Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydro Seeding
Uploaded by
Naveen.M.NOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydro Seeding
Uploaded by
Naveen.M.NCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydroseeding EC-4
Objectives
EC Erosion Control ;
SE Sediment Control
TR Tracking Control
WE Wind Erosion Control :
Non-Stormwater
NS
Management Control
Waste Management and
WM
Materials Pollution Control
Legend:
; Primary Objective
: Secondary Objective
Targeted Constituents
Description and Purpose
Sediment ;
Hydroseeding typically consists of applying a mixture of wood Nutrients
fiber, seed, fertilizer, and stabilizing emulsion with hydro-
Trash
mulch equipment, to temporarily protect exposed soils from
Metals
erosion by water and wind.
Bacteria
Suitable Applications Oil and Grease
Hydroseeding is suitable for soil disturbed areas requiring Organics
temporary protection until permanent stabilization is
established, and disturbed areas that will be re-disturbed
Potential Alternatives
following an extended period of inactivity.
EC-3 Hydraulic Mulch
Limitations
EC-5 Soil Binders
Hydroseeding may be used alone only when there is
sufficient time in the season to ensure adequate vegetation EC-6 Straw Mulch
establishment and coverage to provide adequate erosion EC-7 Geotextiles and Mats
control. Otherwise, hydroseeding must be used in
EC-8 Wood Mulching
conjunction with mulching (i.e., straw mulch).
Steep slopes are difficult to protect with temporary seeding.
Temporary seeding may not be appropriate in dry periods
without supplemental irrigation.
Temporary vegetation may have to be removed before
permanent vegetation is applied.
Temporary vegetation is not appropriate for short term inactivity.
January 2003 California Stormwater BMP Handbook 1 of 3
Construction
www.cabmphandbooks.com
EC-4 Hydroseeding
Implementation
In order to select appropriate hydroseeding mixtures, an evaluation of site conditions shall be
performed with respect to:
- Soil conditions - Maintenance requirements
- Site topography - Sensitive adjacent areas
- Season and climate - Water availability
- Vegetation types - Plans for permanent vegetation
The local office of the U.S.D.A. Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) is an excellent
source of information on appropriate seed mixes.
The following steps shall be followed for implementation:
Avoid use of hydroseeding in areas where the BMP would be incompatible with future
earthwork activities and would have to be removed.
Hydroseeding can be accomplished using a multiple step or one step process. The multiple
step process ensures maximum direct contact of the seeds to soil. When the one step
process is used to apply the mixture of fiber, seed, etc., the seed rate shall be increased to
compensate for all seeds not having direct contact with the soil.
Prior to application, roughen the area to be seeded with the furrows trending along the
contours.
Apply a straw mulch to keep seeds in place and to moderate soil moisture and temperature
until the seeds germinate and grow.
All seeds shall be in conformance with the California State Seed Law of the Department of
Agriculture. Each seed bag shall be delivered to the site sealed and clearly marked as to
species, purity, percent germination, dealer's guarantee, and dates of test. The container
shall be labeled to clearly reflect the amount of Pure Live Seed (PLS) contained. All legume
seed shall be pellet inoculated. Inoculant sources shall be species specific and shall be
applied at a rate of 2 lb of inoculant per 100 lb seed.
Commercial fertilizer shall conform to the requirements of the California Food and
Agricultural Code. Fertilizer shall be pelleted or granular form.
Follow up applications shall be made as needed to cover weak spots and to maintain
adequate soil protection.
Avoid over spray onto roads, sidewalks, drainage channels, existing vegetation, etc.
Costs
Average cost for installation and maintenance may vary from as low as $300 per acre for flat
slopes and stable soils, to $1600 per acre for moderate to steep slopes and/or erosive soils.
2 of 3 California Stormwater BMP Handbook January 2003
Construction
www.cabmphandbooks.com
Hydroseeding EC-4
Installed
Hydroseeding
Cost per Acre
Ornamentals $400 - $1600
High Density Turf Species $350
Bunch Grasses $300 - $1300
Annual $350 - $650
Fast Growing
Perennial $300 - $800
Native $300 - $1600
Non-Competing
Non-Native $400 - $500
Sterile Cereal Grain $500
Source: Caltrans Guidance for Soil Stabilization for Temporary Slopes, Nov. 1999
Inspection and Maintenance
Inspect BMPs prior to forecast rain, daily during extended rain events, after rain events,
weekly during the rainy season, and at two-week intervals during the non-rainy season.
Areas where erosion is evident shall be repaired and BMPs re-applied as soon as possible.
Care should be exercised to minimize the damage to protected areas while making repairs, as
any area damaged will require re-application of BMPs.
Where seeds fail to germinate, or they germinate and die, the area must be re-seeded,
fertilized, and mulched within the planting season, using not less than half the original
application rates.
Irrigation systems, if applicable, should be inspected daily while in use to identify system
malfunctions and line breaks. When line breaks are detected, the system must be shut down
immediately and breaks repaired before the system is put back into operation.
Irrigation systems shall be inspected for complete coverage and adjusted as needed to
maintain complete coverage.
References
Stormwater Quality Handbooks Construction Site Best Management Practices (BMPs) Manual,
State of California Department of Transportation (Caltrans), November 2000.
Guidance Document: Soil Stabilization for Temporary Slopes, State of California Department of
Transportation (Caltrans), November 1999.
January 2003 California Stormwater BMP Handbook 3 of 3
Construction
www.cabmphandbooks.com
You might also like
- NRLMDocument3 pagesNRLMNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Right To InformationDocument19 pagesRight To InformationNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- SoE Report 2009.Document194 pagesSoE Report 2009.Naveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Report To The People On Environment and Forests 2010 11Document52 pagesReport To The People On Environment and Forests 2010 11Naveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates CriteriaDocument16 pagesExchange Rates CriteriaNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Anthropology Syllabus For UPSC Mains ExamDocument5 pagesAnthropology Syllabus For UPSC Mains ExamNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates CriteriaDocument16 pagesExchange Rates CriteriaNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- IndiaDocument129 pagesIndiashricanadaNo ratings yet
- KalmeghDocument15 pagesKalmeghNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Iesc 107Document18 pagesIesc 107Naveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- IpecacDocument22 pagesIpecacNaveen.M.N100% (1)
- ISABGOLDocument28 pagesISABGOLNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Honey PlantDocument15 pagesHoney PlantNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Holy-Thistle Silybum Marianum: Prepared by PHK-820Document14 pagesHoly-Thistle Silybum Marianum: Prepared by PHK-820Naveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- Ornamental Trees of BangaloreDocument2 pagesOrnamental Trees of BangaloreNaveen.M.N100% (1)
- Trees BangaloreDocument51 pagesTrees BangaloreNaveen.M.N100% (1)
- Liquorice Glyricizzia Glabra 2003 ReadyDocument24 pagesLiquorice Glyricizzia Glabra 2003 ReadyNaveen.M.NNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- One-Dimensional Swell or Settlement Potential of Cohesive SoilsDocument12 pagesOne-Dimensional Swell or Settlement Potential of Cohesive SoilsRedhi Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Soil-Spring Stiffness KDocument1 pageSoil-Spring Stiffness KChartree LertsimaNo ratings yet
- World Pineapple Production: An Overview Hossain MF: DOI: 10.18697/ajfand.76.15620Document14 pagesWorld Pineapple Production: An Overview Hossain MF: DOI: 10.18697/ajfand.76.15620Reader of Down HillNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement, PrinciplesDocument28 pagesGround Improvement, PrinciplesElija NareNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients in Plant Tissue Culture (N, MG, S)Document32 pagesMacronutrients in Plant Tissue Culture (N, MG, S)bukankhadam100% (1)
- Agricultural MeteorologyDocument129 pagesAgricultural Meteorologymganpat@gmail.com92% (12)
- Nissan Cabstar e Model Tl0 Series Electronic Service ManualDocument22 pagesNissan Cabstar e Model Tl0 Series Electronic Service Manualpaulfrazier090185apo99% (128)
- ES - Q1 - Summative Test 1Document9 pagesES - Q1 - Summative Test 1Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Manual Swat CupDocument29 pagesManual Swat CupFernandoSaudContreras100% (2)
- Francis SantosDocument7 pagesFrancis SantosDianne Laurice Magnaye RodisNo ratings yet
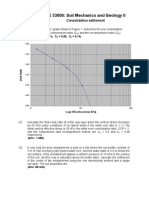
- Consolidation TutorialDocument6 pagesConsolidation TutorialJavidaNo ratings yet
- Sand Cone Method: Measurement in The FieldDocument2 pagesSand Cone Method: Measurement in The FieldAbbas tahmasebi poorNo ratings yet
- Mecánica de Suelos - ExamplesDocument13 pagesMecánica de Suelos - ExamplesHarold MantillaNo ratings yet
- Rubric For BookDocument1 pageRubric For Bookapi-491143171No ratings yet
- BWDB Technical Specification For Civil Works, First Edition - 1995Document119 pagesBWDB Technical Specification For Civil Works, First Edition - 1995Mohaiminul KarimNo ratings yet
- PARTES - TurbineMeterManual212FDocument16 pagesPARTES - TurbineMeterManual212FronaldNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Mined Tunnels in Challenging Site ConditionDocument11 pagesDesign and Construction of Mined Tunnels in Challenging Site ConditionManish Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Expansive Soil With Rice Husk Ash PDFDocument10 pagesStabilization of Expansive Soil With Rice Husk Ash PDFKiarith LópezNo ratings yet
- Role of Seed Priming in Improving Seed G 07e993d4Document9 pagesRole of Seed Priming in Improving Seed G 07e993d4Muhammad AfnanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Awareness ReviewerDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Awareness Reviewerуважать другихNo ratings yet
- Material's Engr ReviewerDocument221 pagesMaterial's Engr ReviewerMarijoy MarquezNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL AND INDUSTRIAL CORROSION (AutoRecovered)Document15 pagesENVIRONMENTAL AND INDUSTRIAL CORROSION (AutoRecovered)Sozdar Argoshi100% (1)
- Test 51Document8 pagesTest 51MinhChau HoangNo ratings yet
- Determination of PB, Cu, CR, Fe, ZN, Ni and CD Contents of Soil Dust Samples in Schools Around Onitsha MetropolisDocument65 pagesDetermination of PB, Cu, CR, Fe, ZN, Ni and CD Contents of Soil Dust Samples in Schools Around Onitsha MetropolisSkilled ScienceNo ratings yet
- Permanent Deformation Parameters of FineDocument19 pagesPermanent Deformation Parameters of FineUdo SantosNo ratings yet
- (1st Term - 2023) Basic 5 1Document44 pages(1st Term - 2023) Basic 5 1Kingsley OnyegbuleNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Pupuk Trichokompos Terhadap PERTUMBUHAN BIBIT MATOA (Pometia Pinnata) Pada Media Tanah UltisolDocument8 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Pupuk Trichokompos Terhadap PERTUMBUHAN BIBIT MATOA (Pometia Pinnata) Pada Media Tanah UltisolAgung MarsudiNo ratings yet
- Land DegradationDocument4 pagesLand DegradationSaiyan VegetaNo ratings yet
- Letter To Raise Awareness For The Growing Issue of Soil DegradationDocument4 pagesLetter To Raise Awareness For The Growing Issue of Soil DegradationAryan TomarNo ratings yet
- A. Choose The Correct OptionDocument3 pagesA. Choose The Correct OptionBhavika PirakaNo ratings yet