Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell As A Unit of Life (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)
Uploaded by
jrpyro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 2
Original Title
Cell as a Unit of Life [Science Form 1_Short Notes]
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentScience Form 1 Chapter 2
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesCell As A Unit of Life (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)
Uploaded by
jrpyroScience Form 1 Chapter 2
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
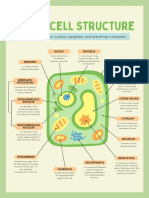
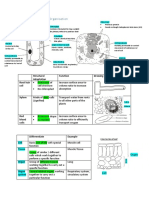
CHAPTER 2: CELL AS A UNIT OF LIFE Characteristics & functions of each animal cells’ parts: -
CELLS Cell Part Characteristic Function
- Support the cell
Basic unit of living thing. Thick layer of cellulose
Cell Wall - Maintain the shape of
Differ in size, shape & function. around cell membrane
cell
2 types: - Animal cells & Plant cells.
Controls what goes in &
Cell Membrane Thin layer around the cell
ANIMAL CELLS out of cell
Consists of nucleus & Has the functions of
Variable / irregular shapes. Protoplasm
cytoplasm nucleus & cytoplasm
General structure: - Place where chemical
Watery, jelly-like &
Cytoplasm process (metabolism)
colourless mixture in cell
occurred
Controls all of activities
Nucleus Contains chromosomes
in cell
- Cell sap contains water
Characteristics & functions of each animal cells’ parts: - that dissolves sugar &
Cell Part Characteristic Function Large space that contains salt
Vacuoles
Thin layer around the Controls what goes in & cell sap - Cell sap makes cell firm
Cell Membrane (taking water) or makes
cell out of cell
cell wilt (losing water)
Consists of nucleus & Has the functions of
Protoplasm Chlorophyll traps light
cytoplasm nucleus & cytoplasm Tiny discs shape that
Chloroplast energy to make food
Watery, jelly-like & Place where chemical contain chlorophyll
colourless mixture in process (metabolism) (photosynthesize)
Cytoplasm
cell occurred Tiny grains of starch in
Starch Granules Represent stored food
cytoplasm
Contains Controls all of activities
Nucleus
chromosomes in cell
Small but numerous Stores water, liquids & SIMILARITIES & DIFFERENCES BETWEEN ANIMAL & PLANT
Vacuoles
tiny spaces food particles CELLS
PLANT CELLS Similarities of both cells: -
- Have nuclei.
Regular / fixed shapes - Have cell membranes.
General structure: - - Have cytoplasm.
Differences between both cells: -
- Plant cells have cellulose cell wall, chloroplasts, starch
granules, cell sap (in vacuoles).
- Vacuoles in plant cells are larger compared to animal
cells.
- Plant cells have fixed shapes while animal cells have
variable shape.
UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS
Made up of one cell only.
Example: Amoeba, bacterium, euglena, paramecium, yeast.
Very tiny & can only be seen under microscope.
Most of unicellular organisms are microorganisms.
MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
Made up of more than one cell.
Example: Earthworm, hydra, spirogyra
Various in sizes. Some are tiny & can only be seen under
microscope while others are big & clearly visible.
CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS IN THE HUMAN BODY
Organization of cells in human body:
Cells Tissues Organs Systems Human
Tissue is made up of groups / layer of similar cells. Every cell
in a tissue performs the same types of function.
Organ is made up of groups of different types of tissues.
Different types of tissues perform different functions.
Body system is made up of various types of organs that working
together to perform a main body function.
You might also like
- Instruction: This Question Paper Consists of Section A, Section B and Section C. Answer All TheDocument21 pagesInstruction: This Question Paper Consists of Section A, Section B and Section C. Answer All TheedmundNo ratings yet
- Revision Summary - Science Form 1Document8 pagesRevision Summary - Science Form 1Beevy GB100% (1)
- Form 2 Experiment 7.2Document3 pagesForm 2 Experiment 7.2Rhys Alden100% (1)
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 1Document7 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 1gayathiremathibalanNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Module Chapter 6 Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesForm 3 Module Chapter 6 Electricity and MagnetismJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- F2 CHP 3 Nutrition (Chinese)Document18 pagesF2 CHP 3 Nutrition (Chinese)ChuahSiewHoon100% (2)
- Form 1 Chapter 3 NotesDocument24 pagesForm 1 Chapter 3 NotesAjuntha Kuppan100% (3)
- Form 1 Science NotesDocument19 pagesForm 1 Science NotesTanYeeTingNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Tamil Upsr Exercises PDFDocument8 pagesBahasa Tamil Upsr Exercises PDFNaresh Kumar0% (1)
- Form 2 Science Project Syuen YeeDocument13 pagesForm 2 Science Project Syuen YeeKanmaneNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 6Document9 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6naza9775100% (7)
- B (Ii) - Ideas For Opening and Closing PDFDocument6 pagesB (Ii) - Ideas For Opening and Closing PDFsyedzaqhwan100% (1)
- Form 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5Document8 pagesForm 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5Kelvin100% (1)
- National Grid Network PylonDocument5 pagesNational Grid Network PylonLim Zi ChengNo ratings yet
- Ask T2 Praktis 1.1Document15 pagesAsk T2 Praktis 1.1NOOR HIDAYAH BINTI MOKHTAR Moe100% (1)
- F1 C3Document19 pagesF1 C3NajwaAbdullah0% (1)
- SC F2 CH1Document59 pagesSC F2 CH1amalina rohaizan50% (2)
- OMG 5 English Form 2 - Unit 4Document6 pagesOMG 5 English Form 2 - Unit 4maaran sivam100% (1)
- Science Form 3 CHAPTER 1Document8 pagesScience Form 3 CHAPTER 1loga yuthrashreeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 3 Biodiversity (COMPACT AND SHORT NOTES) - VERY HELPFULDocument3 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 3 Biodiversity (COMPACT AND SHORT NOTES) - VERY HELPFULDania Subra88% (8)
- Persoalan Novel Sejambak BaktiDocument1 pagePersoalan Novel Sejambak Baktiiyla100% (7)
- Science Year 4 (Short Note) : Theme 1: Investigating Living ThingsDocument8 pagesScience Year 4 (Short Note) : Theme 1: Investigating Living ThingsHasmi HassanNo ratings yet
- Soalan Science Tingkatan 1Document8 pagesSoalan Science Tingkatan 1Sabri AwangNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Exam Science Form 2 2011 - LatestDocument22 pagesMid Year Exam Science Form 2 2011 - LatestTan Phei Ling75% (4)
- Exercise Science Form 1 KSSM Conversion UnitDocument2 pagesExercise Science Form 1 KSSM Conversion UnitWan ShuhaimiNo ratings yet
- (Worksheet) Ungkapan Algebra 3 PDFDocument1 page(Worksheet) Ungkapan Algebra 3 PDFfazidah aini IsmailNo ratings yet
- Science Folio Form2 (Nutrition)Document12 pagesScience Folio Form2 (Nutrition)shahandsome100% (6)
- English Form 2 March Test 2017Document8 pagesEnglish Form 2 March Test 2017Rosy Nurul Hidayati YahyaNo ratings yet
- Kertas BM Exam 2Document4 pagesKertas BM Exam 2Zarif Zikry Zakwan50% (2)
- Form 1 Mathematics (Chapter 1: Rational Numbers) Arithmetic OperationsDocument3 pagesForm 1 Mathematics (Chapter 1: Rational Numbers) Arithmetic OperationsSharuvindan Nair100% (1)
- Form 2 KSSM Exercise Chapter 7Document2 pagesForm 2 KSSM Exercise Chapter 7Wan ShuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 - Chapter 1.1 by KelvinDocument33 pagesScience Form 1 - Chapter 1.1 by KelvinKelvin100% (2)
- F2 Science Extra Knowledge KBAT Questions Chapter 1 The World Through Our SenseDocument1 pageF2 Science Extra Knowledge KBAT Questions Chapter 1 The World Through Our SenseRoxen WooNo ratings yet
- Spending Money: Writing Task: Reply To An EmailDocument1 pageSpending Money: Writing Task: Reply To An EmailJosue Perales AsmatNo ratings yet
- Set Form 1 DLPDocument30 pagesSet Form 1 DLPthaashaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 2Document1 pageForm 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 2Kelvin100% (2)
- Science Folio Form 2 (Nutrition)Document15 pagesScience Folio Form 2 (Nutrition)Larry Song93% (14)
- Formula Mathematics Pt3Document4 pagesFormula Mathematics Pt3Nur AribahNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 RadioactivityDocument19 pagesScience Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 Radioactivitysakinah100% (1)
- Note Expansion Year 6Document8 pagesNote Expansion Year 6Zureida EdaNo ratings yet
- Quick Notes Form 2 (Science)Document11 pagesQuick Notes Form 2 (Science)FishGlobNo ratings yet
- 1 Form 2 Chapter 2 Nutrition Paper 1 Answer All Questions. Each ...Document9 pages1 Form 2 Chapter 2 Nutrition Paper 1 Answer All Questions. Each ...Amira Jasmin JayaNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 1, Form 1...... Experiment of PendulumDocument5 pagesScience Chapter 1, Form 1...... Experiment of PendulumKasthuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biodiversity Form 2 KSSMDocument34 pagesChapter 1 Biodiversity Form 2 KSSMAthirah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- F2 CHP 2 Ecosystem (Chinese)Document12 pagesF2 CHP 2 Ecosystem (Chinese)ChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Bab 1Document23 pagesScience Form 1 Bab 1Nurul Aqilah80% (10)
- Teaching Learning Module KSSR Semakan 2017 Science Year 1 1st EditionDocument98 pagesTeaching Learning Module KSSR Semakan 2017 Science Year 1 1st Editionabq36161713No ratings yet
- 03 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB3-Emie2LP PDFDocument22 pages03 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB3-Emie2LP PDFEve NgewNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggeris: Tingkatan 1Document11 pagesBahasa Inggeris: Tingkatan 1SITI NUR IQMA BINTI SAMSUDIN Moe100% (1)
- Cells, Tissues and OrgansDocument6 pagesCells, Tissues and OrgansatheelNo ratings yet
- Simplified Notes For Biology StudiesDocument56 pagesSimplified Notes For Biology Studiesabi_5dec94100% (5)
- Green Spring Sale PosterDocument1 pageGreen Spring Sale Posterkhayra umairahNo ratings yet
- Canva ExampleDocument1 pageCanva Exampleapi-565439029No ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesShakib al molik100% (1)
- Green and Peach Organic Natural Plant Cell Biology PosterDocument1 pageGreen and Peach Organic Natural Plant Cell Biology PosterMackenzie ElyseNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Organisation: Structural Adaptation Function Drawing (Learn To Draw) Root Hair CellDocument10 pagesCell Structure and Organisation: Structural Adaptation Function Drawing (Learn To Draw) Root Hair CellJules VNo ratings yet
- Is The of Life. It Is of And: Cell AND Cell Basic Unit Composed Different Structures Each HasDocument6 pagesIs The of Life. It Is of And: Cell AND Cell Basic Unit Composed Different Structures Each HasShaweh TogononNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument54 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Cells/Organ Elles Structures Functions: NucleusDocument8 pagesCells/Organ Elles Structures Functions: NucleusHazimah MohiddinNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: History of BiologyDocument6 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: History of BiologyLauraLópezGiraldoNo ratings yet
- 1 Determinant of MorbidityDocument55 pages1 Determinant of MorbidityGrace88 2016No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge Local Examination Syndicate General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Biology 9266/2Document14 pagesUniversity of Cambridge Local Examination Syndicate General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Biology 9266/2Samson AmosNo ratings yet
- Group Two'S Seminar Work: Topic: Enzyme Regulation Allosteric Regulation and Models OutlineDocument13 pagesGroup Two'S Seminar Work: Topic: Enzyme Regulation Allosteric Regulation and Models OutlineOluwasegun ModupeNo ratings yet
- Predicting The Response of Molluscs To The Impact of Ocean AcidificationDocument43 pagesPredicting The Response of Molluscs To The Impact of Ocean Acidificationmji makNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal FluidDocument3 pagesCerebrospinal FluidlecturioNo ratings yet
- Terra Rosa Emag #20Document61 pagesTerra Rosa Emag #20Terra Rosa100% (1)
- BOS Correspondences On Chakras and AurasDocument9 pagesBOS Correspondences On Chakras and AurasDaniel EnglishNo ratings yet
- Connect (4) New QuestionDocument18 pagesConnect (4) New QuestionGeorge ElsabaNo ratings yet
- Cysteamine - Full Profile - 170917Document11 pagesCysteamine - Full Profile - 170917Walter MendozaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Docking in Structure-Based Drug DesignDocument33 pagesMolecular Docking in Structure-Based Drug DesignIvan Tubert-BrohmanNo ratings yet
- Acupuntura OcularDocument4 pagesAcupuntura OcularratamanoNo ratings yet
- Biosep Short OverviewDocument9 pagesBiosep Short OverviewMeyakorberNo ratings yet
- Toxicity of Clay Occulation of The Toxic Dino Agellate, Karenia Brevis, To Estuarine Invertebrates and SHDocument12 pagesToxicity of Clay Occulation of The Toxic Dino Agellate, Karenia Brevis, To Estuarine Invertebrates and SHinousseNo ratings yet
- Erickson's Psycho-Social Theory of DevelopmentDocument29 pagesErickson's Psycho-Social Theory of Developmentexodo loverNo ratings yet
- Tu Eindhoven PHD ThesisDocument7 pagesTu Eindhoven PHD ThesisHelpWritingAPaperManchester100% (2)
- TLC DLCDocument67 pagesTLC DLCchandra shekharNo ratings yet
- Om Biomerieux Reagents Ot-43871 Package Insert-43871Document3 pagesOm Biomerieux Reagents Ot-43871 Package Insert-43871Salomon SalomonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacogenetics: An Introduction: Alain Li-Wan-Po and Peter Farndon Introduce The Science ofDocument3 pagesPharmacogenetics: An Introduction: Alain Li-Wan-Po and Peter Farndon Introduce The Science ofDhuha NawabNo ratings yet
- Maslows Hierarchy of NeedsDocument10 pagesMaslows Hierarchy of NeedsOne-rl Isa-pn100% (1)
- Review On Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles - Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism PDFDocument24 pagesReview On Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles - Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism PDFKarol EsMaNo ratings yet
- Population Ecology: Aecc-I +3 1 YearDocument32 pagesPopulation Ecology: Aecc-I +3 1 YearAnita kumari SahuNo ratings yet
- Big Six PDFDocument4 pagesBig Six PDFmotibaNo ratings yet
- NParks GDP Guidelines Version 3Document214 pagesNParks GDP Guidelines Version 3Lim Kang HaiNo ratings yet
- Draft Update Review Artikel Farmakologi Bawang Dayak 040423Document29 pagesDraft Update Review Artikel Farmakologi Bawang Dayak 040423Zuliar PermanaNo ratings yet
- Travel With An Ease While Not Putting Uneven Stress On Your Back - Caring Hands PhysiotherapyDocument1 pageTravel With An Ease While Not Putting Uneven Stress On Your Back - Caring Hands Physiotherapycaringhands physiotherapyNo ratings yet
- Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1Document9 pagesBiology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1robert100% (32)
- Bioreactor Types (Industrial Notes)Document23 pagesBioreactor Types (Industrial Notes)anjaliNo ratings yet
- Introduction History and Development of MicrobiologyDocument17 pagesIntroduction History and Development of Microbiologymoses samuelNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 4 Stains PDFDocument3 pagesEXERCISE 4 Stains PDFOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet