Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TerminationForm 201702
Uploaded by
Mohd Farhan ShahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TerminationForm 201702
Uploaded by
Mohd Farhan ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
RATIO VRL Workshop
No Question(s) Guided solution(s)
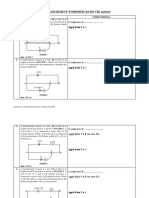
❶ A potentiometer consists of a wire AB of 100 cm in
length as shown in FIGURE 1. When a cell with emf G reads zero ……VAC=ξx…….
x is connected to the potentiometer, the balance length
AC is 75 cm. Determine x. 𝝆𝒍
Knowing that 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 = 𝑰 ( 𝑨 ) → 𝑽 ∝ 𝑹 ; 𝑽 ∝ 𝒍
2.5 V Apply Ratio V α l :
V R L
2.5 100 cm
C ξx 75 cm
A B
x 𝟐. 𝟓 𝟏𝟎𝟎
=
G 𝝃𝒙 𝟕𝟓
FIGURE 1 ξx = 1.875 V
❷ A potentiometer consists of a wire AB of 100 cm in
length as shown in FIGURE 1. When a cell with emf G reads zero …VAC = ξ = 0.75 V….
0.75 V is connected to the potentiometer, determine the
balance length AC. 𝝆𝒍
Knowing that 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 = 𝑰 ( 𝑨 ) → 𝑽 ∝ 𝑹 ; 𝑽 ∝ 𝒍
1.5 V Apply Ratio V α l :
V R L
1.5 100 cm
C 0.75 V lAC
A B
= 0.75 V 𝟏. 𝟓 𝟏𝟎𝟎
=
G 𝟎. 𝟕𝟓 𝒍𝑨𝑪
FIGURE 2 lAC = 50 cm
prepared by chongyokelai Friday, July 27, 2018
❸ A potentiometer consists of a wire AB of 100 cm in G reads zero … ξ1 = VAC ….
length and 40 resistance as shown in FIGURE 3. A
cell of emf 1.5 V is connected in series with 2.0 𝝆𝒍
Knowing that 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 = 𝑰 ( 𝑨 ) → 𝑽 ∝ 𝑹 ; 𝑽 ∝ 𝒍
external resistor. When a cell with emf 1 is connected
to the potentiometer, the balance length AC is 65 cm. V R L
Determine 1. 1.5 V (2 + 40) = 42Ω
1.5 V 2.0 Ω V AB 40 Ω 100 cm
VAC 65 cm
Apply Ratio V α R for wire AB :
C 𝟏.𝟓 𝟒𝟐
A B = 𝟒𝟎 VAB = 1.43 V
𝑽𝑨𝑩
1 Apply Ratio V α l :
𝟏.𝟒𝟑 𝟏𝟎𝟎
G = 𝟔𝟓 VAC = 0.93 V
𝑽𝑨𝑪
FIGURE 3
∴ ξ1 = 0.93 V
❹ A potentiometer consists of a wire CE of 100 cm in
length and 40 resistance as shown in FIGURE 4. A G reads zero … VCD = ξ1 ….
cell of emf 1.5 V and 2.0 internal resistance is
connected in series with 2.0 external resistor. When 𝝆𝒍
Knowing that 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 = 𝑰 ( 𝑨 ) → 𝑽 ∝ 𝑹 ; 𝑽 ∝ 𝒍
a cell with emf 1 is connected to the potentiometer, the
balance length CD is 45.5 cm. Determine 1. V R L
1.5 2+2+40 = 44Ω
VCE 40 Ω 100 cm
1.5 V, 2 2 VCD 45.5 cm
A B
Apply Ratio V α R for wire CE :
𝟏.𝟓 𝟒𝟒
D = VCE = 1.36 V
C E 𝑽𝑪𝑬 𝟒𝟎
Apply Ratio V α l:
1 𝟏.𝟑𝟔 𝟏𝟎𝟎
F G
= VCD = 0.6188 V
𝑽𝑪𝑫 𝟒𝟓.𝟓
∴ ξ1 = 0.6188 V
FIGURE 4
prepared by chongyokelai Friday, July 27, 2018
❺ FIGURE 5 shows a potential divider consisting of a G reads zero … VXQ = ξ ….
wire XY of length 1.0 m and resistance 5.0 Ω. A cell 𝝆𝒍
Knowing that 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 = 𝑰 ( 𝑨 ) → 𝑽 ∝ 𝑹 ; 𝑽 ∝ 𝒍
of emf 2.0 V with internal resistance 0.5 Ω is
connected in series with a 3.0 Ω resistor. When V R L
another cell with emf ε is connected to the potential 2.0 V 0.5+3+5 = 8.5 Ω
divider, the balance length XQ is 76.2 cm. Calculate VXY 5Ω 100 cm
ε. VXQ 76.2 cm
2.0 V, 0.5 3 Apply Ratio V α R for wire XY :
𝟐.𝟎 𝟖.𝟓
= 𝟓 VXY = 1.176 V
𝑽𝑿𝒀
Apply Ratio V α l:
Q 𝟏.𝟏𝟕𝟔 𝟏𝟎𝟎
X Y = VXQ = 0.896 V
𝑽
𝑿𝑸 𝟕𝟔.𝟐
∴ ξ = 0.896 V
G FIGURE 5
❻ A potentiometer consists of a wire CE of 100 cm in Hints : concept you need open circuit reads emf, ε
length and 40 resistance as shown in FIGURE 6. A Closed circuit reads terminal voltage, Vt
cell of emf 1.5 V with eligible internal resistance is (a) G reads zero … VCD = ξ ….
connected in series with 2.0 external resistor. 𝝆𝒍
(a) with suis S open, the balanced length is 68 cm,
Knowing that 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 = 𝑰 ( 𝑨 ) → 𝑽 ∝ 𝑹 ; 𝑽 ∝ 𝒍
determine the value of . V R L
(b) with suis S closed, the balance length is 55.5 cm, 1.5 V 2 + 40 = 42 Ω
determine the internal resistance of ε. VCE 40 Ω 100 cm
(a) VCD = ξ 68 cm
1.5 V 2 (b) VCD = Vt 55.5 cm
A B
Apply Ratio V α R for wire CE :
D 1.5 42
C E = 40 VCE = 1.429 V
VCE
, r
1.429 100
G (a) Apply Ratio V α l: = ξ = 0.972 V
F ξ 68
1.429 100
3 S (b) Apply Ratio V α l: = 55.5 Vt = 0.793V
Vt
FIGURE 6
prepared by chongyokelai Friday, July 27, 2018
𝟎. 𝟕𝟗𝟑
𝑽𝒕 = 𝑰𝑹 → 𝑰 = = 𝟎. 𝟐𝟔𝟒 𝑨
𝟑
ξ=𝑰 (𝒓 + 𝑹)
0.972 =0.264(r+3)
r = 0.682 Ω
❼ A slide wire potentiometer AB with the length of 100
cm is used to compared emf with two resistance 80Ω (a) G reads zero … VAJ = Vacross 80Ω ….
and 20Ω as shown in Figure 7. With the galvanometer 𝝆𝒍
showing zero deflection, determine the balance length, Knowing that 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 = 𝑰 ( 𝑨 ) → 𝑽 ∝ 𝑹 ; 𝑽 ∝ 𝒍
l
(a) With switches S1 and S2 closed and the two V R L
cells with negligible internal resistance, 2.0 100 cm
(b) With switch S1 opened and S2 closed. VAJ = 80 Ω lAJ
V80Ω
𝜀1 = 2.0 𝑉 1.5 80+20 Ω
J Apply Ratio V α R for circuit below :
A B 𝟏.𝟓 𝟏𝟎𝟎
l = 𝟖𝟎 VAJ = 1.2 V
𝑽𝑨𝑱
G Apply Ratio V α l:
𝟐 𝟏𝟎𝟎
80 Ω 20 Ω Z = lAJ =60 cm
𝟏.𝟐 𝒍
𝑨𝑱
S2 (b) G reads zero … VAJ = 1.5V ….
S1
V R L
2.0 100 cm
VAJ = 1.5 lAJ
𝜀 = 1.5 𝑉
Apply Ratio V α l:
FIGURE 7 𝟐 𝟏𝟎𝟎
= 𝒍 lAJ =75 cm
Ans : (a) 60 cm ; (b) 75 cm 𝟏.𝟓 𝑨𝑱
prepared by chongyokelai Friday, July 27, 2018
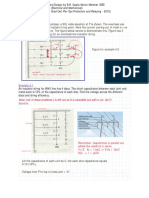
❽ FIGURE 8 shows a light dimmer consisting of 150 Ω
variable resistor, 220 V voltage source and a light bulb. 𝝆𝒍
Knowing that 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 = 𝑰 ( 𝑨 ) → 𝑽 ∝ 𝑹 ; 𝑹 ∝ 𝒍
The slider moves between x = 0 to x = 1. If it is at x =
0.3, calculate the voltage of the bulb.
V R L
220 V 150 Ω 1
x=1 Vbulb R 0.3
220 V Apply Ratio R α l for circuit below :
x=0 𝟏𝟓𝟎 𝟏
= 45 Ω
𝑹 𝟎.𝟑
Apply Ratio V α R:
𝟐𝟐𝟎 𝟏𝟓𝟎
= 66 V
𝑽𝒃𝒖𝒍𝒃 𝟒𝟓
prepared by chongyokelai Friday, July 27, 2018
𝑅2
❾ FIGURE 8shows an arrangement of resistance R1 = 𝑉 = [𝑅
1 +𝑅2 ]
3.0 and R2 = 2.0 which are arrange in parallel to a
12.0 V driver source. Determine the potential 2
difference across resistance R2. 𝑉 = [[2+3] ](12)
= 4.8 V
R1 = 3
12 V
R2 = 2
V
FIGURE 8
❿ (i) Describe how to balance the Wheatstone Bridge. 𝑹𝒙 𝟓𝟔
= 𝟏𝟒
𝟏𝟎
(ii) Calculate the value of RX when the Wheatstone
Bridge shown in FIGURE 9 is in equilibrium
position. 𝑹𝒙 = 𝟒𝟎Ω
RX 56
G
10 14
40 V
FIGURE 9
~ Selamat Maju Jaya dalam UPS2 ~
prepared by chongyokelai Friday, July 27, 2018
You might also like
- A Practical Total Synthesis of CocaineDocument13 pagesA Practical Total Synthesis of CocaineRodrigo Fernanda100% (4)
- 19 04 20 p2 PDFDocument32 pages19 04 20 p2 PDFGovind SajuNo ratings yet
- NULL MEASUREMENT WORKSHOP (Soalan)Document4 pagesNULL MEASUREMENT WORKSHOP (Soalan)faris zainuddinNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 03 To Investigate The Voltage Distribution Over A Suspension Insulator String With Guard RingDocument3 pagesLab Experiment 03 To Investigate The Voltage Distribution Over A Suspension Insulator String With Guard RingFaixan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Op-AmpDocument43 pagesOp-AmpHriday TejwaniNo ratings yet
- L4 - Diode 1Document29 pagesL4 - Diode 1amonNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 1Document3 pagesExperiment # 1Mahnoor SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Practical Applications: Design, Simulation and Implementation - 2019 Week 0 Assignment SolutionDocument12 pagesOp-Amp Practical Applications: Design, Simulation and Implementation - 2019 Week 0 Assignment SolutionSalil ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Lic LabDocument15 pagesLic Labpratik kumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Meter Bridge Exp 2Document3 pagesExperiment 2 Meter Bridge Exp 2swaroop swastik pradhan75% (4)
- 3 Phase CKTDocument42 pages3 Phase CKTDeepa ShreeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 ADocument42 pagesChapter 32 AmaheshNo ratings yet
- 05 AC CircuitsDocument44 pages05 AC CircuitsGusty WidyawatiNo ratings yet
- DGD 3 SolutionsDocument13 pagesDGD 3 Solutionsyasa akooNo ratings yet
- Overhead Line Insulators: Example 4.1Document11 pagesOverhead Line Insulators: Example 4.1e TalalNo ratings yet
- Overhead Line and Substation InsulationDocument11 pagesOverhead Line and Substation InsulationAnkat Rao RaoNo ratings yet
- TP2 MohamedElleuch INDP1D PDFDocument16 pagesTP2 MohamedElleuch INDP1D PDFKarim DesignerNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit FundamentalsDocument19 pagesElectric Circuit FundamentalsSana NgaNo ratings yet
- Exp9 s04Document8 pagesExp9 s04SITI HAJAR AzizNo ratings yet
- Power Amps 6Document17 pagesPower Amps 6Jacobo Palmeiro JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Unit 4 Part-2Document20 pagesOp-Amp Unit 4 Part-2Jos BatlarNo ratings yet
- Power Amps 6Document17 pagesPower Amps 6Wilson MartinezNo ratings yet
- DGD 4 SolutionsDocument10 pagesDGD 4 Solutionsyasa akooNo ratings yet
- Expt No 4Document3 pagesExpt No 4puja maneNo ratings yet
- Ieai Lab File: Name: Yuvan Saroya ROLL NO.: 2K18/PSY/16 M.Tech Psy 1St SemDocument26 pagesIeai Lab File: Name: Yuvan Saroya ROLL NO.: 2K18/PSY/16 M.Tech Psy 1St SemNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Problem Grade 1 2 3 4 Total: 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and CircuitsDocument207 pagesProblem Grade 1 2 3 4 Total: 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuitsmiguel axelNo ratings yet
- ELECS CompilationDocument74 pagesELECS CompilationRaine LopezNo ratings yet
- Eee 1102Document26 pagesEee 1102Rayhanul Islam LamunNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 (Meter Bridge)Document4 pagesExpt 1 (Meter Bridge)deepakrambhakt07No ratings yet
- Transitor 3Document22 pagesTransitor 3HpA SaúlNo ratings yet
- ENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Final Examination: Tuesday, June 29, 2004 Time: 3:30 - 6:30 PMDocument6 pagesENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Final Examination: Tuesday, June 29, 2004 Time: 3:30 - 6:30 PMTaha EtemNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 02 To Investigate The Voltage Distribution Over A Suspension Insulator StringDocument3 pagesLab Experiment 02 To Investigate The Voltage Distribution Over A Suspension Insulator StringFaixan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument52 pagesElectric CircuitsTejesh Shami100% (1)
- ELE302 NotesDocument70 pagesELE302 NotesAnmol PanchalNo ratings yet
- BJT DC Bias - 2023Document22 pagesBJT DC Bias - 2023Samer SeifNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 8Document3 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 8Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- Bogotá, D.C., 20 de Noviembre de 2019 Problemas Ela1 Problemas Propuestos: 1. in The Circuit of Figure A, The Diode Is IdealDocument6 pagesBogotá, D.C., 20 de Noviembre de 2019 Problemas Ela1 Problemas Propuestos: 1. in The Circuit of Figure A, The Diode Is IdealFelipe GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Clipper Clamper CircuitsDocument15 pagesClipper Clamper CircuitsAnilaSaghirNo ratings yet
- Oscillators 3Document8 pagesOscillators 3LJ TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Hour Exam #1 Review ProblemsDocument9 pagesHour Exam #1 Review ProblemsNajmoAdenNo ratings yet
- Problem 1Document6 pagesProblem 1CAO MINH TRÍNo ratings yet
- Module 2 SolutionDocument26 pagesModule 2 SolutionCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Full Wave Rectifier (Center Tapped)Document4 pages1.2 Full Wave Rectifier (Center Tapped)Mahnoor SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Ec Ii Unit3Document23 pagesEc Ii Unit3Unmesh PeriNo ratings yet
- CURRENT - L3 Class 3Document2 pagesCURRENT - L3 Class 3Gokul RanghamannarNo ratings yet
- 01 TutorialDocument3 pages01 Tutorialee23m052No ratings yet
- Emailing AC - Exp - 04 - StudentDocument4 pagesEmailing AC - Exp - 04 - StudentNafiul BariNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 03: Problem 1 A Full-Wave, 4-Diode Bridge Rectifier Circuit With ADocument11 pagesHomework Assignment 03: Problem 1 A Full-Wave, 4-Diode Bridge Rectifier Circuit With AFavas PNo ratings yet
- Using The Agilent 54621A Digital Oscilloscope As A Curve Tracer For A BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor)Document6 pagesUsing The Agilent 54621A Digital Oscilloscope As A Curve Tracer For A BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor)RodNo ratings yet
- Worked Solutions Chapter 4 Electronics: 4.1 Analysing Electronic CircuitsDocument9 pagesWorked Solutions Chapter 4 Electronics: 4.1 Analysing Electronic Circuits123HopperNo ratings yet
- To Study The Voltage Gain of A Common Emitter and Common AmplifierDocument4 pagesTo Study The Voltage Gain of A Common Emitter and Common AmplifierSagar RawalNo ratings yet
- Selected Q - Current Electricity - VIDocument4 pagesSelected Q - Current Electricity - VIarohi yadavNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesFrom EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- MenuDocument1 pageMenuMohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Pelan Rumah PDFDocument1 pagePelan Rumah PDFMohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Graphic Stimuli and Short Texts Set 1Document6 pagesGraphic Stimuli and Short Texts Set 1Mohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Graf 1516 NewDocument13 pagesGraf 1516 NewMohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Should Parents Be Held Responsible For The Crimes of Their Children?Document6 pagesShould Parents Be Held Responsible For The Crimes of Their Children?Mohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module Form 4 SPM CandidatesDocument5 pagesChemistry Module Form 4 SPM CandidatesMohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Jadual KasarDocument22 pagesJadual KasarMohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Tingkatan 4 Front PageDocument2 pagesModul Fizik Tingkatan 4 Front PageMohd Farhan Shah0% (1)
- MODUL FIZIK TINGKATAN 4 Front PageDocument2 pagesMODUL FIZIK TINGKATAN 4 Front PageMohd Farhan Shah0% (1)
- Road To Wellness: Abang SayangDocument2 pagesRoad To Wellness: Abang SayangMohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Three Chicks Eight Dresses Five Ducks Four Pencils Seven Gold FishDocument3 pagesThree Chicks Eight Dresses Five Ducks Four Pencils Seven Gold FishMohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Buah Potong (Assorted)Document5 pagesBuah Potong (Assorted)Mohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- D 2 M 1 T 1 NbmgbjgyuDocument2 pagesD 2 M 1 T 1 NbmgbjgyuMohd Farhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument8 pagesOrigin and Structure of The EarthRobin Suarez ViladoNo ratings yet
- G3412 - 450 KW Performance DataDocument3 pagesG3412 - 450 KW Performance DataJacob De CasillasNo ratings yet
- Psychometric Development and Validation of GaslightingDocument15 pagesPsychometric Development and Validation of GaslightingYang ZhangNo ratings yet
- ASUS U47A Repair GuideDocument5 pagesASUS U47A Repair GuideCarlos ZarateNo ratings yet
- Pearson Product-Moment Correlation Coefficient Table of Critical ValuesDocument2 pagesPearson Product-Moment Correlation Coefficient Table of Critical ValuesOdy AjjaNo ratings yet
- Research FinalDocument29 pagesResearch FinalLaw VesperaNo ratings yet
- Numerical ModelDocument61 pagesNumerical ModelAlbert AguileraNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Unit: Dr. Sowmya BJDocument146 pagesArithmetic Unit: Dr. Sowmya BJtinni09112003No ratings yet
- GB-T 5137.1-2002 Test Methods of Safety Glazing Materials Used On Road Vehicles Part1 Mechanical Properties TestsDocument14 pagesGB-T 5137.1-2002 Test Methods of Safety Glazing Materials Used On Road Vehicles Part1 Mechanical Properties TestsRandyzhuNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Review Solutions PDFDocument11 pagesCH 12 Review Solutions PDFOyinkansola OsiboduNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 CH 6 Assertion Reason QuestionsDocument5 pagesGrade 10 CH 6 Assertion Reason QuestionsVidhun 8ANo ratings yet
- Script Track IP TermuxDocument5 pagesScript Track IP TermuxAsepNo ratings yet
- JSF + JPA + JasperReports (Ireport) Part 2 - Ramki Java BlogDocument7 pagesJSF + JPA + JasperReports (Ireport) Part 2 - Ramki Java BlogMartin MurciegoNo ratings yet
- Awodey, Categories For Everybody - PsDocument196 pagesAwodey, Categories For Everybody - PsΣωτήρης Ντελής100% (3)
- Apl 220014Document2 pagesApl 220014Elprince MidoNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity Modeling and Measurement of TSV in 3D ICDocument4 pagesSignal Integrity Modeling and Measurement of TSV in 3D IC張志榮No ratings yet
- Gps Vehicle Tracker User Manual: PrefaceDocument13 pagesGps Vehicle Tracker User Manual: PrefaceFedericoNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: Overview of Graphics SystemsDocument25 pagesComputer Graphics: Overview of Graphics Systemsshibina balakrishnanNo ratings yet
- HST TrainingDocument11 pagesHST TrainingRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Estimating QuotientsDocument7 pagesEstimating Quotientssheila mae neri100% (1)
- Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images - H. Maitre (Wiley, 2008) WWDocument411 pagesProcessing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images - H. Maitre (Wiley, 2008) WWbehzad100% (4)
- The Kemetic Tree of LifeDocument1 pageThe Kemetic Tree of LifeFlorin CiudinNo ratings yet
- TOFD Dead Zone CalculatorDocument4 pagesTOFD Dead Zone CalculatorWill SmithNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus MIdTermsDocument5 pagesPre Calculus MIdTermsLamette Austria Ayong0% (1)
- Chem Cheat Sheet MasterDocument6 pagesChem Cheat Sheet MasteradamhamelehNo ratings yet
- Comptector & Chiller (Cdu) Controller (Fx32C Series) : Precaution For UseDocument5 pagesComptector & Chiller (Cdu) Controller (Fx32C Series) : Precaution For UseFcma0903100% (1)
- Petrom OMV Norm DEF 2001 Rom Eng Rev.2 2009-06-01Document61 pagesPetrom OMV Norm DEF 2001 Rom Eng Rev.2 2009-06-01luciandu100% (1)
- Low Temperature Plastics - EnsingerDocument4 pagesLow Temperature Plastics - EnsingerAnonymous r3MoX2ZMTNo ratings yet