Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mini - Tab For STA
Uploaded by
milanstrOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mini - Tab For STA
Uploaded by
milanstrCopyright:
Available Formats
Minitab for STA Engineers
Jim Martin
6-Sigma Master Black Belt
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Today’s Topics
• Getting Minitab • Basic Statistics
• Help / StatGuide • Means, variance &
• Project Manager proportions tests
• Session window • Power & Sample size
• Worksheets & data • Control charts*
• File types .mpj & .mtw • Quality Tools
• Window menu • Useful Graphs
*not “real time” when done in Minitab 2
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Getting Minitab onto your PC
• Make a request at www.request.ford.com
to get Minitab installed.
• Current version in use at Ford Motor
Company is release 15.
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Help / StatGuide
• overview
• how to
• examples
• data
• see also
4
Help, then drill down to a subject on the left
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Help / StatGuide
173 worksheets of data are provided to
try out different Minitab analyses!!!
5
C:\Program Files(x86)\Minitab 15\English\Sample Data
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Project Manager
Project Manager icon
6
Note: The Project Manager is minimized when Minitab is first opened.
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Session window
The session window icon is a scroll
1. The session window keeps a running
chronology of all of the analyses that you
have performed. You must save as a Minitab
Project (filename.mpj) to retain this history.
2. It can be edited, i.e. text can be deleted
and/or added.
3. Analyses can be cut & pasted into emails,
presentations, etc.
4. It can also be printed, File → Print Session
Window. 7
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Worksheets
Worksheet icon is a tiny worksheet
1. Worksheets hold all of your raw data.
2. This is not Excel – no formula can be placed in a cell
3. Columns, rows and cells can be inserted or deleted.
4. Columns should be given descriptive names since
Minitab thrives on columnar data.
5. Columns can be stacked together for analysis (or
unstacked based on subscripts in another column).
6. You can have multiple worksheets in a project file, so
give them descriptive names as well.
7. Three data types: Numeric, Date/time & Text
8. Missing data are shown with an asterisk, “*”
8
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
File types .mpj & .mtw
• Filename.mtw is used for storing worksheets
(data) only.
• Does not keep your analyses or graphs
• Graphs can be regenerated in Minitab from the
data at any time.
• Saves disk space.
• Filename.mpj is used to store the project,
including all analyses and graphs.
• Graphs take memory, so only a limited number
can be kept open during a session.
9
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Window menu
Window → Cascade 10
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Window menu
Note: minimized windows
will not “tile”
Window → Tile 11
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Basic Statistics
• Display Descriptive Statistics…
• Graphical Summary…
• Tests for variances (variable data)
• Tests for means (variable data)
• Tests for proportions (attribute data)
• Correlation…
• Normality Test…
Stat → Basic Statistics 12
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Display Descriptive Statistics
A new twist for you...
Stat → Basic Statistics → Display Descriptive Statistics… 13
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Display Descriptive Statistics
From the Session Window (click on the scroll icon):
————— 9/18/2008 1:52:07 PM ————————————————————
Welcome to Minitab, press F1 for help.
Retrieving project from file: 'C:\Documents and Settings\jmartin6\My
Documents\EXAMPLE.MPJ'
Descriptive Statistics: Length
Variable Origin N N* Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median
Length Length1 75 0 10.114 0.129 1.114 6.873 9.431 10.136
Length2 50 0 11.957 0.103 0.732 10.493 11.521 11.995
Variable Origin Q3 Maximum
Length Length1 10.843 12.749
Length2 12.519 13.948
Stat → Basic Statistics → Display Descriptive Statistics… 14
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Graphical Summary
Stat → Basic Statistics → Graphical Summary…
15
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Graphical Summary
Stat → Basic Statistics → Graphical Summary…
16
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for variances (variable data)
“Equal variances” is an assumption used by
many Hypothesis Tests and should be tested
beforehand.
• When comparing two variances, σ2, use the
2 Variances test.
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2 Variances...
• When comparing more than two variances, use
Test for Equal Variances.
Stat → ANOVA → Test for Equal Variances...
17
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for variances (variable data)
2-Variances, both samples in one column, but delineated by labels in “Origin” column
three
possible
data
formats
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2 Variances... 18
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for variances (variable data)
For
Normal
data
For Non-
normal
data
The difference in
variances is
significant at 99.8%
confidence
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2 Variances... 19
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for means (variable data)
• Comparing one mean to a standard when
σ is known, e.g. comparing the average
pH of a sample of bottles of wine with the
average pH of a 2001 vintage wine.
Use 1-Sample Z test.
• Comparing one mean to a standard when
σ is unknown, e.g. comparing average net
weight of a sample of cereal boxes to the
stated net weight of 16 oz.
Use 1-Sample t test.
Stat → Basic Statistics
20
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for means (variable data)
• Comparing the means of two different samples
when σ is unknown, e.g. comparing the average
thickness of a machined part to its average
before the process was improved.
Use 2-Sample t test.
• Comparing the means of two samples that are
dependent or related in a “pair wise” way, e.g.
comparing the average wear of two samples of
different manufacturer’s brake shoes mounted
on the same vehicles, e.g. Manufacturer A on
Left Rear, Manufacturer B on Right Rear:
Use Paired t test.
Stat → Basic Statistics
21
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for means (variable data)
2-Sample t test, samples in different columns, Length 1 and Length2
Do not check. Remember,
variances were not equal
when we tested them
(P-value < 0.05).
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2-Sample t...
22
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for means (variable data)
Two-Sample T-Test and CI: Length2, Length1
Two-sample T for Length2 vs Length1
N Mean StDev SE Mean
Length2 50 11.957 0.732 0.10
Length1 75 10.11 1.11 0.13
Difference = mu (Length2) - mu (Length1)
Estimate for difference: 1.84263
95% CI for difference: (1.51578, 2.16947)
T-Test of difference = 0 (vs not =): T-Value = 11.16 P-Value = 0.000 DF = 122
The difference in means is significant with 99.9% confidence
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2-Sample t...
23
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for means (variable data)
• So far, we’ve tested for a “difference” in
means (a two-tailed test), but a mean can
also be greater than or less than another
mean (or a standard).
• If you want to test whether a mean is
“greater than” or “less than” another mean
(or a standard), use the Options button.
• One-tailed tests have a bit more statistical
Power. More on Power later.
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2-Sample t...
24
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for means (variable data)
Variable Origin N N* Mean SE Mean StDev Minimum Q1 Median
Length Length1 75 0 10.114 0.129 1.114 6.873 9.431 10.136
Length2 50 0 11.957 0.103 0.732 10.493 11.521 11.995
QUESTION: The sample mean of Length2 is greater than the sample mean
of Length1 by 1.843, but can we say with 95% confidence that the Length2
sample comes from a population whose mean is at least 1.8 mm greater
than the population from which Length1 data was sampled?
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2-Sample t...
25
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for means (variable data)
Note the order listed
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2-Sample t...
26
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Tests for means (variable data)
Two-Sample T-Test and CI: Length2, Length1
Two-sample T for Length2 vs Length1
N Mean StDev SE Mean
Length2 50 11.957 0.732 0.10
Length1 75 10.11 1.11 0.13
Difference = mu (Length2) - mu (Length1)
Estimate for difference: 1.84263
95% lower bound for difference: 1.56897
T-Test of difference = 1.8 (vs >): T-Value = 0.26 P-Value = 0.398 DF = 122
ANSWER: NO, WE CANNOT SAY THAT µ Length2 - µ Length1 > 1.8 !!!
Stat → Basic Statistics → 2-Sample t...
27
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Power and Sample Size
• When a Hypothesis Test indicates that a
difference is not statistically significant (p-value
> chosen α), is this really true or did you have a
sample size too small to detect the difference?
• Power (1 - β) is the chance of detecting a
difference (Ha) when that difference is real.
• Confidence (1- α) is the chance of correctly
concluding that there is no difference (Ho) when
the difference is not real.
Stat → Power and Sample Size 28
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Power and Sample Size
• A widget assembly line has been running well at
a supplier for three years. The supplier wishes
to move this line into a plant across town. The
move is approved and implemented. 30 pcs of
data are gathered on the sole Special
Characteristic, the mean is compared to the
historical value and the difference is found to be
insignificant. (StDev = 0.027, α = 0.05)
• What is the Power of this sample of 30 pieces?
Stat → Power and Sample Size 29
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Power and Sample Size
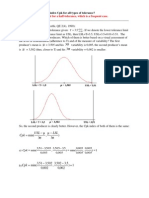
First, how large of a difference in means can this sample of 30 detect?
Stat → Power and Sample Size 30
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Power and Sample Size
From the Session Window:
Power and Sample Size
1-Sample t Test
Testing mean = null (versus not = null)
Calculating power for mean = null + difference
Alpha = 0.05 Assumed standard deviation = 0.027
Sample Answer: Given a St Dev of 0.027 and a
Size Power Difference 95% confidence level, this sample of 30
30 0.95 0.0183919 can detect a difference in means as small
as 0.018.
Stat → Power and Sample Size 31
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Power and Sample Size
Second, if we want to detect a mean shift of 0.01, does this sample of
30 have enough Power to detect a mean shift that small?
Stat → Power and Sample Size 32
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Power and Sample Size
Power and Sample Size
1-Sample t Test
Testing mean = null (versus not = null)
Calculating power for mean = null + difference
Alpha = 0.05 Assumed standard deviation = 0.027
Sample Answer: Given a St Dev of 0.027
and a 95% confidence level, this
Difference Size Power
sample of 30 has only a 50%
0.01 30 0.500554 chance (a coin flip) of detecting a
mean shift as small as 0.01.
We need a larger sample!
Stat → Power and Sample Size 33
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Power and Sample Size
Lastly, if we want to detect a mean shift of 0.01 at a Power of 95% and
Confidence of 95%, what sample size do we need?
Stat → Power and Sample Size 34
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Power and Sample Size
Power and Sample Size
1-Sample t Test
Testing mean = null (versus not = null)
Calculating power for mean = null + difference
Alpha = 0.05 Assumed standard deviation = 0.027
Sample Target
Difference Size Power Actual Power
0.01 97 0.95 0.950634
Answer: We need a sample size of 97 pieces to detect a mean shift of 0.01!
(Obviously, it is best to do this test before you collect your data.)
Stat → Power and Sample Size 35
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Control Charts
• Variables Charts for Subgroups
– Xbar-R…
– Xbar-S… (similar to Xbar-R & will not be shown)
• Variables Charts for Individuals
– I-MR… (similar to Xbar-R & will not be shown)
• Attribute Charts (will not be shown)
– P…
– NP…
– C…
– U…
36
Stat → Control Charts
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Control Charts
This column tells
Minitab where
subgroups start & end
37
Stat → Control Charts → Variables Charts for Subgroups → Xbar-R...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
These numbers
Control Charts indicate the test
that failed.
(see slide 40)
38
Stat → Control Charts → Variables Charts for Subgroups → Xbar-R...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Control Charts
Control chart data can also be
arranged as subgroups across
columns.
39
Stat → Control Charts → Variables Charts for Subgroups → Xbar-R...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Control Charts: Out-of-Control tests
40
Stat → Control Charts → Variables Charts for Subgroups → Xbar-R...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Attribute Control Charts
Here’s where to find the
Attribute control charts.
41
Stat → Control Charts → Attribute Charts
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Quality Tools
• Pareto Chart…
• Cause & Effect…
• Capability Analysis
• Gage Study
Stat → Quality Tools 42
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Pareto chart...
• Utilizes attribute data, not variable data.
• Allows you to look for “Big Hitter” warranty
issues or “Significant Few” defects (using
the 80/20 rule).
• Useful in scoping down a Black Belt or
Green Belt project.
• Very powerful in management
presentations!
Stat → Quality Tools → Pareto chart... 43
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Pareto chart...
Defects noted in one long column, perhaps as they occurred.
Stat → Quality Tools → Pareto chart... 44
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Pareto chart...
Pareto Chart of Damage
9
8 100
7
80
6
Percent
Count
5 60
4
3 40
2
20
1
0 0
Damage Scratch Chip Bend Dent
Count 4 2 1 1
Percent 50.0 25.0 12.5 12.5
Cum % 50.0 75.0 87.5 100.0
Stat → Quality Tools → Pareto chart... 45
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Pareto chart...
Data organized as a table of
Defect Labels and Frequencies.
Stat → Quality Tools → Pareto chart... 46
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Pareto chart...
Pareto Chart of Defects
100
400
80
300
Percent
60
Count
200
40
100 20
0 0
Defects s s
ke
t si rt r
re
w lip s u Pa he
C
Ga Ho Ot
Sc in
g
y i ve et
e
in
g
iss ak ct pl
is
s M Le fe om
M De In
c
Count 274 59 43 19 10 18
Percent 64.8 13.9 10.2 4.5 2.4 4.3
Cum % 64.8 78.7 88.9 93.4 95.7 100.0
Stat → Quality Tools → Pareto chart... 47
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Cause-and-Effect...
• Allows you to create a C&E Diagram without having to
draw it yourself.
• Defaults to the usual categories:
– Personnel
– Machines
– Material
– Methods
– Measurement
– Environment
• Categories can be changed/customized.
Stat → Quality Tools → Cause-and-Effect... 48
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Cause-and-Effect...
Stat → Quality Tools → Cause-and-Effect... 49
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Cause-and-Effect...
Stat → Quality Tools → Cause-and-Effect... 50
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Cause-and-Effect...
Cause-and-Effect Diagram
Measurements Material Personnel
C ontamination
U ntrained operators
O ut of calibration
Inclusions
N ew v endor Relief operators
Lack resolution
H ardness S abotage
Lack precision (R&R) C hemistry
U ntrained appraisers
Wrong coolant
Machining
Problems
O ut of coolant
Dirty w orkstation Improper S P C
practices O ut of adjustment
Dull cutters
H igh temps 1st P iece approv al not
giv en
M aintenance ov erdue
Env ironment Methods Machines
Stat → Quality Tools → Cause-and-Effect... 51
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
• Determines whether a process is
producing parts within specification.
• Calculates Cp/Cpk & Pp/Ppk for use with
normal data.
• Estimates PPM<LSL, PPM>USL & Total
PPM for “within” and “overall” variation.
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis 52
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis 53
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis 54
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Box-Cox… 55
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Estimate… 56
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Options… 57
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
Process Capability of Length
LSL USL
P rocess D ata Within
LS L 6 Overall
Target *
USL 13 P otential (Within) C apability
S ample M ean 10.8515 Cp 1.19
S ample N 125 C P L 1.65
S tD ev (Within) 0.981878 C P U 0.73
S tD ev (O v erall) 1.33454 C pk 0.73
O v erall C apability
Pp 0.87
PPL 1.21
PPU 0.54
P pk 0.54
C pm *
6.0 7.5 9.0 10.5 12.0 13.5
O bserv ed P erformance E xp. Within P erformance E xp. O v erall P erformance
P P M < LS L 0.00 P P M < LS L 0.39 P P M < LS L 138.80
P P M > U S L 32000.00 P P M > U S L 14330.14 P P M > U S L 53710.06
P P M Total 32000.00 P P M Total 14330.52 P P M Total 53848.86
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis 58
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
• Some processes are not normally distributed.
– Physical boundaries, e.g. flatness, hard stops, etc.
– One-sided tolerances, e.g. 20 Nm minimum.
• Capability Indices (Cp/Cpk, Pp/Ppk) were developed for
describing Normal data only.
• If the process is in-control & stable, you have three
transformation options...
– Box-Cox (available from Capability Analysis menu)
– Johnson
– Individual Distribution Identification
• Warning: The purpose of data transformation is to
achieve the best fit, not to find the highest Ppk!
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Nonnormal... 59
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
Process Capability of Flatness
Predicts flatness < 0 ?
LSL USL
P rocess Data W ithin
LS L 0 Ov erall
Target *
USL 12 P otential (Within) C apability
S ample M ean 1.68769 Cp 0.89
S ample N 1000 C P L 0.25
S tDev (Within) 2.23766 C P U 1.54
S tDev (O v erall) 2.21747 C pk 0.25
O v erall C apability
Pp 0.90
PPL 0.25
PPU 1.55
P pk 0.25 Too low?
C pm *
0 5 10 15 20 25
O bserv ed P erformance E xp. Within P erformance E xp. O v erall P erformance
P P M < LS L 0.00 PPM < LS L 225358.52 P P M < LS L 223303.29
P P M > U S L 7000.00 PPM > U SL 2.03 P P M > U SL 1.66
P P M Total 7000.00 PPM Total 225360.55 P P M Total 223304.95
60
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis
Process Capability of Flatness
Zero is a Boundary
LB USL
P rocess Data Within
LB 0 Overall
Target *
USL 12 P otential (Within) C apability
S ample M ean 1.68769 Cp *
S ample N 1000 C PL *
S tDev (Within) 2.23766 C P U 1.54
S tDev (O v erall) 2.21747 C pk 1.54
O v erall C apability
Pp *
Median = 1.0307. PPL *
PPU 1.55
Better, but not the P pk 1.55 Too high?
correct answer. C pm *
0 5 10 15 20 25
O bserv ed P erformance E xp. Within P erformance Exp. O v erall P erformance
P P M < LB 0.00 P P M < LB * P P M < LB *
P P M > U S L 7000.00 P P M > U S L 2.03 P P M > U S L 1.66
P P M Total 7000.00 P P M Total 2.03 P P M Total 1.66
61
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis: Non-normal
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Nonnormal... 62
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis: Non-normal
Process Capability of Flatness
Johnson Transformation with SL Distribution Type
0.001 + 1.006 * Log( X - 0.025 )
U S L*
P rocess Data transformed data O v erall C apability
LB 0 Pp *
Target * PPL *
USL 12 PPU 0.81
S ample M ean 1.68769 P pk 0.81
S ample N 1000
E xp. O v erall P erformance
S tDev 2.21692
P P M < LB *
S hape1 0.000645512
PPM > USL *
S hape2 1.00571
P P M Total *
Location 0.0248553
A fter Transformation
LB* *
Target* *
U S L* 2.49766
S ample M ean* -0.00694113
S tDev * 1.02443
O bserv ed P erformance
P P M < LB 0.00
P P M > U S L 7000.00
P P M Total 7000.00
-3.75 -2.50 -1.25 0.00 1.25 2.50
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Nonnormal... → Johnson 63
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis: Non-normal
Process Capability of Flatness
Using Box-Cox Transformation With Lambda = 0
LB* U S L*
P rocess Data transformed data Within
LB 1e-006 O v erall
Target *
USL 12 P otential (Within) C apability
S ample M ean 1.68769 Cp *
S ample N 1000 C PL *
S tD ev (Within) 2.23766 C P U 0.84
S tD ev (O v erall) 2.21747 C pk 0.84
A fter Transformation O v erall C apability
LB* -13.8155 Pp *
Target* * PPL *
U S L* 2.48491 P P U 0.84
S ample M ean* 0.032764 P pk 0.84
S tD ev (Within)* 0.970767 C pm *
S tD ev (O v erall)* 0.978339
-12.0 -9.6 -7.2 -4.8 -2.4 0.0 2.4
O bserv ed P erformance E xp. Within P erformance E xp. O v erall P erformance
P P M < LB 0.00 P P M < LB* * P P M < LB* *
P P M > U S L 7000.00 P P M > U S L* 5768.73 P P M > U S L* 6097.79
P P M Total 7000.00 P P M Total 5768.73 P P M Total 6097.79
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Normal... → Box-Cox... 64
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis: Non-normal
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Nonnormal... → Individual Dist. 65
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis: Non-normal
Probability Plot for Flatness
G oodness of F it Test
N ormal - 95% C I Lognormal - 95% C I
99.99 99.99 N ormal
A D = 97.664
99 99
P -V alue < 0.005
90 90
P er cent
P er cent
Lognormal
50 50
A D = 0.410
10 10 P -V alue = 0.342
1 1
3-P arameter Lognormal
0.01 0.01 A D = 0.294
0 10 20 30 0.01 0.10 1.00 10.00 100.00 P -V alue = *
Flatness Flatness
E xponential
3-P arameter Lognormal - 95% C I E xponential - 95% C I A D = 13.461
99.99 99.99
P -V alue < 0.003
90
99 50
P er cent
P er cent
90
50
10 Highest P-Value
10
1
of the 14 tested
1
0.01 0.01
distributions!
0.01 0.10 1.00 10.00 100.00 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Flatness - T hr eshold 0 00 001 0 10 1 00 000 0 00 000
0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 10
. 0.
10
Flatness
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Nonnormal... → Individual Dist. 66
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis: Non-normal
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Nonnormal... 67
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Capability Analysis: Non-normal
Process Capability of Flatness
Calculations Based on Lognormal Distribution Model
LB USL
P rocess Data O v erall C apability
LB 0 Pp *
Target * PPL *
USL 12 PPU 0.60
S ample M ean 1.68769 P pk 0.60
S ample N 1000
E xp. O v erall P erformance
Location 0.032764
P P M < LB *
S cale 0.978094
P P M > U S L 6086.98
O bserv ed P erformance P P M Total 6086.98
P P M < LB 0.00
P P M > U S L 7000.00
P P M Total 7000.00
Since these data were
created using the Lognormal
distribution, this is the correct
answer! See how easy it
would be to overstate or
0 4 8 12 16 20 24
understate
28
capability?
Stat → Quality Tools → Capability Analysis → Nonnormal... → Distribution 68
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Gage Study
• Gage Linearity and Bias Study...
• Gage R&R Study (Crossed)...
• Gage R&R Study (Nested)...
• See the material in Share Point:
NAV B&E STA > Training > Gage R and R
Measurement Systems Analysis_10.3.ppt
Stat → Quality Tools → Gage Study 69
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Graph
• Scatterplot…
• Histogram…
• Boxplot…
• Pie chart…
Stat → Graph 70
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Scatterplot...
• Allows you to look for relationships
between two variable data sets.
• You may add a best-fit regression line.
• You may indicate that the points come
from different groups (identified by another
column in the worksheet).
Stat → Graph → Scatterplot... 71
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Scatterplot...
Stat → Graph → Scatterplot... 72
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Scatterplot...
weak or no
relationship
Stat → Graph → Scatterplot... 73
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Histogram...
• Allows you to graphically assess a data
set for Normality.
• Allows you to add a Normal distribution
and visually assess for fit.
• Allows you to identify Mixtures (bi-modal
or tri-modal distributions).
• Allows you to compare two or more data
sets on the same histogram.
Stat → Graph → Histogram... 74
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Histogram...
Stat → Graph → Histogram... 75
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Histogram...
Stat → Graph → Histogram... 76
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Boxplot...
• Allows you to see the min, max, 1st, 2nd &
3rd quartiles of a data set.
• Allows you to identify outliers in the data.
• Allows you to graphically compare two data
sets for differences in center & spread!
77
Stat → Graph → Boxplot...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Boxplot...
78
Stat → Graph → Boxplot...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Boxplot...
Isn’t it easy to see the
difference in these two
data sets? Good for
Presentations/projects.
79
Stat → Graph → Boxplot...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Pie chart...
80
Stat → Graph → Pie chart...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
Pie chart...
Main Title
Subtitle 1
Subtitle 2
C ategory
A BC Tool
Dynatool
Footnote 1
Footnote 2
81
Stat → Graph → Pie chart...
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
QUESTIONS?
82
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
This presentation is available in SharePoint
NAV B&E STA > Training > Minitab
Minitab for STA Engineers.pdf
83
Copyright © 2016 Ford Motor Company. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Six Sigma QuizDocument37 pagesSix Sigma Quizshahin ahmed100% (1)
- Six Sigma Presentation FinalDocument38 pagesSix Sigma Presentation FinalnayanvmNo ratings yet
- Acronyms - Six Sigma - LeanDocument3 pagesAcronyms - Six Sigma - LeantorrespacNo ratings yet
- A Fictitious Six Sigma Green Belt Part IDocument19 pagesA Fictitious Six Sigma Green Belt Part IhalilpashaNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Black Belt Project On: Reduction in Breakage in BiscuitsDocument42 pagesSix Sigma Black Belt Project On: Reduction in Breakage in BiscuitsHombing Haryanto100% (1)
- 03 - BB Manual - Measure - v12 - 4 PDFDocument154 pages03 - BB Manual - Measure - v12 - 4 PDFRicardo BravoNo ratings yet
- Lean and Six Sigma - Not For AmateursDocument6 pagesLean and Six Sigma - Not For AmateursmsasgesNo ratings yet
- Six SigmaDocument37 pagesSix SigmaAmit Shankar Choudhary100% (1)
- Flexsim Supplemental Training: Applied Simulation, Modeling and Analysis Using FlexsimDocument22 pagesFlexsim Supplemental Training: Applied Simulation, Modeling and Analysis Using FlexsimmsidNo ratings yet
- Lean Vs Six SigmaDocument23 pagesLean Vs Six SigmabowbeforeallahNo ratings yet
- 2 - Analyze - X SiftingDocument55 pages2 - Analyze - X SiftingParaschivescu CristinaNo ratings yet
- Just in Time System (2) 10000Document24 pagesJust in Time System (2) 10000John GriffiesNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing & TPMDocument2 pagesLean Manufacturing & TPMEdward GermánNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Case Studies - Vytra Call Center PDFDocument2 pagesSix Sigma Case Studies - Vytra Call Center PDFVbaluyoNo ratings yet
- IASSC Yellow Belt Body of Knowledge1 PDFDocument3 pagesIASSC Yellow Belt Body of Knowledge1 PDFShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Construction of a Pasig Riverside Green Building condominiumDocument38 pagesConstruction of a Pasig Riverside Green Building condominiumMehrad SarabandiNo ratings yet
- Tools and Techniques for Lean Six Sigma ProjectsDocument64 pagesTools and Techniques for Lean Six Sigma ProjectsKamal KannanNo ratings yet
- GB 6 Sigma Productivity Solutions PDFDocument2 pagesGB 6 Sigma Productivity Solutions PDFJHCPNo ratings yet
- Green Belt ProjectDocument5 pagesGreen Belt ProjectIeva ValpētereNo ratings yet
- The 5 Core ToolDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- TÜV SÜD Certified Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification: 180 Minutes 100Document14 pagesTÜV SÜD Certified Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification: 180 Minutes 100Ankit Jha0% (1)
- Value Stream Mapping: Dr. Richard E. WhiteDocument19 pagesValue Stream Mapping: Dr. Richard E. WhiteSamir ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Design For Six Sigma Training BrochureDocument1 pageDesign For Six Sigma Training Brochureexamplecg100% (2)
- Ford DFSSDocument8 pagesFord DFSSiangardiner.iow5796100% (1)
- Ernest DMAIC ProjectDocument38 pagesErnest DMAIC ProjectErnesto Manuel0% (1)
- FlexSim TPDocument72 pagesFlexSim TPrajasekharjvNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Key Terms (LSSGB)Document8 pagesGlossary of Key Terms (LSSGB)Sweety ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma BB Sample Questions PDFDocument2 pagesSix Sigma BB Sample Questions PDFnaacha457No ratings yet
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma Seeks To Improve The Quality of Process Outputs by Identifying andDocument4 pagesSix Sigma: Six Sigma Seeks To Improve The Quality of Process Outputs by Identifying andsophy8922No ratings yet
- Project Reviews and Examples: © 2001 Conceptflow 0Document36 pagesProject Reviews and Examples: © 2001 Conceptflow 0Michael WuNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma For Chemical Engineers: George LiebermannDocument39 pagesSix Sigma For Chemical Engineers: George LiebermannDave CNo ratings yet
- How To Use Minitab 1 BasicsDocument28 pagesHow To Use Minitab 1 Basicsserkan_apayNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Precision and Accuracy: Precise Process Is One With Accurate Process Is One WhichDocument27 pagesConcepts of Precision and Accuracy: Precise Process Is One With Accurate Process Is One WhichsareenaikbalNo ratings yet
- Value Stream Mapping Visualizes Production ProcessDocument41 pagesValue Stream Mapping Visualizes Production ProcessNOSHEEN MEHFOOZ100% (1)
- Project selection guidelines and ideasDocument7 pagesProject selection guidelines and ideaschteo1976No ratings yet
- Eum Lean Guide PDFDocument106 pagesEum Lean Guide PDFElena Presura - ChirilescuNo ratings yet
- Design For Six Sigma - An OverviewDocument50 pagesDesign For Six Sigma - An OverviewDiana BlueseaNo ratings yet
- CSSBB Exam Practice QuestionsDocument63 pagesCSSBB Exam Practice QuestionsSyed Danish AlamNo ratings yet
- Minitab GuideDocument21 pagesMinitab GuideBlazieNo ratings yet
- School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering: Assignment-1Document5 pagesSchool of Mechanical and Materials Engineering: Assignment-1Ismail HussainNo ratings yet
- SIPOCDocument27 pagesSIPOCEliot Juarez100% (1)
- Product Order Cycle Time Six Sigma Case StudyDocument2 pagesProduct Order Cycle Time Six Sigma Case StudySteven BonacorsiNo ratings yet
- Define Phase PDFDocument159 pagesDefine Phase PDFtata sudheerNo ratings yet
- TQM Versus Six SigmaDocument16 pagesTQM Versus Six Sigmaapi-3751356No ratings yet
- Om - 3M CaseDocument18 pagesOm - 3M CaseBianda Puspita Sari100% (1)
- Certified Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt TrainingDocument2 pagesCertified Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt TrainingChuckie GarciaNo ratings yet
- Six SigmaDocument35 pagesSix SigmaVeeresh Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Maynard Operation Sequence TechniqueDocument9 pagesProject Report On Maynard Operation Sequence TechniqueEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Field DataDocument84 pagesEvaluation of Field DatajcesarcerriNo ratings yet
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Project For Supply Chain: Dock-to-Stock Part of Customer Supply ChainDocument7 pagesLean Six Sigma Black Belt Project For Supply Chain: Dock-to-Stock Part of Customer Supply ChainAmit AnandNo ratings yet
- CLSSGB Self-Study - April 2020Document64 pagesCLSSGB Self-Study - April 2020Sravan KrNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesSix Sigma Sample Questionsbreezeee100% (1)
- " Oncept Ustomer": SolutionsDocument1 page" Oncept Ustomer": SolutionsJac DNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Is A Business Management Strategy Originally Developed byDocument11 pagesSix Sigma Is A Business Management Strategy Originally Developed byharshil_shah007No ratings yet
- An Application of SMED Methodology PDFDocument4 pagesAn Application of SMED Methodology PDFIng Raul OrozcoNo ratings yet
- JIT Operations Management Week 14Document37 pagesJIT Operations Management Week 14Muhammad Arsalan ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Green Belt Course ManualDocument34 pagesGreen Belt Course ManualKaranShinde100% (1)
- Process Improvement Simplified: A How-to-Book for Success in any OrganizationFrom EverandProcess Improvement Simplified: A How-to-Book for Success in any OrganizationNo ratings yet
- LAN Speed TestDocument4 pagesLAN Speed TestmilanstrNo ratings yet
- Ford EcoBoost 1.6L Engine AnalysisDocument22 pagesFord EcoBoost 1.6L Engine Analysismilanstr100% (1)
- Cqi 14 Warranty Key Terms PDFDocument13 pagesCqi 14 Warranty Key Terms PDFSelvaraj SimiyonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Tests for Materials, Components and Footwear Hardness TestingDocument70 pagesLaboratory Tests for Materials, Components and Footwear Hardness TestingmilanstrNo ratings yet
- Automotive Supplier Quality RequirementsDocument13 pagesAutomotive Supplier Quality RequirementsmilanstrNo ratings yet
- Air Contaminants and Industrial Hygiene VentilationDocument236 pagesAir Contaminants and Industrial Hygiene Ventilationmilanstr100% (3)
- Automotive Supplier Quality RequirementsDocument13 pagesAutomotive Supplier Quality RequirementsmilanstrNo ratings yet
- Structural Stability: Roberto Crocetti (R C) Per Johan Gustafson (P J G) Kent Persson (K P) Per Erik Austrell (P E A)Document38 pagesStructural Stability: Roberto Crocetti (R C) Per Johan Gustafson (P J G) Kent Persson (K P) Per Erik Austrell (P E A)sheikNo ratings yet
- Statistika U Proizvodnji CP, CPK, (En)Document10 pagesStatistika U Proizvodnji CP, CPK, (En)milanstrNo ratings yet
- Lotus 7 Car Chassis Structure CalculationDocument24 pagesLotus 7 Car Chassis Structure Calculationmilanstr100% (1)
- Laboratory Tests for Materials, Components and Footwear Hardness TestingDocument70 pagesLaboratory Tests for Materials, Components and Footwear Hardness TestingmilanstrNo ratings yet
- KUKA KR C2 KR C3 Operating HandbookDocument57 pagesKUKA KR C2 KR C3 Operating HandbookmilanstrNo ratings yet
- Predict Storage Tank Heat Transfer Precisely Rev2Document16 pagesPredict Storage Tank Heat Transfer Precisely Rev2zefiloNo ratings yet
- Thread GalingDocument2 pagesThread GalingSpoonful BurnsideNo ratings yet
- ANSYS FE Modeler: Converting Meshes to CAD GeometryDocument17 pagesANSYS FE Modeler: Converting Meshes to CAD GeometrymilanstrNo ratings yet
- Thread GalingDocument2 pagesThread GalingSpoonful BurnsideNo ratings yet
- KR C2 KR C3 Operator ControlDocument167 pagesKR C2 KR C3 Operator ControlmilanstrNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Variable Charts PDFDocument34 pagesLecture 12 Variable Charts PDFMohd Nazri SalimNo ratings yet
- CPK Index - How To Calculate For All Types of TolerancesDocument15 pagesCPK Index - How To Calculate For All Types of TolerancesGaurav Narula100% (6)
- Basic Introduction To Clean RoomsDocument8 pagesBasic Introduction To Clean Roomsalternativo95No ratings yet
- Shot Peening OverviewDocument6 pagesShot Peening OverviewmilanstrNo ratings yet
- Construction drawing abbreviation guideDocument27 pagesConstruction drawing abbreviation guidemilanstrNo ratings yet
- CPK PDFDocument16 pagesCPK PDFRamirez ElNo ratings yet
- Thread GalingDocument2 pagesThread GalingSpoonful BurnsideNo ratings yet
- VBA INVENTOR Vba InventorDocument36 pagesVBA INVENTOR Vba InventormilanstrNo ratings yet
- GD&T Pocket GiudeDocument33 pagesGD&T Pocket Giudepepe51100% (2)
- Creating Sketches in The Sketch Mode-I: Learning ObjectivesDocument72 pagesCreating Sketches in The Sketch Mode-I: Learning ObjectivesDileep NaraharasettyNo ratings yet
- Vault12 Tech What S New Us EnglishDocument9 pagesVault12 Tech What S New Us EnglishmilanstrNo ratings yet
- Basic Adams TutorialDocument100 pagesBasic Adams TutorialsaptagunungNo ratings yet
- Keystone - Contractors - Book 16 05 12 FinalDocument9 pagesKeystone - Contractors - Book 16 05 12 Finalfb8120No ratings yet
- How to Get Nigeria Passport in 40 StepsDocument42 pagesHow to Get Nigeria Passport in 40 Stepsgynn100% (1)
- Smart Card PresentationDocument4 pagesSmart Card PresentationNitika MithalNo ratings yet
- ION8650 DatasheetDocument11 pagesION8650 DatasheetAlthaf Axel HiroshiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper About Cebu PacificDocument8 pagesResearch Paper About Cebu Pacificwqbdxbvkg100% (1)
- Motorola l6Document54 pagesMotorola l6Marcelo AriasNo ratings yet
- A Study of Arcing Fault in The Low-Voltage Electrical InstallationDocument11 pagesA Study of Arcing Fault in The Low-Voltage Electrical Installationaddin100% (1)
- Interpretation 1Document17 pagesInterpretation 1ysunnyNo ratings yet
- About Kia Motors Corporation: All-NewDocument19 pagesAbout Kia Motors Corporation: All-NewWessam FathiNo ratings yet
- Study apparel export order processDocument44 pagesStudy apparel export order processSHRUTI CHUGH100% (1)
- Rbalance Rotor Balancing ProcedureDocument2 pagesRbalance Rotor Balancing ProcedureBradley NelsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: The Catering Service Industry Topic: Catering Service Concept Digest (Discussion)Document5 pagesUnit 3: The Catering Service Industry Topic: Catering Service Concept Digest (Discussion)Justin MagnanaoNo ratings yet
- TT1 2lecture SpinningDocument29 pagesTT1 2lecture SpinninghaiNo ratings yet
- Tdi Hazid TemplateDocument11 pagesTdi Hazid TemplateAnonymous rwojPlYNo ratings yet
- Rural Perception of SUV CarsDocument29 pagesRural Perception of SUV CarsritusinNo ratings yet
- 2021 A Review of Image Based Pavement Crack Detection AlgorithmsDocument7 pages2021 A Review of Image Based Pavement Crack Detection Algorithmsgandhara11No ratings yet
- Data IntegrationDocument7 pagesData IntegrationHan MyoNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal: Retail Environment Design To Create Brand ExperienceDocument3 pagesProject Proposal: Retail Environment Design To Create Brand ExperienceMithin R KumarNo ratings yet
- Speaking Telephone RoleplaysDocument2 pagesSpeaking Telephone RoleplaysremimiguelNo ratings yet
- bq76pl455 RegistersDocument132 pagesbq76pl455 RegistersAhmet KARANo ratings yet
- Final Mother DairyDocument59 pagesFinal Mother DairyAnup Dcruz100% (4)
- Designing An Electrical Installation - Beginner GuideDocument151 pagesDesigning An Electrical Installation - Beginner GuideFrankie Wildel100% (4)
- Ed TechDocument19 pagesEd TechAlexie AlmohallasNo ratings yet
- Design Guide For Slug Force Calculation ProcedureDocument6 pagesDesign Guide For Slug Force Calculation ProcedurePratik PatreNo ratings yet
- ADVOCACY AND LOBBYING NDocument7 pagesADVOCACY AND LOBBYING NMwanza MaliiNo ratings yet
- TESA Doorclosers and Door Operators PDFDocument46 pagesTESA Doorclosers and Door Operators PDFDawood Shaik Abdul CadarNo ratings yet
- Employee Training and DevelopmentDocument33 pagesEmployee Training and DevelopmentMoogii50% (2)
- MS For The Access Control System Installation and TerminationDocument21 pagesMS For The Access Control System Installation and Terminationwaaji snapNo ratings yet
- SUTI Report - Metro ManilaDocument87 pagesSUTI Report - Metro ManilaIvan Harris TanyagNo ratings yet
- Insulation e BookDocument48 pagesInsulation e BookAl7amdlellah100% (1)