Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Define Control System
Uploaded by
Karen Arganosa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesOriginal Title
control.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesDefine Control System
Uploaded by
Karen ArganosaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Karen M.
Argañosa Assignment
BSCpE801A Control Systems
1. Define Control System
A control system is a set of mechanical or electronic devices that regulates other
devices or systems by way of control loops. Typically, control systems are
computerized. Control systems are a central part of industry and of automation.
2. Methods used in controlling a system
An open-loop control system utilizes an actuating device to control the process
directly without using feedback. In contrast to an open-loop control system, a
closed-loop control system utilizes an additional measure of the actual output to
compare the actual output with the desired output response. The measure of
the output is called the feedback signal.
3. Mathematical procedures to control a system
Linear Differential Equations - in control system design the most common
mathematical models of the behavior of interest are, in the time domain, linear
ordinary differential equations with constant coefficients, and in the frequency.
State Variable Descriptions - instead of working with many different types of
higher-order differential equations that describe the behavior of the system, it is
possible to work with an equivalent set of standardized first-order vector
differential equations that can be derived in a systematic way.
Transfer Functions - the transfer function of a linear, time-invariant system is the
ratio of the Laplace transform of the output Y(s) to the Laplace transform of the
corresponding input U(s) with all initial conditions assumed to be zero
Frequency Response - the frequency response of a system is given by its transfer
function G(s) evaluated at s = jw, that is, G( jw). The frequency response is a very
useful means characterizing a system, since typically it can be determined
experimentally, and since control system specifications are frequently expressed
in terms of the frequency response.
4. Electronic devices used in controlling a system (atleast 5 examples)
Sensors, Microcontrollers, Inductors, Transformer, Batteries
5. Give atleast 5 applications of a control system
Automobile steering control system, a manual control system for regulating the
level of fluid in a tank, process temperature and pressure controls, robot,
refrigerator.
6. Define feedback control
A feedback control system is a control system that tends to maintain a
prescribed relationship of one system variable to another by comparing
functions of these variables and using the difference as a means of control.
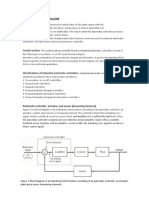
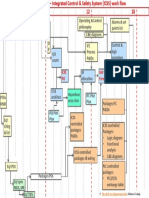
7. Give an illustration of feedback control
8. Define operational amplifiers
An operational amplifier (or an op-amp) is an integrated circuit (IC) that
operates as a voltage amplifier. An op-amp has a differential input. That is, it has
two inputs of opposite polarity. An op-amp has a single output and a very high
gain, which means that the output signal is much higher than input signal.
9. What is the relationship behind operational amplifiers to feedback control?
If we connect the output of an op-amp to its inverting input and apply a voltage
signal to the noninverting input, we find that the output voltage of the op-amp
closely follows that input voltage.As Vin increases, Vout will increase in
accordance with the differential gain. However, as Vout increases, that output
voltage is fed back to the inverting input, thereby acting to decrease the
voltage differential between inputs, which acts to bring the output down. What
will happen for any given voltage input is that the op-amp will output a voltage
very nearly equal to Vin, but just low enough so that there’s enough voltage
difference left between Vin and the (-) input to be amplified to generate the
output voltage.
You might also like
- Compromise Agreement Custody & SupportDocument3 pagesCompromise Agreement Custody & SupportMon80% (35)
- Child Support Agreement On Consent For Waiver of ArrearsDocument1 pageChild Support Agreement On Consent For Waiver of ArrearsKaren Arganosa100% (1)
- Wiley Nonlinear Finite Elements For Continua and Structures Ted Belytschko Wing Kam Liu Brian Moran PDFDocument2 pagesWiley Nonlinear Finite Elements For Continua and Structures Ted Belytschko Wing Kam Liu Brian Moran PDFAntal CsukaNo ratings yet
- ME3405 Mechatronics Lab Student Name: Iskander Otorbayev Student Number: 180015732Document12 pagesME3405 Mechatronics Lab Student Name: Iskander Otorbayev Student Number: 180015732Iskander OtorbayevNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersDocument6 pagesMechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- Smith Predictor Desc enDocument8 pagesSmith Predictor Desc entalljatNo ratings yet
- Unidad 1: Introducción Al Análisis de Sistemas de Control: Asignatura Teoría de Control 1 Prof. Mariela Cerrada LozadaDocument45 pagesUnidad 1: Introducción Al Análisis de Sistemas de Control: Asignatura Teoría de Control 1 Prof. Mariela Cerrada LozadaedissonNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System: Presented by Imran Basha SyedDocument35 pagesLinear Control System: Presented by Imran Basha SyedSyed Imran BashaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Controllers: Control ActionsDocument3 pagesAutomatic Controllers: Control ActionsRakeeb BalochNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document18 pagesLecture 01lana_salahadinNo ratings yet
- Basics of Control Eng 1Document26 pagesBasics of Control Eng 1Hezron gibronNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Process Under ControlDocument9 pagesFigure 1 Process Under ControlKajalNo ratings yet
- OCW - Control Systems - I (EE 503) - AY 2016-17 - 2017-18 PDFDocument100 pagesOCW - Control Systems - I (EE 503) - AY 2016-17 - 2017-18 PDFCiczmockingbird TsvkAdm100% (1)
- Control Systems - 1Document18 pagesControl Systems - 1H. ZNADNo ratings yet
- Ce Mod1Document22 pagesCe Mod1AYUSH CHANDRANo ratings yet
- Process Control SystemsDocument6 pagesProcess Control SystemsRae angelo AgonoyNo ratings yet
- A Simple Fuzzy Excitation Control System (Avr)Document6 pagesA Simple Fuzzy Excitation Control System (Avr)Mmillion AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control Systems: Rezel A. Sto. Tomas, Ece 1Document10 pagesFeedback and Control Systems: Rezel A. Sto. Tomas, Ece 1kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Classical Control SystemsDocument30 pagesIntroduction to Classical Control SystemsRajasekhar AtlaNo ratings yet
- BMCS Lab 1Document7 pagesBMCS Lab 1Sameera WaseemNo ratings yet
- TEL 433 Lect 01 NOTE IntroductionDocument9 pagesTEL 433 Lect 01 NOTE IntroductionTestimonyNo ratings yet
- Vtusolution.in - Introduction to Control SystemsDocument122 pagesVtusolution.in - Introduction to Control Systemsbujangadp123No ratings yet
- Control System Engineering: InstructorsDocument49 pagesControl System Engineering: InstructorsHANSANo ratings yet
- Note 1: Lecture Notes of Control Systems I - ME 431/analysis and Synthesis of Linear Control System - ME862Document6 pagesNote 1: Lecture Notes of Control Systems I - ME 431/analysis and Synthesis of Linear Control System - ME862MessiNo ratings yet
- 000 Digital Control LecturesDocument67 pages000 Digital Control LecturesPX PRNo ratings yet
- CH4 Control SystemDocument10 pagesCH4 Control SystemMahmoud YasseinNo ratings yet
- Title: Introduction To Control System and Their Real Life Application and ExamplesDocument4 pagesTitle: Introduction To Control System and Their Real Life Application and ExampleskalimullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument21 pagesChapter OnetimketaNo ratings yet
- LCS Activity 1 PDFDocument4 pagesLCS Activity 1 PDFForce XNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument8 pagesControl SystemAnil MugaliNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument72 pagesNotes026Himani GautamNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control Chapter 1Document19 pagesIndustrial Control Chapter 1Qayyum AqasyahNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Control System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument21 pagesUnit 1 - Control System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inAltmash RazaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignDocument14 pagesTopic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignxREDCivicCometxNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control System Chapter 1. Introduction To Control SystemDocument9 pagesFeedback and Control System Chapter 1. Introduction To Control SystemJefferson BaptistaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems NotesDocument50 pagesControl Systems NotesEEE CRRNo ratings yet
- 1-Analysis and Design Objectives and Open Loop and Closed Loop Control SystemDocument33 pages1-Analysis and Design Objectives and Open Loop and Closed Loop Control SystemAzhar AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ControlDocument44 pagesChapter 4 ControlFootball HDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document22 pagesChapter 01Abiyot egataNo ratings yet
- 2019handout1 Automatic Control SystemsDocument91 pages2019handout1 Automatic Control SystemsMU Len GANo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Introduction To Control System and Mathematical ReviewDocument43 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To Control System and Mathematical ReviewFaez FeakryNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Control System ExplainedDocument6 pagesClosed Loop Control System ExplainedMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Effect Relationship For TheDocument5 pagesEffect Relationship For TheByron MawoyoNo ratings yet
- Lcs Activity 1: Aditya Rai ROLL NO.: 1826028 M7 MechatronicsDocument4 pagesLcs Activity 1: Aditya Rai ROLL NO.: 1826028 M7 MechatronicsForce XNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 NotesDocument43 pagesUnit-1 NotesMD SHAHRIARMAHMUDNo ratings yet
- Bcs (Unit 1)Document23 pagesBcs (Unit 1)sivamani CHINNASWAMYNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering: 2 Marks Questions & AnswersDocument16 pagesControl Engineering: 2 Marks Questions & AnswersLakshumaiah MajjariNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering: HapterDocument45 pagesControl Engineering: Hapterkyaw phone htetNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Control Systems - What are Control Systems and their Basic ElementsDocument41 pagesIntroduction to Control Systems - What are Control Systems and their Basic ElementsAbubaker MuzayinNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Unit I NotesDocument55 pagesControl Systems Unit I NotesShabbir AliNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Control SystemsDocument11 pages1 - Introduction To Control SystemsKenzie WalipiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control SystemDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemMikias YimerNo ratings yet
- Control System Applied Principles of ControlDocument23 pagesControl System Applied Principles of ControlAngelus Vincent GuilalasNo ratings yet
- Ec3351 Control SystemsDocument18 pagesEc3351 Control SystemsParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Closed-Loop Control Systems ExplainedDocument9 pagesClosed-Loop Control Systems ExplainedBhimsen ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Unit I NotesDocument43 pagesUnit I Notesaravinth69601No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Control SystemDocument86 pagesUnit 1 Control SystemVijay Ct67% (3)
- Control SystemlDocument44 pagesControl SystemlSolid Work and Mechanical software TutorialNo ratings yet
- Draw and Explain Closed Loop System: AssignmentDocument3 pagesDraw and Explain Closed Loop System: AssignmentSameer ArifNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Control Systems - www.rgpvnotes.inDocument21 pagesUnit 1 - Control Systems - www.rgpvnotes.inpeacepalharshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document29 pagesChapter 1Sanji KarunaNo ratings yet
- Control System PPT DO1Document11 pagesControl System PPT DO1Luis AndersonNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Electrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsFrom EverandElectrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsNo ratings yet
- EqweDocument6 pagesEqweKaren ArganosaNo ratings yet
- Constructivist Vs Traditional Effective PDFDocument8 pagesConstructivist Vs Traditional Effective PDFKaren ArganosaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Sessions 20-23 Slides 1-10 ContinuityDocument4 pagesWeek 6 Sessions 20-23 Slides 1-10 ContinuityKaren ArganosaNo ratings yet
- Orem's Self-Care Theory Contribution to NursingDocument9 pagesOrem's Self-Care Theory Contribution to NursingGusri RahayuNo ratings yet
- Theories of Industrial RelationsDocument38 pagesTheories of Industrial RelationsTanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Design Technique of Bandpass FIR Filter Using Various Window FunctionDocument6 pagesDesign Technique of Bandpass FIR Filter Using Various Window FunctionSai ManojNo ratings yet
- Advances in Adaptive Control Theory GradDocument165 pagesAdvances in Adaptive Control Theory GradedumacerenNo ratings yet
- Sebastian Ramos CV: Computer Vision ResearcherDocument4 pagesSebastian Ramos CV: Computer Vision ResearcherKhaled RaoufNo ratings yet
- VNU-HCM Course Syllabus for Analyzing and Designing Management Information SystemsDocument11 pagesVNU-HCM Course Syllabus for Analyzing and Designing Management Information Systemsmeoww meoNo ratings yet
- Software DesignDocument169 pagesSoftware Designnirmala100% (1)
- OOAD Course OverviewDocument2 pagesOOAD Course Overviewsaravana priyaNo ratings yet
- Just in Time (JIT) ProductionDocument15 pagesJust in Time (JIT) Productionanseferns21No ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- CS330 L1Document101 pagesCS330 L1dorathiNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Multiple Choice Questions and Answers SanfoundryDocument13 pagesDigital Signal Processing Multiple Choice Questions and Answers SanfoundryShanmuga Raju SNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020-22 PYQ Heat and ThermodynamicsDocument208 pagesJEE Main 2020-22 PYQ Heat and Thermodynamicspankaj baidNo ratings yet
- BPR QuizDocument18 pagesBPR QuizgigipapasNo ratings yet
- LAB 3: Difference Equations, Z-Transforms, Pole-Zero Diagrams, Bibo Stability and Quantization EffectsDocument5 pagesLAB 3: Difference Equations, Z-Transforms, Pole-Zero Diagrams, Bibo Stability and Quantization EffectsAnthony BoulosNo ratings yet
- Ijsetr Vol 3 Issue 10 2680 2686 PDFDocument7 pagesIjsetr Vol 3 Issue 10 2680 2686 PDFANIYIE ONYEKANo ratings yet
- CT Delta Sigma ADC TutorialDocument77 pagesCT Delta Sigma ADC TutorialhomaNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument32 pagesSDLCNijith NTNo ratings yet
- SAD Week 2 Approaches To System DevelopmentDocument44 pagesSAD Week 2 Approaches To System DevelopmentJohn Mark PumarasNo ratings yet
- 2 HamiltonDocument80 pages2 HamiltonRajeshNo ratings yet
- Guide To SQL 8th Edition Pratt Test BankDocument10 pagesGuide To SQL 8th Edition Pratt Test BankJillianMontoyasepza100% (13)
- GC2 - 03 Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument42 pagesGC2 - 03 Chemical Thermodynamicsalthea villanuevaNo ratings yet
- POSADocument5 pagesPOSASushruth D BelagurNo ratings yet
- Implementasi Metode Windowing Rectangular, Hamming, Hann, Dan Kaiser Pada Filter Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Menggunakan Raspberry PiDocument6 pagesImplementasi Metode Windowing Rectangular, Hamming, Hann, Dan Kaiser Pada Filter Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Menggunakan Raspberry PiRahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- Ijert Ijert: Speed Control of DC Motor Using Digital Control SystemDocument3 pagesIjert Ijert: Speed Control of DC Motor Using Digital Control SystemArturo ChaconNo ratings yet
- Principe S de Technique Ban CaireDocument1 pagePrincipe S de Technique Ban CaireFarid FaridNo ratings yet
- Adsp QuesDocument5 pagesAdsp Quesselva33No ratings yet