Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pneumonia
Uploaded by
camille pabustan100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
145 views3 pagespneumonia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentpneumonia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
145 views3 pagesPneumonia
Uploaded by
camille pabustanpneumonia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
PNEUMONIA
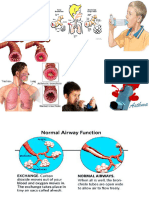
Inflammation of the pulmonary parenchyma
An acute respiratory disorder characterized by inflammation of lung tissue and alveoli
filled with exudate.
o Classification of Pneumonia
Community-acquired pneumonia
CAP S. pneumonia, H influenza
Hospital-acquired (nosocomial) pneumonia (HAP) Escherichia coli, H.
influenza, klebsiella species
Pneumonia in the immune compromised host
Aspiration pneumonia
o Predisposing factors
Conditions that produced mucus or bronchial obstruction
Immunosuppressed patient
Smoking
Prolonged immobility
Nothing-by-mouth NPO status
Respiratory therapy with improperly cleaned equipment
Advanced age
o Pathophysiology
Bacterial pneumonia (Mycoplasma pneumonia) is transmitted by infected
respiratory droplets through person-to-person contact
↓
Acute stage of respiratory infection occurs within the ciliated cells the airways
Infiltration of the tracheobronchial tree
↓
Inflammatory process extends into the alveolar area, resulting in edema and
exudation
↓
An inflammatory reaction can occur in the alveoli, producing an exudate that
interferes with the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide
↓
Blood by passes the alveoli without gas exchange occurring. This is seen with
obstruction of the distal airways PNEUMONIA
↓
A ventilation- perfusion mismatch occurs in the affected area of the lungs
o Signs and Symptoms
FEVER AND CHILLS
FAST BRETHING (tachypnea), NASAL FLARING AND DYSPNEA
INTERCOSTAL RETRACTIONS (chest indrawing)
PRODUCTIVE COUGH (with greenish and rusty sputum)
PLEURITIC CHEST PAIN
DULLNESS OVER AREA OF CONSOLIDATION
Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, malaise
FLUSHED FACE AND DILATED PUPILS
RELATIVELY LOW PULSE
RUSTY SPUTUM WITH HACKING PAROXYMAL COUGH
DIMINISHED CHEST MOVEMENT ON AFFECTED SIDE
83
o Diagnostic Procedures
CHEST X-RAY (confirmatory test)
SPUTIM GRAM STAIN (gram negative or gram positive)
SPUTUM CULTURE- to specify the bacterial agents
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT –leukocytosis
ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES- hypoxemia
o Treatment
Antibiotic:
Penicillin G (drug of choice)
Ampicillin, amoxicillin
Cephalosporin’s (keflin)
Aminoglycoside (Gentamycin)
Non antibiotic Drug
Bronchodilators (THEOPHYLLINE)
Expectorants (GUAIFENESIN)
Symptomatic Treatment
Absolute bed rest
Position change every 2 hours
Fluids
Oxygen mist or mechanical ventilation for respiratory failure
Pain relievers for pleurisy pain
Expectorants
o Nursing Management
Provide rest in the proper position (semi-fowler’s) and change position
Maintain a patient airway (suctioning of secretion if needed) (coughing)
Administer oxygen as indicated
Monitor vital signs (respirations, rr, temperature , ABGs)
INCREASE FLUID UNLESS CONTRAINDICATED (npo), I&O monitoring
and observe for dehydration:
o Sunken fontanels
o Thirst
o Dry skin and mucous membrane
o Poor skin turgor or non-elastic skin
o Rapid thread pulse
o Dehydration fever
o Lethargy
PROVIDE A BLANCE DIET- (high in calories, proteins, vitamins.)
o Gradually progressing from liquids to solids for infants shift from
diluted to full strength formula
PROMOTE COMFORT BY cool baths, skin care, analgesics if ordered,
calm environment
Prevention and Control
PREVENT COMMON COLDS, INFLUENZA, OTHER RESPIRATORY
INFECTIONS
Hib (anti haemophilus influenza B)
Immunization with pneumonia vaccine
Avoid exposure to environmental, physical conditions and contributory
factors.
84
4 STAGES OF PNEUMONIA
1. LUNG ENGORGEMENT
Heavy lung
Dark red in color
Exuding a bubbly, blood tinged froth
2. RED HEPATIZATION
Lung is still heavy
Sinks in water
Looks like a piece of red granite
3. GREY HEPATIZATION
Red color changes to gray
Looks like ordinary granite
Softer and tears more easily
When pressed, exudates a purulent fluid
4. STAGE OF RESOLUTION
Inflammatory exudates is either absorbed by the blood stream or
Expectorated
LOBAR PNEMONIA- if a substantial portion of one or more lobes is involved
BRONCHOPNEUMONIA- describes a pneumonia that is distributed in a patchy fashion,
START FROM THE BRONCHUS, BRONCHIOLES AND SPREAD TO THE ALVEOLI
85
You might also like
- Dengue Biology ProjectDocument14 pagesDengue Biology ProjectRohit Bhunia88% (8)
- Pulmonary Consolidation SyndromesDocument141 pagesPulmonary Consolidation SyndromesGiorgos Doukas KaranasiosNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia: Ang Gobonseng, Ed Gerard R. MedclerkDocument66 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia: Ang Gobonseng, Ed Gerard R. MedclerkRyn Anfone100% (2)
- Pneumonia Study GuideDocument5 pagesPneumonia Study GuideMartha Marty BalintNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument21 pagesPneumoniaZunaira RaheenNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Lobar PneumoniaDocument16 pagesTopic 5 Lobar PneumoniaAmro AzrakNo ratings yet
- The Lung Pathology Lab Encoded PDFDocument85 pagesThe Lung Pathology Lab Encoded PDFJustinNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders: Parainfluenza, RSV, RhinovirusDocument5 pagesRespiratory Disorders: Parainfluenza, RSV, RhinovirusSoojung Nam100% (1)
- Sistem Respirasi Sesak Napas: Problem Based LearningDocument61 pagesSistem Respirasi Sesak Napas: Problem Based LearningAkbar IskandarNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease FinalDocument16 pagesCommunicable Disease FinalPatziedawn Gonzalvo50% (2)
- 2023 UsDocument10 pages2023 UswisgeorgekwokNo ratings yet
- Basic Skills For Clients With Oxygenation ProblemsDocument3 pagesBasic Skills For Clients With Oxygenation ProblemsAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia CBLDocument22 pagesPneumonia CBLImAlien OrGodNo ratings yet
- Chronic Dry CoughDocument119 pagesChronic Dry CoughUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Emergencies Flashcards CompleteDocument109 pagesEmergencies Flashcards Completemkct111No ratings yet
- Subject Seminar ON Approach To StridorDocument68 pagesSubject Seminar ON Approach To StridorAimhigh_PPMNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia 1Document35 pagesPneumonia 1suheel raiNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument9 pagesPneumoniaKenneth UbaldeNo ratings yet
- LEQ PaedsDocument5 pagesLEQ PaedsAtiqah ShahNo ratings yet
- CcroupDocument53 pagesCcroupOlivia BernadiNo ratings yet
- Adult PathophysiologyDocument163 pagesAdult PathophysiologyRuthaliya IbrahimNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 13 Respiratory Infectious DiseasesDocument12 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 13 Respiratory Infectious DiseasesViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesDiseases of Respiratory SystemRupak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Pedia Rotation CroupDocument2 pagesPedia Rotation CroupKaren ArandiaNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument9 pagesPneumonianachiketpanchal8No ratings yet
- Pulmonary ConditionsDocument42 pagesPulmonary ConditionsMinetteNo ratings yet
- Pcap Didactics ChanDocument61 pagesPcap Didactics ChanValerie Anne BebitaNo ratings yet
- Acute Lobar PneumoniaDocument15 pagesAcute Lobar PneumoniaJasmin RanganiNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation ReviewerDocument8 pagesOxygenation ReviewerDamie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia: Presented By: Dian HadinataDocument24 pagesBronchopneumonia: Presented By: Dian HadinataRickyNo ratings yet
- 1respiratory System DisordersDocument10 pages1respiratory System DisordersArvin MalondrasNo ratings yet
- The System: RespiDocument219 pagesThe System: Respilalaine22dale100% (1)
- CD FinalDocument16 pagesCD FinalPatziedawn GonzalvoNo ratings yet
- Asthma 1Document79 pagesAsthma 1DanishMandiNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Presented byDocument16 pagesTuberculosis: Presented bySuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- NCM 109Document18 pagesNCM 109Grace Jane HannaNo ratings yet
- Therapy PulmonologyDocument22 pagesTherapy PulmonologyCavinpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingDocument23 pagesApproach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingKashif Burki100% (2)
- CROUPDocument39 pagesCROUPJake MillerNo ratings yet
- MS LEC Reviewer Oxygenation ProblemsDocument8 pagesMS LEC Reviewer Oxygenation ProblemsVinzii DrtNo ratings yet
- NCP PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Pneumoniajulz_otso6359No ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Shervin GolbariDocument24 pagesPneumonia: Shervin GolbarisgolbariNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument50 pagesPneumoniaannududi378556No ratings yet
- Finals LecDocument14 pagesFinals LecSheena Patricia ArasulaNo ratings yet
- BronchiolitisDocument17 pagesBronchiolitisRizky DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Ruminant AspirationDocument15 pagesRuminant AspirationMilky Jayne Pulido BulusanNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: By: Jonaline VanguardiaDocument6 pagesPneumonia: By: Jonaline VanguardiaVanNo ratings yet
- Laryngitis, Laryngeal Paralysis, DDX of Stridor, StertorDocument44 pagesLaryngitis, Laryngeal Paralysis, DDX of Stridor, StertorDurand S. KhadkaNo ratings yet
- MS Continuation ofDocument13 pagesMS Continuation ofAngelica Joan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis Pathophysiology: MycobacteriaDocument10 pagesAcute Appendicitis Pathophysiology: MycobacteriaUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Diseases of The PharynxDocument33 pagesAcute and Chronic Diseases of The Pharynxnena twtNo ratings yet
- L2 PneumoniaDocument12 pagesL2 Pneumoniajojoanoo15No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Module 16Document70 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Module 16weissNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia in Children: Monocytogenes, Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument1 pagePneumonia in Children: Monocytogenes, Chlamydia TrachomatisAlcala, Mariaden A.100% (1)
- Respiratory System: SecretionsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: SecretionsMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System2Document134 pagesRespiratory System2Darell M. BookNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Restrictive DisordersDocument212 pagesWeek 4 Restrictive Disordersdelrosariojm87No ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseVinceNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesFrom EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis: A Practical GuideFrom EverandAnaphylaxis: A Practical GuideAnne K. EllisNo ratings yet
- Edward JennerDocument5 pagesEdward JennerAnto FreistyawanNo ratings yet
- Enteric FeverDocument51 pagesEnteric FeverBinayaNo ratings yet
- The Annual Production Cycle For Influenza Vaccine: Catherine GerdilDocument4 pagesThe Annual Production Cycle For Influenza Vaccine: Catherine GerdilAntonio MoncayoNo ratings yet
- Bakteri Anaerob: Morfologi, Fisiologi, Epidemiologi, Diagnosis, Pemeriksaan Sy. Miftahul El J.TDocument46 pagesBakteri Anaerob: Morfologi, Fisiologi, Epidemiologi, Diagnosis, Pemeriksaan Sy. Miftahul El J.TADINo ratings yet
- More Than 30 Colleges Now Say Covid Vaccines Will Be Mandatory For Fall 2021Document2 pagesMore Than 30 Colleges Now Say Covid Vaccines Will Be Mandatory For Fall 2021SydneyNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument3 pagesExpanded Program On Immunizationapi-2658787986% (7)
- 09 Science Notes ch13 Why Do We Fall Ill PDFDocument3 pages09 Science Notes ch13 Why Do We Fall Ill PDFthiruNo ratings yet
- How To Design Pre-Study Experiments For Viral Clearance StudiesDocument3 pagesHow To Design Pre-Study Experiments For Viral Clearance Studiesplastioid4079No ratings yet
- Taiwan Pet RegulationsDocument2 pagesTaiwan Pet RegulationsCarlosNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 VACCINATION POLICY With IATF RESOLUTIONSDocument11 pagesCOVID 19 VACCINATION POLICY With IATF RESOLUTIONSImags GamiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DeasesDocument12 pagesRespiratory DeasesheniNo ratings yet
- B Inggris Tahun 1997Document4 pagesB Inggris Tahun 1997amirahalimaNo ratings yet
- Care of Health Care Workers: Healthcare Workers' Risk and ManagementDocument16 pagesCare of Health Care Workers: Healthcare Workers' Risk and ManagementRocky CamaliganNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Citrus Juices and Apple Vinegar On Gram Positive and Gram Negative BacteriaDocument5 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Citrus Juices and Apple Vinegar On Gram Positive and Gram Negative BacteriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Nevalga Last ActivityDocument3 pagesNevalga Last ActivityJessa100% (1)
- Yagyopathy For Preventing Microorganism Based DiseaesesDocument22 pagesYagyopathy For Preventing Microorganism Based Diseaesessatyabrat27100% (1)
- Chest and LungsDocument49 pagesChest and LungsChala KeneNo ratings yet
- Peds NBME QuestionsDocument14 pagesPeds NBME QuestionsAjay RoopeshNo ratings yet
- Dengue DeseaseDocument3 pagesDengue DeseasenandaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Antibodies PropertiesDocument3 pagesNotes On Antibodies PropertiesBidur Acharya100% (1)
- Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesNarrative ReportRoxenette Gil Bernales PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Whooping CoughDocument72 pagesWhooping Coughwengie100% (1)
- LP 4-ImmunoprophylaxisDocument15 pagesLP 4-ImmunoprophylaxismlinaballerinaNo ratings yet
- Pet Parade Rules and WaiverDocument1 pagePet Parade Rules and WaiverJanice Helsley-JundaNo ratings yet
- AntigenDocument16 pagesAntigenAsad ShalmaniNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: Pathogenic Virus:: Hepatitis ADocument2 pagesDatasheet: Pathogenic Virus:: Hepatitis ADutch CharmingNo ratings yet
- Necrotic Enteritis in ChickensDocument3 pagesNecrotic Enteritis in ChickensHendra PranotogomoNo ratings yet
- BookletDocument14 pagesBookletIndra KelanaNo ratings yet
- Medical History: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageMedical History: Republic of The PhilippinesmelyNo ratings yet