Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Junos Layer 3 Vpns (Jl3V) Course Overview: P VMX#SW
Uploaded by
Sanjin ZuhricOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Junos Layer 3 Vpns (Jl3V) Course Overview: P VMX#SW
Uploaded by
Sanjin ZuhricCopyright:
Available Formats
Junos Layer 3 VPNs (JL3V)
Course Overview
JL3V (Course 5) is a three-day instructor led course and designed to
provide students with MPLS-based Layer 3 virtual private network
(VPN) knowledge and configuration examples.
JL3V study guide includes an overview of MPLS Layer 3 VPN
concepts, scaling Layer 3 VPNs, Internet access, Interprovider
L3VPNs, and Multicast for Layer 3 VPNs.
JL3V study guide covers Junos operating system-specific
implementations of Layer 3 VPNs. This course is based on the Junos
OS Release 15.1R2.9.
Through reading and practicing on vMX virtual hands-on home lab
(ESXi or KVM), students will gain experience in configuring and
monitoring the Junos OS for Layer 3 VPNs and in device operations.
Download vMX from https://www.juniper.net/support/downloads/?
p=vmx#sw after creating a guest account. Guest account takes 3
business days to be approved.
Few Instructional Video’s of BGP and L3VPN are provided as a bonus
download.
Prerequisites
Students should have intermediate-level networking knowledge and
an understanding of OSPF, ISIS, BGP, and Junos policy. Students
should have experience configuring MPLS label-switched paths
using Junos. Students should also attend the Introduction to the
Junos Operating System (IJOS), Junos Routing Essentials (JRE),
Junos Intermediate Routing (JIR) and the Junos MPLS Fundamentals
(JMF) courses prior to attending this class. Bonus prerequisite
courses are provided for an entry-level student to start with IJOS,
JRE and ramp up to JIR, JMF before reading JL3V.
Deploying vMX on ESXi Video
The Bonus video is about deploying vMX on vSphere ESXi server.
One can also learn how to configure vMX basic host settings such
as host-name, root password, ssh service and basic
management/data connectivity.
Objectives of JL3V Course is
After successfully completing this course, you should be able to:
• Describe the value of MPLS VPNs.
• Describe the differences between provider-provisioned VPNs and
customer-provisioned VPNs.
• Describe the differences between Layer 2 VPNs and Layer 3 VPNs.
• List the provider-provisioned MPLS VPN features supported by the
Junos OS software.
• Describe the roles of a CE device, PE router, and P router in a BGP
Layer 3 VPN.
• Describe the format of the BGP routing information, including VPN-
IPv4 addresses and route distinguishers.
• Describe the propagation of VPN routing information within an AS.
• List the BGP design constraints to enable Layer 3 VPNs within a
provider network.
• Explain the operation of the Layer 3 VPN data plane within a
provider network.
• Create a routing instance, assign interfaces to a routing instance,
create routes in a routing instance, and import/export routes from a
routing instance using route distinguishers/route targets.
• Describe the purpose of BGP extended communities, configure
extended BGP extended communities, and use BGP extended
communities.
• List the steps necessary for proper operation of a PE-CE dynamic
routing protocol.
• List the troubleshooting and monitoring techniques for routing
instances.
• Explain the difference between the bgp.l3vpn table and the inet.0
table of a routing instance.
• Monitor the operation of a CE-PE dynamic routing protocol.
• Explain the operation of a PE multi-access interface in a Layer 3
VPN and list commands to modify that behavior.
• Describe ways to support communication between sites attached
to a common PE router.
• Provision and troubleshoot hub-and-spoke Layer 3 VPNs,
• Describe the flow of control traffic and data traffic in a hub-and-
spoke Layer 3 VPN.
• Describe QoS mechanisms available in L3VPNs.
• Configure L3VPN over GRE tunnels.
• Describe the RFC 4364 VPN options.
• Describe the carrier-of-carriers model.
• Configure the carrier-of-carriers and "Option C" configuration.
• Describe the flow of control and data traffic in a draft-rosen
multicast VPN.
• Describe the configuration steps for establishing a draft-rosen
multicast VPN.
• Monitor and verify the operation of draft-rosen multicast VPNs.
• Describe the flow of control traffic and data traffic in a next-
generation multicast VPN.
• Describe the configuration steps for establishing a next-generation
multicast VPN.
• Describe the configuration steps for establishing a next-generation
multicast VPN.
• Monitor and verify the operation of next-generation multicast
VPNs.
• Describe the flow of control traffic and data traffic when using
MPVNs for Internet multicast.
• Describe the configuration steps for enabling internet multicast
using MVPNs.
• Monitor and verify the operation of MVPN internet
multicast.Course Contents
Chapter 1: Course Introduction
Chapter 2: MPLS VPNs
• MPLS VPNs
• Provider-Provisioned VPNs
Chapter 3: Layer 3 VPNs
• Layer 3 VPN Terminology
• VPN-IPv4 Address Structure
• Operational Characteristics
Chapter 4: Basic Layer 3 VPN Configuration
• Preliminary Steps
• PE Router Configuration
• Lab: Layer 3 VPN with Static and BGP Routing
Chapter 5: Layer 3 VPN Scaling and Internet Access
• Scaling Layer 3 VPNs
• Public Internet Access Options
• Lab: LDP over RSVP Tunnels and Public Internet Access
Chapter 6: Layer 3 VPNs – Advanced Topics
• Exchanging Routes between Routing Instances
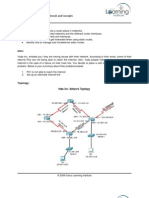
• Hub-and-Spoke Topologies
• Layer 3 VPN CoS Options
• Layer 3 VPN and GRE Tunneling Integration
• Layer 3 VPN and IPsec Integration
• Layer 3 VPN Egress Protection
• BGP prefix-independent convergence (PIC) edge for MPLS VPNs
• VRF Localization
• Provider Edge Link Protection
• Support for configuring more than 3 million L3VPN Labels
• Lab: GRE Tunneling
Chapter 7: Interprovider Backbones for Layer 3 VPNs
• Hierarchical VPN Models
• Carrier-of-Carriers Model
• Option C Configuration
• Lab: Carrier of Carrier Layer 3 VPNs
Chapter 8: Troubleshooting Layer 3 VPNs
• Working with Multiple Layers
• Troubleshooting Commands on a PE Device
• Multi-Access Interfaces in Layer 3 VPNs
• PE and CE-based Traceroutes
• Layer 3 VPN Monitoring Commands
• Lab: Troubleshooting Layer 3 VPNs
Chapter 9: Draft Rosen Multicast VPNs
• Multicast Overview
• Draft Rosen MVPN Overview
• Draft Rosen MVPN Operation
• Configuration
• Monitoring
Chapter 10: Next Generation Multicast VPNs
• Multicast VPN Overview
• Next-Generation MVPN Operation
• Configuration
• Monitoring
• Internet Multicast
• Ingress Replication
• Internet Multicast Signaling and Data Plane
• Configuring MVPN Internet Multicast
• Monitoring MVPN Internet Multicast
• Lab: MVPN Internet Multicast
Tags
JL3V, Juniper, JNPR, MPLS, label, RFC 4364, L3VPN, L2VPN, BGP Layer 3 VPN,
Layer 3 VPN, BGP VPN, VPRN, Layer 2 VPN, Kompella, VPNv4, VPN IPv4, VRF,
PE, CE-PE, logical-system, virtual router, Virtual route forwarding, routing
instance, route, MPBGP, MBGP, MP-BGP, Multi-Protocol BGP, route
distinguishers, RD, InterAS VPN, Type A, Type B, Type C, NG MVPN, MVPN, draft-
rosen, rosen, Multicast VPN, CSC, CsC, Carrier Supporting Carrier, Carrier of
Carrier’s, JUNOS, vMX, MX, 15.1R3,JNCIE, JNCIP, Core, Cisco, CCIE-SP, LDP,
martini, Service Provider, SP, Telco, Telecommunications, Telecom, core, super
core, provider network, provider, provider core, planning, WAN SDN
You might also like
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- Junos Layer 3 VPNs (JL3V) PDFDocument2 pagesJunos Layer 3 VPNs (JL3V) PDFAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Implementing Mpls Layer 3 VPNS: Software Module in The Cisco Ios XR System Management Configuration GuideDocument112 pagesImplementing Mpls Layer 3 VPNS: Software Module in The Cisco Ios XR System Management Configuration GuideChavara MatekweNo ratings yet
- PT15510 PDFDocument4 pagesPT15510 PDFCuong HaNo ratings yet
- l3vpn Asr9000Document80 pagesl3vpn Asr9000kmadNo ratings yet
- VPN l3Document1,557 pagesVPN l3sachindjjNo ratings yet
- Nexus VPN l3vpn Configuration GuideDocument60 pagesNexus VPN l3vpn Configuration GuideSon Vu TruongNo ratings yet
- Running OcNOS in GNS3 Quick Start Guide 06 23Document24 pagesRunning OcNOS in GNS3 Quick Start Guide 06 23wvdvaart.scoutingNo ratings yet
- Lab10-DNS ReBinding - BGPDocument13 pagesLab10-DNS ReBinding - BGPHuyTrần MinhNo ratings yet
- CCIE Routing & Switching Version 5.0 - VPNDocument6 pagesCCIE Routing & Switching Version 5.0 - VPNbomoarebunNo ratings yet
- Implementing Interprovider Layer 3 VPN Option BDocument26 pagesImplementing Interprovider Layer 3 VPN Option BBon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- Multiprotocol BGP MPLS VPN: Finding Feature InformationDocument14 pagesMultiprotocol BGP MPLS VPN: Finding Feature InformationDenis UdovenkoNo ratings yet
- Junos MPLS 第二層 (Junos Layer 2 VPNs)Document3 pagesJunos MPLS 第二層 (Junos Layer 2 VPNs)Li KangNo ratings yet
- B Release Notes Asr9k r742Document43 pagesB Release Notes Asr9k r742rkrao77No ratings yet
- Implementing Interprovider Layer 3 VPN Option ADocument26 pagesImplementing Interprovider Layer 3 VPN Option ABon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- Doc6 Mpls VPNDocument59 pagesDoc6 Mpls VPNUmair Ali SoomroNo ratings yet
- Layer 3 MPLS VPN Enterprise Consumer GuideDocument81 pagesLayer 3 MPLS VPN Enterprise Consumer GuideKarpov AnatolyNo ratings yet
- L3VPNDocument26 pagesL3VPNyassminbgNo ratings yet
- JL2V 21 A Lab GuideDocument184 pagesJL2V 21 A Lab GuideJustinNo ratings yet
- MVPN Ingress Replication ConfiguringDocument18 pagesMVPN Ingress Replication ConfiguringBon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- Cisco Network EngineerDocument20 pagesCisco Network EngineerAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Junos Mpls and VPNS: Student GuideDocument236 pagesJunos Mpls and VPNS: Student Guideusmanali991No ratings yet
- Configuring l2ckt To l3vpnDocument26 pagesConfiguring l2ckt To l3vpnBon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- Junos® OS Layer 3 VPNs User Guide For Routing DevicesDocument1,438 pagesJunos® OS Layer 3 VPNs User Guide For Routing DevicesAdrian IonitaNo ratings yet
- Config L2circuit To l2vpnDocument18 pagesConfig L2circuit To l2vpnBon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- CCNP ENCOR v8 Chapter & Final Exam Design DocumentsDocument19 pagesCCNP ENCOR v8 Chapter & Final Exam Design DocumentsManuel RojasNo ratings yet
- Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-As SupportDocument72 pagesConfiguring Multicast VPN Inter-As Supportmad maranNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Sistem Proxy Server Menggunakan Protokol Wccpv2 Dengan Konfigurasi Multi RouterDocument7 pagesPerancangan Sistem Proxy Server Menggunakan Protokol Wccpv2 Dengan Konfigurasi Multi RouterthetaplakNo ratings yet
- Running Multiple OcNOS VMs in EVE NG Quick Start Guide 07023Document30 pagesRunning Multiple OcNOS VMs in EVE NG Quick Start Guide 07023Ajit PatelNo ratings yet
- Implementing MPLS Layer 2 VPNsDocument40 pagesImplementing MPLS Layer 2 VPNsTameta DadaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Actualtests 642-889 v2013-11-29 by Tomer 76qDocument50 pagesCisco Actualtests 642-889 v2013-11-29 by Tomer 76qnandomironNo ratings yet
- VPN OverviewDocument30 pagesVPN OverviewPhong TrầnNo ratings yet
- Renewal Application Adult01Document15 pagesRenewal Application Adult01ry esgNo ratings yet
- B l3vpn CG Asr9000 63xDocument200 pagesB l3vpn CG Asr9000 63xkinglive_scribNo ratings yet
- Implementation of MPLS L3VPN Using GNS3: Akshay, Pooja AhlawatDocument5 pagesImplementation of MPLS L3VPN Using GNS3: Akshay, Pooja AhlawatDavidNo ratings yet
- History of VPN, Technology: Marc Debaerdemaeker BELNET, Network EngineerDocument14 pagesHistory of VPN, Technology: Marc Debaerdemaeker BELNET, Network Engineereabhishek222No ratings yet
- Remote Access Mpls VPNS: Finding Feature InformationDocument12 pagesRemote Access Mpls VPNS: Finding Feature InformationzoopiNo ratings yet
- Day 5.1Document72 pagesDay 5.1Namrata PaudelNo ratings yet
- Ccna3 3.0-07 STPDocument9 pagesCcna3 3.0-07 STPOscar FryNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document7 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNo ratings yet
- Term Project: Topic: Mpls VPNDocument8 pagesTerm Project: Topic: Mpls VPNPulavarthi Krishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Ixia T DS IxNetwork BroadbandDocument24 pagesIxia T DS IxNetwork BroadbandThành Trung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CCNA3Document11 pagesCCNA3vinbha11100% (1)
- MPLS Layer 3 VPNDocument106 pagesMPLS Layer 3 VPNNguyen Vu ThanhNo ratings yet
- B l3vpn CG Asr9000 67xDocument242 pagesB l3vpn CG Asr9000 67xgx zoliNo ratings yet
- Ccna BrochureDocument1 pageCcna BrochureMaybe CcieNo ratings yet
- INE CCIE DCv2 ATC 01300 VXLAN PDFDocument64 pagesINE CCIE DCv2 ATC 01300 VXLAN PDFAndhi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- 300 515 SpviDocument2 pages300 515 Spvihector_ninoskaNo ratings yet
- Ixia T DS IxNetwork Routing and SwitchingDocument27 pagesIxia T DS IxNetwork Routing and SwitchingThành Trung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BCNP Exam TopicsDocument2 pagesBCNP Exam TopicsMyth OsNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Network VirtualizationDocument29 pagesA Survey of Network VirtualizationMahender BishtNo ratings yet
- Jncip Ent NoteDocument4 pagesJncip Ent NoteSoumya KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Evpn PDFDocument130 pagesEvpn PDFAlex10505No ratings yet
- QoS CoursDocument88 pagesQoS CoursELMOUDDEN RachadNo ratings yet
- Network Training Ppt1Document277 pagesNetwork Training Ppt1aravindanjulie100% (1)
- RFT 999Document26 pagesRFT 999pantelimon11No ratings yet
- Brian Linkletter NetdevDocument19 pagesBrian Linkletter NetdevedvansilvaNo ratings yet
- CCNP Cisco Course Outline Exam DescriptiDocument5 pagesCCNP Cisco Course Outline Exam DescripticosmaswaridzaiNo ratings yet
- Multicast-VPN - IP Multicast Support For MPLS VPNsDocument166 pagesMulticast-VPN - IP Multicast Support For MPLS VPNsVũ Hải QuânNo ratings yet
- December 18, 2020: Announcement: New Cisco Partner Program - Integrator RoleDocument3 pagesDecember 18, 2020: Announcement: New Cisco Partner Program - Integrator RoleSanjin ZuhricNo ratings yet
- ACI Fabric Operations Partner v2021Document31 pagesACI Fabric Operations Partner v2021Sanjin ZuhricNo ratings yet
- ESA-Resources Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesESA-Resources Cheat SheetSanjin ZuhricNo ratings yet
- Cisco Umbrella: Proposal ForDocument15 pagesCisco Umbrella: Proposal ForSanjin ZuhricNo ratings yet
- 0 Readme FirstDocument294 pages0 Readme FirstSanjin ZuhricNo ratings yet
- Iz HCIE RS v1.0 - Decrypted - Clean PDFDocument384 pagesIz HCIE RS v1.0 - Decrypted - Clean PDFSanjin ZuhricNo ratings yet
- It ReportDocument6 pagesIt ReportOnahNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS For DummiesDocument29 pagesCisco IOS For DummiesGary LuNo ratings yet
- Citrix Most Used Port ListDocument18 pagesCitrix Most Used Port ListsudharaghavanNo ratings yet
- 210-060-Exam DumpDocument94 pages210-060-Exam DumpErick VarelaNo ratings yet
- 9.2.1.11 Packet Tracer - Configuring Named Standard ACLs Instructions IGDocument2 pages9.2.1.11 Packet Tracer - Configuring Named Standard ACLs Instructions IGOmar Gomez VasquezNo ratings yet
- Itt300 - Lab1Document6 pagesItt300 - Lab1Bella UnknwnNo ratings yet
- MoP - Management SWITCH & UAT SDC v0.1Document58 pagesMoP - Management SWITCH & UAT SDC v0.1Samuel ChristianNo ratings yet
- Mediaaccess Tg784: Wireless Voip GatewayDocument5 pagesMediaaccess Tg784: Wireless Voip GatewaykallesvenNo ratings yet
- Nse4 Manual FortinetDocument46 pagesNse4 Manual FortinetCiro100% (5)
- WIFI HackDocument2 pagesWIFI HackParth A ShahNo ratings yet
- Socket ProgrammingDocument6 pagesSocket ProgrammingJuan CarlosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Case StudyDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Case Studyd9700380No ratings yet
- Reference Models in Communication NetworksDocument7 pagesReference Models in Communication NetworksPRODIP DEBNo ratings yet
- Acl 4.2.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1Document3 pagesAcl 4.2.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1Emerson Emerson AemersonNo ratings yet
- DCC Practical-4Document8 pagesDCC Practical-4Noor alam ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Aruba Campus Access Webinar Part 1Document63 pagesAruba Campus Access Webinar Part 1Juan Francisco AriasNo ratings yet
- VowifiDocument23 pagesVowifiSudip Pradhan100% (1)
- Cacti Host Template Mikrotik 0.8.8a Rev1Document103 pagesCacti Host Template Mikrotik 0.8.8a Rev1aedinNo ratings yet
- Sans BoundDocument9 pagesSans BoundriyazahmedkNo ratings yet
- 4.4.2.11 Lab - Troubleshooting ACL Configuration and Placement - ILMDocument16 pages4.4.2.11 Lab - Troubleshooting ACL Configuration and Placement - ILMnoelle ganyouNo ratings yet
- Subscriber Access Ipv4 Ipv6 Dual StackDocument146 pagesSubscriber Access Ipv4 Ipv6 Dual StackTuPro FessionalNo ratings yet
- Expressway Cisco PDFDocument7 pagesExpressway Cisco PDFerika985No ratings yet
- Exinda 4062 - Quick Start Guide: WAN Optimization Made EasyDocument1 pageExinda 4062 - Quick Start Guide: WAN Optimization Made EasyLuis FernandoNo ratings yet
- ACN AssignmentDocument2 pagesACN AssignmentmetallicamegadNo ratings yet
- IT430 E-Commerce Solved MID Term Paper 04Document5 pagesIT430 E-Commerce Solved MID Term Paper 04Rimsha TariqNo ratings yet
- SRE InterviewDocument6 pagesSRE InterviewPrinceNo ratings yet
- Sangfor IAM User ManualDocument914 pagesSangfor IAM User Manualmuhammad -No ratings yet
- LPI Testking 102-500 v2020-01-18 by Oscar 57qDocument26 pagesLPI Testking 102-500 v2020-01-18 by Oscar 57qAbdellatif Ait jloulatNo ratings yet
- MacDocument2 pagesMactaeNo ratings yet
- The Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellFrom EverandThe Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- The Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerFrom EverandThe Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (34)
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyFrom EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (421)
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityFrom EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationFrom EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- So You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community That Will ListenFrom EverandSo You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community That Will ListenRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (24)
- The Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldFrom EverandThe Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (104)
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- More Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingFrom EverandMore Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (23)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Industrial Cybersecurity: ICS, Industry 4.0, and IIoTFrom EverandPractical Industrial Cybersecurity: ICS, Industry 4.0, and IIoTNo ratings yet
- Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowFrom EverandTen Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (388)
- Python for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldFrom EverandPython for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldNo ratings yet
- How to Start a Blog with WordPress: Beginner's Guide to Make Money by Writing OnlineFrom EverandHow to Start a Blog with WordPress: Beginner's Guide to Make Money by Writing OnlineRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Web Copy That Sells: The Revolutionary Formula for Creating Killer Copy That Grabs Their Attention and Compels Them to BuyFrom EverandWeb Copy That Sells: The Revolutionary Formula for Creating Killer Copy That Grabs Their Attention and Compels Them to BuyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Kill All Normies: Online Culture Wars From 4Chan And Tumblr To Trump And The Alt-RightFrom EverandKill All Normies: Online Culture Wars From 4Chan And Tumblr To Trump And The Alt-RightRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (240)
- React.js Design Patterns: Learn how to build scalable React apps with ease (English Edition)From EverandReact.js Design Patterns: Learn how to build scalable React apps with ease (English Edition)No ratings yet
- An Internet in Your Head: A New Paradigm for How the Brain WorksFrom EverandAn Internet in Your Head: A New Paradigm for How the Brain WorksNo ratings yet
- TikTok Algorithms 2024 $15,000/Month Guide To Escape Your Job And Build an Successful Social Media Marketing Business From Home Using Your Personal Account, Branding, SEO, InfluencerFrom EverandTikTok Algorithms 2024 $15,000/Month Guide To Escape Your Job And Build an Successful Social Media Marketing Business From Home Using Your Personal Account, Branding, SEO, InfluencerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)