Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fagaceae: The Oak and Beech Family
Uploaded by
Mirna BulaciosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fagaceae: The Oak and Beech Family
Uploaded by
Mirna BulaciosCopyright:
Available Formats
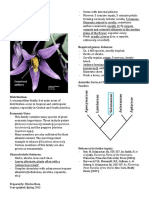
Fagaceae Economic Uses:
- This family is the source of a majority of the
The Oak and Beech Family world’s hardwood timbers, the most notable
7 genera being oak, beech and chestnut.
900 species - Commercial cork is derived from the bark of
the Mediterranean cork oak (Quercus suber).
- Many species of chestnut, but especially
Sweet Chestnut (Castanea sativa), are grown
for their large, edible nuts.
- The Iowa state tree is the Red Oak (Q. rubra).
Rosids: Reduced Phylogeny of Required Families
Male
flowers
Female
flowers Characteristic features:
- Trees and shrubs.
- Flowers: unisexual (monoceious); usually 6
reduced/inconspicuous tepals; 4 to many
stamens; 3(-12) carpels, connate in an
inferior ovary.
- Male inflorescences in dangling catkins.
- Female inflorescences in sessile clusters.
- Fruit: a nut, associated with a spiny or scaly
cupule.
Required genus: Quercus
References for further inquiry:
- Govaerts, R. & Frodin, D.G. World Checklist and
Distribution: Bibliography of Fagales (Betulaceae, Corylaceae,
Widespread in tropical to temperate regions of Fagaceae and Ticodendraceae). Richmond, Royal
the northern hemisphere. In total, Fagaceae Botanic Gardens, Kew (1998).
represents a huge biomass, possibly exceeded - Heywood, V.H., Brummitt, R.K., Culham, A., &
only by the conifers. This family also has a long Seberg, O. Fagaceae. Pp. 147-149. In: Flowering
fossil record, with the origin dated to about 90 Plant Families of the World. New York, Firefly
million years ago. Books (2007).
Prepared by: Mischa Olson
Year updated: Spring 2013
You might also like
- Plants of the World: An Illustrated Encyclopedia of Vascular PlantsFrom EverandPlants of the World: An Illustrated Encyclopedia of Vascular PlantsNo ratings yet
- Malvaceae: The Mallow FamilyDocument1 pageMalvaceae: The Mallow FamilyAbhik PatraNo ratings yet
- Flora Zambesiaca Volume 13 Part 2:: Eriospermaceae, Dracaenaceae, Arecaceae (Palmae), Pontederiaceae, Bromeliaceae, MayacaceaeFrom EverandFlora Zambesiaca Volume 13 Part 2:: Eriospermaceae, Dracaenaceae, Arecaceae (Palmae), Pontederiaceae, Bromeliaceae, MayacaceaeNo ratings yet
- Guide To Organic CertificationDocument3 pagesGuide To Organic CertificationSUPER INDUSTRIAL ONLINENo ratings yet
- Solanaceae: The Potato FamilyDocument1 pageSolanaceae: The Potato FamilyAbhik PatraNo ratings yet
- Brassicaceae NotesDocument1 pageBrassicaceae Notessamuel mainaNo ratings yet
- The "Primitive" Flowering PlantsDocument36 pagesThe "Primitive" Flowering PlantsAkif waniNo ratings yet
- Fabaceae (Leguminosae) : The Pea, Bean and Mimosa FamilyDocument1 pageFabaceae (Leguminosae) : The Pea, Bean and Mimosa Familyarul prakashamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- Punicaceae: Pollinated and Cross-PollinatedDocument7 pagesPunicaceae: Pollinated and Cross-PollinatedAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Bittrich 2018Document8 pagesBittrich 2018David FigueroaNo ratings yet
- SyandanDocument10 pagesSyandanMikel MillerNo ratings yet
- A208 P10 Activity SheetDocument5 pagesA208 P10 Activity SheetLim Liang XuanNo ratings yet
- BGY3103 Lecture 8Document109 pagesBGY3103 Lecture 8NURUL NAZIRA BINTI ROSMAN / UPMNo ratings yet
- T3 BrassicaceaeDocument37 pagesT3 BrassicaceaeRohith M SNo ratings yet
- Hamamelidaceae - : The Witch Hazel FamilyDocument9 pagesHamamelidaceae - : The Witch Hazel FamilyQaisarNo ratings yet
- Poaceae: The Grass FamilyDocument1 pagePoaceae: The Grass FamilyAbhik PatraNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - LAB3 - Woody AngiospermsDocument9 pagesGroup 7 - LAB3 - Woody Angiospermsdario albaNo ratings yet
- Agave and Yucca: Tough Plants For Tough TimesDocument18 pagesAgave and Yucca: Tough Plants For Tough TimesrisanchezmNo ratings yet
- Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) : The Carrot FamilyDocument1 pageApiaceae (Umbelliferae) : The Carrot FamilyHamid AwanNo ratings yet
- Lecture1aFagaceae FagusDocument48 pagesLecture1aFagaceae FagusMiki MikiNo ratings yet
- Avenue PlantsDocument27 pagesAvenue Plantsamyra SreenathNo ratings yet
- Types and Characteristics: Leonard Neil C. Jubane Swiza Aimee B. CastallaDocument5 pagesTypes and Characteristics: Leonard Neil C. Jubane Swiza Aimee B. CastallaJocelyn CorpuzNo ratings yet
- GYMNOSPERMS (A)Document4 pagesGYMNOSPERMS (A)Aprille CastroNo ratings yet
- Family SystematicsDocument5 pagesFamily SystematicsJoshua Laurence PalconNo ratings yet
- Giant Hogweed TIPS 2017 WEBDocument4 pagesGiant Hogweed TIPS 2017 WEBo______oNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Related LiteratureXenia Kim MorenoNo ratings yet
- Birds of The WorldDocument7 pagesBirds of The WorldJhormanRafaelPineroHernandezNo ratings yet
- Taxodium Distichum PDFDocument1 pageTaxodium Distichum PDFS_GyaltsenNo ratings yet
- BOT LEC CHAPTER 23 AngiospermsDocument6 pagesBOT LEC CHAPTER 23 AngiospermsAUBREY JOY SALENo ratings yet
- Frutos Amazonia 4Document1 pageFrutos Amazonia 4baenatNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms I. GYMNOSPERMS - Derived From The Greek Has Two ClassesDocument3 pagesGymnosperms I. GYMNOSPERMS - Derived From The Greek Has Two ClassesKate G.No ratings yet
- Birch - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesBirch - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMark AbNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Floristics of Monocots: - . - Aroids, Lilies, Orchids - .Document66 pagesDiversity and Floristics of Monocots: - . - Aroids, Lilies, Orchids - .Rifqi Fathul ArroisiNo ratings yet
- Handout 11 Identifying Plant FamiliesDocument6 pagesHandout 11 Identifying Plant FamiliesAsma BzourNo ratings yet
- Plants AnalysistreesDocument10 pagesPlants AnalysistreesRaymart GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Eco MuseumDocument19 pagesEco MuseumAyema MubeenNo ratings yet
- Selecting Shrubs For The LandscapeDocument16 pagesSelecting Shrubs For The LandscapeEco SuperiorNo ratings yet
- Corylus AvellanaDocument2 pagesCorylus AvellanaNVAzirNo ratings yet
- Plant Taxonomy (Spermatopsida, Seed Plants) : Arrangement: ©fong Khi Yung (Raffles Institution)Document11 pagesPlant Taxonomy (Spermatopsida, Seed Plants) : Arrangement: ©fong Khi Yung (Raffles Institution)Lim YHNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - LAB4 - Plants of The PairiesDocument12 pagesGroup 7 - LAB4 - Plants of The Pairiesdario albaNo ratings yet
- R.B. (PG) College, Agriculture Campus, Agra: DR - Pushpendra KarhanaDocument85 pagesR.B. (PG) College, Agriculture Campus, Agra: DR - Pushpendra Karhananaina dakshNo ratings yet
- CaesalpiniaceaeDocument6 pagesCaesalpiniaceaePrerna JindalNo ratings yet
- Materia Medica of Western Herbs - (PG 393 - 394)Document2 pagesMateria Medica of Western Herbs - (PG 393 - 394)corallyNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperm and AngiospermDocument6 pagesGymnosperm and AngiospermAJNo ratings yet
- Families - Comparisions - Sundar Notes Final - 25.10.23Document20 pagesFamilies - Comparisions - Sundar Notes Final - 25.10.23priyamprakash0107No ratings yet
- Kelompok 9 Keanekaragaman TumbuhanDocument20 pagesKelompok 9 Keanekaragaman TumbuhanNur Hasnah Putri0% (1)
- Plant Systematics FinalsDocument5 pagesPlant Systematics FinalsJessaLagdameoBeatrizNo ratings yet
- Botanical NamesDocument15 pagesBotanical NamesthanveerNo ratings yet
- Vanda Lamellata Var. BoxalliiDocument4 pagesVanda Lamellata Var. BoxalliiErik LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Poaceae - The Grasses: Wisconsin Flora "Wordle"Document15 pagesPoaceae - The Grasses: Wisconsin Flora "Wordle"Cipta Adi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Plantclassification 120808061114 Phpapp02Document31 pagesPlantclassification 120808061114 Phpapp02Sendaydiego Rainne GzavinNo ratings yet
- Brassicaceae NotesDocument2 pagesBrassicaceae Notessamuel maina100% (1)
- Flowering Plant Families, UH BotanyDocument3 pagesFlowering Plant Families, UH Botanysatyam kumar jatavNo ratings yet
- 888 Okrjrrnrkn Ajaajajsj Oi9090i JNBJ Fwwi1i1i SA-6013Document4 pages888 Okrjrrnrkn Ajaajajsj Oi9090i JNBJ Fwwi1i1i SA-6013Red DiggerNo ratings yet
- Bluejay 413 Art 130Document9 pagesBluejay 413 Art 130Bailey AnneNo ratings yet
- Portulacaria AfraDocument4 pagesPortulacaria AfrajvnraoNo ratings yet
- Characters Distribution and Types of BrassicaseaeDocument11 pagesCharacters Distribution and Types of Brassicaseaesamuel mainaNo ratings yet
- Cacti and SucculentsDocument10 pagesCacti and SucculentsjanaNo ratings yet
- Eclipta AlbaDocument9 pagesEclipta AlbaMaria MarquezNo ratings yet
- Adapting To SurviveDocument2 pagesAdapting To SurviveFaiez Ali33% (3)
- PTERIDOPHYTADocument16 pagesPTERIDOPHYTAshriya shuklaNo ratings yet
- Gettingto Know Plants BookDocument14 pagesGettingto Know Plants BookSOMEONE OUT Of your knowledgeNo ratings yet
- Monteith QJRMS81Document27 pagesMonteith QJRMS81amitraj2385No ratings yet
- Synthetic Grass DIY Installation GuideDocument26 pagesSynthetic Grass DIY Installation GuideNirav PathakNo ratings yet
- Do Not Write On This Page. Fill in The Missing Code On The Answer SheetDocument12 pagesDo Not Write On This Page. Fill in The Missing Code On The Answer SheetlucyrafaNo ratings yet
- April 21, 2015 Central Wisconsin ShopperDocument24 pagesApril 21, 2015 Central Wisconsin ShoppercwmediaNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Capacity of Phenolic Phytochemicals From Various Cultivars of PlumsDocument6 pagesAntioxidant Capacity of Phenolic Phytochemicals From Various Cultivars of PlumsSevcan ErsanNo ratings yet
- Control Water Supply Industrial Valves en 04Document5 pagesControl Water Supply Industrial Valves en 04Somu DahiyaNo ratings yet
- BioFoodComp4 0Document4,231 pagesBioFoodComp4 0Bruce Jrsn MonzonNo ratings yet
- Ecological Surveys of Forest Service Research Natural Areas in CaliforniaDocument183 pagesEcological Surveys of Forest Service Research Natural Areas in CaliforniaPACIFIC SOUTHWEST RESEARCH STATION REPORTNo ratings yet
- Unit II Ode To AutumnDocument22 pagesUnit II Ode To AutumnVinodh Ashok Kumar100% (1)
- Sabai Srcosmos PDFDocument6 pagesSabai Srcosmos PDFKousik PaikNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Desho Grass For Their Agronomic Performances and Nutritive Values in Highland and Midland Areas of Guji Zone, Southern Oromia, EthiopiaDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Desho Grass For Their Agronomic Performances and Nutritive Values in Highland and Midland Areas of Guji Zone, Southern Oromia, EthiopiaFantahunNo ratings yet
- NDS - Healthy DietDocument13 pagesNDS - Healthy DietSmitha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Eleven Madison Park MenuDocument4 pagesEleven Madison Park Menuapi-316832327No ratings yet
- Garden Design Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGarden Design Lesson Planapi-286042559No ratings yet
- Mung Beans (Autosaved)Document14 pagesMung Beans (Autosaved)ClaireSobredilla-JuarezNo ratings yet
- Gardenia - Wikipedia PDFDocument33 pagesGardenia - Wikipedia PDFSnigdha NaikNo ratings yet
- Info GraphicDocument1 pageInfo Graphicshizuka ichikaNo ratings yet
- Aloe VeraDocument54 pagesAloe Verasyamkavitha100% (3)
- How To Grow Vegetables Broad BeansDocument3 pagesHow To Grow Vegetables Broad BeansVani TranNo ratings yet
- Oil PalmDocument2 pagesOil PalmPOLTAKSIHOMBINGNo ratings yet
- Training Material - FAP & PHDocument35 pagesTraining Material - FAP & PHHafiz M FaheemNo ratings yet
- Introduction of StemDocument19 pagesIntroduction of Stemmaha ChNo ratings yet
- Storage Life Improvement of Custard Apple (Annona Squamosa L.) Fruits CV Balanagar' by Postharvest Application of AntioxidantsDocument5 pagesStorage Life Improvement of Custard Apple (Annona Squamosa L.) Fruits CV Balanagar' by Postharvest Application of AntioxidantsShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Effect of Ca, K, MN and B On Post-Drought Stress Recovery in Tea (Camellia Sinensis (Document3 pagesComparative Effect of Ca, K, MN and B On Post-Drought Stress Recovery in Tea (Camellia Sinensis (Felipe NevesNo ratings yet
- Malts and Malting - Dennis BriggsDocument787 pagesMalts and Malting - Dennis BriggsFederico Guillermo Ernst Webb78% (9)
- CP 123 and SSP12 Flow DiagramDocument6 pagesCP 123 and SSP12 Flow DiagramKarisma Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- The Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldFrom EverandThe Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (411)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (110)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (596)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (35)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- Root to Leaf: A Southern Chef Cooks Through the SeasonsFrom EverandRoot to Leaf: A Southern Chef Cooks Through the SeasonsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)