Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract Jurnal 2
Uploaded by
Mentari Indah Sari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageabstrak jurnal
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentabstrak jurnal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageAbstract Jurnal 2
Uploaded by
Mentari Indah Sariabstrak jurnal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Journal reading
Ruxolitinib is effective and safe in Japanese patients with
hydroxyurea-resistant or hydroxyurea-intolerant polycythemia
Vera with splenomegaly
Keita Kirito, Kenshi Suzuki, Koichi Miyamura, Masahiro Takeuchi, Hiroshi Handa,
Shinichiro Okamoto, et al int J Hematol, September 27 2017
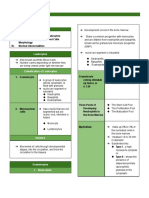
Polycythemia Vera is the One of the chronic myeloproliferative disorders
characterized by clonal proliferation of myeloid cells in which the bone marrow
produces too many red blood cells. Preclinical studies identified activating
mutations in the Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2) gene as the underlying molecular cause for
aberrant hematopoiesis and myeloproliferative disease.
Is a randomized, open-label, multicenter, phase 3 study evaluating the
efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib in patient with PV patients were randomized 1 : 1
to receive ruxolitinib 10 mg twice daily or BAT (best available therapy a total of
18 Japanese patients with 6 randomized to ruxolitinib and 12 randomized to BAT.
Primary analysis occurred after all patients completed week 48. The composited
primary endpoint was the percentage of patients of patients who achieved both
hematocrit control and a spleen response at week 32. Secondary endpoints included
the percentage of patients who achieved CHR (complete hematologic remission) at
week 32 and the percentage of patients who maintained the primary response ay
week 48.
The Japanese cohort had a greater proportion of younger patients (median
age, 57 vs 62 years), patient with hydroxyurea resistant (100 vs 94.5%), and patients
carrying a JAK2V17F mutation (100 vs 94.5%). Group had smaller proportion of
man (50% vs 60%) and patients had a shorter duration (4.2 vs 8.2% years), had
fewer occurrence of prior thromboembolic events (16.7 vs 35.5%) and had smaller
spleen (826 vs 1195 cm3) at baseline higher proportions of Japanese patients had
received ≥ 3 phlebotomies 24 weeks prior to randomization (50% vs 30.9%).
In conclusion, Ruxolitinib was superior to BAT in providing hematocrit
control, reducing splenomegaly, and improved symptoms in Japanese patient with
PV. ruxolitinib may be a potential new treatment option in Japanese patients with
PV who have an inadequate response to or have unacceptable side effect from
hydroxyurea
Will be presented by Noveldy Calzoum Bachry
On Friday, January 19th 2018
You might also like
- Skenario C Blok 20Document64 pagesSkenario C Blok 20Mentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Emergencies: Dispnu ?Document35 pagesRespiratory Emergencies: Dispnu ?Mentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Iron OverloadDocument9 pagesIron OverloadMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Natural Disaster On ChildrenDocument20 pagesImpacts of Natural Disaster On ChildrenMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Tugas Jurnal Rehab 2015Document8 pagesTugas Jurnal Rehab 2015Mentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Highlights: 2017 G P, D, e M H B P ADocument2 pagesHighlights: 2017 G P, D, e M H B P AJamie LittleNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb IschaemiaDocument23 pagesAcute Limb IschaemiaMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Skenario A Blok 19 Kelompok L1: PsoriasisDocument10 pagesSkenario A Blok 19 Kelompok L1: PsoriasisMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Case-control methodology checklistDocument3 pagesCase-control methodology checklistMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Skenario A Blok19Document15 pagesSkenario A Blok19Mentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Anti Malaria ResistanceDocument7 pagesAnti Malaria ResistanceMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Skenario E Blok 23 Kelompok 3: Tutor: DR - Nursanti Apriyanti, SP - PADocument20 pagesSkenario E Blok 23 Kelompok 3: Tutor: DR - Nursanti Apriyanti, SP - PAMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Skenario A Blok 19: Kelompok L8 Tutor: Dr. Linda Trisna, SP.M (K)Document14 pagesSkenario A Blok 19: Kelompok L8 Tutor: Dr. Linda Trisna, SP.M (K)Mentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- BSB LaundryDocument1 pageBSB LaundryMentari Indah SariNo ratings yet
- Skenario C Blok 8Document2 pagesSkenario C Blok 8Arrisalatunnuriyah AnamNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Drug Therapy and Interactions in Pediatric Oncology - A Pocket Guide-Springer International Publishing (2017) PDFDocument223 pagesDrug Therapy and Interactions in Pediatric Oncology - A Pocket Guide-Springer International Publishing (2017) PDFkrajonessNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative Disorders PDFDocument52 pagesMyeloproliferative Disorders PDFBoneyJalgar100% (3)
- Investigation and Management of Erythrocytosis: ReviewDocument6 pagesInvestigation and Management of Erythrocytosis: ReviewCamilo CaceresNo ratings yet
- ICKSH2019 AbstractBookDocument396 pagesICKSH2019 AbstractBookRimaNo ratings yet
- Hematology Review Section on Blood Cells and DevelopmentDocument79 pagesHematology Review Section on Blood Cells and DevelopmentLUZVIMINDA GORDONo ratings yet
- A Review On The Role of C Kit SCF System in Hematological MalignanciesDocument5 pagesA Review On The Role of C Kit SCF System in Hematological MalignanciesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- HepatosplenomegalyDocument52 pagesHepatosplenomegalySundar NatarajanNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cell Disorders: Neoplastic Diseases of The BloodDocument81 pagesWhite Blood Cell Disorders: Neoplastic Diseases of The BloodMiguel Cuevas Dolot100% (1)
- Diagnosis and Clinical Manifestations of Essential ThrombocythemiaDocument27 pagesDiagnosis and Clinical Manifestations of Essential ThrombocythemiaValeria GamboaNo ratings yet
- Alvin Ip PDFDocument68 pagesAlvin Ip PDFmochkurniawanNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Differential Diagnosis in Neoplastic Hematopathology CRCDocument874 pagesAtlas of Differential Diagnosis in Neoplastic Hematopathology CRCJuan RivasNo ratings yet
- Jack 2Document5 pagesJack 2Josue BarralNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloproliferative DiseasesDocument84 pagesChronic Myeloproliferative DiseasesKayzee CruzNo ratings yet
- Hematology ReviewerDocument26 pagesHematology ReviewerYo Issei HyodonoNo ratings yet
- Short Cases: Gastroenterology Part 2 Exam PrepDocument48 pagesShort Cases: Gastroenterology Part 2 Exam PrepMobeen RazaNo ratings yet
- 1607613832Document646 pages1607613832Andrei-Dorin BicaNo ratings yet
- LMMC ManagementDocument44 pagesLMMC ManagementLuciano LaranjeiraNo ratings yet
- Essential ThrombocytosisDocument5 pagesEssential ThrombocytosisDina MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Pathology Revision E6.5Document130 pagesPathology Revision E6.5vikashchahal1987No ratings yet
- 2016 EdBookDocument931 pages2016 EdBookvarun7189100% (1)
- Non-Hodgkin'S Lymphoma: Oliveros Francis!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Document48 pagesNon-Hodgkin'S Lymphoma: Oliveros Francis!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!francis00090No ratings yet
- Polycythemia Vera and Cerebrovascular EventsDocument67 pagesPolycythemia Vera and Cerebrovascular EventsChristian Gallardo, MD100% (1)
- Hema 2Document31 pagesHema 2Mark SyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Polycythemia Vera: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Polycythemia Vera: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Up To Date LMMCDocument23 pagesUp To Date LMMCLuciano LaranjeiraNo ratings yet
- FS13 PolycythemiaVera FactSheetDocument7 pagesFS13 PolycythemiaVera FactSheetMala 'emyu' UmarNo ratings yet
- Hematology Lec MidtermDocument10 pagesHematology Lec MidtermLoren EscotoNo ratings yet
- Haematopathology 3:: Leucocytosis/LeucopeniaDocument113 pagesHaematopathology 3:: Leucocytosis/LeucopeniaarwaNo ratings yet
- B Lood: Bleeding and Thrombosis in The Myeloproliferative DisordersDocument13 pagesB Lood: Bleeding and Thrombosis in The Myeloproliferative DisordersJicko Street HooligansNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative DisorderDocument36 pagesMyeloproliferative DisorderKalpana ShahNo ratings yet