Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Instructor's Guide For How To Use A Data Evaluation Job Aid For Decision Making
Uploaded by
api-332617418Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Instructor's Guide For How To Use A Data Evaluation Job Aid For Decision Making
Uploaded by
api-332617418Copyright:
Available Formats
The Fleming Group
Instructor’s Guide for How to Use a Data Evaluation
Job Aid for Decision Making
A Framework for Decision Making
Presented to
Dr. Mary Norris Thomas
Nuong Nguyen, Tawn Gillihan, Jeff Kitts, and Corey Wallace
July 16, 2018
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 1 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
INSTRUCTOR’S GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Instructor’s Guide Table of Contents ............................................................................................................ 2
Instructor’s Guide for Teaching How to Use the Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid for Decision-
making........................................................................................................................................................... 3
What is a Job Aid? ..................................................................................................................................... 3
Background ............................................................................................................................................... 3
Learning Objectives................................................................................................................................... 3
Workshop Description .............................................................................................................................. 4
Before You Begin........................................................................................................................................... 4
Instructor Preparation .............................................................................................................................. 4
Recommended Tools ................................................................................................................................ 4
Materials Needed for Learners ................................................................................................................. 4
Materials Needed for Instructor ............................................................................................................... 5
Learner Prerequisites ................................................................................................................................ 5
Target Audience ........................................................................................................................................ 5
Planning Discussions and Guided Practice................................................................................................ 5
Recommendations for Guided Practice and Feedback ............................................................................. 5
Reference/Primary Source Material ......................................................................................................... 6
Introduction .................................................................................................................................................. 7
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) ............................................................................................................... 8
Step One: Relevancy ..................................................................................................................................... 9
Step Two: Validity ....................................................................................................................................... 10
Step Three: Reliability ................................................................................................................................. 11
Step Four: Completeness ............................................................................................................................ 12
Job Aid Q&A ................................................................................................................................................ 13
Background ............................................................................................................................................. 13
Job Aid ......................................................................................................................................................... 14
Demonstration and Practice ....................................................................................................................... 15
Wrap Up ...................................................................................................................................................... 16
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 2 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
INSTRUCTOR’S GUIDE FOR TEACHING HOW TO USE THE EVALUATION
OF DATA FRAMEWORK JOB AID FOR DECISION-MAKING
What is a Job Aid?
A job aid is a stand-alone reference tool, usually in the form of a poster, that is used by someone who
needs immediate information and guidance on following a process, completing a task, or accessing
information. The job aid in this training is intended to be used by the learners to guide them in the
decision-making process.
Background
The purpose of this training is to provide a useful job aid for making data-driven decisions and provide
practice opportunities to familiarize users with the decision-making framework. Training will be offered
as a 90-minute, face-to-face, instructor-led session using materials developed by the design team.
Given how much content is covered, the group and Dr. Thomas agreed on 90 minutes for the training.
The primary source material for the training is the professional journal article “Making Sound Decisions:
A Framework for Judging the Worth of Your Data,” co-authored by Dr. Mary Thomas, CEO of The
Fleming Group, LLC (Guerra-Lopez & Thomas, 2011).
“To know what you know and what you do
not know, that is true knowledge.”
—Confucius
Learning Objectives
At the end of training, learners will be familiar with the job aid and how it is used to make data-based
decisions. The learners will determine if the data are relevant, valid, reliable, and complete.
Upon completion of the training, learners should be able to:
Match the following data quality terms with their definitions: relevant, valid, reliable, and
complete.
List the potential decisions based on data quality and give an example of each.
Recognize key questions for evaluating data qualities.
Using the job aid and a sample data set, the learner will be able to follow the flowchart to an
appropriate conclusion, based on a scenario provided by the instructor.
Identify the data quality concept that applies to various scenarios provided by the instructor.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 3 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
Workshop Description
The Fleming Group is an executive consulting firm that applies evidenced-based practices to produce
measurable outcomes of value for commercial, non-profit, and government markets. The goal is to
expose entry-level supervisors and managers to effective decision-making practices early in their career
development. The 90-minutes training will provide an introduction to this data evaluation process.
Effective decision-making practices, as defined in Guerra-Lopez & Thomas (2011), are based on data that
are evaluated to be relevant, valid, reliable, and complete. By instructing leaders in sound data
evaluation methods, The Fleming Group adds value to the clients and society as the clients make
important decisions. The training fits the Fleming Group’s mission of performance improvement
through evidence-based practices.
The topics for the instructor-led session include relevant, valid, reliable, and complete data, and the
decision-making flowchart.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
The purpose of this project is to provide an engaging instructional guide and a job aid to introduce
learners to a method of evaluating data to make sound decisions. Training will be offered as a 90-
minute, face-to-face, instructor-led session using materials developed by the design team.
The instructor guide provides sample scenarios in each of the four decision-making areas. These
scenarios are examples only and may be used as they are shown, modified, or replaced with scenarios
that pertain to the target audience.
Instructor Preparation
Prior to facilitating this training session, the instructor should:
Review the primary source material published by Guerra-Lopez and Thomas (2011)
Review the instructor guide including the job aid
Collect the materials needed for the training location
Print copies of the job aid
Provide supplies for learners
Print a sign-in sheet and have learners sign in for each session for recordkeeping
Recommended Tools
Sample data set
Materials Needed for Learners
Pencil
Paper
Job aid
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 4 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
Materials Needed for Instructor
Before beginning this module, check that the following items are available in the training room:
Whiteboard Directions to the restrooms and
Dry erase markers breakrooms
Dry erase board eraser Directions to the emergency exit
Projector Water
Screen Pencils
Laptop connector Paper
Power Outlet First aid kit
Wheelchair accessible seating Emergency evacuation/response guide
Learner Prerequisites
None for this module
Target Audience
Learners are new managers, entry-level supervisors, team leads, or managers who have not previously
been exposed to sound decision-making training or the method for evaluating the worth of data used in
decision-making processes. The rationale is to expose leaders to effective decision-making practices
early in their development.
Planning Discussions and Guided Practice
Discussion dynamics and appropriate methods of guided practice will vary depending on group size,
industry, time and space considerations. Plan in advance for the group discussion and guided practice.
Ensure that adequate time and communication strategies are in place to lead the learners through the
use of the job aid. Printed copies of the job aid must be provided to each learner, and the job aid must
be used to move through Steps A through D.
Class size is a factor in familiarization training, group discussion, and guided practice. For this reason, the
instructor may choose to limit class size and offer multiple sessions for larger numbers of learners. The
ideal group size is four to five learners. Make sure to include diversity in race, ethnicity, age,
experiences, and gender. The small group will allow more time for discussion and feedback from the
instructor.
Recommendations for Guided Practice and Feedback
For small groups, it may be appropriate to allow impromptu sharing and discussion.
Each learner may be asked to report back, or the instructor may request volunteers to comment
on the guided practice.
For larger groups, determine in advance whether the learners will be placed into smaller
discussion groups.
Groups may elect a scribe to capture discussion points from the larger group and may elect a
reporter to summarized feedback.
Learners may be invited to give feedback in writing via the use of a journal, post-it notes, large
poster paper, whiteboard, group texts, or other means.
Instructors may review group responses and provide a summary at the end of each discussion or
training session.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 5 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
Primary Source Material
Guerra-Lopez, I. & Thomas, M. (2011). Making sound decisions: A framework for judging the worth of
your data. Performance Improvement, 50 (5).
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 6 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
INTRODUCTION
Time: 8 Minutes
Introduction Brief introductions by the instructor and learners.
Activity Ask learners to recount a decision they made or know about
that was a disaster. Why was the decision a disaster? Were
the data lacking, not properly evaluated, or was the decision
not aligned with the desired outcomes?
Overview The order is important - follow the guide in this order:
Explain two general rules of the 1. Relevancy
decision-making guide 2. Validity
3. Reliability
4. Completeness
Proceed to the next level only if the answer is Yes to each
quality key question. If the answer is No, then stop and
exclude that data.
Practicing the objective of evaluating data for sound decision-
Objectives making is the primary goal for the training. The learners will
practice evaluating the quality of the data in the aspects of
relevance, validity, reliability, and completeness.
At the close of training, learners will be able to define the
concepts of data qualities and apply the concepts to a data
evaluation scenario using the job aid.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 7 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQ)
Time: 5 Minutes
Questions/Answers
Are the learners expected to master decision-making after completing this course?
No, the learners are not expected to have mastery in decision-making. They should be able to
generally define the data qualities of Relevant, Valid, Reliable, and Complete. They should be able to
move through the job aid with the sample scenario, following the steps to the end of a process.
Why do we have to teach the four data qualities in order?
The data qualities lead to decision points on the job aid and must be followed in the proper sequence
for the job aid to be useful.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 8 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
STEP ONE: RELEVANCY
Time: 13 Minutes
Activate Prior Ask learners, “What do you think the word relevant means when
Knowledge making a decision?”
Relevant data are related to questions that must be answered to
make a decision
Definitions
Irrelevant data are additional information that is not needed to make
a decision
Are the data I have important to my decision?
Do the data answer a question about the decision?
Do the data relate to a performance indicator that is important?
Related Questions Do the data relate to a time period that affects my decision?
If yes, the data are relevant and should be considered when making
the decision.
If no, then the data are irrelevant and should be ignored.
Joe is a single adult who enjoys outdoor activities and wants to
purchase a home. The real estate agent tells Joe the home he is
visiting is in a great school district. Is this information relevant to Joe’s
search for a home? Next, the real estate agent tells Joe the home is
Example near a lake with biking paths and hiking trails.
Is this information relevant to Joe’s search for a home?
The school district information is not relevant since Joe does not have
children. The lake and trails are relevant since Joe enjoys outdoor
activities.
Demonstrate the location of Relevant on the job aid. Ask learners to
think about a time when they were faced with making a decision
about a similar situation. Are the data relevant or irrelevant in this
Guided Practice
scenario, such as when they purchased a home or other big-ticket
items?
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 9 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
STEP TWO: VALIDITY
Time: 13 Minutes
Activate Prior Ask learners, “What do you think the words valid and invalid means
Knowledge in regard to data?”
Valid is a true measure of what it is supposed to measure.
Definitions Invalid does not measure what it is supposed to measure; therefore
you should exclude invalid data from the decision process.
Do the data tell me something of value?
Are the data that I have meaningful?
Do the data accurately tell me something about an indicator of
Related Questions
interest?
Are the data representative of the indicator of interest?
Marcia receives monthly performance numbers from a production
team at a distant location. The numbers seem much higher than
usual, and she is not sure the information is accurate. If Marcia
Example
contacts the team lead and the numbers are verified, are the data
valid? If the team lead admits a mistake in the report that needs to
be corrected, were the data invalid?
Demonstrate the location of Validity on the job aid and ask learners
to provide examples of a measure of workforce performance, such
Guided Practice
as interpreting production levels. Ask learners how they would
determine the validity of the data in this scenario.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 10 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
STEP THREE: RELIABILITY
Time: 13 Minutes
Ask learners, “What would you consider to be a reliable source for
Activate Prior
investment advice?
Knowledge
Reliable data have the quality of being trustworthy or of performing
consistently well. They are consistent across a variety of measures. It may
come from credible sources and is precise enough to be useful for
Definitions decision-making.
Unreliable data cannot be relied upon or trusted. They may come from
an untrustworthy source or vary across measures.
Do I have enough confidence in the data that I would put my job on the
line?
Related Questions Are the sources of the data credible?
Were the data generated in a credible way?
Do any of the data points contradict each other?
William overhears two strangers in a pub talking about the next big stock
release which should triple overnight. He is looking for good investments
and is always open to an investment tip. He calls his stockbroker the next
day, but his broker does not know anything about it. He suggests William
Example invest in another stock that William’s brokerage is managing.
Should William trust the information he overheard in the pub? Is that
information reliable?
Should he take his broker’s advice and invest in the stock managed by the
agency? Which tip is reliable and which is unreliable?
Ask learners to demonstrate the location of Reliability on the job aid and
to provide examples of reliable versus unreliable data in a scenario, such
Guided Practice
as investing in the stock market. Ask learners how they would determine
the reliability of the information from each source.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 11 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
STEP FOUR: COMPLETENESS
Time: 13 Minutes
Activate Prior Ask learners, “If it were an extremely hot day at the beach, should you
Knowledge run and dive into the waves?”
Complete data are those that include ALL relevant information, including
Definitions risks, costs, consequences, and other possible ramifications. Complete
data answer all your questions.
Complete data are data those that include ALL relevant information,
Related Questions including risks, costs, consequences, and other possible
ramifications. Complete data answer all your questions.
The Miller family are driving along the highway and decide to take a
break at a rest stop next to a beach. As soon as they tumble out of the
Example car, the kids go running into the waves. Is it safe for the children to swim
in the ocean in this location? What information is missing from the
Miller’s decision-making process?
Demonstrate the location of Completeness on the job aid and ask them
to provide examples of complete versus incomplete data in this scenario,
Guided Practice such as dangerous tides, private property, or lack of a lifeguard. Ask
learners how they would determine the completeness of the data in this
scenario?
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 12 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
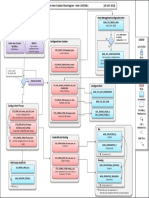
JOB AID Q&A
Time: 5 minutes
Background
The job aid is the only document learners will receive for the training. Learners will be able to
perform the guided practice exercises and conduct actual data evaluations with only the job aid
as a reference. This job aid is about evaluating data to support a decision process. The job aid
will be delivered in as a Microsoft Word document for ease of use. This job aid is to be two
pages: a front side and back side of one sheet paper. This introduction page is for development
reference and will not be included in job aid. The job aid needs to address the following
questions.
Job Aid Questions to be Answered Responses
Why A data evaluation method is a foundational process for making
Informed decisions.
What The data evaluation flowchart is for systematic data evaluation.
When Use the Data Evaluation Job Aid when you need to make
informed decisions
How The diagram and text of the job aid are stand-alone and self-
explanatory for learners to succeed in completing a data
evaluation task. The job aid supports performance by putting
the needed resource into the learners’ hand whenever needed,
rather than loading information into the learners’ mind that
may not be recalled when needed.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 13 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
JOB AID
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 14 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
DEMONSTRATION AND PRACTICE
Time: 13 Minutes
Demonstrate how to use the job aid from start to finish. Learners practice using
the scenario practice problem below.
Instructor Modeling
You currently rent an apartment and are interested in buying a house. You’ve
visited a mortgage bank and obtained pre-qualified numbers for a loan. You’ve
collected and researched the following information.
Combined yearly take-home income: $80,000
Savings and funds available for a down payment: $60,000
Current monthly rent: $2,500
Pre-qualified for a loan of up to 400,000 at the current interest rate of
4.5%.
Scenario Practice Problem Percent of take-home income you can afford a house payment: 30%
Real estate tax and insurance costs combined is about 3% of the total
house cost.
Recent average selling prices of homes in areas of interest: $550,000
Working through the job aid, the learner will evaluate those data qualities and
may arrive at the conclusions below.
Are the data relevant?
The provided data appears to be relevant.
Independent Practice
Are the data valid?
The provided data appears to be valid.
Are the data reliable?
The provided data are only reliable for a limited timeframe. Housing
market prices and interest rates can change quickly. Employment status
with related income can also change quickly.
Are the data complete? Do I have sufficient data to proceed with a decision?
The data provided are not complete. Other data variables need to be
defined before proceeding with a decision.
o Tax interest income should be defined.
o The amount of reserve funds required needs to be defined. Risk
consequences of losing a job for any reason including taking
care of family members should be considered as part of the
reserve funds data.
o Reserve funds for appliances and immediately needed house
repairs should be considered.
o Risks and related consequences of the needing to move for
employment or family reasons should be defined.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 15 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
The Fleming Group
WRAP UP
Time: 7 Minutes
Facts about something that can be used in calculating, reasoning, or planning.
Data/Datum
Hint: Use datum as a singular word and data as plural.
Relevant data are related to questions that must be answered to make an effective
Relevant
decision.
Valid Data points are a true measure of what it is supposed to measure
Reliable Data points are consistent across a variety of measures
In the real world, it is not always possible to have all data available when making
decisions. Also, even when using the data evaluation job aid, one’s decisions will not
always be error-proof.
The learners will learn how to make informed decisions based on the best quality data
Complete
available to them at the time. Learners should not be led to believe that training in data
evaluation will lead to perfect decisions.
As data changes due to correction or new information, the learner should be able to
reevaluate and respond using the job aid.
Instructor’s Guide Evaluation of Data Framework Job Aid Training 16 | Page
© 2018 The Fleming Group, LLC, All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Intro Stats 5th Edition by Richard D de Veaux Ebook PDFDocument42 pagesIntro Stats 5th Edition by Richard D de Veaux Ebook PDFdelmar.jackson88497% (36)
- Introduction To Spring Framework (Presentation - 143 Slides)Document143 pagesIntroduction To Spring Framework (Presentation - 143 Slides)ammayi100100% (1)
- Capstoneproject Status Report Presentation NguyenDocument11 pagesCapstoneproject Status Report Presentation Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Responsibility Matrix NguyenDocument2 pagesResponsibility Matrix Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Stakeholder Analysis NguyenDocument4 pagesStakeholder Analysis Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Statement of Work NguyenDocument4 pagesStatement of Work Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Writing Objectives NguyenDocument3 pagesWriting Objectives Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Reading Strategies For First Graders Logical Framework (Logframe) ChartDocument4 pagesReading Strategies For First Graders Logical Framework (Logframe) Chartapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Charter NguyenDocument1 pageCharter Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Gantt Chart Nguyen v2Document15 pagesGantt Chart Nguyen v2api-332617418No ratings yet
- Communication Plan NguyenDocument2 pagesCommunication Plan Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography NguyenDocument6 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Project Proposal NguyenDocument4 pagesProject Proposal Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Memo Isd NguyenDocument1 pageMemo Isd Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Risk Analysis NguyenDocument4 pagesRisk Analysis Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Literature Review NguyenDocument5 pagesLiterature Review Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Storyboard Nguyen Module 1Document21 pagesStoryboard Nguyen Module 1api-332617418No ratings yet
- Bibliography Entry ReviewDocument1 pageBibliography Entry Reviewapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Capstone Report NguyenDocument35 pagesCapstone Report Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Teacher Guide NguyenDocument9 pagesTeacher Guide Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Returning Group 1 Design Project ReportDocument13 pagesReturning Group 1 Design Project Reportapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Final Capstone Presentation NguyenDocument4 pagesFinal Capstone Presentation Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- One Page Capstone Summary NguyenDocument1 pageOne Page Capstone Summary Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Backward Design NguyenDocument13 pagesBackward Design Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Storyboard Nguyen Module 2-7Document52 pagesStoryboard Nguyen Module 2-7api-332617418No ratings yet
- Mapping Assure Addie Paper NguyenDocument7 pagesMapping Assure Addie Paper Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Instruction Design Essay NguyenDocument4 pagesInstruction Design Essay Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Active Learning Mini Design Returning Team OneDocument11 pagesActive Learning Mini Design Returning Team Oneapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Objective and Test Items NguyenDocument4 pagesObjective and Test Items Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Project Definition The Fleming GroupDocument9 pagesProject Definition The Fleming Groupapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Needs Assessment NguyenDocument8 pagesNeeds Assessment Nguyenapi-332617418No ratings yet
- Osama Quantum ComputingDocument49 pagesOsama Quantum ComputingErvin HodzicNo ratings yet
- Matlab Robotics ToolboxDocument20 pagesMatlab Robotics ToolboxRajesh RavindranNo ratings yet
- Wansview IP Camera ManualDocument54 pagesWansview IP Camera ManualMaria Jose PareaNo ratings yet
- 21 InfotainmentDocument10 pages21 InfotainmentIqtidar ANo ratings yet
- What Is SPSSDocument4 pagesWhat Is SPSSElla Marie BaricuatroNo ratings yet
- Trees: Discrete Structures For ComputingDocument48 pagesTrees: Discrete Structures For ComputingLê Văn HoàngNo ratings yet
- PCG Log BookDocument22 pagesPCG Log BookPardon Gabriel ChinhamoNo ratings yet
- Elt Test Set (Ets) Operation Manual 570-1000 Revision ADocument28 pagesElt Test Set (Ets) Operation Manual 570-1000 Revision Anixon_b_2000No ratings yet
- Artikel B.inggrisDocument4 pagesArtikel B.inggrisNaya BelajarNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Teams EnglishDocument14 pagesMicrosoft Teams Englishapi-321004552No ratings yet
- Ict-112-Lec-1812s Week 19-Long Quiz 004Document9 pagesIct-112-Lec-1812s Week 19-Long Quiz 004Allick Fitzgerald Nanton Jr.No ratings yet
- Haryana With CommentsDocument148 pagesHaryana With Commentsmanojkumartomar7513No ratings yet
- CH 06Document106 pagesCH 06Ray Vega LugoNo ratings yet
- Config Item Creation Flow2Document1 pageConfig Item Creation Flow2sen2985100% (1)
- Apply File Io Operation in JavaDocument18 pagesApply File Io Operation in JavaEdwin LapatNo ratings yet
- Gaz Classifieds 220514Document6 pagesGaz Classifieds 220514Digital MediaNo ratings yet
- Vogue Color Book PDFDocument4 pagesVogue Color Book PDFhellomoscaNo ratings yet
- PAT GR 10 Learner 1 April 2016Document19 pagesPAT GR 10 Learner 1 April 2016khadijaosman33% (3)
- Electrical Engineering Department: Practical Work (Lab 2) Dee 20023 Semiconductor Devices Program: Dep / DTKDocument7 pagesElectrical Engineering Department: Practical Work (Lab 2) Dee 20023 Semiconductor Devices Program: Dep / DTKSarahmei MeiNo ratings yet
- Toastmasters 430A Online Meeting Tips PDFDocument3 pagesToastmasters 430A Online Meeting Tips PDFHrishikesh ChavanNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth at Command SetDocument33 pagesBluetooth at Command SetAnkur KunduNo ratings yet
- Lo Datasources: Logistic Cockpit (LC) Is A Technique To Extract Logistics Transaction Data From R/3Document4 pagesLo Datasources: Logistic Cockpit (LC) Is A Technique To Extract Logistics Transaction Data From R/3Dennis VuNo ratings yet
- SO Snippet ENASEDocument10 pagesSO Snippet ENASEamanswaraj007No ratings yet
- Computer BasicsDocument94 pagesComputer Basicssanthosh hkNo ratings yet
- 3D Incompressible Navier-Stokes Solver Lower-Gauss-Seidel AlgorithmDocument1 page3D Incompressible Navier-Stokes Solver Lower-Gauss-Seidel Algorithmscience1990No ratings yet
- HqO Configurability GuideDocument14 pagesHqO Configurability GuideNick AranowNo ratings yet
- Data Analyst Job DescriptionDocument16 pagesData Analyst Job DescriptionjannatbluebirdNo ratings yet
- ModelingGuyedTowers TRNC01641 1 0001Document19 pagesModelingGuyedTowers TRNC01641 1 0001Kidd TornoNo ratings yet