Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Telecommunication Questions
Uploaded by
Bikash ChandraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Telecommunication Questions
Uploaded by
Bikash ChandraCopyright:
Available Formats
Telecommunication-I
Signals and System
1. Define signals and system. Identify various signals and systems given in figure.
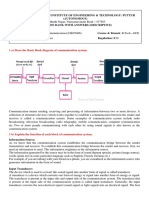
2. Define telecommunication or communication. Draw the basic block diagram of a typical
communication system and describe each component in brief/Identify each component of
communication system involved in transmitting voice.
3. How a signal is degraded during transmission from one place to another?
4. Classify signals and describe them with proper diagram.
5. How signal strength can be measured. (Ans: signal energy, signal power). Find the
strength/suitable measure for the given signals - Problems.
6. Define the following signals:
a. Step
b. Impulse
c. Ramp
d. Pulse
e. Sinusoidal
f. Exponential
7. Signal operations: time shifting, time scaling, and time inversion examples
8. Sampling property/theorem of unit impulse function.
Component of Signals and Orthogonality, Signal Comparison-correlation
9. Find the value of constant c so that the error e between the two signals is the minimum.
10. Find the component of one signal in the form of another signal – problems
11. Show that signal is a generalized form of vector.
12. Find the condition for two vectors/signals to be orthogonal. Problems
13. Explain best friend, worst friend and complete strangers in terms of correlation coefficient between
two signals.
14. Find the correlation coefficient Cn between two signals. Problems
15. Describe the application of correlation to signal detection in communications.
Signal Transmission over a communication channel
16. What is meant by distortionless transmission?
17. Show that for distortionless transmission, the amplitude response H () must be a constant
and the phase response h ( ) must be a linear function of . Draw the wave shape of
H ( ) . Problems.
18. Explain why human ear can recognize amplitude distortion, although it is relatively
insensitive to phase distortion.
19. What are the types of distortion? Define dispersion and its effect on digital communication.
20. What is meant by frequency-selective fading, how can it be minimized?
21. State and prove Parseval’s theorem to find signal energy. Problems.
22. Define essential BW, ESD, PSD. Problems
23. Show that the energy of a modulated signal is half of the energy of the message signal.
24. Autocorrelation functions. Problems
Information Theory
25. Briefly explain the relationship between probability and information.
26. Define entropy (H) used in information theory. Problems
27. Shannon’s capacity (C) of AWGN channel. Problems
28. Derive the capacity of AWGN channel with infinite BW.
29. Source coding and channel coding theorem
30. Huffman method of code compression. Find the code efficiency and redundancy.
Problems for binary source, r-ary source and extended source coding.
31. Capacity and transition diagram of BSC. Problems
32. Write short notes on the following:
a. Compact code/ Huffman code
b. Hamming sphere
c. BSC, Channel matrix
You might also like
- The Ovation NX Amplifier V2.0 8Document57 pagesThe Ovation NX Amplifier V2.0 8marginwalker77100% (1)
- Project Report On UpsDocument53 pagesProject Report On Upsamit431mittal100% (6)
- Digital Communication MCQ Sanfoundry PDFDocument210 pagesDigital Communication MCQ Sanfoundry PDFRakesh VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Tag MC LarenDocument34 pagesTag MC LarenelekossNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsFrom EverandDigital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Bits Edu Campus Electronics and Communication Department Subject Name: Digital Communication Subject Code: 2161001Document3 pagesBits Edu Campus Electronics and Communication Department Subject Name: Digital Communication Subject Code: 2161001Mansi ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Adc QBDocument5 pagesAdc QBAjay kumarNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication: A Paper Prepared OnDocument16 pagesWireless Communication: A Paper Prepared OnAmey KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Ec2311 - Communication EngineeringDocument9 pagesEc2311 - Communication EngineeringBharath RamanNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationsDocument11 pagesDigital Communicationsveeramaniks408No ratings yet
- CU7102 Advanced Digital Communication Techniques Question BankDocument11 pagesCU7102 Advanced Digital Communication Techniques Question BankSuresh HakunamatataNo ratings yet
- Ec2311 - Communication Engineering PDFDocument9 pagesEc2311 - Communication Engineering PDFThasleema BanuNo ratings yet
- PSTS 23344Document67 pagesPSTS 23344dravinatha9704No ratings yet
- Our Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromDocument2 pagesOur Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromRajesh KananNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Question BankDocument7 pagesComputer Networks Question BankrahupiNo ratings yet
- CT Part A&B QBDocument6 pagesCT Part A&B QBPeriyar Selvam KNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Analog CommunicationDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Analog CommunicationThiru DaaNo ratings yet
- Ec6651 Ec Rejinpaul Iq Am19Document2 pagesEc6651 Ec Rejinpaul Iq Am19Abirami MutharasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Manoj NaikNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering (Autonomous) : Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument38 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering (Autonomous) : Electronics and Communication EngineeringSohail MohammedNo ratings yet
- CT 2 Marks QBDocument7 pagesCT 2 Marks QB6060 Lisha priya.CNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument2 pagesUnit ISanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Sardar Raja College of Engineering, Alangulam: Micro Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesSardar Raja College of Engineering, Alangulam: Micro Lesson PlanramarajanenggNo ratings yet
- Mod C A C M 4 C MDocument17 pagesMod C A C M 4 C MJKNo ratings yet
- Assignment PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment PDFPrisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Lab Final Doc SRN PDFDocument90 pagesAnalog Communication Lab Final Doc SRN PDFChaitanya ReddyNo ratings yet
- VARUN KumarDocument9 pagesVARUN KumarVaSuNo ratings yet
- Cseitquestions - Blogspot.In Cseitquestions - Blogs Pot - in Cseitquestions - Blogspot.InDocument23 pagesCseitquestions - Blogspot.In Cseitquestions - Blogs Pot - in Cseitquestions - Blogspot.IndeepikaNo ratings yet
- List of Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesList of Important Questions4025 deeptika pNo ratings yet
- Certain Topics in Telegraph Transmission Theory - H. NyquistDocument28 pagesCertain Topics in Telegraph Transmission Theory - H. NyquistlisusedNo ratings yet
- Pulse Modulation Lecture Notes 01 Year V For Presentation-1Document9 pagesPulse Modulation Lecture Notes 01 Year V For Presentation-1Umarr A SesayNo ratings yet
- DC Question BankDocument6 pagesDC Question BankBha RathNo ratings yet
- Ec 1207 Analog and Digital Communication QBDocument4 pagesEc 1207 Analog and Digital Communication QBnofeelingrahulNo ratings yet
- Question Bank PDFDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank PDFkdtkopNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument44 pagesCommunicationNilupul WijeratneNo ratings yet
- Definitions DcomDocument9 pagesDefinitions DcomRabia Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Communication Systems: AnalogDocument67 pagesChapter 4: Communication Systems: AnalogtutulkarNo ratings yet
- Pyq AdcDocument6 pagesPyq AdcDharmisha panjriNo ratings yet
- Ec8395 Ce Notes 2Document127 pagesEc8395 Ce Notes 2makNo ratings yet
- Communication: (Important Formulae and Concepts)Document4 pagesCommunication: (Important Formulae and Concepts)tutulkarNo ratings yet
- Overview : Stochastic SignalsDocument4 pagesOverview : Stochastic SignalsAMIR SOHAILNo ratings yet
- Adc QBDocument5 pagesAdc QBApki mautNo ratings yet
- EC8651 TLRF RejinpaulDocument2 pagesEC8651 TLRF RejinpaulDeepa SushmaNo ratings yet
- CS2204 Analog & Digital Communication Question BankDocument16 pagesCS2204 Analog & Digital Communication Question BankJesse VincentNo ratings yet
- Ee 09 702 Analog and Digital Communication Model QPDocument2 pagesEe 09 702 Analog and Digital Communication Model QPGīřïşh McNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkDocument5 pagesTask 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkDamianMiloNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - DCDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank - DCDivya KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- 45CTE1Document2 pages45CTE1Rohit TodkarNo ratings yet
- Solved QuestionsDocument3 pagesSolved QuestionsSoumyadeep DasNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Department of Ece Subject Code:141304 Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication Year/Sem:II/IIIDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank: Department of Ece Subject Code:141304 Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication Year/Sem:II/IIIShanmuga PriyaNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkDocument10 pagesTask 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual Workgabriel tejadaNo ratings yet
- Ec35a5 Simulation of Communication Systems Question PaperDocument2 pagesEc35a5 Simulation of Communication Systems Question Paperanilnv.itdNo ratings yet
- LIC100Document2 pagesLIC100Manoj Harsule100% (1)
- Possible QuestionsDocument2 pagesPossible QuestionsDr-Priyadarsan ParidaNo ratings yet
- DC I-II Completed K.vinothDocument9 pagesDC I-II Completed K.vinothkvinothscetNo ratings yet
- ADC Full Noted PDFDocument79 pagesADC Full Noted PDFVenkatesh TNo ratings yet
- C C C C !!Document7 pagesC C C C !!guruvigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- Ec8395 Ce Part ADocument13 pagesEc8395 Ce Part AmakNo ratings yet
- Draw and Explain PAM Generation System. 16. Draw Neat Diagram For PAM, PPM AND PWMDocument2 pagesDraw and Explain PAM Generation System. 16. Draw Neat Diagram For PAM, PPM AND PWMThiyagarajan KNo ratings yet
- AV324 - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesAV324 - Tutorial 1bharath bodduNo ratings yet
- 1 A) Draw The Basic Block Diagram of Communication SystemDocument29 pages1 A) Draw The Basic Block Diagram of Communication SystemBhargava GNo ratings yet
- DigiComm Tut 3Document4 pagesDigiComm Tut 3Js JsNo ratings yet
- Who Am IDocument1 pageWho Am IBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Dear Sir,: Saturday (6 April, 2019) at Narayanganj (Barodi Loknath Temple, Langalband & ISKCON Temple)Document1 pageDear Sir,: Saturday (6 April, 2019) at Narayanganj (Barodi Loknath Temple, Langalband & ISKCON Temple)Bikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Pvkzwii Av E'B DigDocument2 pagesPvkzwii Av E'B DigBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Dear Sir,: Saturday (6 April, 2019) at Narayanganj (Barodi Loknath Temple, Langalband & ISKCON Temple)Document1 pageDear Sir,: Saturday (6 April, 2019) at Narayanganj (Barodi Loknath Temple, Langalband & ISKCON Temple)Bikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- QPSKDocument1 pageQPSKBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology, Gazipur: Expt. No: Date of Expt .Document1 pageDhaka University of Engineering & Technology, Gazipur: Expt. No: Date of Expt .Bikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Memristor ProgramDocument2 pagesMemristor ProgramBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- All Thanks Goes To The Man Who Have Created This Website - Welcome To My DocumentDocument1 pageAll Thanks Goes To The Man Who Have Created This Website - Welcome To My DocumentBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- It Seems To Me That You Are GeniousDocument1 pageIt Seems To Me That You Are GeniousBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Semi LogDocument1 pageSemi LogBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
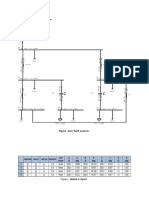
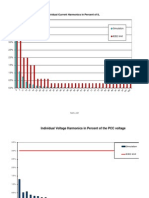
- Figure: Bus7 Fault Analysis .: Global G ReportDocument3 pagesFigure: Bus7 Fault Analysis .: Global G ReportBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- All Thanks Goes To The Man Who Have Created This Website - Welcome To My DocumentDocument1 pageAll Thanks Goes To The Man Who Have Created This Website - Welcome To My DocumentBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Semi LogDocument1 pageSemi LogBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram of Jamalpur SubstationDocument1 pageSingle Line Diagram of Jamalpur SubstationBikash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Complementary Symmetrical Input Stages in Audio AmplifiersDocument2 pagesAdvantages of Complementary Symmetrical Input Stages in Audio Amplifiersapi-3701386100% (1)
- 3.two Marks QuestionsDocument20 pages3.two Marks QuestionsPullareddy AvulaNo ratings yet
- Synthesized Function Generators: DS360 - Ultra-Low Distortion Function GeneratorDocument4 pagesSynthesized Function Generators: DS360 - Ultra-Low Distortion Function Generatorwwl1981No ratings yet
- Distortion Modeling of PIN Diode Switches and Attenuators - CaverlyDocument4 pagesDistortion Modeling of PIN Diode Switches and Attenuators - CaverlySinisa HristovNo ratings yet
- Tda7057aq PDFDocument16 pagesTda7057aq PDFnikolaNo ratings yet
- AN 1112 v1.1 PDFDocument11 pagesAN 1112 v1.1 PDFsivakumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Simulation of Leakage Current On Ceramic Insulator Under Clean Fog ConditionDocument6 pagesComputer Simulation of Leakage Current On Ceramic Insulator Under Clean Fog ConditionKamello AssisNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Calculator WEG-1 00Document35 pagesHarmonic Calculator WEG-1 00Gustavo TecheiraNo ratings yet
- SR 20 ManualDocument48 pagesSR 20 ManualCarlos Eduardo Zapata LibrerosNo ratings yet
- EFF100.Operations Manual.121209Document10 pagesEFF100.Operations Manual.121209dulyeNo ratings yet
- 8565a OsmDocument463 pages8565a Osmjrumianowski100% (1)
- 4 - Practical Transistor Servicing - William C. CaldwellDocument106 pages4 - Practical Transistor Servicing - William C. CaldwellVinicius UebeNo ratings yet
- DTM5 3jpsmDocument22 pagesDTM5 3jpsmJason McLeodNo ratings yet
- Yamaha EMX5014C SMDocument178 pagesYamaha EMX5014C SMPony_37100% (1)
- Twintex Datasheet DDS Fucntion Generator 201612Document15 pagesTwintex Datasheet DDS Fucntion Generator 201612LopezinNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Adonai PDFDocument8 pagesDatasheet Adonai PDFFrancisco FerrerNo ratings yet
- 450968421DDS Tutorial Rev12-2-99Document122 pages450968421DDS Tutorial Rev12-2-99Adriana ValoNo ratings yet
- An Electronic AmplifierDocument26 pagesAn Electronic Amplifierriz2010No ratings yet
- Ansi Asa S3.22 - 2014Document54 pagesAnsi Asa S3.22 - 20147620383tlNo ratings yet
- Transistor Design PDFDocument33 pagesTransistor Design PDFtomhankss100% (1)
- Tapco Mix120 Service Manual Plastic Power JackDocument15 pagesTapco Mix120 Service Manual Plastic Power JackMontserrat AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Telephone SystemDocument13 pagesTelephone SystemFalcon ManNo ratings yet
- RFcharacterization - IMD TestingDocument9 pagesRFcharacterization - IMD TestingpatopickNo ratings yet
- Am Plic AdoresDocument6 pagesAm Plic Adoresnekros05No ratings yet
- Od-5010 - Ed.1.2 (Procedure For Measuring Lab Power Source Characteristics)Document13 pagesOd-5010 - Ed.1.2 (Procedure For Measuring Lab Power Source Characteristics)JesusNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Analyser SpecificationsDocument25 pagesSpectrum Analyser Specificationsapi-3704005100% (2)