Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermoluminescent Dosimeter: How It Works
Uploaded by
punitg_2Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermoluminescent Dosimeter: How It Works
Uploaded by
punitg_2Copyright:
Available Formats
Thermoluminescent Dosimeter Page 1 of 1
Home - Education Resources - NDT Course Material - Radiation
-
Radiation Safety
Introduction
Thermoluminescent Dosimeter Background Information
X-Radiation
Gamma Radiation
Thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLD) are often used Health Concerns
instead of the film badge. Like a film badge, it is worn for a
Radiation Theory
period of time (usually 3 months or less) and then must be Nature of Radiation
processed to determine the dose received, if any. Sources of High Energy
Rad
Thermoluminescent dosimeters can measure doses as low Rad for Ind Radiography
as 1 millirem, but under routine conditions their low-dose Decay and Half-life
Energy, Activity, Intensity
capability is approximately the same as for film badges. and Exposure
TLDs have a precision of approximately 15% for low Interaction with Matter
Ionization
doses. This precision improves to approximately 3% for Radiosensitivity
high doses. The advantages of a TLD over other personnel Measures Related to
monitors is its linearity of response to dose, its relative energy independence, and its Biological Effects
sensitivity to low doses. It is also reusable, which is an advantage over film badges. Biological Effects
However, no permanent record or re-readability is provided and an immediate, on the job Biological Factors
Stochastic (Delayed) Effects
readout is not possible. -Cancer
-Leukemia
-Genetic Effects
How it works -Cataracts
A TLD is a phosphor, such as lithium fluoride (LiF) or calcium fluoride (CaF), in a solid Nonstochastic (Acute)
Effects
crystal structure. When a TLD is exposed to ionizing radiation at ambient temperatures, Symptoms
the radiation interacts with the phosphor crystal and deposits all or part of the incident
Safe Use of Radiation
energy in that material. Some of the atoms in the material that absorb that energy become NRC & Code of Federal
ionized, producing free electrons and areas lacking one or more electrons, called holes. Regs
Imperfections in the crystal lattice structure act as sites where free electrons can become Exposure Limits
Controlling Exposure
trapped and locked into place. -Time-Dose Calculation
-Distance-Intensity Calc
HVL Shielding
Heating the crystal causes the crystal lattice to vibrate, releasing the trapped electrons in Safety Controls
the process. Released electrons return to the original ground state, releasing the captured Responsibilities
Procedures
energy from ionization as light, hence the name thermoluminescent. Released light is Survey Techniques
counted using photomultiplier tubes and the number of photons counted is proportional to
Radiation Safety
the quantity of radiation striking the phosphor. Equipment
Radiation Detectors
Survey Meters
Instead of reading the optical density (blackness) of a film, as is done with film badges, Pocket Dosimeter
the amount of light released versus the heating of the individual pieces of Audible Alarm Rate Meters
Film Badges
thermoluminescent material is measured. The "glow curve" produced by this process is Thermoluminescent
then related to the radiation exposure. The process can be repeated many times. Dosimeter
Video Clips
References
Quizzes
http://www.ndt-ed.org/EducationResources/CommunityCollege/RadiationSafety/radiatio... 1/5/2011
You might also like
- Project Management Book PDFDocument55 pagesProject Management Book PDFSerigne Mbaye Diop94% (16)
- Thoughful Investor NotesDocument4 pagesThoughful Investor NotesRd Patel83% (6)
- Date Company Code Bank RefDocument16 pagesDate Company Code Bank RefSrinivas YNo ratings yet
- Aztech+700WR-3G User ManualDocument57 pagesAztech+700WR-3G User Manualkero_the_hero67% (3)
- Hospital Building Civil ProjectDocument128 pagesHospital Building Civil ProjectArun Ragu100% (6)
- Clarion Technologies: at A GlanceDocument7 pagesClarion Technologies: at A GlanceChetan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Presentstion Dr. NazishDocument48 pagesPresentstion Dr. NazishFouzia NoorNo ratings yet
- Apeksha FinalDocument26 pagesApeksha FinalAshish MOHARENo ratings yet
- Personl Monitorng RSOindustrialDocument79 pagesPersonl Monitorng RSOindustrialJie DVNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety: Presented by Mohammad Naeem Operation Theatre Technologist Lecturer GCUFDocument41 pagesRadiation Safety: Presented by Mohammad Naeem Operation Theatre Technologist Lecturer GCUFNaim50% (2)
- Dosimetry: Film Badge DosimetersDocument3 pagesDosimetry: Film Badge DosimetersmahaNo ratings yet
- Apeksha FinalDocument25 pagesApeksha FinalAshish MOHARENo ratings yet
- Radiation FundamentalsDocument46 pagesRadiation FundamentalsRichard mwanaNo ratings yet
- Unit4, Atomic&MolecularPhysics, InfraRed Spectros PDFDocument43 pagesUnit4, Atomic&MolecularPhysics, InfraRed Spectros PDFanujjuetNo ratings yet
- Thermoluminecent Dosimeters: Nayana.M M.Sc. Radiation Physics Calicut UniversityDocument18 pagesThermoluminecent Dosimeters: Nayana.M M.Sc. Radiation Physics Calicut UniversityKopi TiamNo ratings yet
- Radio Glass DosimeterDocument18 pagesRadio Glass DosimeterPhongNo ratings yet
- Cocoon Training Manual+++++++++Document14 pagesCocoon Training Manual+++++++++이태훈No ratings yet
- Introduction To Optical Spectroscopy (Chapters 6-7)Document27 pagesIntroduction To Optical Spectroscopy (Chapters 6-7)GlenNo ratings yet
- Introduction For CXRDocument53 pagesIntroduction For CXRLuna WhiteNo ratings yet
- Sources of AttenuationDocument3 pagesSources of AttenuationShabbir KhanNo ratings yet
- OSL PaperDocument9 pagesOSL PaperHarpreet sainiNo ratings yet
- Selecting Dosimetry Systems For Application in Pulsed X-Ray SourcesDocument19 pagesSelecting Dosimetry Systems For Application in Pulsed X-Ray SourcesEric GozzerNo ratings yet
- Reviwe of Termal LensDocument32 pagesReviwe of Termal Lensreza vahdaniNo ratings yet
- Moderator: Dr. S. Kalpana Presenter: Dr. AnjaliDocument89 pagesModerator: Dr. S. Kalpana Presenter: Dr. Anjaliايه سلام خضير عباس تقنيات البصرياتNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity and Its ApplicationDocument58 pagesRadioactivity and Its ApplicationBipin SunarNo ratings yet
- Atomic & Nuclear PhysicsDocument9 pagesAtomic & Nuclear PhysicsPyay Lin ThantNo ratings yet
- SBM1602Document61 pagesSBM1602Dhanalakshmi StridaraneNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing TechniquesDocument58 pagesRadiographic Testing TechniquesnurdinNo ratings yet
- Wavelength and Temperature Dependence of Continuous-Wave Laser Absorptance in Kapton Thin FilmsDocument9 pagesWavelength and Temperature Dependence of Continuous-Wave Laser Absorptance in Kapton Thin FilmssankhaNo ratings yet
- Laser Application: IntroductionDocument8 pagesLaser Application: IntroductionArjay CarolinoNo ratings yet
- RE ShieldingDocument32 pagesRE ShieldingWaleed TayyabNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Spectroscopies and NMRDocument30 pagesVibrational Spectroscopies and NMRAmjed AL-KAHTEEBNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Coating Thickness by X-Ray Spectrometry: Standard Test Method ForDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Coating Thickness by X-Ray Spectrometry: Standard Test Method Forsivaraja kNo ratings yet
- Radiology in Orthodontics-Dr - Kavitha / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument85 pagesRadiology in Orthodontics-Dr - Kavitha / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Materials Safety Training: Radiation Protection ProgramDocument34 pagesRadioactive Materials Safety Training: Radiation Protection Programfgdgrte gdfsgdNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection Aspects of Proton Particle Beam 1686060236Document2 pagesRadiation Protection Aspects of Proton Particle Beam 1686060236Sri vennila SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Princip Medicine NuclearDocument53 pagesPrincip Medicine Nuclearhendrypakpahan100% (1)
- Radiographic Testing (RT) (10) : DefinitionDocument31 pagesRadiographic Testing (RT) (10) : DefinitionIbnu SenaNo ratings yet
- WritemepleasetodayDocument40 pagesWritemepleasetodayMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Training On RT - ASNT Level IIDocument72 pagesTraining On RT - ASNT Level IIAguara OghenevwedeNo ratings yet
- USP 851 Espectro y EscáteringDocument6 pagesUSP 851 Espectro y EscáteringgustavoesanchezNo ratings yet
- X RayDocument53 pagesX RayMama CassNo ratings yet
- Part 1 NDT-RT1Document23 pagesPart 1 NDT-RT1TEBATSONo ratings yet
- Application of Caf (MN) Thermoluminescence Dosimeters in Mixed Neutron-Photon EnvironmentsDocument6 pagesApplication of Caf (MN) Thermoluminescence Dosimeters in Mixed Neutron-Photon EnvironmentsROHITNo ratings yet
- p31220 RadioactivityDocument14 pagesp31220 RadioactivityAHKEEL LESTER JONESNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection: Principles and Practices: Dr. V. MeenakshisundaramDocument39 pagesRadiation Protection: Principles and Practices: Dr. V. MeenakshisundaramDarmala laxmiNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument1 pageActivityTomy GeorgeNo ratings yet
- NDT Radiographic TestingDocument93 pagesNDT Radiographic TestingMuhammad Rizal PambudiNo ratings yet
- SunscreensDocument3 pagesSunscreensRamón OlivasNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Materials Safety Training: Radiation Protection ProgramDocument34 pagesRadioactive Materials Safety Training: Radiation Protection ProgramkhurshedlakhoNo ratings yet
- MSC 2nd Sem Physics Topic Atomic&MolecularPhysics Unit4Document53 pagesMSC 2nd Sem Physics Topic Atomic&MolecularPhysics Unit4Madni BhuttaNo ratings yet
- X-Ray: X-Radiation (Composed of X-Rays) Is A FormDocument18 pagesX-Ray: X-Radiation (Composed of X-Rays) Is A FormFDELNo ratings yet
- Radiation MITDocument34 pagesRadiation MITAhmed shabanNo ratings yet
- Absorbance, Absorpsion SpectrumDocument15 pagesAbsorbance, Absorpsion SpectrumDebasish BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- laserinophthalmology-180821172741Document82 pageslaserinophthalmology-180821172741Apps OmNo ratings yet
- Laser Radiation HazardsDocument16 pagesLaser Radiation HazardsLarryKnappNo ratings yet
- 6626518Document151 pages6626518OsamaNo ratings yet
- 10-DetectorComparison-LINAC ComponentsDocument13 pages10-DetectorComparison-LINAC ComponentsMohamed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Intro To NDTDocument39 pagesIntro To NDTNallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- 20 Bio Medical LasersDocument77 pages20 Bio Medical Laserskaushik4208No ratings yet
- Article Minimising False Alarms Rosemount en 72138Document1 pageArticle Minimising False Alarms Rosemount en 72138Abdelhakim ChaouchNo ratings yet
- Protecting Your Laser DiodeDocument30 pagesProtecting Your Laser DiodebseptrianiNo ratings yet
- Cy Complete PDFDocument225 pagesCy Complete PDFAakarshNo ratings yet
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Laser / IPL Technology for Skin Care: A Comprehensive Technical and Informative TextbookFrom EverandLaser / IPL Technology for Skin Care: A Comprehensive Technical and Informative TextbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
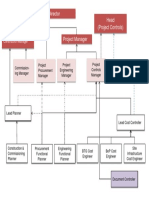
- Construction Project Management Organizational ChartDocument1 pageConstruction Project Management Organizational Chartpunitg_2No ratings yet
- Edelweiss Review 2020 - Brokerage Charges, Margin, Demat AccountDocument20 pagesEdelweiss Review 2020 - Brokerage Charges, Margin, Demat Accountpunitg_2No ratings yet
- Project Director: Construction Manager EHS Manager Qa/Qc ManagerDocument1 pageProject Director: Construction Manager EHS Manager Qa/Qc Managerpunitg_2No ratings yet
- New Org Chart - LNT PowerDocument1 pageNew Org Chart - LNT Powerpunitg_2No ratings yet
- The Overview of Gold Etfs and Its Various Positive Features: Mohdsaleem Matloobullah KhanDocument11 pagesThe Overview of Gold Etfs and Its Various Positive Features: Mohdsaleem Matloobullah Khanpunitg_2No ratings yet
- FIL Stock MarketDocument15 pagesFIL Stock Marketrahulak57No ratings yet
- Appendix E3m - Tube Properties (Metrics) For Cooper TubesDocument2 pagesAppendix E3m - Tube Properties (Metrics) For Cooper TubesRandistya FahmyNo ratings yet
- E04m PDFDocument2 pagesE04m PDFAbu Izzan Al BunyNo ratings yet
- Appendix E1Document10 pagesAppendix E1ehasayinNo ratings yet
- CeRFS Low PDFDocument10 pagesCeRFS Low PDFDeepak RathoreNo ratings yet
- Axis Gold ETF11Document61 pagesAxis Gold ETF11punitg_2No ratings yet
- It Is With Great Sense of GratitudeDocument2 pagesIt Is With Great Sense of GratitudeehasayinNo ratings yet
- Trading Account - ChargesDocument6 pagesTrading Account - Chargespunitg_2No ratings yet
- 11 TradeDocument3 pages11 Tradepunitg_2No ratings yet
- Trading Account - Open A Free Trading Account Online in 11 MinsDocument5 pagesTrading Account - Open A Free Trading Account Online in 11 Minspunitg_2No ratings yet
- NSE11 - National Stock Exchange of India LTDDocument1 pageNSE11 - National Stock Exchange of India LTDpunitg_2No ratings yet
- Free online equity trading servicesDocument2 pagesFree online equity trading servicespunitg_2No ratings yet
- Securities Transaction Tax11234Document2 pagesSecurities Transaction Tax11234punitg_2No ratings yet
- Trading Holidays For The Calendar Year 2014Document1 pageTrading Holidays For The Calendar Year 2014punitg_2No ratings yet
- About Kotak Gold ETF (KGETF) Scheme FactsDocument3 pagesAbout Kotak Gold ETF (KGETF) Scheme Factspunitg_2No ratings yet
- Performance - Gold - The Economic Times11Document5 pagesPerformance - Gold - The Economic Times11punitg_2No ratings yet
- List 11 of Top 10 Gold ETFs Offered in India - BankbazaarDocument17 pagesList 11 of Top 10 Gold ETFs Offered in India - Bankbazaarpunitg_2No ratings yet
- Larsen & Toubro Limited MSQ Up Gradation (Epcc 1) Project: LT/MSQ/P/UT/011Document11 pagesLarsen & Toubro Limited MSQ Up Gradation (Epcc 1) Project: LT/MSQ/P/UT/011punitg_2No ratings yet
- Larsen & Toubro Limited MSQ (Epcc 1) Up Gradation: LT/MSQ/P/DPT//007Document4 pagesLarsen & Toubro Limited MSQ (Epcc 1) Up Gradation: LT/MSQ/P/DPT//007punitg_2No ratings yet
- Installing Static Equipment ProcedureDocument7 pagesInstalling Static Equipment Procedurepunitg_2No ratings yet
- MPTDocument4 pagesMPTbhavin_jsmNo ratings yet
- 1 Procedure For Radiography TestingDocument9 pages1 Procedure For Radiography Testingpunitg_2No ratings yet
- Larsen & Toubro Limited MSQ (Epcc-1) Upgadation Project: ContentsDocument5 pagesLarsen & Toubro Limited MSQ (Epcc-1) Upgadation Project: Contentspunitg_2No ratings yet
- NC 306 29JUL2010Document1 pageNC 306 29JUL2010punitg_2No ratings yet
- Dual-Band Band Pass Filters Using Stub-Loaded ResonatorsDocument3 pagesDual-Band Band Pass Filters Using Stub-Loaded ResonatorsfracosoeNo ratings yet
- Qtiplot Manual enDocument390 pagesQtiplot Manual enjovita georgeNo ratings yet
- Konica Bizhub 7272 - User ManualDocument436 pagesKonica Bizhub 7272 - User Manualfaco1723No ratings yet
- The Contemporary WorldDocument9 pagesThe Contemporary WorldDennis RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Eaton 9130 Rack 700-3000vaDocument4 pagesEaton 9130 Rack 700-3000vaJose Luis PintoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Dinamika Struktur Shape Function - Kelompok 6Document8 pagesTugas Dinamika Struktur Shape Function - Kelompok 6Mochammad Choirul RizkyNo ratings yet
- OTC13998Document15 pagesOTC13998Raifel MoralesNo ratings yet
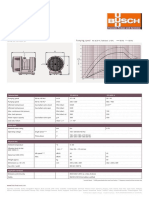
- Fossa FO 0015 0035 A Technical Data en 9aaDocument2 pagesFossa FO 0015 0035 A Technical Data en 9aaFatih YAŞARNo ratings yet
- SDLC Phases Feasibility Analysis RequirementsDocument4 pagesSDLC Phases Feasibility Analysis RequirementsBrandon Mitchell0% (1)
- Air Car SeminarDocument24 pagesAir Car SeminarSatyajit MenonNo ratings yet
- Samsung DRAM Module Handling Guide - 1128 - 10090119049407 PDFDocument9 pagesSamsung DRAM Module Handling Guide - 1128 - 10090119049407 PDFreza_azadNo ratings yet
- 2007 Output Stops RemovedDocument45 pages2007 Output Stops RemovedAisyah DzulqaidahNo ratings yet
- Abstract Substructure Conc - Frame Westgate RealDocument4 pagesAbstract Substructure Conc - Frame Westgate RealTashamiswa MajachaniNo ratings yet
- Easi-Pay Guide via e-ConnectDocument29 pagesEasi-Pay Guide via e-ConnectKok WaiNo ratings yet
- Is 15560 - 2005Document12 pagesIs 15560 - 2005kalpanaadhiNo ratings yet
- Imageclass Lbp611cn 613cdw 2Document2 pagesImageclass Lbp611cn 613cdw 2Maulana Ikhwan SadikinNo ratings yet
- Din en 1561 - en - 1997-08Document21 pagesDin en 1561 - en - 1997-08AlissonFernandes17No ratings yet
- Grade 9 ICT Network Configuration GuideDocument15 pagesGrade 9 ICT Network Configuration GuideMark Anthony Nieva RafalloNo ratings yet
- How To Read Architect DrawingDocument32 pagesHow To Read Architect DrawingKutty Mansoor50% (2)
- Google Earth y Civil CadDocument3 pagesGoogle Earth y Civil CadRodneyNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE MUSIC AND ARTS EXAMDocument4 pagesCOMPREHENSIVE MUSIC AND ARTS EXAMChris Patlingrao100% (1)
- Warfighter WWII Keyword SheetDocument4 pagesWarfighter WWII Keyword SheetMadWelshWizardNo ratings yet
- MG585 Set Up and Service ManualDocument16 pagesMG585 Set Up and Service Manualoscar albertoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Course Project-1Document27 pagesEnvironmental Science Course Project-1vaishnaviNo ratings yet
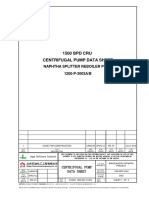
- D16021.1200.RE.10-003 REV.1 Datasheet (1200-P-3003AB)Document3 pagesD16021.1200.RE.10-003 REV.1 Datasheet (1200-P-3003AB)anwar sadatNo ratings yet