Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HCC Alarms Discreption 95-103
Uploaded by
amr_karimmCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HCC Alarms Discreption 95-103
Uploaded by
amr_karimmCopyright:
Available Formats
Alarms
5.67.2 Corrective Actions
Figure 11 Workflow for Hardware Error: SFP Alarm Corrective Actions
Note: To clear the alarm, perform the corrective action below on-site.
Replace the SFP module, see Replacing an SFP, Reference [17].
5.68 HCC
Hop Communication Channel (HCC)
Communication is lost on the HCC, between the MMU and the far-end MMU.
SpecificProblem HCC
Source All MMUs
AlarmType CommunicationAlarm
Severity Major
ProbableCause Unavailable
5.68.1 Consequences
It is not possible to access the Far End.
5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03 83
Alarm Descriptions
5.68.2 Corrective Actions
Figure 12 Workflow for HCC Alarm Corrective Actions, Part 1
84 5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03
Alarms
Figure 13 Workflow for HCC Alarm Corrective Actions, Part 2
5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03 85
Alarm Descriptions
Figure 14 Workflow for HCC Alarm Corrective Actions, Part 3
86 5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03
Alarms
Figure 15 Workflow for HCC Alarm Corrective Actions, Part 4
Perform the following steps:
1. Make sure that the configuration of the near-end and the far-end is
according to the Site Installation Documentation (SID).
• If the configuration of the near-end and the far-end is according to the
SID, go to Step 2.
5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03 87
Alarm Descriptions
• If the configuration of the near-end and the far-end is not according to
the SID, take corrective actions. If the HCC alarm is not cleared after
the correction, go to Step 2.
2. Check the RF input level.
• If the RF input level is according to the link budget, go Step 3.
• If the RF input level is not according to the link budget, go to Step 4.
If the RF input level is above -30 dBm, consult network design
department to address upfading.
3. Perform a cold restart of the MMU and restart MINI-LINK Craft.
Caution!
A cold restart will disturb the traffic.
• If the HCC alarm is cleared after the restart, monitor the hop for further
HCC alarms. If the HCC alarm reoccurs, go to Step 13.
• If the HCC alarm is not cleared after the restart, go to Step 13.
4. Make sure that the RF output level of the near-end and the far-end is
according to the link budget planning.
• If the RF output level of the near-end and the far-end is according to
the link budget planning, go to Step 5.
• If the RF output level of the near-end and the far-end is not according
to the link budget planning, consult the transmission design department
for corrective actions.
5. Check if the RF input level is below the threshold level for BER 10-6 for the
current configuration.
• If the RF input level is below the threshold level for BER 10-6 for the
current configuration, go to Step 6.
• If the RF input level is not below the threshold level for BER 10-6 for the
current configuration, go to Step 13.
6. On-site action: Perform an RF loop test on the near-end RAU. Turn off the
RAU transmitter on the far-end during the test.
• If the RF input power is about -50 dBm (± 10 dB) on the near-end RAU
during the test, go to Step 7.
• If the RF input power is not about -50 dBm (± 10 dB) on the near-end
RAU during the test, replace the RAU on the near-end. Describe the
88 5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03
Alarms
fault on the Blue Tag and send it to the Repair Center together with
the faulty RAU.
Note: HCC alarms will be automatically masked during an RF loop test,
that is, HCC alarm disappears during the loop test. The RF loop
test cannot be used to define the faulty unit. The RF loop test only
shows if the RF input level is correct.
7. Check if RF Output Level alarm is active on the far-end RAU.
• On-site action: If the RF Output Level alarm is active, replace the RAU
on the far-end. Describe the fault on the Blue Tag and send it to the
Repair Center together with the faulty RAU.
• If the RF Output Level alarm is not active, go to Step 8.
8. On-site action: Check fading conditions and weather circumstances.
• If link performance is affected by propagation issues, consult the
transmission design department on how to address the link budget.
• If link performance is not affected by propagation issues, go to Step 9.
9. On-site action: Check for possible obstacles interfering with the line of sight.
• If there are obstacles, consult the transmission design department.
• If there are no obstacles, go to Step 10.
10. On-site action: Make sure the antennas are aligned correctly on the
near-end and the far-end to meet the link budget target.
• If the antennas are aligned correctly, go to Step 11.
• If the antennas are not aligned correctly, take corrective actions.
11. Check the status of the RF input level, that can be stable or can vary over
time indicating multipath fading. If you are unsure, monitor the RF input
level for 24 hours to find cyclic variations.
• If the RF input level is stable, go to Step 12.
• If the RF input level decrease is intermittent or periodic, consult the
transmission design department to analyze the possible multipath
fading.
12. On-site action: Perform an RF loop test on the far-end RAU. Turn off the
RAU transmitter on the near-end during the test.
• If the RF input power is about -50 dBm (± 10 dB) on the far-end RAU
during the test, go to Step 17.
• If the RF input power is not about -50 dBm (± 10 dB) on the far-end
RAU during the test, replace the RAU on the far-end. Describe the
fault on the Blue Tag and send it to the Repair Center together with
the faulty RAU.
5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03 89
Alarm Descriptions
Note: HCC alarms will be automatically masked during an RF loop test,
that is, HCC alarm disappears during the loop test. The RF loop
test cannot be used to define the faulty unit. The RF loop test only
shows if the RF input level is correct.
13. On-site action: Perform an interference test, see Verifying an Installation,
Reference [22]. Record the highest received RF input level while scanning
the whole bandwidth and compare it to the acceptable interference values.
• If the received RF input level exceeds the defined value, consult the
transmission design department.
• If the received RF input level does not exceed the defined value, go
to Step 14.
14. On-site action: Replace the MMU on the near-end.
• If the HCC alarm is cleared after the replacement, describe the fault
on the Blue Tag and send it to the Repair Center together with the
faulty MMU.
• If the HCC alarm is not cleared after the replacement, reuse the initial
MMU, and go to Step 15.
15. On-site action: Replace the MMU on the far-end.
• If the HCC alarm is cleared after the replacement, describe the fault
on the Blue Tag and send it to the Repair Center together with the
faulty MMU.
• If the HCC alarm is not cleared after the replacement, reuse the initial
MMU, and go to Step 16.
16. On-site action: Replace the RAU on the near-end.
• If the HCC alarm is cleared after the replacement, describe the fault
on the Blue Tag and send it to the Repair Center together with the
faulty RAU.
• If the HCC alarm is not cleared after the replacement, reuse the initial
RAU, and go to Step 17.
17. On-site action: Replace the RAU on the far-end.
• If the HCC alarm is cleared after the replacement, describe the fault
on the Blue Tag and send it to the Repair Center together with the
faulty RAU.
• If the HCC alarm is not cleared after the replacement, reuse the initial
RAU, and go to Step 18.
18. On-site action: Make sure that the polarization on the near-end and the
far-end is set according to the link budget planning.
• If the polarization on the near-end and the far-end is correctly set, go
to Step 19.
90 5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03
Alarms
• If the polarization on the near-end and the far-end is not correctly set,
take corrective actions.
19. On-site action: Replace the antenna on the near-end.
• If the HCC alarm is cleared after the replacement, describe the fault
on the Blue Tag and send it to the Repair Center together with the
faulty antenna.
• If the HCC alarm is not cleared after the replacement, reinstall the initial
antenna, and go to Step 20.
20. On-site action: Replace the antenna on the far-end. Describe the fault
on the Blue Tag and send it to the Repair Center together with the faulty
antenna.
For more information on how to replace the RAU, see Replacing a Radio
Unit, Reference [15].
For more information on antenna alignment and antenna installation, see
Installing Outdoor Equipment, Reference [5].
For more information on how to replace the MMU, see Replacing an MMU,
Reference [13].
5.68.3 Alarm Clearance
The alarm is cleared when access to the Far End is recovered.
5.69 High BER (Major)
Bit Error Ratio (BER)
The threshold for Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) High BER is passed
(BER threshold level). Probable causes are the following:
• Fading (flat or selective)
• Bad antenna alignment
• Link budget calculation not correct
• Presence of Interferers
SpecificProblem High BER
Source RAU IF (1+1)
AlarmType CommunicationAlarm
Severity Major
5/1543-HRA 901 20-V11 Uen J | 2014-12-03 91
You might also like
- Traffic Node AMM 2pDocument2 pagesTraffic Node AMM 2pMuhammad Rizki Amri100% (1)
- DUW & DUS Commissioning CommandDocument6 pagesDUW & DUS Commissioning CommandMENANI Zineddine100% (1)
- How To Upgrade TN Software BaselineDocument33 pagesHow To Upgrade TN Software BaselineAnjul Ramachandran80% (5)
- Transmission Installation and ConfigurationsDocument29 pagesTransmission Installation and Configurationsoliv1912100% (4)
- How To Solve RCC AlarmDocument8 pagesHow To Solve RCC AlarmWaleed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ericsson Alarms Handling ProcessDocument16 pagesEricsson Alarms Handling ProcessAjay WaliaNo ratings yet
- Format DUW 41Document27 pagesFormat DUW 41putra100% (5)
- MiniLink TN ConfigurationDocument5 pagesMiniLink TN Configurationmohsin ahmadNo ratings yet
- Installation For MoshellDocument2 pagesInstallation For MoshellNam Song Hau CTONo ratings yet
- Base Band 6630 IntegrationDocument28 pagesBase Band 6630 IntegrationAnonymous BQlWtZX3INo ratings yet
- External Alarm With 2 DUL Boards in RBS6601Document4 pagesExternal Alarm With 2 DUL Boards in RBS6601arkom0% (2)
- Configure Ericsson CLIDocument11 pagesConfigure Ericsson CLIandres1988maturin67% (9)
- DUG Commissioning Step by StepDocument36 pagesDUG Commissioning Step by StepAnonymous QFXKsONo ratings yet
- Guideline About Traffic Node EricssonDocument3 pagesGuideline About Traffic Node EricssonIgroufa NaguibNo ratings yet
- Cargar Backup de Base Band 6630Document16 pagesCargar Backup de Base Band 6630Mawel Castillo Peña100% (3)
- Easy Step Commissioning and Integration LTE DUS DUL 41 02 RBS (AutoRecovered)Document5 pagesEasy Step Commissioning and Integration LTE DUS DUL 41 02 RBS (AutoRecovered)sidney TeahNo ratings yet
- ERICSSON Node B Commissioning and IntegrationDocument34 pagesERICSSON Node B Commissioning and Integrationzakirmmughal75% (8)
- DCN Configuration Via CliDocument10 pagesDCN Configuration Via Clipankajeng100% (4)
- Installing New Software Package On DUGDocument14 pagesInstalling New Software Package On DUGAhmed Fouad50% (2)
- Solucion Jave RBS Element ManagerDocument3 pagesSolucion Jave RBS Element Managermanulink1100% (3)
- 4G BASEBAND MOSHELL COMMANDSDocument106 pages4G BASEBAND MOSHELL COMMANDSsidney Teah90% (10)
- Integration Baseband 6630/6620 Manual MethodDocument5 pagesIntegration Baseband 6630/6620 Manual Methodsidney Teah100% (2)
- BB CommandDocument3 pagesBB CommandAnonymous BQlWtZX3INo ratings yet
- TN Alarm DescriptionDocument219 pagesTN Alarm DescriptionPankaj Kumar Keshari100% (7)
- Moshell CommandsDocument4 pagesMoshell CommandsRui BeloNo ratings yet
- Show various device configuration and status informationDocument2 pagesShow various device configuration and status informationpanincong100% (2)
- TN Installation2Document25 pagesTN Installation2Javed MalikNo ratings yet
- Router 6471 Introduction and SIU - TCU Upgrade OpportunityDocument22 pagesRouter 6471 Introduction and SIU - TCU Upgrade Opportunityдмитрий ивановNo ratings yet
- Mini-Link TN R4 Licenses InstallationDocument13 pagesMini-Link TN R4 Licenses InstallationRafael0% (1)
- Bbu Alarm DescriptionsDocument36 pagesBbu Alarm DescriptionsJabNo ratings yet
- Ericsson Licenses Emergency Reset Key PDFDocument1 pageEricsson Licenses Emergency Reset Key PDFMENANI Zineddine67% (3)
- Tcu IntegrationDocument5 pagesTcu IntegrationSajid Saeed100% (9)
- Integration Baseband 5212 - 5216 Ericsson Manual MethodDocument7 pagesIntegration Baseband 5212 - 5216 Ericsson Manual Methodjcardenas55100% (5)
- Ericsson Basic MO CommandsDocument4 pagesEricsson Basic MO CommandsJoana FalcãoNo ratings yet
- Minilink User GuideDocument42 pagesMinilink User Guiderichard njenga100% (3)
- Set IP Address and Check Node ConnectivityDocument8 pagesSet IP Address and Check Node Connectivityrichard njenga100% (3)
- Ericsson Microwave ProductsDocument155 pagesEricsson Microwave Productshassan100% (1)
- Moshell CommandsDocument2 pagesMoshell CommandsEdu Mmoja Mutai100% (2)
- Guide To Configuration File Upload & Download Using Web LMT For BTS3900Document8 pagesGuide To Configuration File Upload & Download Using Web LMT For BTS3900Abouelhassan GalalNo ratings yet
- Alarm ResolutionDocument6 pagesAlarm ResolutionOpeyemi DadaNo ratings yet
- How To Change Faulty DuwDocument2 pagesHow To Change Faulty DuwEunice Bid M100% (3)
- MINI-LINK Craft User GuideDocument20 pagesMINI-LINK Craft User GuideDavid Olayinka Mosaku83% (24)
- XPIC System and XPD TestDocument2 pagesXPIC System and XPD TestDoyi100% (9)
- MINI-LINK Craft Online HelpDocument7 pagesMINI-LINK Craft Online HelpAnonymous Q6W9ADri090% (1)
- 6352 DS PDFDocument2 pages6352 DS PDFLafi FahedNo ratings yet
- SPD LTE RF Channel Troubleshooting Guide 20120718 A 1 0Document44 pagesSPD LTE RF Channel Troubleshooting Guide 20120718 A 1 0Ahmed GamalNo ratings yet
- 2G 3G Interference Analysis Caused by RTWP PDFDocument31 pages2G 3G Interference Analysis Caused by RTWP PDFDemarco Dayanghirang FormalejoNo ratings yet
- 0044-092-05 - Fireray One User Guide EnglishDocument16 pages0044-092-05 - Fireray One User Guide EnglishVladimir BukaricaNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Network Interference GuideDocument31 pagesWCDMA Network Interference GuideIfank NeutronNo ratings yet
- Coverage Optimization: 秘密 Proprietary Confidential▲Document24 pagesCoverage Optimization: 秘密 Proprietary Confidential▲DativaNo ratings yet
- Attenuation Measurement White Paper FinalDocument7 pagesAttenuation Measurement White Paper Finalm_agasenNo ratings yet
- Align Microwave Antennas GuideDocument29 pagesAlign Microwave Antennas GuideMd Al-AminNo ratings yet
- Alignment of The Microwave AntennasDocument29 pagesAlignment of The Microwave AntennasChristopher Bennett100% (3)
- Alarms On RTNDocument157 pagesAlarms On RTNCostin CalistruNo ratings yet
- Take Notes: Handover Problem Trobleshooting Adjustment and ImplementationDocument1 pageTake Notes: Handover Problem Trobleshooting Adjustment and ImplementationAnonymous pTtEWaaNo ratings yet
- R9 Mini - ManualDocument2 pagesR9 Mini - ManualTomas PilkaNo ratings yet
- Alarm Trans DescriptionDocument2 pagesAlarm Trans Descriptionarief bijaksonoNo ratings yet
- CQT Troubleshoooting V1.0Document10 pagesCQT Troubleshoooting V1.0KhangTranNo ratings yet
- Receiver Level Test TS-830 KenwoodDocument3 pagesReceiver Level Test TS-830 KenwoodIvo MFNo ratings yet
- University of North Carolina at Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument7 pagesUniversity of North Carolina at Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringVishal GewaliNo ratings yet
- Mini Link 6600Document2 pagesMini Link 6600amr_karimm67% (9)
- FactSheet TPS Controllers ORION enDocument2 pagesFactSheet TPS Controllers ORION enlacda83No ratings yet
- HUAWEI SMU02B Monitoring Unit Data Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesHUAWEI SMU02B Monitoring Unit Data Sheet PDFMorroJopal100% (1)
- Configure WANDocument1 pageConfigure WANamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- 1 TN Management IntroductionDocument2 pages1 TN Management Introductionamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- The Configure VLAN PageDocument1 pageThe Configure VLAN Pageamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- RBS Telnet-NCLI Commands PDFDocument2 pagesRBS Telnet-NCLI Commands PDFamr_karimm100% (1)
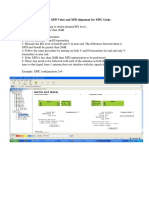
- Checking XPD Value and XPD Alignment For XPIC LinksDocument1 pageChecking XPD Value and XPD Alignment For XPIC Linksamr_karimm0% (1)
- Configuring Native Ethernet MINI-LINK TN ETSI Operating Instruction PDFDocument13 pagesConfiguring Native Ethernet MINI-LINK TN ETSI Operating Instruction PDFamr_karimm100% (1)
- Configure WAN PDFDocument1 pageConfigure WAN PDFamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Configuration of Switch Port PDFDocument1 pageConfiguration of Switch Port PDFamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Configuration of Switch PortDocument1 pageConfiguration of Switch Portamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- NEC NEO IntDocument1 pageNEC NEO Intamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Change IPASO IDUDocument3 pagesChange IPASO IDUamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- NEC Colour CodeDocument4 pagesNEC Colour CodeSamySamirNo ratings yet
- B10 BSSDocument2 pagesB10 BSSamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Change IPASO IDUDocument3 pagesChange IPASO IDUamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Change IPASO IDUDocument3 pagesChange IPASO IDUamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Alcatel lucent offline commissioning stepsDocument2 pagesAlcatel lucent offline commissioning stepsamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Shelter 1camerasDocument11 pagesShelter 1camerasamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- For Mobinil Project: Choose Free Run For The First Site As The Source of Timing, & For The Opposite Site Choose STM 1 PortDocument1 pageFor Mobinil Project: Choose Free Run For The First Site As The Source of Timing, & For The Opposite Site Choose STM 1 Portamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Gcm02-Mt-Ing4 New1 PDFDocument57 pagesGcm02-Mt-Ing4 New1 PDFabdel jabbar67% (3)
- How To Activate The E1's PortsDocument10 pagesHow To Activate The E1's PortsSallamtyNo ratings yet
- B10 BSSDocument2 pagesB10 BSSamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Ipasolink Nodal Split Mount Range PDFDocument2 pagesIpasolink Nodal Split Mount Range PDFsyqnamNo ratings yet
- B10 BSSDocument2 pagesB10 BSSamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- Upgrades Call Centre SystemDocument3 pagesUpgrades Call Centre Systemamr_karimmNo ratings yet
- En PS TS RS 005 - 0814Document4 pagesEn PS TS RS 005 - 0814amr_karimmNo ratings yet
- ltc4054-4.2, ltc4054x-4.2 LinearDocument17 pagesltc4054-4.2, ltc4054x-4.2 LinearMile MartinovNo ratings yet
- 1) Wat Is Component Controller & Parts of Component Controller?Document7 pages1) Wat Is Component Controller & Parts of Component Controller?jenibmwNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Business Studies Teacher's CD-ROM: Help NotesDocument8 pagesIGCSE Business Studies Teacher's CD-ROM: Help NotesReaz FiemNo ratings yet
- Lab 7: Amplitude Modulation and Complex Lowpass Signals: ECEN 4652/5002 Communications Lab Spring 2020Document28 pagesLab 7: Amplitude Modulation and Complex Lowpass Signals: ECEN 4652/5002 Communications Lab Spring 2020bushrabatoolNo ratings yet
- Implement Oracle Configurator Functional FlowDocument28 pagesImplement Oracle Configurator Functional FlowAntoineNo ratings yet
- Job PostingDocument1 pageJob Postingjames curcioNo ratings yet
- Payroll System AnalysisDocument16 pagesPayroll System AnalysisOswel MugabeNo ratings yet
- Lindell V Dominion Smartmatic Exhibit 2Document21 pagesLindell V Dominion Smartmatic Exhibit 2UncoverDCNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Developer/2000 For The WebDocument20 pages1.1 Introduction To Developer/2000 For The WebsadicosadicoNo ratings yet
- User Acceptance On Tax ApplicationDocument5 pagesUser Acceptance On Tax ApplicationAJHSSR JournalNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server Installation and SetupDocument34 pagesMicrosoft Exchange 2000 Server Installation and SetupsenhydNo ratings yet
- CyberArk Enterprise Password Vault 4-28-2014 enDocument2 pagesCyberArk Enterprise Password Vault 4-28-2014 enRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Programming: Lecture 10 - Event-Driven Programming Part 1Document26 pagesUnit 1 - Programming: Lecture 10 - Event-Driven Programming Part 1Bob LongNo ratings yet
- Correlation AnalysisDocument20 pagesCorrelation AnalysisVeerendra NathNo ratings yet
- ABS CBN Case StudyDocument3 pagesABS CBN Case Studyprinces mendozaNo ratings yet
- Atlas Systems OverviewDocument8 pagesAtlas Systems OverviewJoaquin Manuel Macias MartinezNo ratings yet
- The 2015 ENFSI Fingerprint Working Group TestingDocument9 pagesThe 2015 ENFSI Fingerprint Working Group TestingRuben_Monroy_ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper PVTC: Building Standards in Educational and Professional TestingDocument7 pagesSample Paper PVTC: Building Standards in Educational and Professional Testingsamey21No ratings yet
- VDISP subroutine for boundary conditionsDocument4 pagesVDISP subroutine for boundary conditionsNrl SyafiniNo ratings yet
- 'Daily Lesson Plan 2023 Class 8Document4 pages'Daily Lesson Plan 2023 Class 8hamza ShahidNo ratings yet
- Records Management Program Deliverables: Session 1 - October 11, 2017Document9 pagesRecords Management Program Deliverables: Session 1 - October 11, 2017Patricia Lorayne YapNo ratings yet
- DC Motor DrivesDocument11 pagesDC Motor DrivesVikram NikhilNo ratings yet
- TG 9780199400591 PDFDocument100 pagesTG 9780199400591 PDFkhurram ShehzadNo ratings yet
- How To Implement Birth and Death Tecnique in Ansys Workbench - ResearchGateDocument13 pagesHow To Implement Birth and Death Tecnique in Ansys Workbench - ResearchGatechethanNo ratings yet
- Oracle Service Bus 12c Development GuideDocument5 pagesOracle Service Bus 12c Development GuideImran MominNo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle ManagementDocument42 pagesRevenue Cycle ManagementAman Desai100% (2)
- 2.0 Sample Mid Career Agile Project ManagerDocument2 pages2.0 Sample Mid Career Agile Project ManagerParthoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Capability Level in Dealing With IT Business Transformation Competition Using Cobit Framework 5 (Case Study at Airasia Indonesia)Document6 pagesAnalysis of Capability Level in Dealing With IT Business Transformation Competition Using Cobit Framework 5 (Case Study at Airasia Indonesia)zoom 1234No ratings yet
- RetextDocument86 pagesRetextAndrei Cosmin TrîncăNo ratings yet
- It DBMS RecDocument77 pagesIt DBMS RecLokeshkumar Ramasamy100% (1)
- Infineon-Future Requirements For Automotive Hardware Security-Whitepaper-V01 00-ENDocument18 pagesInfineon-Future Requirements For Automotive Hardware Security-Whitepaper-V01 00-ENRavindra BNo ratings yet