Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DOME 15 Recap Text 1 PDF
Uploaded by
Aditya Varma YalamanchiliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DOME 15 Recap Text 1 PDF
Uploaded by
Aditya Varma YalamanchiliCopyright:
Available Formats
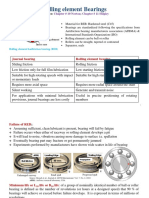
CHAPTER 15
Rolling Contact Bearings
Summary
LO 1. State the func:on of bearing and understand the types of rolling contact
bearings and the principle of self-aligning bearing
Bearing is a mechanical element that permits rela:ve mo:on between two parts, like the shaC
and the housing, with minimum fric:on. The bearing supports the shaC and holds it in correct
posi:on. The bearing takes up the forces that act on the shaC and transmits them to the
founda:on.
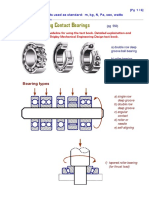
Depending upon the type of rolling element, the bearings are classified as ball bearing,
cylindrical roller bearing, taper roller bearing, and needle bearing. Depending upon the
direc:on of load, the bearings are also classified as radial bearing and thrust bearing.
In self-aligning bearing, the external surface of the bearing bush is made spherical and the bush
is free to roll in its seat and align itself with the journal. This principle is used in self-aligning ball
bearing and spherical roller bearing.
LO 2. List the guidelines for selec:on of bearing type
For low and medium radial loads, ball bearings are used, whereas for heavy loads, roller
bearings are selected. Self-aligning ball bearings and spherical roller bearings are used in
applica:ons where misalignment between the axes of shaC and housing exists. Deep groove
ball bearings, angular contact bearings, and spherical roller bearings are suitable in applica:ons
where the load ac:ng on the bearing consists of two components viz. radial and thrust. Taper
roller bearings are used where rigidity is the main considera:on.
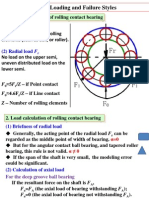
LO 3. Explain the terms sta:c load capacity, dynamic load capacity, equivalent
bearing load, and specify Stribeck's and load life rela:onships
Sta:c load carrying capacity of a bearing is the sta:c load which corresponds to a total
permanent deforma:on of balls and races, at the most heavily stressed point of contact, equal
to 0.0001 of the ball diameter.
http://onlinecourses.flipick.com/CMContent/Library/Assests/Video/36486/index.html 29/11/18, 4F37 PM
Page 1 of 4
Dynamic load carrying capacity of a bearing is the radial load in radial bearings (or thrust load in
thrust bearings) that can be carried for a minimum life of one million revolu:ons. The minimum
life in this defini:on is the L10 life, which 90% of the bearings will reach or exceed before fa:gue
failure.
Equivalent dynamic load is the constant radial load in radial bearings (or thrust load in thrust
bearings), which if applied to the bearing would give same life as that which the bearing will
aZain under actual condi:on of forces. The equivalent dynamic load is given by,
P = X V F r + Y Fa
Stribeck's rela:onship is given by,
k d2 z
Co = 5
The load-life rela:onship is given by,
p
L10 = ( C
P)
LO 4. Underline the guidelines for selec:on of bearing life and load factor
The life of bearing for automobile cars and trucks is 50 and 100 million revolu:ons; respec:vely.
In industrial applica:ons, the bearing life is taken as 12000 to 20000 h for machines used for
one shiC per day and 40000 to 60000 h for con:nuously operated machines.
Load factors are used in applica:ons involving gear, chain, and belt drives. The load factor is 1.2
to 1.4 for gear drives with electric motor, 2 to 3.5 for belt drive and 1.5 for chain drive.
LO 5. Know the basic procedure for selec:on of bearing and selec:on of taper roller
bearings from manufacturer's catalogue
Selec:on of bearing begins with the calcula:on of radial and axial forces ac:ng on the bearing.
From these forces, the equivalent dynamic load is calculated by,
P = X F r + Y Fa
Assuming suitable bearing life, the dynamic load capacity is calculated by,
C = P (L10)1/p
It is checked whether the bearing of selected series has the required dynamic capacity. If not,
the bearing of the next series is selected and the procedure is repeated. Ball bearings are thus,
selected by the trial and error procedure.
http://onlinecourses.flipick.com/CMContent/Library/Assests/Video/36486/index.html 29/11/18, 4F37 PM
Page 2 of 4
In taper roller bearing, even if the external force ac:ng on the bearing is purely radial, it induces
a thrust reac:on within the bearing. The thrust component Fa created due to radial load Fr is
given by,
0.5 Fr
Fa = Y
In the preliminary stages, the value of Y is taken as 1.5. The equivalent dynamic load for single-
row taper roller bearings is given by,
P = Fr when (Fa / Fr) ≤ e
P = 0.4 Fr + Y Fa when (Fa / Fr) > e
ACer calcula:ng dynamic load, the procedure of bearing selec:on is same as that of other types
of bearings.
LO 6. Describe the method for selec:on of bearings for cyclic load, speeds, and for
a given reliability
When the bearing is subjected to cyclic loads and speeds, the equivalent dynamic load is
calculated by,
‾‾‾‾‾‾‾
∑ N P3 ‾
√[ ∑ N ]
3
Pe =
The bearing life (L) for a given reliability (R) is calculated by,
1/b
loge ( R1 )
( L10 ) = [ log
)]
L
e( R
1
90
The dynamic load capacity of the bearing is based on L10 life calculated by above rela:onship.
LO 7. Discuss needle bearings, their advantages, and applica:ons
Needle bearings have cylindrical rollers of very small diameter and rela:vely long length. Many
:mes, needle bearings are used without the races. They are compact and lightweight compared
with other types of bearings. Needle bearings are used in applica:ons involving oscillatory
mo:on such as piston pin bearings, rocker arms, and universal joints.
LO 8. Iden:fy the causes of bearing failures alongwith the methods of lubrica:on
and moun:ngs of bearings
http://onlinecourses.flipick.com/CMContent/Library/Assests/Video/36486/index.html 29/11/18, 4F37 PM
Page 3 of 4
There are four main causes of bearing failure viz. abrasive wear, corrosive wear, pimng, and
scoring.
There are two types of lubricants for rolling contact bearings viz. oil and grease. Oil is more
effec:ve in carrying fric:onal heat and feeds more easily into contact areas of the bearing under
load. The advantages of grease lubricated bearings are simple housing design, less maintenance
cost, beZer sealing against rust, and less possibility of leakage.
The basic principle of bearing moun:ng is to restrict the displacement of inner as well as outer
race in axial direc:on by posi:ve means. There are several methods to restrict the displacement
such as providing shoulders for the shaC or the housing and use of locknut, snap ring, or cover
plates.
http://onlinecourses.flipick.com/CMContent/Library/Assests/Video/36486/index.html 29/11/18, 4F37 PM
Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine Bearings Lubrication in Hydrodynamic BearingsFrom EverandInternal Combustion Engine Bearings Lubrication in Hydrodynamic BearingsNo ratings yet
- Design of BearingsDocument21 pagesDesign of BearingsJehan DhanushkeNo ratings yet
- Rolling Element Bearing SlidesDocument39 pagesRolling Element Bearing SlidesVELMURUGAN MNo ratings yet
- Bearing NoteDocument21 pagesBearing NoteShahir IsmailNo ratings yet
- CH 11: Rolling-Contact Bearings: Bearing TypesDocument9 pagesCH 11: Rolling-Contact Bearings: Bearing TypesBhuwaneshwar DahalNo ratings yet
- Inno2020 - T4 - Rolling-Contact BearingsDocument9 pagesInno2020 - T4 - Rolling-Contact BearingsGhostNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingDocument44 pagesRolling Contact BearingMuhammad Waleed Khan 940-FET/BSME/F20No ratings yet
- Load Ratings, Equivalent Loads and Bearing Life: EngineeringDocument10 pagesLoad Ratings, Equivalent Loads and Bearing Life: EngineeringSiddharth GajjarNo ratings yet
- Bearing SelectionDocument6 pagesBearing SelectiondaryonoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Design of Antifriction BearingsDocument19 pagesUnit 6 - Design of Antifriction BearingsKunal Ahiwale100% (1)
- Rolling Contact BearingsDocument26 pagesRolling Contact BearingsHariharan HemarajanNo ratings yet
- Me 301 Chapter 11Document19 pagesMe 301 Chapter 11Melissa RokaNo ratings yet
- Machine Element Design MEC 331 Machine Element Design MEC 331Document30 pagesMachine Element Design MEC 331 Machine Element Design MEC 331Aqil AzadNo ratings yet
- Rolling-Contact BearingsDocument9 pagesRolling-Contact Bearingskats2404No ratings yet
- Rating Life of BearingsDocument5 pagesRating Life of BearingsSh.nasirpurNo ratings yet
- TDocument33 pagesTTheodoros AtheridisNo ratings yet
- Bearing Life Calculation - Bearing Loads & Speeds - American Roller BearingDocument7 pagesBearing Life Calculation - Bearing Loads & Speeds - American Roller BearingNNOUBAIHNo ratings yet
- Rolling Element Bearings Childs2014Document53 pagesRolling Element Bearings Childs2014joshuaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Rolling Element Bearings PDFDocument28 pages8 - Rolling Element Bearings PDFPradyunn HoraNo ratings yet
- 23-Rolling Contact BearingsDocument19 pages23-Rolling Contact Bearingstooocoool100% (1)
- Roller Bearings Final - SummarizedDocument28 pagesRoller Bearings Final - SummarizedIdo RaizbergNo ratings yet
- Calculate Bearing Life (Timken)Document8 pagesCalculate Bearing Life (Timken)jacksonholland8335100% (2)
- Chapter 11 Rolling Contact BearingsDocument9 pagesChapter 11 Rolling Contact BearingsDhinesh3693No ratings yet
- BearingsDocument32 pagesBearingsSujit SonawaneNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Bearings UpdatedDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 6 Bearings UpdatedMuhammad Azrul100% (1)
- Rolling Contact Bearings: Dodi MulyadiDocument43 pagesRolling Contact Bearings: Dodi MulyadiManojKumar MNo ratings yet
- 1587401068Document5 pages1587401068yfmihweasaNo ratings yet
- Itatech Activity Group ExcavationDocument12 pagesItatech Activity Group ExcavationÜlgen ÜmitNo ratings yet
- III Rolling Contact BearingsDocument32 pagesIII Rolling Contact BearingsRodrigo SousaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Dynamic and Static Radial Load RatingsDocument2 pagesDefinition of Dynamic and Static Radial Load RatingsalfreliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 11 Bearing IIDocument43 pagesLecture - 11 Bearing IIwkho0007No ratings yet
- L10In (1/p O) ) : F'N+F Nat.Document5 pagesL10In (1/p O) ) : F'N+F Nat.SANKARANNo ratings yet
- University of Hail: BearingsDocument37 pagesUniversity of Hail: BearingsSHADES 4 ALLNo ratings yet
- 6 0Document26 pages6 0klawsisNo ratings yet
- Contact Rolling Bearing PDFDocument19 pagesContact Rolling Bearing PDFjanuzajmuchNo ratings yet
- Rolling Element BearingDocument7 pagesRolling Element BearingkrishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Rolling Contact Bearing-2Document33 pagesChapter 7 Rolling Contact Bearing-2Abaziz Mousa OutlawZzNo ratings yet
- Selection of Antifriction BearingsDocument22 pagesSelection of Antifriction BearingsSunil MandoreNo ratings yet
- 41 Rolling Contact BearingsDocument11 pages41 Rolling Contact BearingsPRASAD326100% (3)
- 1 3 Rolling Contact Bearings RNR 25012021Document31 pages1 3 Rolling Contact Bearings RNR 25012021potnuru Jaivanth100% (1)
- Rolling Contact Bearings: Bearing TypesDocument6 pagesRolling Contact Bearings: Bearing Typessofyan samNo ratings yet
- 5 BearingDocument13 pages5 Bearingarbazkhan13218980No ratings yet
- 05-Chapter 11-BearingsDocument30 pages05-Chapter 11-BearingsOk SokNo ratings yet
- How Unbalance Affects Bearing LifeDocument8 pagesHow Unbalance Affects Bearing Lifeagrocel_bhv5591No ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingDocument4 pagesRolling Contact BearingDivyang MistryNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingDocument12 pagesRolling Contact Bearingاحمد عبدالهادي ربيع سعيدNo ratings yet
- Bantalan (Bearing) : Dedison Gasni, PH.DDocument32 pagesBantalan (Bearing) : Dedison Gasni, PH.DAldo JennerNo ratings yet
- Timken-Engineering-Manual 10424Document8 pagesTimken-Engineering-Manual 10424panji hastawirataNo ratings yet
- 11 Rolling: ContactbearingsDocument29 pages11 Rolling: ContactbearingsAndres Alberto Osorio YupanquiNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingDocument31 pagesRolling Contact Bearingpotnuru JaivanthNo ratings yet
- Bearing SelectionDocument22 pagesBearing SelectionAbhishek ShindeNo ratings yet
- Bearing CalculationDocument10 pagesBearing CalculationAniket SankpalNo ratings yet
- Vibration Transmission Through Rolling Element Bearings, Part I Bearing StiffnessDocument21 pagesVibration Transmission Through Rolling Element Bearings, Part I Bearing StiffnessApoorvaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Slides 11th Ed - AccessibleDocument121 pagesCH 11 Slides 11th Ed - AccessibleHasan AmerNo ratings yet
- Conventional BearingDocument8 pagesConventional BearingWaqasNo ratings yet
- 7a-Design of Rolling BearingsDocument33 pages7a-Design of Rolling BearingsSOUBHIK ROYNo ratings yet
- Dte - Rolling Contact BearingsDocument32 pagesDte - Rolling Contact Bearingspotnuru Jaivanth100% (1)
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlFrom EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlNo ratings yet
- Sliding Contact Bearings Sliding Contact Bearings: r c μ n p r c μ n pDocument4 pagesSliding Contact Bearings Sliding Contact Bearings: r c μ n p r c μ n pAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- DOME 20 Recap Text 1 PDFDocument3 pagesDOME 20 Recap Text 1 PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- DOME 18 Recap Text 1 PDFDocument3 pagesDOME 18 Recap Text 1 PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- DOME - 13 - Recap - Text - 1 PDFDocument4 pagesDOME - 13 - Recap - Text - 1 PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements - Chapter 11: 29/11/18, 4F35 PM Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesDesign of Machine Elements - Chapter 11: 29/11/18, 4F35 PM Page 1 of 4Aditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Fric%on Clutches Fric%on Clutches: μ P D d D d μ PDocument2 pagesFric%on Clutches Fric%on Clutches: μ P D d D d μ PAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Dome - 18 - PFP 1 - S - 01 PDFDocument4 pagesDome - 18 - PFP 1 - S - 01 PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- PU BOOK Gott and Duggan PDFDocument145 pagesPU BOOK Gott and Duggan PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Artikel PDFDocument21 pagesArtikel PDFGuia Mae Vallente PairatNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements - Chapter 15: 29/11/18, 4E34 PM Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesDesign of Machine Elements - Chapter 15: 29/11/18, 4E34 PM Page 1 of 4Aditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements - Chapter 16: 6 μ log 6 (30 ×) 10 log 3Document9 pagesDesign of Machine Elements - Chapter 16: 6 μ log 6 (30 ×) 10 log 3Aditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements - Chapter 13: Step I: Belt TensionsDocument11 pagesDesign of Machine Elements - Chapter 13: Step I: Belt TensionsAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements - Chapter 20: A M (Q+ ZDocument6 pagesDesign of Machine Elements - Chapter 20: A M (Q+ ZAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- PU A Framework For Practical Work PDFDocument22 pagesPU A Framework For Practical Work PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- PU in Biology Art PDFDocument9 pagesPU in Biology Art PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Inquiry in Science Education: International Perspectives: Eva Krugly-Smolska and Peter C. Taylor, Section EditorsDocument23 pagesInquiry in Science Education: International Perspectives: Eva Krugly-Smolska and Peter C. Taylor, Section EditorsAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Assessment Strategy For Physics Laboratory CoursesDocument7 pagesA Comprehensive Assessment Strategy For Physics Laboratory CourseskalikadeviNo ratings yet
- Understanding Evidence in Scientific Disciplines: Identifying and Mapping The Thinking Behind The Doing' and Its Importance in Curriculum DevelopmentDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Evidence in Scientific Disciplines: Identifying and Mapping The Thinking Behind The Doing' and Its Importance in Curriculum DevelopmentAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- PU Art Ros Richard Assess PDFDocument30 pagesPU Art Ros Richard Assess PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument20 pagesDepreciationAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Theresia Marsintauli P.Document9 pagesTheresia Marsintauli P.Gusti MuhammadNo ratings yet
- British Steel Sections Datasheets PDFDocument18 pagesBritish Steel Sections Datasheets PDFSérgio BernardesNo ratings yet
- Pipe Cold Bending (HBG)Document15 pagesPipe Cold Bending (HBG)Haries Bugarin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document3 pagesChapter 7jinnah01No ratings yet
- K-Factor Rated Transformer For Deal With Harmonic Generating LoadsDocument4 pagesK-Factor Rated Transformer For Deal With Harmonic Generating Loadsp41005679No ratings yet
- Pure VDocument2 pagesPure VMorris MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Dieseal Level ControllerDocument1 pageDieseal Level ControllersanjaybmscseNo ratings yet
- 5 Common Motor Load Types: Load Profile (Speed Range, Torque and Power)Document2 pages5 Common Motor Load Types: Load Profile (Speed Range, Torque and Power)arieldimacaliNo ratings yet
- Coins and Coin MakingDocument2 pagesCoins and Coin MakingDwitney BethelNo ratings yet
- 5 Smart Charge SystemDocument4 pages5 Smart Charge Systemlitieuduy100% (1)
- SML V eDocument4 pagesSML V eShiftdown GarageNo ratings yet
- ZCAST Brochure WebDocument8 pagesZCAST Brochure WebSrashmiNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Asansor Kabin SecenekleriDocument4 pagesHyundai Asansor Kabin SecenekleriShruti PatkarNo ratings yet
- 112-High Strength Bolting PDFDocument68 pages112-High Strength Bolting PDFJanesha100% (2)
- German Level 2 - Student Workbook PDFDocument100 pagesGerman Level 2 - Student Workbook PDFAndrew Antwan100% (3)
- BOQ CulvertDocument38 pagesBOQ CulvertDeepak_pethkarNo ratings yet
- Cathodic PresentDocument51 pagesCathodic Presentravi chandra mavuri100% (1)
- Design of UFP-coupled Post-Tensioned Timber Shear WallsDocument10 pagesDesign of UFP-coupled Post-Tensioned Timber Shear WallsRafael Arízaga BravoNo ratings yet
- Rosie Revere Teaching GuideDocument5 pagesRosie Revere Teaching GuideAbrams Books100% (1)
- Lauire Baker and Other Architects PDFDocument8 pagesLauire Baker and Other Architects PDFmoni_john_1No ratings yet
- MPU3242 Innovation Management Udesa Business Plan: Green BricksDocument51 pagesMPU3242 Innovation Management Udesa Business Plan: Green BricksSiti Hajar Mohamed100% (1)
- F 111 Aardvark Manual PDFDocument2 pagesF 111 Aardvark Manual PDFPotpourri0% (3)
- DCP-7010, MFC-7420 PL AR-2Document33 pagesDCP-7010, MFC-7420 PL AR-2DuplessisNo ratings yet
- S-000-1676-0001V - 11 - ITP For Piping WorkDocument47 pagesS-000-1676-0001V - 11 - ITP For Piping WorkVO DINH TRI100% (2)
- The Classical and Vernacular LSDocument5 pagesThe Classical and Vernacular LSLucien SteilNo ratings yet
- Ashutosh Jaiswal Resume (NEW)Document2 pagesAshutosh Jaiswal Resume (NEW)api-3707632No ratings yet
- Zilift Torque Converter IIDocument2 pagesZilift Torque Converter IIChrisitian UribeNo ratings yet
- Anotec 90-09 Solid Stick AnodesDocument2 pagesAnotec 90-09 Solid Stick AnodesMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Maersk Intrepid PDFDocument8 pagesMaersk Intrepid PDFMauricio RicardezNo ratings yet
- Rajesh SutharDocument89 pagesRajesh SutharkiradoooNo ratings yet