Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction Report Gangren 1. Definition
Uploaded by
Bem Stikes PpniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction Report Gangren 1. Definition
Uploaded by
Bem Stikes PpniCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION REPORT GANGREN b.
Urine
Examination found the presence of
1. Definition glucose in the urine. The examination is done
Gangrene is tissue death, usually associated by Benedict (reduction). The results can be
with cessation of blood flow to the affected area. seen through the color changes in urine: green
(+), yellow (++), red (+++), and red brick
2. Etiology (++++).
Gas gangrene occurs due to infection by c. Puschult culture
clostridium bacteria, which is an aerobic bacteria Know the type of germs in the wound and
(grown when there is no oxygen). During its provide antibiotics that suit the type of germs.
growth, clostridium produces gas, so the
infection is called gangrene gas. 7. Complications
1. Dry gangrene
3. Classification 2. Wet gangrene
Gangrene is a result of cell death in large 3. Gang gangrene
quantities, gangrene can be classified as dry or 4. Gangren internal
wet. 5. Fournier's gangrene
1. Dry ganggren extends slowly with only a few
symptoms. 8. Medical Management
2. Wet gangrene is an area where dead tissue is 1. Improve the general state of the patient with
rapidly expanding. adequate nutrition
2. Provision of platelet anti aggregation if
5. Manifestasi Clinis necessary, hypolipidemic and anti-
1. Usually manifested with severe sudden pain hertensi
that occurs 1 to 4 days after injury, pain 3. If suspected of a gangrene, immediately
caused by gas and edema in injury tissue. given broad-spectrum antibiotics,
2. Around the normal looking wound is brightly although for destroying clostridia only
colored and taut but then becomes dark. needed penicillin.
3. The stench of the liquid comes out of the 4. Conducted removal of damaged tissue.
wound. Gases and fluids retained increased Sometimes if the circulation is very
local pressure and disrupted the blood supply bad, part or all of the limbs must be
and drainage of visible and necrotic muscle. amputated to prevent the spread of
infection.
6.Diagnostic Examination 5. High pressure oxygen therapy (hyperbaric
DIAGNOSIS oxygen) can also be used to treat
Diagnosis of diabetic gangrene is established by : gangrene skin wide. Patients are placed in a
1. Anamnesis / clinical symptoms room containing oxygen high
2. Physical examination of "Physis diagnostic" pressure, which will help kill clostridia.
3. Laboratory examination. 6. Clean the wound on the skin thoroughly.
7. Be alert to signs of infection (redness, pain,
Laboratory tests are : discharge, swelling).
a. Blood examination
Blood tests include: GDS> 200 mg / dl,
fasting blood sugar> 120 mg / dl and two
post-prandial hours> 200 mg / dl.
You might also like
- Gangrene Is The Death of TissueDocument2 pagesGangrene Is The Death of TissuerahulbafnaeNo ratings yet
- 프레젠테이션 9Document9 pages프레젠테이션 9LEENo ratings yet
- Treatment of Gangrene in Homeopathy: ( (ISSN:2474-1361)Document6 pagesTreatment of Gangrene in Homeopathy: ( (ISSN:2474-1361)amelia henitasariNo ratings yet
- Gas Gangrene X-Ray InterpretationDocument18 pagesGas Gangrene X-Ray InterpretationarullNo ratings yet
- GANGRENEDocument27 pagesGANGRENEYvonneNo ratings yet
- TBL2 - GangreneDocument53 pagesTBL2 - Gangreneyouservezeropurpose113No ratings yet
- Gangrene: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Management: Dr. Sukanta Sen IIMSAR, HaldiaDocument27 pagesGangrene: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Management: Dr. Sukanta Sen IIMSAR, HaldiaSouvik MuhuriNo ratings yet
- GANGRENEDocument37 pagesGANGRENERick Ghosh (Shreyam)No ratings yet
- Gas GangreneDocument6 pagesGas GangreneIwan AchmadiNo ratings yet
- Surgery Mcqs PDFDocument43 pagesSurgery Mcqs PDFjcc50% (2)
- A Case of Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Successfully Treated With AcitretinDocument3 pagesA Case of Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Successfully Treated With Acitretindr_RMNo ratings yet
- GangreneDocument6 pagesGangrenedrnmraoNo ratings yet
- GangreneDocument5 pagesGangreneNader Smadi100% (2)
- GangreneDocument10 pagesGangreneNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Mucormycosis of Colon: Report of Two Cases in COVID-19Document3 pagesMucormycosis of Colon: Report of Two Cases in COVID-19International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Facilitator: Mr. Benedict Dwight LepitenDocument26 pagesFacilitator: Mr. Benedict Dwight LepitenEmmanuelle Soroño AmoresNo ratings yet
- Non Clos EcoliDocument2 pagesNon Clos EcoliNatalie Sarah MoonNo ratings yet
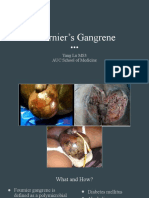
- Fournier's Gangrene: Yang Lu MS3 AUC School of MedicineDocument15 pagesFournier's Gangrene: Yang Lu MS3 AUC School of MedicineYang JunNo ratings yet
- GangreneDocument24 pagesGangreneDr. Saiba Asghar MalikNo ratings yet
- GI Disorders - IBDDocument5 pagesGI Disorders - IBDmollymaheshwari00No ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease IBD: Crohn's Disease Ulcerativ e ColitisDocument29 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease IBD: Crohn's Disease Ulcerativ e ColitisMuhammad Usman IqbalNo ratings yet
- PDF LP Ulkus DM - CompressDocument15 pagesPDF LP Ulkus DM - Compressdedi pratamaNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathic Treatment of Typhoid Fever: A Case Report: January 2022 8 (2) :2-7Document6 pagesHomoeopathic Treatment of Typhoid Fever: A Case Report: January 2022 8 (2) :2-7Aishwarya JoshiNo ratings yet
- 12 CasesDocument3 pages12 CasessharenNo ratings yet
- Sub Epidermal Blister Formation. Immunofluorescence Reveals Iga Present Within Dermal PapillaeDocument6 pagesSub Epidermal Blister Formation. Immunofluorescence Reveals Iga Present Within Dermal PapillaeRabia RabiaNo ratings yet
- GANGRENE3Document16 pagesGANGRENE3faizi gNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Addison's Disease, Adrenoleukodystrophy, Hemochromatosis, Hyperpigmentation, PrednisoloneDocument3 pagesKeywords: Addison's Disease, Adrenoleukodystrophy, Hemochromatosis, Hyperpigmentation, PrednisoloneLeslie CruzNo ratings yet
- Gangrene by DR Shriram MundheDocument20 pagesGangrene by DR Shriram MundheShriram mundheNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument4 pagesGoutapi-3822433100% (1)
- Komplikasi FrakturDocument3 pagesKomplikasi FrakturDwi Tantri SPNo ratings yet
- Aiims NOV 2010: SolutionsDocument25 pagesAiims NOV 2010: SolutionsPranav DevaniNo ratings yet
- General Surgery SEQDocument15 pagesGeneral Surgery SEQFatima Arshad100% (1)
- Gas GangreneDocument21 pagesGas GangreneSyaIra SamatNo ratings yet
- Final Joint DisorderDocument5 pagesFinal Joint DisorderAngelica PabelloNo ratings yet
- Doshi 2009Document4 pagesDoshi 2009Salsa BilaNo ratings yet
- SelulitisDocument37 pagesSelulitiswindhymonicaNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing FasciitisDocument45 pagesNecrotizing FasciitisKuchai BaruNo ratings yet
- Crusted (Norwegian) Scabies Following Systemic and Topical Corticosteroid TherapyDocument4 pagesCrusted (Norwegian) Scabies Following Systemic and Topical Corticosteroid TherapysfiahyusnitaNo ratings yet
- Piis246812531930038x PDFDocument1 pagePiis246812531930038x PDFleah asheNo ratings yet
- 42thilak EtalDocument3 pages42thilak EtaleditorijmrhsNo ratings yet
- A Patient With Caustic Ingestion Injury: Brinna Anindita Budi WidodoDocument27 pagesA Patient With Caustic Ingestion Injury: Brinna Anindita Budi WidodoBrinna Anindita SatriaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Pharmacotherapy: Case Study On Dengue Fever With ThrombocytopeniaDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Pharmacotherapy: Case Study On Dengue Fever With ThrombocytopeniaHanna La MadridNo ratings yet
- GangreneDocument19 pagesGangreneAmany SaifNo ratings yet
- Severe Necrotising Soft Tissue Infections: Other SstisDocument4 pagesSevere Necrotising Soft Tissue Infections: Other SstisAkriti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Block 3 Final: GIDocument8 pagesBlock 3 Final: GIBegNo ratings yet
- MR 22-11-22Document30 pagesMR 22-11-22abeeNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox 1Document7 pagesChickenpox 1Nica Joy CandelarioNo ratings yet
- B - Ch. 2 Inflammation and HealingDocument4 pagesB - Ch. 2 Inflammation and HealingRay Sophia CuberoNo ratings yet
- GIT OSPE Pathology - Final-2 PDFDocument29 pagesGIT OSPE Pathology - Final-2 PDFafaq alismailiNo ratings yet
- Q FeverDocument28 pagesQ FeverAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach in Generalized Pustular Psoriasis One Case Report 63a04e949936aDocument8 pagesClinical Approach in Generalized Pustular Psoriasis One Case Report 63a04e949936aThomas UtomoNo ratings yet
- NO Title: ContentDocument35 pagesNO Title: ContentradicalmpNo ratings yet
- RJZ 269Document3 pagesRJZ 269Saffa AzharaaniNo ratings yet
- Lofgren Syndrome Poster PresentationDocument1 pageLofgren Syndrome Poster PresentationShayan IqbalNo ratings yet
- SurgeryDocument14 pagesSurgeryVinit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Week 13 NCMB 312 Lect NotesDocument18 pagesWeek 13 NCMB 312 Lect NotesAngie BaylonNo ratings yet
- Efusi Pleura PPT - Id.en (Repaired)Document17 pagesEfusi Pleura PPT - Id.en (Repaired)fitriaNo ratings yet
- Actinomycetes BovisDocument11 pagesActinomycetes BovisPrathamesh RanawadeNo ratings yet
- Icm 1Document15 pagesIcm 1stephaaNo ratings yet
- Sarcoidosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandSarcoidosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Epreuve Anglais EG@2022Document12 pagesEpreuve Anglais EG@2022Tresor SokoudjouNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modelling and Design of Electrical DevicesDocument69 pagesNumerical Modelling and Design of Electrical Devicesfabrice mellantNo ratings yet
- SyncopeDocument105 pagesSyncopeJohn DasNo ratings yet
- A Review of Service Quality ModelsDocument8 pagesA Review of Service Quality ModelsJimmiJini100% (1)
- S4 HANALicensing Model External V19Document28 pagesS4 HANALicensing Model External V19Edir JuniorNo ratings yet
- Owners Manual Air Bike Unlimited Mag 402013Document28 pagesOwners Manual Air Bike Unlimited Mag 402013David ChanNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 4 - (Week 6)Document8 pagesStatistics and Probability: Quarter 4 - (Week 6)Jessa May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Bba VDocument2 pagesBba VkunalbrabbitNo ratings yet
- Adjective & VerbsDocument3 pagesAdjective & VerbsDennis BerkNo ratings yet
- CSE 202.04 Inspection of Concrete StructuresDocument67 pagesCSE 202.04 Inspection of Concrete StructuresJellyn BaseNo ratings yet
- Biological Assets Sample ProblemsDocument4 pagesBiological Assets Sample ProblemsKathleenNo ratings yet
- Form Expense ClaimDocument2 pagesForm Expense Claimviedelamonde_3868443No ratings yet
- Manual For Tacho Universal Edition 2006: Legal DisclaimerDocument9 pagesManual For Tacho Universal Edition 2006: Legal DisclaimerboirxNo ratings yet
- Building and Structural Construction N6 T1 2024 T2Document9 pagesBuilding and Structural Construction N6 T1 2024 T2FranceNo ratings yet
- Mozal Finance EXCEL Group 15dec2013Document15 pagesMozal Finance EXCEL Group 15dec2013Abhijit TailangNo ratings yet
- CS8CHP EletricalDocument52 pagesCS8CHP EletricalCristian ricardo russoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Signal and Power Integrity PDFDocument46 pagesFundamentals of Signal and Power Integrity PDFjaltitiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Basic ProbabilityDocument37 pagesChapter 4 - Basic Probabilitynadya shafirahNo ratings yet
- 1.SDH Basics PDFDocument37 pages1.SDH Basics PDFsafder wahabNo ratings yet
- Binary OptionsDocument24 pagesBinary Optionssamsa7No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETSDocument5 pagesLesson Plan For Implementing NETSLisa PizzutoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Retail LoansDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Retail LoansSameer ShahNo ratings yet
- Ecs h61h2-m12 Motherboard ManualDocument70 pagesEcs h61h2-m12 Motherboard ManualsarokihNo ratings yet
- 2016 W-2 Gross Wages CityDocument16 pages2016 W-2 Gross Wages CityportsmouthheraldNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument11 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationnmclaughNo ratings yet
- Genomic Tools For Crop ImprovementDocument41 pagesGenomic Tools For Crop ImprovementNeeru RedhuNo ratings yet
- CS-6777 Liu AbsDocument103 pagesCS-6777 Liu AbsILLA PAVAN KUMAR (PA2013003013042)No ratings yet
- 레벨 테스트Document2 pages레벨 테스트BNo ratings yet
- Automatic Gearbox ZF 4HP 20Document40 pagesAutomatic Gearbox ZF 4HP 20Damien Jorgensen100% (3)
- EGurukul - RetinaDocument23 pagesEGurukul - RetinaOscar Daniel Mendez100% (1)