Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Part II
Uploaded by
Giing FernandezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Part II
Uploaded by
Giing FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
COM413 – Principles of Communication
Ways in which electronic communication are classified: FULL DUPLEX
- People communicating with one another over the
According to the transmission modes: telephone can talk and listen simultaneously.
- Transmission can occur in both directions at the same
TYPE / MODES OF ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS time.
1. SIMPLEX
- is the simplest way in which electronic communication is
conducted is one-way communications.
- information travels in one direction only.
FULL/FULL DUPLEX
- it is possible to transmit and receive simultaneously
but not necessarily between the same locations.
According to the type of intelligence signal transmitted.
2. DUPLEX – is the bulk of electronic communication is two-way. TYPES OF INTELLIGENCE
HALF DUPLEX 1. ANALOG SIGNAL – is a smoothly and continuously varying voltage or
- is the form of two-way communication in which only current.
one party transmit at a time.
- transmissions can occur in both directions but not
at the same time.
2. DIGITAL SIGNAL – do not vary continuously but change in steps or in
discrete increments.
Prepared by: ENGR. MARK JOMMEL S. NASOL
COM413 – Principles of Communication
According to the transmitted signal PHASE MODULATION (PM)
- when the amount of phase shift of a constant-frequency
BASEBAND SIGNAL carrier is varied in accordance with a modulating signal.
- information is transmitted directly over the medium.
- is the original voice, video or digital signal’s directly into the medium. TYPES OF PULSE MODULATION
MODULATED SIGNAL AMPLITUDE-SHIFT KEYING (ASK)
- is the modulated carrier is amplified and sent to the antenna for FREQUENCY-SHIFT KEYING (FSK)
transmission.
PHASE-SHIFT KEYING (PSK)
QUADRATURE AMPLITUDE MODULATION (QAM)
MODULATION
- is the process of impressing low-frequency information signals MODULATION AT THE TRANSMITTER
onto a high-frequency carrier signal.
- systematic alteration of a carrier wave in accordance with the
message.
TYPES OF MODULATION
1. CONTINUOUS WAVE MODULATION
- is the carrier wave is simply sinusoidal waveform.
2. PULSE MODULATION
- is the carrier is a periodic train of pulses.
TYPES OF CONTINUOUS WAVE MODULATION
TYPES OF CONTINUOUS WAVE MODULATION
1. AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
- is the process of changing the amplitude of a relatively high
frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous
value of the modulating signal.
2. ANGLE MODULATION
- is an analog modulation scheme in which the angle of a
relatively high-frequency carrier signal is varied in
accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of an
information signal.
TWO CLASSIFICATIONS OF ANGLE MODULATION
FREQUENCY MODULATION (FM)
- is a system in which the amplitude of the modulated
carrier is kept constant, while its frequency and rate of
change are varied by the modulating signal.
Prepared by: ENGR. MARK JOMMEL S. NASOL
COM413 – Principles of Communication
TYPES OF PULSE MODULATION MULTIPLEXING AT THE TRANSMITTER
MODULATION AT THE RECEIVER MULTIPLEXING AT THE RECEIVER
MULTIPLEXING
- is the process of allowing two or more signals to share the same
medium or channel.
THREE BASIC TYPES OF MULTIPLEXING
1. FREQUENCY-DIVISION MULTIPLEXING (FDM)
- is the intelligence signals modulate subcarriers that are
then added together, and the composite signal is used to
modulate the carrier.
2. TIME-DIVISION MULTIPLEXING (TDM)
- is the multiple intelligence signals are sequentially
sampled, and a small piece of each is used to modulate the
carrier.
3. CODE-DIVISION MULTIPLEXING (CDM)
- is the signals to be transmitted are converted to digital
data that is then uniquely coded with a faster binary code.
Prepared by: ENGR. MARK JOMMEL S. NASOL
COM413 – Principles of Communication
Prepared by: ENGR. MARK JOMMEL S. NASOL
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
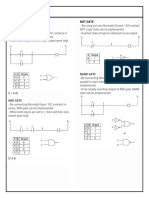
- Boolean Algebra or Gate: Jessa Fernandez PCEIT-03-801ADocument2 pagesBoolean Algebra or Gate: Jessa Fernandez PCEIT-03-801AGiing FernandezNo ratings yet
- Library Management System: Bacarra, Rachel Anne H. Fernandez, Jessa NDocument7 pagesLibrary Management System: Bacarra, Rachel Anne H. Fernandez, Jessa NGiing FernandezNo ratings yet
- LAB 1-Intro To Asmbly Lang ToolsDocument14 pagesLAB 1-Intro To Asmbly Lang ToolsGiing FernandezNo ratings yet
- COM413 - Principles of CommunicationDocument2 pagesCOM413 - Principles of CommunicationGiing FernandezNo ratings yet
- PP02Document3 pagesPP02Giing FernandezNo ratings yet
- Romel Mañaol Aquino: Career Objective ContactDocument1 pageRomel Mañaol Aquino: Career Objective ContactGiing FernandezNo ratings yet
- Philippine MapDocument36 pagesPhilippine MapGiing Fernandez100% (1)
- Letter CutDocument2 pagesLetter CutGiing FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Railway-4 Permanent Way & Alignment (Lecture-4)Document17 pagesRailway-4 Permanent Way & Alignment (Lecture-4)OBIDUR RAHMAN 1701085No ratings yet
- 390 Track Bolt M0079195Document2 pages390 Track Bolt M0079195joshpbenzNo ratings yet
- D8 9M-2012PVDocument16 pagesD8 9M-2012PVvishesh dharaiya0% (4)
- Online Bank SynopsisDocument7 pagesOnline Bank SynopsisPrashant VermaNo ratings yet
- Brosur Hari GuruDocument8 pagesBrosur Hari GuruFitri SharifNo ratings yet
- 690 2004Document19 pages690 2004RahilaHammadNo ratings yet
- Make A Project of Calculator in Visual BasicDocument9 pagesMake A Project of Calculator in Visual BasicCHITRA MINI96% (23)
- 1 Pre-Lab: Lab 07: Sampling, Convolution, and FIR FilteringDocument12 pages1 Pre-Lab: Lab 07: Sampling, Convolution, and FIR Filteringdemetrickn0% (1)
- FE Yeet GUIDocument3 pagesFE Yeet GUINobodyNo ratings yet
- En 10268Document4 pagesEn 10268Alex LacerdaNo ratings yet
- Aes MatlabDocument32 pagesAes MatlabbalajithrillerNo ratings yet
- Plotting in MatlabDocument7 pagesPlotting in Matlabpride3351No ratings yet
- Heat ConductionDocument11 pagesHeat ConductionAlex Samuel SilvaNo ratings yet
- G3508 - 600kvaDocument7 pagesG3508 - 600kvaJim Patrick ChombaNo ratings yet
- 888 Gallant Security Services Corp NewDocument12 pages888 Gallant Security Services Corp Newnareyes11No ratings yet
- Agroforestry: A Sustainable Land-Use System For Food and WoodDocument72 pagesAgroforestry: A Sustainable Land-Use System For Food and WoodAlok PatraNo ratings yet
- NTSE MAT Chattisgarh Paper 2011 PDFDocument14 pagesNTSE MAT Chattisgarh Paper 2011 PDFKareena GuptaNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Guide - Sensors Alarms1Document14 pagesStep-By-Step Guide - Sensors Alarms1Andy_kokoNo ratings yet
- (W. Wireline) Motor PGM365 DatasheetDocument7 pages(W. Wireline) Motor PGM365 Datasheetgonzalo andres HernandezNo ratings yet
- LC 2539Document16 pagesLC 2539Kelly JonesNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy: ACTIVITY 1: Forget Me NotDocument5 pagesMedia and Information Literacy: ACTIVITY 1: Forget Me NotShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- 3BSE035980-600 A en System 800xa Control 6.0 AC 800M Configuration PDFDocument580 pages3BSE035980-600 A en System 800xa Control 6.0 AC 800M Configuration PDFWaqas AnjumNo ratings yet
- Accounts Payable by ORACLEUGDocument164 pagesAccounts Payable by ORACLEUGPraveenReddyBNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety of Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S)Document20 pagesOccupational Health and Safety of Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S)hitm357100% (1)
- Driving Goods VehiclesDocument336 pagesDriving Goods VehiclesAsmawi AkhirNo ratings yet
- SAP Material Management MRP Mechanics MRP Type "VB" Re-Order PointDocument15 pagesSAP Material Management MRP Mechanics MRP Type "VB" Re-Order PointmohhitNo ratings yet
- Fiocchi USA Catalogue 2010Document60 pagesFiocchi USA Catalogue 2010Mario LopezNo ratings yet
- TGS8100 Product InfomationDocument10 pagesTGS8100 Product Infomationbemxgm-1No ratings yet
- Trodat Standard Self Inking Stamp and Accessory Mini CatalogDocument12 pagesTrodat Standard Self Inking Stamp and Accessory Mini CatalogpromotesourceNo ratings yet
- NessusDocument23 pagesNessusShivaprakash TimmapurNo ratings yet