratings yet
- Fosroc Solvent 102 resin cleaning solventDocument2 pagesFosroc Solvent 102 resin cleaning solventShaikhRizwanNo ratings yet
- BS en 1393 1997Document18 pagesBS en 1393 1997karthikkumar T RNo ratings yet
- Gnaser H., Huber B., Ziegler C. - Nanocrystalline TiO2 For Photocatalysis (2004) PDFDocument32 pagesGnaser H., Huber B., Ziegler C. - Nanocrystalline TiO2 For Photocatalysis (2004) PDFoscuraNo ratings yet
- Yeom 2012Document10 pagesYeom 2012Deysi Suarez GomezNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental ManagementDocument12 pagesJournal of Environmental ManagementAjeng FadillahNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruptions NotesDocument24 pagesVolcanic Eruptions NotesKarthikesan MakNo ratings yet
- Biocides in Gas & Oil 2017: Prepared By: Biocide Information Limited EmailDocument39 pagesBiocides in Gas & Oil 2017: Prepared By: Biocide Information Limited EmailSérgio - ATC do BrasilNo ratings yet
- WHMIS Handbook PDFDocument22 pagesWHMIS Handbook PDFNNo ratings yet
- Manual of Methods OF Analysis of Foods: Pesticide ResiduesDocument270 pagesManual of Methods OF Analysis of Foods: Pesticide ResiduesAnonymous XuiUo2ThNo ratings yet
- Lecture notes on basic inorganic chemistry IIDocument24 pagesLecture notes on basic inorganic chemistry IIRSLNo ratings yet
- Analytical Techniques for Evaluating Quality of Herbal DrugsDocument7 pagesAnalytical Techniques for Evaluating Quality of Herbal DrugsZaidNo ratings yet
- Is 10204 PDFDocument4 pagesIs 10204 PDFDimple EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument6 pagesMotionRobert willaimsNo ratings yet
- Induction Sealing - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesInduction Sealing - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSohail ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Classification of MaterialsDocument46 pagesChapter-1 Classification of MaterialstrfuawlachewNo ratings yet
- Merck Price List 2018 To 2019 Vijay ChemicalsDocument404 pagesMerck Price List 2018 To 2019 Vijay Chemicalsnikhilesh2011No ratings yet