Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.4 The Parts of The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Amelia May0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesOriginal Title
B.IN RESPIRASI.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pages2.4 The Parts of The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Amelia MayCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
2.
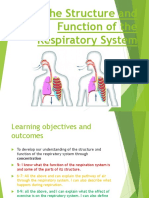
4 The parts of the respiratory system
The respiratory system is divided into two parts:
1. Upper respiratory tract:
This includes the nose, mouth, and the beginning of the trachea (the section that
takes air in and lets it out).
2. Lower respiratory tract:
This includes the trachea, the bronchi, broncheoli and the lungs (the act of
breathing takes place in this part of the system). The organs of the lower
respiratory tract are located in the chest cavity. They are delineated and protected
by the ribcage, the chest bone (sternum), and the muscles between the ribs and the
diaphragm (that constitute a muscular partition between the chest and the
abdominal cavity).
2.5 The act of breathing
The act of breathing has two stages – inhalation and exhalation
Inhalation – the intake of air into the lungs through expansion of chest volume.
Exhalation – the expulsion of air from the lungs through contraction of chest
volume.
Inhalation and exhalation involves muscles:
1. Rib muscles = the muscles between the ribs in the chest.
2. Diaphragm muscle
Muscle movement – the diaphragm and rib muscles are constantly
contracting and relaxing (approximately 16 times per minute), thus causing the
chest cavity to increase and decrease.
During inhalation – the muscles contract:
Contraction of the diaphragm muscle – causes the diaphragm to
flatten, thus enlarging the chest cavity.
Contraction of the rib muscles – causes the ribs to rise, thus
increasing the chest volume. The chest cavity expands, thus reducing
air pressure and causing air to be passively drawn into the lungs. Air
passes from the high pressure outside the lungs to the low pressure
inside the lungs.
During exhalation – the muscles relax:
The muscles are no longer contracting, they are relaxed. The
diaphragm curves and rises, the ribs descend – and chest volume
decreases. The chest cavity contracts thus increasing air pressure and
causing the air in the lungs to be expelled through the upper respiratory
tract. Exhalation, too, is passive. Air passes from the high pressure in
the lungs to the low pressure in the upper respiratory tract.
Inhalation and exhalation are involuntary and therefore their control
requires an effort.
You might also like
- Mechanism of BreathingDocument2 pagesMechanism of BreathingMonikita PerezNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm ArishaDocument3 pagesDiaphragm ArishaAreesha ZubairNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of VentilationDocument14 pagesMechanics of VentilationOsborn BenedicteNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Respiratory Systempaulo_camuaNo ratings yet
- Zenergy Studio - Breathing Yoga PDFDocument20 pagesZenergy Studio - Breathing Yoga PDFparasNo ratings yet
- 1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration ModifiedDocument10 pages1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration Modifiedخالد القرشيNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanism of RespirationDocument22 pages1 Mechanism of RespirationAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Gr. 9 Science LM (AG)Document33 pagesGr. 9 Science LM (AG)Aizalonica GalangNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System of Human Body FactsDocument12 pagesThe Respiratory System of Human Body FactsjulianneboloronNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of breathing explained in 69 wordsDocument18 pagesMechanics of breathing explained in 69 wordsZaliaSubplace S5357No ratings yet
- 1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism: RespirationDocument5 pages1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism: RespirationKelly KohNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument43 pagesRespiratory SystemAbuhuraira RafiqNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة_الثالثة الجاهزة_فسيو_بلك_التنفسي_دفعة_خامسة_Document26 pagesالمحاضرة_الثالثة الجاهزة_فسيو_بلك_التنفسي_دفعة_خامسة_bessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- 18 - Mechanics of Respiration - Prof. Abdelrahman Fahmy - 2020Document5 pages18 - Mechanics of Respiration - Prof. Abdelrahman Fahmy - 2020Hossam BaniisNo ratings yet
- bio notes respiration in animalsDocument3 pagesbio notes respiration in animalssamanthahuangsamanthaNo ratings yet
- Vsp-Ug-5 (RS)Document59 pagesVsp-Ug-5 (RS)6qhx62pr42No ratings yet
- Respiration Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration Lecture Notesamrutha mohandasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MechanicsDocument11 pagesRespiratory MechanicsAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument74 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Thoracic muscles guideDocument23 pagesThoracic muscles guideItadori YujiNo ratings yet
- The respiratory system: structures, functions, and diseasesDocument74 pagesThe respiratory system: structures, functions, and diseasesRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDocument15 pagesPhysiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDivya TripathyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory Systemtarunesh1No ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology - 2021Document39 pagesRespiratory Physiology - 2021Abdikafar AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document15 pagesPresentation 4achsanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument2 pagesRespirationapi-276992608No ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of The Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesThe Structure and Function of The Respiratory SystemVykin OngNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exercises: Mazyad AlotaibiDocument32 pagesBreathing Exercises: Mazyad AlotaibiekaNo ratings yet
- Ncma113-Respiratory and Nursing CareDocument5 pagesNcma113-Respiratory and Nursing Careroldanmarygrace023No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Respiration: Important ConceptsDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Respiration: Important Conceptsamiruddin bahadonNo ratings yet
- MLS221 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument37 pagesMLS221 Respiratory System PhysiologyAbdirazak AliNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of OxygenationDocument50 pagesBasic Concept of OxygenationWiradianto PutroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Respiratory SystemDocument20 pagesChapter 8 - Respiratory Systemmnurnazri10No ratings yet
- The Function of The Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesThe Function of The Respiratory Systemkevinramirezzz365No ratings yet
- تجميع اول محاضره RespiratoryDocument9 pagesتجميع اول محاضره RespiratoryAhmed KadiraNo ratings yet
- 6) RESPIRATORY MUSCLES by DR Hasnain NorthDocument28 pages6) RESPIRATORY MUSCLES by DR Hasnain NorthHasin's QueenNo ratings yet
- Module 9 Lesson 5Document21 pagesModule 9 Lesson 5Faatoots FatsNo ratings yet
- Physiolo Gy: NotesDocument35 pagesPhysiolo Gy: Notesjared mendezNo ratings yet
- PBT 1Document13 pagesPBT 1GeorgeYuanNo ratings yet
- Pubdoc 11 14852 1642Document15 pagesPubdoc 11 14852 1642Husam H.MohammedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Ventilation and Control of Breathing: Moderated by - Dr. Anjali Mehta Presented By-Dr. Sonal SharmaDocument65 pagesMechanics of Ventilation and Control of Breathing: Moderated by - Dr. Anjali Mehta Presented By-Dr. Sonal Sharmamanzoor bhatNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemayuNo ratings yet
- The Vital Respiratory System: Structure and Functions in 37 CharactersDocument18 pagesThe Vital Respiratory System: Structure and Functions in 37 CharactersShinigami AmnerrorNo ratings yet
- University of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonDocument66 pagesUniversity of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonKNo ratings yet
- DR Zainuri - Otot PernapasanDocument37 pagesDR Zainuri - Otot PernapasanAdhiatma DotNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- FU-M3-CU11 Respiratory Function and Nursing CareDocument17 pagesFU-M3-CU11 Respiratory Function and Nursing CareHERLIN HOBAYANNo ratings yet
- VentilationDocument16 pagesVentilationsamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Breathing: Joshua, Youssef, and ApolloDocument28 pagesBreathing: Joshua, Youssef, and ApolloArvinth Guna SegaranNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System-1Document84 pagesRespiratory System-1pranjal raiNo ratings yet
- Human Breathing ProcessDocument12 pagesHuman Breathing Processandy warNo ratings yet
- Prologue 1.1 BackgroundDocument9 pagesPrologue 1.1 BackgroundWulan Yulia DintasariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter 3Document49 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 3Zin Min KhantNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.1 Ventilatory System Sport Science IBDocument4 pagesTopic 2.1 Ventilatory System Sport Science IBAntonio MouNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Larynx: Thyrohyoid MembraneDocument35 pagesAnatomy of The Larynx: Thyrohyoid MembraneVarsha Shende KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Breathing PPT For Teaching Demo by Summer Karyll C. AbanillaDocument18 pagesMechanics of Breathing PPT For Teaching Demo by Summer Karyll C. AbanillaLevis RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MechanismDocument2 pagesMechanismarnelditanNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of BreathingDocument1 pageMechanism of BreathingjaysraelNo ratings yet
- B.ing Amelia May Chrystina (0116048)Document11 pagesB.ing Amelia May Chrystina (0116048)Amelia MayNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesJurnal 2-WPS OfficeAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageDAFTAR PUSTAKA-WPS OfficeAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageDAFTAR PUSTAKA-WPS OfficeAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- 2.4 The Parts of The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pages2.4 The Parts of The Respiratory SystemAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- Senam Kaki Untuk Mengendalikan Kadar Gula Darah ... - Jurnal UmpDocument1 pageSenam Kaki Untuk Mengendalikan Kadar Gula Darah ... - Jurnal UmpAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- E WPS OfficeDocument1 pageE WPS OfficeAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- 123Document15 pages123Amelia MayNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesJurnal 2-WPS OfficeAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- BinatangDocument5 pagesBinatangAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- BinatangDocument5 pagesBinatangAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- Role Play.Document8 pagesRole Play.Amelia MayNo ratings yet
- 2.4 The Parts of The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pages2.4 The Parts of The Respiratory SystemAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- Cghs Rates BangaloreDocument26 pagesCghs Rates Bangaloregr_viswanathNo ratings yet
- Act 342 Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases Act 1988Document26 pagesAct 342 Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases Act 1988Adam Haida & Co100% (1)
- Bagian AwalDocument17 pagesBagian AwalCitra Monalisa LaoliNo ratings yet
- CSOM of Middle Ear Part 2Document55 pagesCSOM of Middle Ear Part 2Anindya NandiNo ratings yet
- MCQS FCPSDocument3 pagesMCQS FCPSDrKhawarfarooq SundhuNo ratings yet
- Class III Cavity Treatment (Procedure, Materials)Document2 pagesClass III Cavity Treatment (Procedure, Materials)Manos KritikosNo ratings yet
- KENCAP Changzhou 2013Document19 pagesKENCAP Changzhou 2013KencapchangzhouNo ratings yet
- Personal Hygiene: The Word Hygiene Means Using Sanitary Principles To Maintain Health. PersonalDocument7 pagesPersonal Hygiene: The Word Hygiene Means Using Sanitary Principles To Maintain Health. PersonalkaushikNo ratings yet
- 1413272524world10 15 14 PDFDocument38 pages1413272524world10 15 14 PDFCoolerAdsNo ratings yet
- EMTALADocument5 pagesEMTALAJimmy MillerNo ratings yet
- Toxic Metabolic Encephalopathy John W. Melton, M.DDocument17 pagesToxic Metabolic Encephalopathy John W. Melton, M.DabdalkhalidNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument46 pagesMemoryMaha Al AmadNo ratings yet
- Reverse Optic Capture of The SingleDocument10 pagesReverse Optic Capture of The SingleIfaamaninaNo ratings yet
- Care for Neonatal PatientsDocument5 pagesCare for Neonatal PatientsJonette Castro HermidaNo ratings yet
- Dance BenefitsDocument9 pagesDance Benefitsapi-253454922No ratings yet
- Bradford Assay To Detect Melamine ConcentrationsDocument3 pagesBradford Assay To Detect Melamine ConcentrationsVibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- 515Document972 pages515solecitodelmarazul100% (6)
- Sepsis Content Concepts MapDocument2 pagesSepsis Content Concepts Mapghodghod1230% (1)
- AAO Glaucoma 2013 - GLA - Syllabus PDFDocument96 pagesAAO Glaucoma 2013 - GLA - Syllabus PDFrwdNo ratings yet
- MRCP PacesDocument243 pagesMRCP PacesTank Tank94% (17)
- Thumb Exercises ActiveDocument6 pagesThumb Exercises ActiveMichael NelsonNo ratings yet
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A ReviewDocument6 pagesStevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Reviewイアン リムホト ザナガNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaCharlie EspinoNo ratings yet
- Multidrug Resistant Gram Negative BacteriaDocument6 pagesMultidrug Resistant Gram Negative BacteriaAniAliciaOrtizCastleNo ratings yet
- Ac PolypDocument18 pagesAc PolypSusmi CmNo ratings yet
- Copy (1) of New Text DocumentDocument2 pagesCopy (1) of New Text DocumentAkchat JainNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Therapy UnitDocument9 pagesUltrasonic Therapy UnitRiya KumariNo ratings yet
- 7 Day Free Guide PDFDocument14 pages7 Day Free Guide PDFGuille RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care With ChecklistDocument5 pagesTracheostomy Care With ChecklistHollan GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic KalpaDocument171 pagesAyurvedic KalparagalwarNo ratings yet
- Horse Training 101: Key Techniques for Every Horse OwnerFrom EverandHorse Training 101: Key Techniques for Every Horse OwnerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Stable Relation: A Memoir of One Woman's Spirited Journey Home, by Way of the BarnFrom EverandStable Relation: A Memoir of One Woman's Spirited Journey Home, by Way of the BarnRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Fitness Evaluation of the HorseFrom EverandFitness Evaluation of the HorseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dressage Training and Competition Exercises for Beginners: Flatwork & Collection Schooling for HorsesFrom EverandDressage Training and Competition Exercises for Beginners: Flatwork & Collection Schooling for HorsesNo ratings yet
- Groundwork with horses: Natural Horsemanship & Groundwork Training for Your HorseFrom EverandGroundwork with horses: Natural Horsemanship & Groundwork Training for Your HorseNo ratings yet
- Horses: 101 Super Fun Facts and Amazing Pictures (Featuring The World's Top 18 Horse Breeds)From EverandHorses: 101 Super Fun Facts and Amazing Pictures (Featuring The World's Top 18 Horse Breeds)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- There's More to Training Horses: 100 Tips, 100 Days, 100% BetterFrom EverandThere's More to Training Horses: 100 Tips, 100 Days, 100% BetterNo ratings yet
- Cavaletti: Cavaletti horse training and groundwork with horsesFrom EverandCavaletti: Cavaletti horse training and groundwork with horsesNo ratings yet
- The Equine Listenology Guide - Essential Horsemanship, Horse Body Language & Behaviour, Groundwork, In-hand Exercises & Riding Lessons to Develop Softness, Connection & Collection.From EverandThe Equine Listenology Guide - Essential Horsemanship, Horse Body Language & Behaviour, Groundwork, In-hand Exercises & Riding Lessons to Develop Softness, Connection & Collection.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Horse training simply explained: Basic Horse training, Foal training, Natural Horsemanship and much moreFrom EverandHorse training simply explained: Basic Horse training, Foal training, Natural Horsemanship and much moreNo ratings yet
- Straight from the Horse's Mouth: How to Talk to Animals and Get AnswersFrom EverandStraight from the Horse's Mouth: How to Talk to Animals and Get AnswersNo ratings yet
- Horse treats Do-It-Yourself - Cookbook for horses: Cookbook for horses - Make your own horse treatsFrom EverandHorse treats Do-It-Yourself - Cookbook for horses: Cookbook for horses - Make your own horse treatsNo ratings yet
- From Stride to Ride; Basic Fundamentals for Beginner Horse TrainersFrom EverandFrom Stride to Ride; Basic Fundamentals for Beginner Horse TrainersNo ratings yet
- Hoof Physics: How to Recognize the Signs of Hoof DistortionFrom EverandHoof Physics: How to Recognize the Signs of Hoof DistortionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Joey: How a Blind Rescue Horse Helped Others Learn to SeeFrom EverandJoey: How a Blind Rescue Horse Helped Others Learn to SeeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (23)
- The Everything Horse Book: Buying, riding, and caring for your equine companionFrom EverandThe Everything Horse Book: Buying, riding, and caring for your equine companionRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Original Horse Bible, 2nd Edition: The Definitive Source for All Things HorseFrom EverandOriginal Horse Bible, 2nd Edition: The Definitive Source for All Things HorseNo ratings yet
- Project Solomon: The True Story of a Lonely Horse Who Found a Home--and Became a HeroFrom EverandProject Solomon: The True Story of a Lonely Horse Who Found a Home--and Became a HeroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Equine Massage: A Practical GuideFrom EverandEquine Massage: A Practical GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)