Professional Documents
Culture Documents
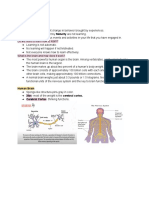
Cerebrum With Spinal Cord: Speech and Hearing
Uploaded by
JJ Lim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesAnatomy of Brain
Original Title
Anatomy of Brain
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnatomy of Brain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesCerebrum With Spinal Cord: Speech and Hearing
Uploaded by
JJ LimAnatomy of Brain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
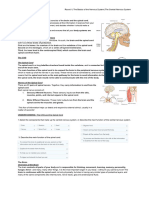
Anatomy of Brain
Names Functions Notes
Cognitive function.
1. Controls mental processes – sensations, consciousness, Speech and
cerebrum memory understanding
2. Controls voluntary movements language.
Motor function
1. Controls muscle contraction to coordinate movements
cerebellum coordinate
2. Maintain balance, posture
1. Relay sensory impulses to the appropriate place in
thalamus relay station
cerebral cortex, spinal cord, brain stem, cerebellum
1. Controls homeostasis (blood temperature, pressure)
Hormone
hypothalamus 2. Controls secretion of hormones by pituitary gland
Homeostasis
3. Controls emotions, sexual arousal, hunger, thirst, sleep
1. Connects cerebrum with spinal cord
involuntary
brain stem 2. Controls involuntary actions
actions
3. Controls alertness (arousal)
1. Controls autonomic nervous system
A) midbrain
2. Controls motor movement
B) pons 1. Controls sleeping, dreaming, walking
C) medulla 1. Controls autonomic nervous system, involuntary actions
oblongata (CCC, breathing rate)
1. Personality, behavior, emotions
intelligence,
frontal lobe 2. Judgement, planning, problem solving
problem-solving
3. Intelligence, concentration, self-awareness
broca’s area 1. Speech
motor cortex/strip 1. Controls voluntary movements
1. Interprets signals from hearing, motor, sensory and
parietal lobe five senses
memory
sensory cortex/strip 1. Interprets sense of touch, pain, temperature
temporal lobe 1. Controls memory and hearing speech and hearing
wernicke area 1. Understanding language
occipital lobe 1. Interprets vision (colour, light, movement) vission
gyrus 1. Folded appearance of the brain
sulcus 1. Groove between gyrus
longitudinal fissure 1. Deep grove that separates left and right hemispheres
lateral fissure 1. Separates frontal lobe and temporal lobe
central salcus 1. Separates frontal lobe and parietal lobe
insula 1. Controls sense of taste 5th lobe
infundibulum 1. Connects hypothalamus and pituitary gland
1. Connects left and right hemispheres of brain
corpus callosum 2. Integrate motor, sensory, and cognitive performances
between left and right cerebral cortex
Intermediate mass 1. Connects left and right thalamus
Pineal gland 1. Controls sleep cycle
1. Controls movement of neck and head
2. Housing and protecting the spinal cord
cervical spine (8)
3. Supporting the head and its movement
4. Facilitating blood flow to the brain
1. Dilate pupil
2. Inhibit salivation (to inhibit digestion) during
thoracic spine (12) 3. Relax airways sympathetic
4. Increase heart rate division
5. Inhibit activity of intestines
1. Controls bladder, reproductive system
lumbar spine (5) 2. Controls genital area (orgasm, ejaculation)
3. Controls adrenal gland to secrete adrenaline
1. Controls bladder, reproductive system
2. Controls genital area (orgasm, ejaculation)
sacral spine (5)
3. Relax rectum
4. Constrict bladder
1. Supports spinal cord
2. Supports body
Coccyx (1)
3. Expands together with pelvic bone during delivery
of baby
central canal 1. Drains cerebrospinal fluid
Fornix 1. major output tract of hippocampus Hippocampus
Consciousness,
Insular Cognitive function, consciousness, homeostasis
homeostasis
You might also like
- Movement Difficulties in Developmental Disorders: Practical Guidelines for Assessment and ManagementFrom EverandMovement Difficulties in Developmental Disorders: Practical Guidelines for Assessment and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: Some of Its Main Functions IncludeDocument3 pagesCentral Nervous System: Some of Its Main Functions IncludeNoemi ReyesNo ratings yet
- BiofeedbackDocument5 pagesBiofeedbackJasmine KashyapNo ratings yet
- Neurologic ExaminationDocument67 pagesNeurologic Examinationሀይደር ዶ.ር100% (1)
- Anatomy of BrainDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Brainfever_159100% (1)
- The University of Lahore, Lahore.: Cerebral PalsyDocument16 pagesThe University of Lahore, Lahore.: Cerebral Palsynosheen murtazaNo ratings yet
- The Role of AYUSH in Mental Well BeingDocument16 pagesThe Role of AYUSH in Mental Well BeingMunja nikhithaNo ratings yet
- Yale Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale With Reference To The Last WeekDocument7 pagesYale Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale With Reference To The Last WeekAnant KhotNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument8 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLaine DerainNo ratings yet
- Basic Overview of NeurologyDocument45 pagesBasic Overview of NeurologyDith Rivelta CallahanthNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument17 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorAasma IsmailNo ratings yet
- Pusher SYndrome Understanding and TreatingDocument9 pagesPusher SYndrome Understanding and TreatingJason ColeNo ratings yet
- 275-Higher Cortical Functions Bedside Examination - Yuttachai LikitjaroenDocument46 pages275-Higher Cortical Functions Bedside Examination - Yuttachai LikitjaroennavneetNo ratings yet
- AP41 MDocument3 pagesAP41 Monix2000No ratings yet
- Brain Injury and Epilepsy: What Is An Epileptic Seizure?Document4 pagesBrain Injury and Epilepsy: What Is An Epileptic Seizure?kaninerNo ratings yet
- Brain and BehaviourDocument9 pagesBrain and BehaviourKenya BaileyNo ratings yet
- DR - Vilasinee Ari Hara KumarDocument44 pagesDR - Vilasinee Ari Hara KumarVilasineeAriHaraKumarNo ratings yet
- Brain StemDocument25 pagesBrain Stemsamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- PSYCH - PsychosomaticdelasalleDocument58 pagesPSYCH - Psychosomaticdelasalleapi-3856051100% (1)
- Sense of Taste: 13 Chemical Receptors in The Taste Cells Threshold For TasteDocument5 pagesSense of Taste: 13 Chemical Receptors in The Taste Cells Threshold For TasteAileen CastilloNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Psychobiology and PsychopathologyDocument106 pagesConcepts of Psychobiology and PsychopathologyArya LekshmiNo ratings yet
- EpilepsyDocument40 pagesEpilepsySajjul ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Dementia Evaluation and TreatmentDocument12 pagesDementia Evaluation and Treatmentrofi modiNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research Design: Mr. Jayesh PatidarDocument48 pagesExperimental Research Design: Mr. Jayesh PatidarKim NaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Floppy InfantDocument44 pagesApproach To Floppy InfantNavya Hegde100% (2)
- 1999 Aversion Therapy-BEDocument6 pages1999 Aversion Therapy-BEprabhaNo ratings yet
- Temporal LobeDocument68 pagesTemporal LobeRupinder GillNo ratings yet
- Executive Function PDFDocument2 pagesExecutive Function PDFpc2webNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of The Origins of Behavioral MedicineDocument16 pagesA Brief History of The Origins of Behavioral MedicineAllie WatrenNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System WordDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System WordJesi QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Psychology SchizopherniaDocument21 pagesPsychology SchizopherniaDevesh SaiNo ratings yet
- The ABC's in Pediatric Assessment and Care: Cymbeline Joan L. Pooten, RN NUM - Pediatric ICUDocument39 pagesThe ABC's in Pediatric Assessment and Care: Cymbeline Joan L. Pooten, RN NUM - Pediatric ICUggrrk7No ratings yet
- BFB For Psycmatric Disorders PDFDocument28 pagesBFB For Psycmatric Disorders PDFratusemut13No ratings yet
- EEG MaturationDocument29 pagesEEG Maturationhm3398No ratings yet
- Common Childhood Mental Health DisordersDocument42 pagesCommon Childhood Mental Health DisordersMsm BeihoNo ratings yet
- Bellack A.s., Hersen M. Eds. Comprehensive Clinical Psychology Volume 3 2000Document367 pagesBellack A.s., Hersen M. Eds. Comprehensive Clinical Psychology Volume 3 2000ontzy26No ratings yet
- Finger To NoseDocument1 pageFinger To NoseAridhotulHaqiyahNo ratings yet
- EpilepsyDocument28 pagesEpilepsyRajeev RanjanNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy - Insights From Bhagavad GitaDocument6 pagesPsychotherapy - Insights From Bhagavad GitaParameshwaran IyerNo ratings yet
- Physical and Neurological ExaminationDocument7 pagesPhysical and Neurological ExaminationMelissa Marie SkillingsNo ratings yet
- Effect of Roods Approach in Diabetic PolyneuropathyDocument6 pagesEffect of Roods Approach in Diabetic Polyneuropathynandhini ragu100% (1)
- Coordination AssessmentDocument30 pagesCoordination AssessmentBhawna PalNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument4 pagesSpinal CordMabel LynNo ratings yet
- Health Locus of Control IDocument2 pagesHealth Locus of Control IAnggita Cahyani RizkyNo ratings yet
- Neuro Behavior DisordersDocument80 pagesNeuro Behavior Disordersmohamadafif_drNo ratings yet
- Conversion DisorderDocument21 pagesConversion DisorderSaputro Abdi100% (1)
- Infant ReflexesDocument1 pageInfant ReflexesJohn Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Care For A Terminally Ill PatientDocument4 pagesSpiritual Care For A Terminally Ill PatientMohd Khairullah Mohd IdzharNo ratings yet
- Stroke RehabilitationDocument16 pagesStroke RehabilitationHafidz Nur IchwanNo ratings yet
- 6-Rourke, B.P. (2005)Document5 pages6-Rourke, B.P. (2005)iilolii.ch3495No ratings yet
- Broca's AphasiaDocument22 pagesBroca's Aphasiaعبدالله_عبدوNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NursingDocument3 pagesPediatric NursingchoobiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Problems Associated With Aging ProcessDocument28 pagesClinical Problems Associated With Aging Processهنادي رازمNo ratings yet
- Adolf Meyer & George Barton3 in OTDocument14 pagesAdolf Meyer & George Barton3 in OTHermito GideonNo ratings yet
- Beck Anxiety InventoryDocument3 pagesBeck Anxiety InventoryABD.NASIR100% (1)
- Study NotesDocument11 pagesStudy NotesvanNo ratings yet
- Iap Guidelines For Epilepsy 2014Document45 pagesIap Guidelines For Epilepsy 2014Karpur ShirsatNo ratings yet
- Functionalism: American Psychology Takes HoldDocument17 pagesFunctionalism: American Psychology Takes HoldTehran DavisNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy Clinical Management.9 PDFDocument24 pagesPhysical Therapy Clinical Management.9 PDFClaudia MicuNo ratings yet
- Neuro ProformaDocument20 pagesNeuro ProformaPraneetha NouduriNo ratings yet
- Suicidal Assessment OSCEDocument3 pagesSuicidal Assessment OSCEJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Stroke History TakingDocument6 pagesStroke History TakingJJ LimNo ratings yet
- L Alcohol HistoryDocument2 pagesL Alcohol HistoryStephanie R. S. HsuNo ratings yet
- Stroke History Taking - Hot Seat ConsultationDocument2 pagesStroke History Taking - Hot Seat ConsultationJJ LimNo ratings yet
- OcdDocument1 pageOcdStephanie R. S. HsuNo ratings yet
- Headache OSCE ExaminationDocument3 pagesHeadache OSCE ExaminationJJ LimNo ratings yet
- The Bleeding Child OSCE HaemophiliaDocument3 pagesThe Bleeding Child OSCE HaemophiliaJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Prematurity OSCE Counselling Child Health Paediatric Non-Clinical Patient EncounterDocument5 pagesPrematurity OSCE Counselling Child Health Paediatric Non-Clinical Patient EncounterJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Bruising OSCE History Taking PaediatricsDocument6 pagesBruising OSCE History Taking PaediatricsJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Serious Complication Includes Mitral Valve Prolapse/ Aortic AneurysmDocument2 pagesSerious Complication Includes Mitral Valve Prolapse/ Aortic AneurysmJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Oedematous Children OSCE Nephrotic NephriticDocument5 pagesOedematous Children OSCE Nephrotic NephriticJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizures Epilepsy OSCE Counselling PaediatricsDocument6 pagesFebrile Seizures Epilepsy OSCE Counselling PaediatricsJJ Lim100% (1)
- Seminar 2Document2 pagesSeminar 2JJ LimNo ratings yet
- Stage 1Document4 pagesStage 1JJ LimNo ratings yet
- English Junk FoodDocument2 pagesEnglish Junk FoodJJ LimNo ratings yet
- C2.26 Urinary Tract Stones SDL SessionDocument3 pagesC2.26 Urinary Tract Stones SDL SessionJJ LimNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of ExplosionsDocument7 pagesThe Chemistry of ExplosionsJJ Lim100% (1)
- Urinalysis Numed FoundationDocument42 pagesUrinalysis Numed FoundationJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Presentation Science ScrapbookDocument16 pagesPresentation Science ScrapbookJJ LimNo ratings yet
- CitationsDocument3 pagesCitationsJJ LimNo ratings yet
- All of MeDocument1 pageAll of MeJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Touching Family Love StoryDocument14 pagesTouching Family Love StoryJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Ker's Physics Definition HandtypedDocument7 pagesKer's Physics Definition HandtypedJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Lit f4 2015Document3 pagesLit f4 2015Shima HamiriNo ratings yet
- Corruption: Name: Lim Zhan Xian Lim Jun Jie Clement Chua Juo HangDocument7 pagesCorruption: Name: Lim Zhan Xian Lim Jun Jie Clement Chua Juo HangJJ LimNo ratings yet
- Clement Print 2Document5 pagesClement Print 2JJ LimNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Laboratory Guide 2011Document8 pagesNeuroanatomy Laboratory Guide 2011Steve BlubaughNo ratings yet
- Brain Thesis StatementDocument5 pagesBrain Thesis Statementzyxnlmikd100% (2)
- 14 Nervous SystemDocument89 pages14 Nervous SystemJose LunaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Preliminary Examination 2023 - 2024 Grade 10 ScienceDocument4 pages3rd Preliminary Examination 2023 - 2024 Grade 10 ScienceJerome Tala-oc100% (1)
- Intro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Document97 pagesIntro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Jojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 TB PinelDocument27 pagesCh3 TB Pinelpixelpaisley12No ratings yet
- The Nervous System-Final PDFDocument57 pagesThe Nervous System-Final PDFCarlo Makiling100% (1)
- Nervous System Lab ReportDocument10 pagesNervous System Lab Reportapi-269985211No ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 3: Nervous System: The Control System of The BodyDocument24 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 3: Nervous System: The Control System of The BodyiNSECTiON 4.0No ratings yet
- Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesDivisions of The Nervous SystemDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- General Principles of NeurologyDocument8 pagesGeneral Principles of NeurologyCARZ 42No ratings yet
- Conductivity (The Ability To Transmit The Impulse To OtherDocument7 pagesConductivity (The Ability To Transmit The Impulse To OtherLizzie FernandoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyChris CHris ChRis100% (1)
- Brain Development at Early YearsDocument16 pagesBrain Development at Early YearsshylajaNo ratings yet
- The Power of Mind NotesDocument8 pagesThe Power of Mind Notestrizzia acostaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 12 & 13 Anaphy Reviewer (Long Quiz)Document12 pagesCh. 12 & 13 Anaphy Reviewer (Long Quiz)googlegirl18No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Neuroscience Fundamentals For Rehabilitation 4th Edition by Lundy EkmanDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Neuroscience Fundamentals For Rehabilitation 4th Edition by Lundy EkmanDonaldSmithwrmc100% (45)
- Medial Medullary Syndrome - WikipediaDocument8 pagesMedial Medullary Syndrome - WikipediaArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Motor Impairments Following StrokeDocument31 pagesMotor Impairments Following StrokeFrancess LeveauNo ratings yet
- Brain Bee R1 P2Document9 pagesBrain Bee R1 P2sarahsyedazakiNo ratings yet
- ABC ConceptDocument115 pagesABC ConceptFrancis PeterosNo ratings yet
- Module Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesModule Nervous SystemMan Gal7No ratings yet
- New PE 1 MODULEDocument52 pagesNew PE 1 MODULECyrus De LeonNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiology: The Central Nervous SystemDocument52 pagesNeurophysiology: The Central Nervous System143roshanNo ratings yet
- ISU Syllabus Nervous System EngDocument15 pagesISU Syllabus Nervous System Engmassa al dalatiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Nervous Systemxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Neurology Work BookDocument73 pagesNeurology Work BookCastleKGNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OBE FinalDocument21 pagesAnatomy OBE FinalCarissa De Luzuriaga-BalariaNo ratings yet
- BDS-Batch 11-Module 1 - CA - Anatomy Question BankDocument2 pagesBDS-Batch 11-Module 1 - CA - Anatomy Question BankcheckmateNo ratings yet
- Chapter 49 Nervous SystemsDocument16 pagesChapter 49 Nervous Systems蔡旻珊No ratings yet