Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Boiler Working Principle
Uploaded by
SabrinaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Boiler Working Principle
Uploaded by
SabrinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Working Principle
Both gas and oil fired boilers use controlled combustion of the fuel to heat water. The key boiler
components involved in this process are the burner, combustion chamber, heat exchanger, and
controls.
The burner mixes the fuel and oxygen together and, with the assistance of an ignition device,
provides a platform for combustion. This combustion takes place in the combustion chamber, and
the heat that it generates is transferred to the water through the heat exchanger. Controls regulate
the ignition, burner firing rate, fuel supply, air supply, exhaust draft, water temperature, steam
pressure, and boiler pressure.
Hot water produced by a boiler is pumped through pipes and delivered to equipment throughout
the building, which can include hot water coils in air handling units, service hot water heating
equipment, and terminal units. Steam boilers produce steam that flows through pipes from areas of
high pressure to areas of low pressure, unaided by an external energy source such as a pump. Steam
utilized for heating can be directly utilized by steam using equipment or can provide heat through a
heat exchanger that supplies hot water to the equipment.
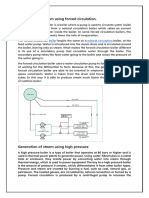
A boiler is an enclosed vessel that provides a means for combustion heat to be transferred to water
until it becomes heated water or steam. The hot water or steam under pressure is then usable for
transferring the heat to a process. Water is a useful and inexpensive medium for transferring heat to
a process. When water at atmospheric pressure is boiled into steam its volume increases about
1,600 times, producing a force that is almost as explosive as gun powder. This causes the boiler to be
an equipment that must be treated with utmost care.
The boiler system comprises of: a feed water system, steam system and fuel system. The feed water
system provides water to the boiler and regulates it automatically to meet the steam demand.
Various valves provide access for maintenance and repair. The steam system collects and controls
the steam produced in the boiler. Steam is directed through a piping system to the point of use.
Throughout the system, steam pressure is regulated using valves and checked with steam pressure
gauges. The fuel system includes all equipment used to provide fuel to generate the necessary heat.
The equipment required in the fuel system depends on the type of fuel used in the system.
The water supplied to the boiler that is converted into steam is called feed water.
The two sources of feed water are:
Condensate or condensed steam returned from the processes and
Makeup water (treated raw water) which must come from outside the boiler room and plant
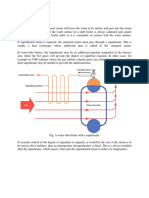
processes. For higher boiler efficiencies, an economizer preheats the feed water using the waste
heat in the flue gas.
You might also like
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- What Is A Boiler: Introduction To BoilersDocument1 pageWhat Is A Boiler: Introduction To BoilersThivin RajNo ratings yet
- The Boiler System Is Made Up ofDocument1 pageThe Boiler System Is Made Up ofThivinrajNo ratings yet
- Boiler Basics PDFDocument5 pagesBoiler Basics PDFEng Waleed MouhammedNo ratings yet
- Steam Boiler Operation and AuxiliariesDocument9 pagesSteam Boiler Operation and Auxiliariesshin deiruNo ratings yet
- Boiler TypesDocument9 pagesBoiler TypesSharif Muhammad HossainNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Generation Plant or Thermal Power StationDocument157 pagesThermal Power Generation Plant or Thermal Power Stationgteklay100% (1)
- Tugas Util (Boiler)Document4 pagesTugas Util (Boiler)AkhmadSumarnoNo ratings yet
- PPS Steam Boiler Operation and AuxiliariesDocument9 pagesPPS Steam Boiler Operation and AuxiliariesAraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BoilersDocument25 pagesIntroduction To BoilersDamith Buddhika Sri WimalarathnaNo ratings yet
- Mech NotesDocument8 pagesMech NotesNihal AhamedNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument42 pagesThermal Power PlantAravind C.KNo ratings yet
- BoilerpptDocument11 pagesBoilerpptFarhan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument5 pagesPower Plant EngineeringMonglafru MogNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power PlantDocument4 pagesHydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power Plantuikeshekhar610No ratings yet
- Us DixitDocument10 pagesUs Dixitmusu MukeshNo ratings yet
- Safety Operating Procedure of A Fire Tube BoilerDocument10 pagesSafety Operating Procedure of A Fire Tube BoilerJan Marvin Tamse0% (1)
- Parts of Boiler and Their FunctionDocument4 pagesParts of Boiler and Their FunctionsadNo ratings yet
- High Pressure BoilerDocument8 pagesHigh Pressure BoilerAnand KalaniNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Steam Power PlantsDocument32 pagesUnit - I Steam Power Plantsrsankarganesh MECH-HICET100% (1)
- HRSGDocument24 pagesHRSGsathishsggsNo ratings yet
- Steam PlantDocument102 pagesSteam PlantPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Class 4. Steam Power PlantDocument37 pagesClass 4. Steam Power PlantsureshlalNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument7 pagesBoiler Mountings and Accessoriessoumik RayhanNo ratings yet
- BodyDocument69 pagesBodyRoi Benedict BuenaNo ratings yet
- Fire Tube BoilerDocument7 pagesFire Tube Boilergalih prasetyo aji gumelarNo ratings yet
- InstrumentationDocument147 pagesInstrumentationAmapola San RafaelNo ratings yet
- What Is A Boiler?: Aux Mach 211 Assignment Week 13 4Cl E/C Bollo, Wilfredo JR, SDocument1 pageWhat Is A Boiler?: Aux Mach 211 Assignment Week 13 4Cl E/C Bollo, Wilfredo JR, SJr BolloNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Lay OutDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plant Lay OutSaheli ChoudhuriNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Marine Boilers PDFDocument48 pages2.1. Marine Boilers PDFBasong San67% (3)
- Boiler: Figure: Fire Tube BoilerDocument9 pagesBoiler: Figure: Fire Tube BoilerNahin AminNo ratings yet
- Expt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantDocument6 pagesExpt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantSajeeb SarkerNo ratings yet
- Boiler Research JonathanDocument3 pagesBoiler Research JonathanJonathan MalamulaNo ratings yet
- Exp No 04 Working of High Pressure Boiler.Document6 pagesExp No 04 Working of High Pressure Boiler.Aasawari MahagaonkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Boiler 2023Document1 pageIntroduction To Boiler 2023yohannesNo ratings yet
- Boiler Design and Operation PDFDocument8 pagesBoiler Design and Operation PDFChungNguyenNo ratings yet
- N BLR Working Types PartsDocument12 pagesN BLR Working Types PartsSuhas KassaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledafifiNo ratings yet
- تقرير محطات الطاقهDocument45 pagesتقرير محطات الطاقهعبد الرحمن إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- High Pressure BoilerDocument58 pagesHigh Pressure BoilerPATIL YASH SANJAYNo ratings yet
- 1.1.power Plant LayoutDocument5 pages1.1.power Plant LayoutBALAMBAL R100% (1)
- Boiler Thermo AssignmentDocument6 pagesBoiler Thermo AssignmentBassam0% (2)
- Introduction To BoilersDocument36 pagesIntroduction To BoilersAdel SukerNo ratings yet
- 05.lecture - 05 - Steam Generator or BoilersDocument26 pages05.lecture - 05 - Steam Generator or BoilersSakib RafeeNo ratings yet
- CoalDocument41 pagesCoalKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Steam Drum Systems As Well As Once-Through Steam Generators (OTSG) SystemsDocument8 pagesSteam Drum Systems As Well As Once-Through Steam Generators (OTSG) SystemsGobardhana swainNo ratings yet
- Components & Working of Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesComponents & Working of Thermal Power PlantAngiras SureshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8: Steam Generators: Fig. 8.1: A Shell Boiler With An EconomizerDocument6 pagesLecture 8: Steam Generators: Fig. 8.1: A Shell Boiler With An EconomizerIjazzzAliNo ratings yet
- On Suratgarh TPPDocument15 pagesOn Suratgarh TPPsubhampce085No ratings yet
- Water Tube Boiler: Babcock and WilcoxDocument8 pagesWater Tube Boiler: Babcock and WilcoxJosue Carubio Ricalde Jr.No ratings yet
- Boiler EconomizerDocument5 pagesBoiler Economizerreyalene gallegos100% (1)
- By: Ladisla, Gyver G. Pecson, Prince Harry B. Sartin, Raymart PDocument11 pagesBy: Ladisla, Gyver G. Pecson, Prince Harry B. Sartin, Raymart PRaymart SartinNo ratings yet
- Boiler Cont.Document9 pagesBoiler Cont.adnan mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Ornos, Janlyn Z. MEL 2 Assessment 1Document4 pagesOrnos, Janlyn Z. MEL 2 Assessment 1Janlyn OrnosNo ratings yet
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocument110 pagesPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewFrom EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewNo ratings yet
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet
- Horizontal Distribution of TemperatureDocument12 pagesHorizontal Distribution of TemperatureS.H EnterpriseNo ratings yet
- Shrijee Fluidized Bed Sugar Dryer (FBD) Flyer-NewDocument2 pagesShrijee Fluidized Bed Sugar Dryer (FBD) Flyer-NewbkarakoseNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document3 pagesUnit 5Yugi YuguNo ratings yet
- TSWF - 900.2 - Earthing Calculation For 110kV OHTL - Rev2Document4 pagesTSWF - 900.2 - Earthing Calculation For 110kV OHTL - Rev2Shinekhuu99No ratings yet
- Bilge System CalculationDocument12 pagesBilge System CalculationMuhammad Habib100% (1)
- New Powerful Reagents Based On Dihalogen/N, N Perhydrodiazepine-2,3-Dithione Adducts For Gold Dissolution: The Ibr CaseDocument6 pagesNew Powerful Reagents Based On Dihalogen/N, N Perhydrodiazepine-2,3-Dithione Adducts For Gold Dissolution: The Ibr CaseUkko PulkkinenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8, 11 Heath Textbook Chemistry 11Document6 pagesChapter 8, 11 Heath Textbook Chemistry 11Venus WangNo ratings yet
- Iso StandarsDocument11 pagesIso StandarsSREENo ratings yet
- Optimization of Labyrinth Seal For Screw Compressor Ht2007-32275Document7 pagesOptimization of Labyrinth Seal For Screw Compressor Ht2007-32275api-3842143No ratings yet
- MEGA AIR - Piston Compressor - EN - 950313 - SmallDocument8 pagesMEGA AIR - Piston Compressor - EN - 950313 - SmallAminSaadaouiNo ratings yet
- 2.pH, Buffers and Isotonic Solutions AbDocument48 pages2.pH, Buffers and Isotonic Solutions AbPasham Venkat ReddyNo ratings yet
- Bolted ConnectionsDocument16 pagesBolted ConnectionsCharizza Montarin CENo ratings yet
- Induction BendingDocument20 pagesInduction BendingAnoop N Kutty100% (4)
- RanikhetDocument2 pagesRanikhetAbhishikta BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument22 pagesHeat ExchangerYashwant SinghNo ratings yet
- Uniheat - Transfer Thermal Unitst II Convective Heat Transfer Thermal UnitsDocument33 pagesUniheat - Transfer Thermal Unitst II Convective Heat Transfer Thermal Unitsaerosanth100% (1)
- Water Cooled Chiller - SOPDocument13 pagesWater Cooled Chiller - SOParunceedee100% (4)
- Chapter 4. Heat Treatment by InductionDocument1 pageChapter 4. Heat Treatment by InductionKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Charge-Coupled DevicesDocument55 pagesCharge-Coupled Devicesmyth100% (1)
- Calculations and Verifications of Shredding Chamber of Two-Shaft Shredder For Crushing of Concrete, Rubber, Plastic and WoodDocument2 pagesCalculations and Verifications of Shredding Chamber of Two-Shaft Shredder For Crushing of Concrete, Rubber, Plastic and WoodEdosael KefyalewNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Introduction To Condensed Matter TheoryDocument154 pagesLecture Notes: Introduction To Condensed Matter Theory谭志阳No ratings yet
- MTE 314 Mechanical Vibrations: Report Experiments 2Document3 pagesMTE 314 Mechanical Vibrations: Report Experiments 2Yomna EmadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Solid, Liquid, and Gas (Grade 3)Document26 pagesLesson 1 - Solid, Liquid, and Gas (Grade 3)Christian TabalanNo ratings yet
- BIW Thinwall Structures PDFDocument3 pagesBIW Thinwall Structures PDFsmani170No ratings yet
- Off Budgell FRCR - VerificationDocument46 pagesOff Budgell FRCR - VerificationAmr MuhammedNo ratings yet
- CH - 12 ElectricityDocument24 pagesCH - 12 ElectricityJency JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Heat and Thermodynamics 34-37 PDFDocument4 pagesHeat and Thermodynamics 34-37 PDFChaudhary Shahzaib AliNo ratings yet
- HJT MBB Half-Cut Bifacial Dual-Glass Module Ska611HdgdcDocument2 pagesHJT MBB Half-Cut Bifacial Dual-Glass Module Ska611HdgdcMarko Maky ZivkovicNo ratings yet
- Lec16 PDFDocument13 pagesLec16 PDFRohan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Example Problem Solutions - Chapter 8Document18 pagesExample Problem Solutions - Chapter 8Nguyen Tien DungNo ratings yet