Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Tuberculosis (TB) ?: Patient Education
Uploaded by
BiniamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Tuberculosis (TB) ?: Patient Education
Uploaded by
BiniamCopyright:
Available Formats
American Thoracic Society
PATIENT EDUCATION | INFORMATION SERIES
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
TB is a contagious disease that is transmitted from person to
person through coughing and breathing in airborne droplets
that contain bacteria. TB primarily affects the lungs, but can
affect any part of the body. As one of the most common
infections in the world, TB remains a major problem in many
countries and among vulnerable populations.
What causes TB? affects the lungs but can cause problems in other parts
TB is caused by slow-growing bacteria called of the body. The classic symptoms of TB in the lungs
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. When these bacteria enter include:
the lungs, they are usually walled off into harmless ■■ Cough lasting more than three weeks
capsules (granulomas) in the lung, causing infection but ■■ Unexplained weight loss
not disease. These capsules may later wake up weeks, ■■ Low-grade fever
months or decades later causing active TB disease. ■■ Night sweats
CLIP AND COPY
Who gets TB infection and TB disease? If you have these symptoms, you should check with
People who are more likely to acquire TB infection your health care provider.
are the following: (1) People recently exposed to How is TB diagnosed?
someone who has symptomatic TB disease; (2) People Given that latent TB infection is asymptomatic, infection
who live in congregate settings with high risk persons; must be diagnosed using a screening test, either a
(3) People who live or have lived in countries where tuberculin skin test (TST) or a blood test called an
TB is common; or (4) People who are health care interferon gamma release assay (IGRA). The TB skin
workers who are in contact with TB patients when test is also called a Mantoux test or a PPD skin test
proper infection control procedures are not followed. because the material used in the skin test is called
Many people who acquire TB infection do not have purified protein derivative (PPD). These tests detect the
symptoms and may never develop TB disease. These immune response our body mounts to components of
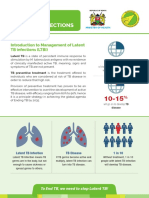
people have latent TB infections (LTBI). However, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A positive result indicates
people with TB infection who have weaker immune that a person has been infected with the tuberculosis
systems due to diabetes, HIV infection, kidney failure, bacteria at some point in his or her life.
or take certain immunosuppressive medications such TB disease is suspected clinically when a person
as TNF-alpha blockers may be more likely to develop presents with the symptoms mentioned above usually
active TB disease with symptoms. together with abnormal findings on a chest x-ray. If
What are the signs and symptoms of TB disease is suspected, the person should be isolated
TB disease? from the public until the diagnosis is made and
Symptoms are usually mild and tend to present over treatment is started as he or she can be contagious and
a period of weeks, months, or sometimes years. TB transmit Mycobacterium tuberculosis to others.
disease symptoms are often initially mistaken for a TB disease is often diagnosed by microscopic
smoker’s cough, allergies, or chronic bronchitis from a examination of three separate samples of sputum
lingering cold or flu infection. TB infection most often (phlegm) often collected on different days. The sputum
Am J Respir Crit Care Med Vol. 195, P7-8, 2017
ATS Patient Education Series © 2017 American Thoracic Society
www.thoracic.org
American Thoracic Society
PATIENT EDUCATION | INFORMATION SERIES
is first looked at under a microscope using a special dye contagious while on treatment. Seeking care right
(acid fast bacillus AFB stain) to see if any tuberculosis away and finding out you have TB is the best way to
bacteria can be found. It is not always positive as stop its spread since treatment of disease helps you
there may be only a small number of bacteria so not be contagious, decreasing transmission.
a culture is always needed. Sputum cultures are
Authors: Monica Campo, MD, MPH, L. Masae Kawamura MD
done to grow the bacteria to confirm the diagnosis Reviewers: Jeffrey Starke, MD, Marianna Sockrider MD, DrPH,
and determine the best combination of drugs for Charles Dela Cruz, MD, PhD, Hrishkesh Kulkarni, MD
treatment. Bronchoscopy is sometimes needed to
obtain lung samples if a patient is unable to produce
sputum. In addition to these tests, chest X-ray and R Action Plan
CT chest imaging are performed to evaluate for any
lung abnormalities. If TB is suspected in a different 4 Symptoms of TB should prompt you to see your
part of the body, a different sample or a tissue biopsy health care provider without delay.
may be needed. (To learn more about bronchoscopy, 4 You should ask specifically about the possibility
see the ATS Patient Information Series “Flexible of TB because the diagnosis may not be on your
Bronchoscopy” at www.thoracic.org/patients) health care provider’s mind.
4 Contact your health care provider if you have
How is TB treated?
had exposure to a person with TB. You should
Treatment of latent TB infection consists of 1 or 2
also contact your provider if you have symptoms
oral medications that kill the bacteria and greatly
of TB and if you have lived, worked, or had
reduces the risk of the infection progressing to TB
prolonged travel in a country or area where TB
disease immediately and later in life. There are several
is common. For example, Asia, Africa, Eastern
treatment options that include isoniazid taken daily
Europe, Central and South America are endemic
for six to nine months, rifampin taken daily for 3 to 4
for TB, as are some inner cities where the poor
months or isoniazid plus rifapentine taken once weekly
and homeless congregate.
for 12 weeks. If you have or are at risk for liver disease,
your doctor may need to follow your liver blood tests
4 TB disease is often preventable! Knowing your
to ensure these medications do not cause any harm. “TB status” is important because, if needed,
treatment of TB infection will kill the few TB
TB disease is usually treated with 4 anti-TB bacteria in your body before it progresses into
medications for at least six months. If TB is in the active TB disease.
bones, brain or other hard-to-reach areas, treatment
will be longer. This can mean taking 6-12 pills per day! Healthcare Provider’s Contact Number:
Many patients find this difficult without the support
of workers trained in providing directly observed
treatment (DOT). DOT is the universal standard
for treating TB worldwide. DOT helps detect side Resources:
effects early and prevents missed doses and breaks in
World Health Organization
treatment that reduce the benefit of treatment and http://www.who.int/tb/en/
can lead to drug-resistant strains of bacteria.
U.S. Centers for Disease Control
How can I prevent TB? https://www.cdc.gov/tb/
TB is spread by tiny airborne droplets created by U.S. National Library of Medicine–Medline Plus
coughing. It is not spread by sharing food, utensils, https://medlineplus.gov/tuberculosis.html
drinks, touching, or having sex. Covering the mouth
and nose when coughing is an important way to stop
This information is a public service of the American Thoracic Society.
the spread of TB and other airborne diseases. If you The content is for educational purposes only. It should not be used as a
have TB disease and are coughing, it is important to substitute for the medical advice of one’s health care provider.
wear a mask and limit contact with others until your
health care provider tells you that you are no longer
www.thoracic.org
You might also like
- TuberculosisDocument2 pagesTuberculosisamr amerNo ratings yet
- Community and HealthDocument6 pagesCommunity and HealthEllee HadesNo ratings yet
- Case Study On TBDocument3 pagesCase Study On TBJamil Lorca75% (8)
- FRSTDocument12 pagesFRSTGuezil Joy DelfinNo ratings yet
- BSN3-9A Tuberculosis or TBDocument4 pagesBSN3-9A Tuberculosis or TBenelrahNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis OrginalDocument11 pagesTuberculosis Orginalthanuja mathew100% (1)
- TuberculosisDocument10 pagesTuberculosisagnescheruseryNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Cause and TransmissionDocument6 pagesTuberculosis: Cause and TransmissionAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Project: Made By:-Swasti Tyagi, Xii-A, 25Document18 pagesBiology Project: Made By:-Swasti Tyagi, Xii-A, 25Swasti TyagiNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument4 pagesTuberculosisMjel Kezhia BarrietaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: by Rohma XI A2, Roll No.-2Document15 pagesTuberculosis: by Rohma XI A2, Roll No.-2fur ballNo ratings yet
- FB3 - 13-Sudeep Koirala-TuberculosisDocument29 pagesFB3 - 13-Sudeep Koirala-Tuberculosisvaskar_karkiNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument55 pagesTuberculosisAfrath Mohamed100% (1)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument20 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionFaraz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument47 pagesGroup 1 - Pulmonary Tuberculosisjhon pauloNo ratings yet
- Case Study Group 4 - XI IPADocument15 pagesCase Study Group 4 - XI IPAkeisya angNo ratings yet
- Lopez, Marian Manuson, Ludy Melu, Anna Victoria Modina, Jayson Montenegro, Matilde Krisha 4dpharmacyDocument19 pagesLopez, Marian Manuson, Ludy Melu, Anna Victoria Modina, Jayson Montenegro, Matilde Krisha 4dpharmacyRyan100% (1)
- PP4 Tuberculosis 1453878076Document43 pagesPP4 Tuberculosis 1453878076khijogpNo ratings yet
- Foundation in Science: Biology IiiDocument63 pagesFoundation in Science: Biology IiiLeong Sze XieNo ratings yet
- Tube Rcul Osis: Prepared byDocument11 pagesTube Rcul Osis: Prepared byBal Ri MekoleuNo ratings yet
- Sneezing: TransmissionDocument13 pagesSneezing: TransmissionMuzammal MollahNo ratings yet
- Paper Analisis HL BlumDocument10 pagesPaper Analisis HL BlumRegina MarshaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB) : CausesDocument4 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis (TB) : CausesNikki TinaNo ratings yet
- PTB Program What Is Tuberculosis?Document6 pagesPTB Program What Is Tuberculosis?allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis TBDocument5 pagesTuberculosis TBHusna AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For TuberculosisDocument7 pagesCase Study For TuberculosisGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- MDR TB CDC PDFDocument2 pagesMDR TB CDC PDFJuliana Dewi HadiNo ratings yet
- TB Dots Treatment in The PhillippinesDocument8 pagesTB Dots Treatment in The Phillippinestmjrsvz84mNo ratings yet
- Diet and Nutrition in TuberculosisDocument23 pagesDiet and Nutrition in TuberculosisParthPatel100% (1)
- NATINAL TB PROG PHDocument83 pagesNATINAL TB PROG PHTherese PeñaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument7 pagesPulmonary TuberculosisEerl Andrea ManzanaresNo ratings yet
- LTBI Fact SheetDocument8 pagesLTBI Fact SheetLarry KivayaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Inflammation of The Thin Tissue Lining Each Air Sac Causes Scarring and Makes The Sacs Less FlexibleDocument8 pagesChronic Inflammation of The Thin Tissue Lining Each Air Sac Causes Scarring and Makes The Sacs Less FlexibleRosalina MarilaoNo ratings yet
- Case Study TuberculosisDocument8 pagesCase Study TuberculosisCharisse SantillanNo ratings yet
- TB - OutlineDocument11 pagesTB - Outlinekent yeeNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument4 pagesDengue FeverDez TabiosNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument6 pagesPulmonary TuberculosisZachary CohenNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional de TrujilloDocument13 pagesUniversidad Nacional de TrujilloWendy Santos MonteroNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument23 pagesTuberculosisKeertana RajagopalNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument6 pagesTuberculosisZechariah NicholasNo ratings yet
- FFTHDocument13 pagesFFTHGuezil Joy DelfinNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions On Tuberculosis (English) : Q: What Is Tuberculosis (TB) ?Document4 pagesFrequently Asked Questions On Tuberculosis (English) : Q: What Is Tuberculosis (TB) ?Mystery ShopperNo ratings yet
- CPH 1mto4 Tuberculosis MartinDocument4 pagesCPH 1mto4 Tuberculosis MartinEDGARDO MARTIN IIINo ratings yet
- Tory O: NameDocument17 pagesTory O: Namejana champakNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: 1. What Is M.tuberculosis?Document3 pagesTuberculosis: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: 1. What Is M.tuberculosis?Quan ThieuNo ratings yet
- What Is TuberculosisDocument2 pagesWhat Is TuberculosisJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- What Causes Tuberculosis?: Who Is at Risk?Document6 pagesWhat Causes Tuberculosis?: Who Is at Risk?Puskesmas GondangNo ratings yet
- By Mayo Clinic Staff: When To See A DoctorDocument5 pagesBy Mayo Clinic Staff: When To See A DoctorKimberly SolisNo ratings yet
- FAQ About Summit County TB InvestigationDocument5 pagesFAQ About Summit County TB InvestigationWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- Power Point 11Document15 pagesPower Point 11zekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- TUBERCULOSISDocument19 pagesTUBERCULOSISSaranya DeviNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Tuberculosis: Lymph System Tuberculosis - PulmonaryDocument5 pagesDisseminated Tuberculosis: Lymph System Tuberculosis - PulmonaryJeanette C. LimNo ratings yet
- TBDocument19 pagesTBJohn Kevin De VeraNo ratings yet
- What Are The Symptoms of TB?Document5 pagesWhat Are The Symptoms of TB?Reden Calubayan OblenaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Unit 1 Lecture - 1Document39 pagesTuberculosis Unit 1 Lecture - 1Kubra Rasool100% (1)
- Lecture Notes TuberculosisDocument6 pagesLecture Notes TuberculosisDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Primary ComplexDocument24 pagesPrimary ComplexEvelyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- TB LeafletDocument12 pagesTB LeafletAnggun PuspaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Get The-Facts PDFDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Get The-Facts PDFdjprh tbdotsNo ratings yet
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- ANA CDC AntibioticStewardship WhitePaperDocument14 pagesANA CDC AntibioticStewardship WhitePaperAndestaNo ratings yet
- Frankenmuth Disease Detective Test 2014 Answer KeyDocument18 pagesFrankenmuth Disease Detective Test 2014 Answer KeyOjasw UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Pandemic - Contagion (2016)Document27 pagesPandemic - Contagion (2016)DusanPaunovicNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical - of Prosopis Farcta Screening - and - Antibacteria PDFDocument7 pagesPhytochemical - of Prosopis Farcta Screening - and - Antibacteria PDFKowan MaqsadNo ratings yet
- Hmi 0520 72 PDFDocument28 pagesHmi 0520 72 PDFVladimir H. ChambiNo ratings yet
- Philippine National AIDS CouncilDocument47 pagesPhilippine National AIDS CouncilNL R Q DONo ratings yet
- 1028 Synopsis LatestDocument12 pages1028 Synopsis LatestRao Amir ZafarNo ratings yet
- EID JournalDocument175 pagesEID JournalArthur Boegaurd100% (1)
- Q3 - Lesson-Plan Cot English 7Document8 pagesQ3 - Lesson-Plan Cot English 7juvelyn abugan100% (2)
- Communicable and Non-Communicable DiseasesDocument46 pagesCommunicable and Non-Communicable DiseasesMohd Al Qassam100% (1)
- UTS Reviewer FINALSDocument15 pagesUTS Reviewer FINALSKarla Jane Kitahama Patosa100% (1)
- Understanding RabiesDocument50 pagesUnderstanding RabiesHarish BishtNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of ImpetigoDocument9 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Impetigonisha_furiNo ratings yet
- Foreword: OIE Terrestrial Manual 2008 IIIDocument8 pagesForeword: OIE Terrestrial Manual 2008 IIIWormInchNo ratings yet
- ParonikiaDocument5 pagesParonikiaNyimas Irina SilvaniNo ratings yet
- AQA Infection and Response Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAQA Infection and Response Knowledge OrganiserDan LiNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Rabies in Pakistan: A Review of Literature.: Farida Bibi Mughal, Bibi Hajira Irshad AliDocument4 pagesEpidemiology of Rabies in Pakistan: A Review of Literature.: Farida Bibi Mughal, Bibi Hajira Irshad AliNimra Naveed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases 1Document6 pagesInfectious Diseases 1api-484776271No ratings yet
- RhinosporidiumDocument16 pagesRhinosporidiumRatnesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Adverse Event Following ImmunizationDocument28 pagesAdverse Event Following ImmunizationLalitKarkiNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases 11th EditionDocument785 pagesEpidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases 11th EditionitlumNo ratings yet
- The Post-Vaccination Syndrome - Post-Vaccination Syndrome - Homeopathy, Vaccination and Autism Website Dr. Tinus SmitsDocument58 pagesThe Post-Vaccination Syndrome - Post-Vaccination Syndrome - Homeopathy, Vaccination and Autism Website Dr. Tinus SmitsChandan BleeNo ratings yet
- Nutri TherapyDocument2 pagesNutri TherapySamuel DiazNo ratings yet
- Disease PreventionDocument3 pagesDisease PreventionCorina ElysaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Standards and Classification of Tuberculosis: CDC WonderDocument20 pagesDiagnostic Standards and Classification of Tuberculosis: CDC Wondereloi moliNo ratings yet
- Syphilis TP: SystemDocument5 pagesSyphilis TP: Systemtesteste testeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IpDocument5 pagesChapter 1 IpJhea Marie LirasanNo ratings yet
- Abscess of The Lung Current Therapeutic OptionsDocument9 pagesAbscess of The Lung Current Therapeutic OptionsTalat AksuNo ratings yet
- Vaccine-Preventable Diseases and Their VaccinesDocument7 pagesVaccine-Preventable Diseases and Their VaccinesgosaNo ratings yet
- General Climaco National High School General Climaco, Toledo City Diagnostic Exam (Mapeh 8)Document3 pagesGeneral Climaco National High School General Climaco, Toledo City Diagnostic Exam (Mapeh 8)blessyroseNo ratings yet