Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vibration Acceptance Criteria
Uploaded by
Amal Ka0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
445 views3 pagesThis document provides vibration acceptance testing limits for centrifugal pumps, fans, and other rotating equipment. It specifies that pump bearing housing vibration should not exceed 6.1 mm/sec when measured at rated speed and flow. For centrifugal fans, maximum vibration on the bearing housing cannot exceed 3.7 mm/sec. Acceptance limits for rigid and flexible foundations/supports are also provided, with rigid supports having lower limits than flexible supports.
Original Description:
Vibration acceptance criteria
Original Title
Vibration acceptance criteria
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides vibration acceptance testing limits for centrifugal pumps, fans, and other rotating equipment. It specifies that pump bearing housing vibration should not exceed 6.1 mm/sec when measured at rated speed and flow. For centrifugal fans, maximum vibration on the bearing housing cannot exceed 3.7 mm/sec. Acceptance limits for rigid and flexible foundations/supports are also provided, with rigid supports having lower limits than flexible supports.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
445 views3 pagesVibration Acceptance Criteria
Uploaded by
Amal KaThis document provides vibration acceptance testing limits for centrifugal pumps, fans, and other rotating equipment. It specifies that pump bearing housing vibration should not exceed 6.1 mm/sec when measured at rated speed and flow. For centrifugal fans, maximum vibration on the bearing housing cannot exceed 3.7 mm/sec. Acceptance limits for rigid and flexible foundations/supports are also provided, with rigid supports having lower limits than flexible supports.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
VIBRATION ACCEPTANCE TESTING FOR CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
OVERHUNG PUMPS
CENTERHUNG PUMPS
VIBRATION ACCEPTANCE
When a performance test is required, bearing housing vibration
shall be measured in the horizontal, vertical, and axial planes. The
measurement shall be taken at the pump's rated speed (+/- 5 pct.)
and from minimum continuous allowable flow to rated flow.
Vibration limits in any plane shall not exceed Vibration limits in
any plane shall not exceed 6.1 mm/sec (0.25 in/sec) 0-peak
velocity.
CENTRIFUGAL FAN
VIBRATION ACCEPTANCE FOR CENTRIFUGAL FANS
Maximum vibration velocity amplitude measured in any plane on the
bearing housing shall not exceed 3.7 mm/sec Pk.
Foundation/ Support Structure class as per ISO 10816-3 :
Rigid Support &Flexible Support :
These support conditions are determined by the relationship
between the machine and foundation flexibilities. If the lowest
natural frequency of the combined machine and support system in
the direction of measurement is higher than its main excitation
frequency by at least 25% , then the support system may be
considered rigid in that direction. All other support systems may be
considered flexible.
As typical examples, large and medium-sized machines with low
speeds, would normally have rigid supports, whereas turbo-
generators or compressors with power greater than 10MW and
vertical machine sets would usually have flexible supports.
In some cases, a support assembly may be rigid in one measuring
direction and flexible in the other. For example, the lowest natural
frequency in the vertical direction may be well above the main
excitation frequency, while the horizontal natural frequency may be
considered less. Such a system would be stiff in the vertical plane
but flexible in the horizontal. In such cases, the vibration should be
evaluated in accordance with the support classification which
corresponds to the measurement direction.
Rigid Support : 3.7mm/sec Pk
Flexible Support : 6.1 mm/sec Pk
Foundation/ Support Structure class as per ISO 10816-3 :
Rigid Support &Flexible Support :
These support conditions are determined by the relationship
between the machine and foundation flexibilities. If the lowest
natural frequency of the combined machine and support system in
the direction of measurement is higher than its main excitation
frequency by at least 25% , then the support system may be
considered rigid in that direction. All other support systems may be
considered flexible.
As typical examples, large and medium-sized machines with low
speeds, would normally have rigid supports, whereas turbo-
generators or compressors with power greater than 10MW and
vertical machine sets would usually have flexible supports.
In some cases, a support assembly may be rigid in one measuring
direction and flexible in the other. For example, the lowest natural
frequency in the vertical direction may be well above the main
excitation frequency, while the horizontal natural frequency may be
considered less. Such a system would be stiff in the vertical plane
but flexible in the horizontal. In such cases, the vibration should be
evaluated in accordance with the support classification which
corresponds to the measurement direction.
Rigid Support : 6.1 mm/sec Pk
Flexible Support : 10.0 mm/sec Pk
You might also like
- Manual Partes d75ksDocument736 pagesManual Partes d75ksvicar_27100% (7)
- Foundation Design For Vibrating Machines PDFDocument2 pagesFoundation Design For Vibrating Machines PDFSheiss Nabi50% (2)
- VibrationDocument4 pagesVibrationzhyhh100% (1)
- Sleeve Vs Antifriction Bearings Selection of The Optimal BearingDocument13 pagesSleeve Vs Antifriction Bearings Selection of The Optimal BearingKamal Arab0% (1)
- Foundation Design Philosophy For Rotating EquipmentDocument6 pagesFoundation Design Philosophy For Rotating EquipmentViswanathan NaraNo ratings yet
- Fans & Blowers-Calculation of PowerDocument20 pagesFans & Blowers-Calculation of PowerPramod B.Wankhade92% (24)
- Blade VibrationDocument8 pagesBlade VibrationAmal Ka100% (1)
- 14 EX5600-6 Principios de Operacion - ToKCA-E-00Document333 pages14 EX5600-6 Principios de Operacion - ToKCA-E-00sebastian67% (3)
- Monitoring and Analysis of Machine VibrationDocument6 pagesMonitoring and Analysis of Machine VibrationAvinashNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 - Typical FFT Showing Gear MisalignmentDocument4 pagesFigure 1 - Typical FFT Showing Gear MisalignmentDario SesarNo ratings yet
- Rotary Screw CompressorDocument4 pagesRotary Screw CompressorNAYEEMNo ratings yet
- SCHROEDER Automatic Recirculation Check ValveDocument14 pagesSCHROEDER Automatic Recirculation Check ValveAli Bari100% (1)
- Training, Class I, Testing, IIb, 1-10Document12 pagesTraining, Class I, Testing, IIb, 1-10luis_hernandez_qNo ratings yet
- BETA MACHINERY Specification For Reciprocating Compressor Pulsation-Vibration Study 2014Document4 pagesBETA MACHINERY Specification For Reciprocating Compressor Pulsation-Vibration Study 2014Radu BabauNo ratings yet
- Rim and Face - Alignment KnowledgeDocument19 pagesRim and Face - Alignment Knowledgevj kumarNo ratings yet
- Article Balancing of Rotor BladesDocument5 pagesArticle Balancing of Rotor BladesAhmedFaissalNo ratings yet
- 07 VogelDocument10 pages07 VogelAnonymous OFwyjaMyNo ratings yet
- 5000 KW Gearbox High Pinion Bearing Temperatures 1644227029Document7 pages5000 KW Gearbox High Pinion Bearing Temperatures 1644227029MC ANo ratings yet
- 2130 - Advanced Fast Balance - 97059 - 1CD PDFDocument432 pages2130 - Advanced Fast Balance - 97059 - 1CD PDFLuisSilva100% (1)
- Windrock 6320 Brochure 2013Document4 pagesWindrock 6320 Brochure 2013Amaury André100% (1)
- Impeller and Centrifugal Pump OutputDocument2 pagesImpeller and Centrifugal Pump Outputejzuppelli8036No ratings yet
- Rolling Element Bearings Vibration AnalysisDocument10 pagesRolling Element Bearings Vibration AnalysisSiva Kulanji100% (1)
- Vibxpert 2 Manual English 112010Document170 pagesVibxpert 2 Manual English 112010santiago6767% (3)
- Alignment Protocol: Siemens LTDDocument6 pagesAlignment Protocol: Siemens LTDhalder_kalyan9216100% (2)
- Bump test guidelinesDocument1 pageBump test guidelinesDaryl DelimanNo ratings yet
- SPM HD Case StoryDocument34 pagesSPM HD Case StorycatraioNo ratings yet
- DFC Install MaintDocument40 pagesDFC Install MaintAvinash Gamit100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pump Operating Range As Per API 610 - LinkedInDocument2 pagesCentrifugal Pump Operating Range As Per API 610 - LinkedInragulNo ratings yet
- Report - Vibration TestDocument26 pagesReport - Vibration TestHugo MaiaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Sopal Gayatri Sanjay. - Coupling Types & ApplicationDocument15 pagesSubmitted By:: Sopal Gayatri Sanjay. - Coupling Types & ApplicationB.AishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Index BalancingDocument22 pagesIndex BalancingShailesh Dalal100% (2)
- BOP Control Unit Sizing ADES With 13-5-8Document4 pagesBOP Control Unit Sizing ADES With 13-5-8Ajay Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Practical Use of Dynamic Vibration AbsorbersDocument4 pagesPractical Use of Dynamic Vibration AbsorbersDan-jones TudziNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Balancing of Rigid - Flexible - Linked PDFDocument119 pagesCh3 Balancing of Rigid - Flexible - Linked PDFAlexis CordovaNo ratings yet
- Balance Quality Requirements of Rigid Rotors - The Practical Application of ISO 1940-1Document11 pagesBalance Quality Requirements of Rigid Rotors - The Practical Application of ISO 1940-1FabbroxNo ratings yet
- Nadella - Needle BearingsDocument230 pagesNadella - Needle Bearingsג'ון ירוקNo ratings yet
- Roots BlowerDocument2 pagesRoots Blowereko bagus sunaryoNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor Case StudyDocument13 pagesCentrifugal Compressor Case Studybbmoksh100% (1)
- Dm200 CatalogDocument6 pagesDm200 CatalogAS_865025438No ratings yet
- Ansi Abma S2.42 PDFDocument40 pagesAnsi Abma S2.42 PDFJohn Jairo Bueno Ortiz100% (1)
- KKM Centrifugal Compressor SystemsDocument8 pagesKKM Centrifugal Compressor SystemsefeNo ratings yet
- Low Speed Fans Application Guide MiningDocument20 pagesLow Speed Fans Application Guide MiningsanthoshdonNo ratings yet
- How Long Will A Bearing Last? Standardized Life Equations Help To AnswerDocument3 pagesHow Long Will A Bearing Last? Standardized Life Equations Help To AnswervijaykhandgeNo ratings yet
- Cementing Unit Mixes FluidsDocument2 pagesCementing Unit Mixes FluidshidayatNo ratings yet
- Article Balancing of Rotor Blades PDFDocument5 pagesArticle Balancing of Rotor Blades PDFClaudio SalicioNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Centrifugal Pump Faults Using Vibration MethodsDocument12 pagesDiagnosis of Centrifugal Pump Faults Using Vibration MethodsHatem ShawkiNo ratings yet
- c137638 - Vibration Characteristics of Diesel Driven Emergency Fire Pump SDocument7 pagesc137638 - Vibration Characteristics of Diesel Driven Emergency Fire Pump SRoberto Trujillo HermitañoNo ratings yet
- Limited End Float Couplings: CautionDocument2 pagesLimited End Float Couplings: CautionsanthoshNo ratings yet
- Foundations For Vibrating MachinesDocument2 pagesFoundations For Vibrating MachinesLavanyan100% (1)
- Introduction To Vibration & Pulsation in Reciprocating Compressors (Beta)Document28 pagesIntroduction To Vibration & Pulsation in Reciprocating Compressors (Beta)FabbroxNo ratings yet
- Pumps and SystemsDocument5 pagesPumps and SystemsYashwant Kumar Saini100% (2)
- Foundations For Vibrating Machines: Home American Canadian General Im-ExportDocument3 pagesFoundations For Vibrating Machines: Home American Canadian General Im-ExportsachinapkarNo ratings yet
- Machine FoundationsDocument3 pagesMachine Foundationssyed Affan0% (1)
- FOUNDATION DESIGN OPTIMIZATION FOR ROTATING EQUIPMENTDocument38 pagesFOUNDATION DESIGN OPTIMIZATION FOR ROTATING EQUIPMENTChiedu OkonduNo ratings yet
- Natural Frequency Testing GuideDocument12 pagesNatural Frequency Testing GuideRais RijalNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis SpecificationsDocument3 pagesVibration Analysis SpecificationsLe Thanh HaiNo ratings yet
- VIBGUARD XPLow-frequency Vibrations - Online Condition Monitoring - WirelessDocument10 pagesVIBGUARD XPLow-frequency Vibrations - Online Condition Monitoring - WirelessLake HouseNo ratings yet
- Civil Design Help Foundation For Machines PDFDocument4 pagesCivil Design Help Foundation For Machines PDFSheissNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design Philosophy For Rotating EquipmentDocument7 pagesFoundation Design Philosophy For Rotating EquipmentKyaw Kyaw AungNo ratings yet
- Theory of Wind Turbine DesignDocument23 pagesTheory of Wind Turbine DesignVikram NikhilNo ratings yet
- Aptd - TCBRDocument8 pagesAptd - TCBRRiteshBhattNo ratings yet
- General Requirements For Machine FoundationsDocument3 pagesGeneral Requirements For Machine Foundationstaz_taz3No ratings yet
- Linear & Manual - ActuatorDocument20 pagesLinear & Manual - ActuatorsviswaNo ratings yet
- Control of Wind TurbinesDocument14 pagesControl of Wind TurbinesSenad SmakaNo ratings yet
- Piping Plan Pocket PalDocument66 pagesPiping Plan Pocket PalmflorespazosNo ratings yet
- 04 Todd BurlingameDocument9 pages04 Todd BurlingameAmal KaNo ratings yet
- 04 Todd BurlingameDocument9 pages04 Todd BurlingameAmal KaNo ratings yet
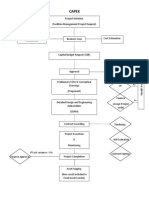
- CAPEXDocument1 pageCAPEXAmal KaNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Loads Piping Stresses and The Effect of Piping On EquipmentDocument40 pagesNozzle Loads Piping Stresses and The Effect of Piping On Equipmentcaesar00100% (6)
- Surge CalculationsDocument21 pagesSurge CalculationscordoNo ratings yet
- Piping Plan Pocket PalDocument66 pagesPiping Plan Pocket PalmflorespazosNo ratings yet
- FTA157 Piping Plan PosterDocument1 pageFTA157 Piping Plan PosterGloria HamiltonNo ratings yet
- PVC Piping Systems-PPFADocument40 pagesPVC Piping Systems-PPFAAmal KaNo ratings yet
- API 510 PC 20 Aug05 PTR 1Document3 pagesAPI 510 PC 20 Aug05 PTR 1Amal KaNo ratings yet
- Xylem Guide To BlowersDocument11 pagesXylem Guide To BlowersAmal KaNo ratings yet
- KentDocument15 pagesKentAmal KaNo ratings yet
- API 510 PC 20 Aug05 PTR 1Document3 pagesAPI 510 PC 20 Aug05 PTR 1Amal KaNo ratings yet
- TechA Calculo NPSHDocument140 pagesTechA Calculo NPSHAmal Ka100% (1)
- Vol 3 No 1 P 27Document10 pagesVol 3 No 1 P 27Az HassanNo ratings yet
- Thesis AndreArsenio TUD FinalDocument166 pagesThesis AndreArsenio TUD FinalAmal KaNo ratings yet
- The STP Guide-Design, Operation and MaintenanceDocument74 pagesThe STP Guide-Design, Operation and MaintenanceRajesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Mohammadi, KeramatDocument104 pagesMohammadi, KeramatObie AkpachioguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document110 pagesChapter 06Avinash VasudeoNo ratings yet
- Project Standards and Specifications Precommissioning Piping Cleaning Rev01Document5 pagesProject Standards and Specifications Precommissioning Piping Cleaning Rev01Tiago HenriquesNo ratings yet
- AFTFathomInstructions PDFDocument532 pagesAFTFathomInstructions PDFAmal KaNo ratings yet
- 2014 CompassDocument540 pages2014 CompassAmal KaNo ratings yet
- PVC Piping Systems-PPFADocument40 pagesPVC Piping Systems-PPFAHarendra RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- Awwa - C905 - (2010) PVC PDFDocument40 pagesAwwa - C905 - (2010) PVC PDFoscarpetroflexNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document110 pagesChapter 06Avinash VasudeoNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer in Irrigation SystemsDocument6 pagesWater Hammer in Irrigation SystemsAmal KaNo ratings yet
- Overhead Hoists and Underhung CranesDocument45 pagesOverhead Hoists and Underhung CranesSurendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer in Pumped Sewer MainsDocument45 pagesWater Hammer in Pumped Sewer MainsAmal KaNo ratings yet
- The New World Standard 150-Ton Crawler CraneDocument8 pagesThe New World Standard 150-Ton Crawler CranenguyenteoNo ratings yet
- GTU-Paper-Analysis PDF All 20052019023808PMDocument13 pagesGTU-Paper-Analysis PDF All 20052019023808PMShubham PatelNo ratings yet
- Machine - EAME Course Catalog 2015 v1 PDFDocument99 pagesMachine - EAME Course Catalog 2015 v1 PDFCarlosNo ratings yet
- Considering The Effect of Crude Oil Viscosity On Pumping Requirements - Campbell Tip of The MonthDocument6 pagesConsidering The Effect of Crude Oil Viscosity On Pumping Requirements - Campbell Tip of The MonthalexescNo ratings yet
- Amca Mev A e 06 07 PDFDocument32 pagesAmca Mev A e 06 07 PDFthijssilderhuisNo ratings yet
- Internal Gear Pump ManualDocument16 pagesInternal Gear Pump ManualKhalid AbdelRahimNo ratings yet
- WQ (11-22kW) Series Submersible Sewage Pumps WQ (30kW and Above) Series Intelligent Submersible Sewage PumpsDocument10 pagesWQ (11-22kW) Series Submersible Sewage Pumps WQ (30kW and Above) Series Intelligent Submersible Sewage PumpsĐông DươngNo ratings yet
- Utilized Mud Pump Parts ListDocument16 pagesUtilized Mud Pump Parts ListJuan Felipe Garza GNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument118 pagesFinal Reportdivmech1988No ratings yet
- WA380-6 Brake SystemDocument26 pagesWA380-6 Brake SystemCharlene Diocadiz100% (1)
- 4143.020.073 2 HL 270 PDF Transmission (Mechanics) Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 page4143.020.073 2 HL 270 PDF Transmission (Mechanics) Mechanical EngineeringАртурNo ratings yet
- Acople R Falk CaireDocument16 pagesAcople R Falk CaireLuis DiazNo ratings yet
- Testing and adjusting standard value table for Komatsu WB146-5 backhoe loaderDocument39 pagesTesting and adjusting standard value table for Komatsu WB146-5 backhoe loaderLuis Gustavo Escobar MachadoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief ValveDocument25 pagesPressure Relief ValvedhananjayNo ratings yet
- RIELO RL - 70mDocument52 pagesRIELO RL - 70mspace recycling levanteNo ratings yet
- 013.0 - 6060 - Central Greasing System - Attachment - CATDocument51 pages013.0 - 6060 - Central Greasing System - Attachment - CAThectorNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief EssentialsDocument33 pagesPressure Relief EssentialsValdasarineNo ratings yet
- Manzel - Graco PumpsDocument16 pagesManzel - Graco Pumpsfriend301283No ratings yet
- TF4JJ PDFDocument992 pagesTF4JJ PDFDelia Maribel Velez Cueva100% (4)
- DT Swiss Shocks XM180 XRcarbon User ManualDocument1 pageDT Swiss Shocks XM180 XRcarbon User ManualcorrabNo ratings yet
- LVDH owners manual provides instructions for vacuum dehydratorDocument26 pagesLVDH owners manual provides instructions for vacuum dehydratorAmit Biswas50% (6)
- Syltherm XLT CatalogDocument27 pagesSyltherm XLT CatalogJose Angel MalumbresNo ratings yet
- Kamoer Pump Catalog v2.0Document124 pagesKamoer Pump Catalog v2.0Helmut PaygateglobalNo ratings yet
- A-RSJV-GEN-IMS-SOP-038 Fueling and Refueling at Site. Rev 01Document13 pagesA-RSJV-GEN-IMS-SOP-038 Fueling and Refueling at Site. Rev 01Ya VinNo ratings yet
- Engineering Laboratory V BDA37201 Fluid Mechanics 2 and Thermodynamic 2Document23 pagesEngineering Laboratory V BDA37201 Fluid Mechanics 2 and Thermodynamic 2Irfan HarrazNo ratings yet
- Slurry Transport Using Centrifugal Pumps - InDICEDocument5 pagesSlurry Transport Using Centrifugal Pumps - InDICECarlos Cortés Ramos20% (5)
- NH3 Catalog 1.19Document108 pagesNH3 Catalog 1.19Jhon MarzanaNo ratings yet
- MMPX Separation System - Alarms and Fault Finding - 1995Document31 pagesMMPX Separation System - Alarms and Fault Finding - 1995Centrifugal SeparatorNo ratings yet