Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rrlyc!!: Typical
Uploaded by
LeninVijayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rrlyc!!: Typical
Uploaded by
LeninVijayCopyright:
Available Formats
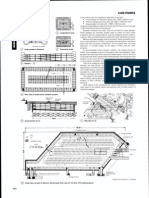
En suite bathrooms corridor
Bathrooms are mainly sited on interior walls, using
mechanical ventilation. For minimum building
width, bathrooms may be one behind the other
between rooms. Luxury bathrooms or economy
shower rooms may be against external walls.
Adjacent pairs of rooms are arranged mirror image
to share common vertical ducts and isolate a 4.6m’ b c 4.8m’
bathroom noise transmission. (See 12.)
Typical fitments: 1500mm bath, with grab bars, 72 Typical arrangements of bathrooms and ducts: (a) is best
shower spray, retractable clothes line and for access to duct but (b) and (c) provide more space for
curtain/screen; WC and washbasin. High-grade vanity top
hotels use 1700mm bath, twin basins set in vanitory
surrounds, WC and bidet. Luxury units include
separate dressing area and shower. Safety
considerations are critical.
Requirements: non-slip, drained surfaces; tiled
walls; acoustic ceiling; mirror over basin; screened, %?lotion and
moisture-proof lighting; panel access to services; services
controlled warmed air inflow/extraction; mixer
valve and thermostat control of hot water; shelf
space, towel racks, toilet roll holder, coat hanger,
electric shaver point, lidded waste bin, tissue
dispenser, toiletry tray/basket. In higher grade hotels:
w
telephone, music relay.
Resident circulations
Gross residential areas add circulation and floor
service spaces to the net room areas (see 13).Gross
factors can range from less than 5 % for chalet and
lodge type buildings with external entrances,
through 20-30% for ‘double-loaded’ central
A
corridors accessed by lifts and stairs, up to 3 5 4 5 %
for single-loaded side corridors and tower buildings.
As a rule emergency stairs must be sited at or near
the ends of each corridor. Lengths of corridors are
limited by travel distances to protected fire escape
stairs as specified in local codes. For corridors with
13 Plan forms for bedroom accommodation
sprinkler systems and fire exits athear opposite ends
allowing two directions of escape, maximum
distances usually range from 45 to 60m (with smoke service room
doors at 30m). Dead-end corridors with one exit are
:1
limited to 7.6m and travel distances within suites of
rooms to 9m.
Minimum fire resistance periods for separation of
exits such as staircases are normally: 1 hour for
buildings up to three storeys, 2 hours for four
storeys or more. Combustible material and surface
duct
-m-
Rrlyc!!
-
flame ratings of linings in exit routes are controlled. I
Large hotels use automatic sprinkler systems, fire mm
mode ventilation switching with alarm, lift and
smoke door activation. Fire alarm, indication panel -
and hydrant systems must be installed, together with
portable and COz extinguishers (for electrical
equipment), in specific areas as required.
corridor
1 guest lobby I
Apart from atrium scenic lifts, guest lifts are best
located off the main lobby within control of the
front desk. Guest and service lifts, normally in the
ratio 2:1, 3:2 or 4:3, are often sited back to back
for economy, the service lifts rising from back-of-
house areas and opening into a separated service
lobby on each floor (see 3,14).Large and high-
grade hotels often require specific provision for
luggage handling. 74 Typical vertical circulation core for 500 bedroom hotel
You might also like
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetDocument8 pagesNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetBadr AlmaazmiNo ratings yet
- FSIDocument4 pagesFSIGukan VenkatNo ratings yet
- Electrical Equipment LayoutDocument3 pagesElectrical Equipment LayoutMeenakshi Td100% (3)
- Fire SafetyDocument8 pagesFire SafetyDinanka JaiswalNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Fire Safety M7 April 2014Document48 pagesMODULE 7 Fire Safety M7 April 2014Shubham GoenkaNo ratings yet
- Group 17 - Fire Detection and Fighting MeasuresDocument19 pagesGroup 17 - Fire Detection and Fighting MeasuresKEERTHI ANANTHNo ratings yet
- Additional Requirements For High Rise BuildingsDocument22 pagesAdditional Requirements For High Rise BuildingsBHASKARA RAMAMNo ratings yet
- Five Stars Hotel - HamidaDocument147 pagesFive Stars Hotel - HamidaHamida Mohammed100% (5)
- General Guidelines For Egress DesignDocument23 pagesGeneral Guidelines For Egress DesignSuraj Kiran100% (2)
- Fire Alarm Notes BS5839Document7 pagesFire Alarm Notes BS5839amintawkNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument15 pagesResearch PaperaldridgeNo ratings yet
- Planning GuidelinesDocument20 pagesPlanning GuidelinesLOBERIANO MERVIE J.No ratings yet
- Theatre Design: Projector Room (Bio Box) : Subsidary RoomsDocument3 pagesTheatre Design: Projector Room (Bio Box) : Subsidary Rooms052 Deepak NaralaNo ratings yet
- Theatre Design: Projector Room (Bio Box) : Subsidary RoomsDocument3 pagesTheatre Design: Projector Room (Bio Box) : Subsidary Rooms052 Deepak NaralaNo ratings yet
- (ARC 326) Saumya - VermaDocument13 pages(ARC 326) Saumya - VermaSaumya VermaNo ratings yet
- NBC 2026 Part 4Document35 pagesNBC 2026 Part 4rishi.aditya62554No ratings yet
- Building Standards and RulesDocument8 pagesBuilding Standards and Rulesthanuja sharonNo ratings yet
- FireDocument1 pageFireArianne SaturnoNo ratings yet
- FireDocument1 pageFireArianne SaturnoNo ratings yet
- IT - Office Design 2.02.22Document58 pagesIT - Office Design 2.02.22VAISHALI RAMESHNo ratings yet
- Acmv Technical ReportDocument10 pagesAcmv Technical Reportarun kurlanNo ratings yet
- Data CollectionDocument9 pagesData CollectionSajithaNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety in Buildings and Codal ProvisionsDocument20 pagesFire Safety in Buildings and Codal Provisionskaushita banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Fire SafetyDocument1 pageFire Safetynasser.alkhamis11No ratings yet
- Fire Fighting - StandpipesDocument41 pagesFire Fighting - StandpipesSedfrey Pekitpekit100% (1)
- NMMC DCR SummaryDocument33 pagesNMMC DCR SummaryRoyal JadhavNo ratings yet
- Fire SystemDocument28 pagesFire SystemTaniya Sara PhilipNo ratings yet
- Shop Sizes & Layouts: External StairsDocument1 pageShop Sizes & Layouts: External Stairschiranjeevi dilipNo ratings yet
- Fire-Fighting Services IN High Rise BuildingsDocument30 pagesFire-Fighting Services IN High Rise BuildingsanasNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Last PartDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Last Partrina ranaNo ratings yet
- BLE Curtains Catalogue 2010 (Email)Document16 pagesBLE Curtains Catalogue 2010 (Email)Branza GeorgeNo ratings yet
- High Rise (Bye Laws)Document59 pagesHigh Rise (Bye Laws)Shikhar Singh100% (1)
- Nbs-Rule-Xii-Xv 2Document36 pagesNbs-Rule-Xii-Xv 2Reymar MungcalNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting NBC Norms SummaryDocument6 pagesFire Fighting NBC Norms SummaryKirti BatraNo ratings yet
- "Commercial Building": Research IN Architectural Design 7Document16 pages"Commercial Building": Research IN Architectural Design 7Mhare Oroceo CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Anthropometric Data For A Shopping MallDocument24 pagesAnthropometric Data For A Shopping MallKris Kiran80% (10)
- Machine Room/Job Site PreparationDocument2 pagesMachine Room/Job Site PreparationAldo Tolaba QuirogaNo ratings yet
- Building Integration: Lifts and StaircaseDocument9 pagesBuilding Integration: Lifts and StaircaseBATMANNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety in Buildings and Codal ProvisionsDocument20 pagesFire Safety in Buildings and Codal ProvisionsKoushali Banerjee100% (1)
- Fire SupressionDocument127 pagesFire SupressionJen AgabinNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety - ConceptDocument15 pagesFire Safety - ConceptReegan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Fire Requirements - UBBLDocument47 pagesFire Requirements - UBBLchipon3150% (2)
- Fire and Electrical Services and Mechanical Services in HospitalDocument29 pagesFire and Electrical Services and Mechanical Services in HospitalANIME LoveNo ratings yet
- Fire RequirementsDocument47 pagesFire Requirementsfaezah adnan100% (11)
- Fire SafetyDocument10 pagesFire Safetyaditya0% (1)
- Fire Alarm System Installation GuideDocument8 pagesFire Alarm System Installation Guideoadipphone7031No ratings yet
- Danang Vietnam (Sheraton) Consolidated Site Visit Report - 20170809Document8 pagesDanang Vietnam (Sheraton) Consolidated Site Visit Report - 20170809Cửu Vân LongNo ratings yet
- Mall StandardsDocument34 pagesMall StandardsJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Technical Catalogue 2017: Fire Ventilation SystemDocument55 pagesTechnical Catalogue 2017: Fire Ventilation SystemConstantin GubavuNo ratings yet
- Fire Detection, Alarm, and Communication SystemsDocument9 pagesFire Detection, Alarm, and Communication SystemsKenzo Braye GeraleNo ratings yet
- Means of Escape Part IVDocument6 pagesMeans of Escape Part IVrmaffireschoolNo ratings yet
- Smoke Control and Day To Day Ventilation For Multi-Storey Residential BuildingsDocument18 pagesSmoke Control and Day To Day Ventilation For Multi-Storey Residential BuildingsJurjus TaplastoNo ratings yet
- F03Document17 pagesF03Harsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Designing For Vehicles PDFDocument3 pagesDesigning For Vehicles PDFNerinel CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Building Codes and Bye-Laws: (Building Regulations For Hill Towns-Srinagar)Document15 pagesBuilding Codes and Bye-Laws: (Building Regulations For Hill Towns-Srinagar)Divya Jandhyala100% (1)
- Inside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryFrom EverandInside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryNo ratings yet
- Two Story Admin BLDG ExtensionDocument8 pagesTwo Story Admin BLDG ExtensionMARY ROSE ANN VILLAS PAYBANo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Commercial Building With Different Slab Arrangements Using ETABSDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design of Commercial Building With Different Slab Arrangements Using ETABSronald torresNo ratings yet
- House Plan by IBBOS CONSTRUCTION-LDESIGNDocument1 pageHouse Plan by IBBOS CONSTRUCTION-LDESIGNIbrahim MubarakNo ratings yet
- Imperial BSRDocument193 pagesImperial BSRniroshniroshNo ratings yet
- Pritzker Award Winning Architects: S N K HDocument47 pagesPritzker Award Winning Architects: S N K HNami KazumiNo ratings yet
- Rules Net Plot Area and Computation of FSIDocument21 pagesRules Net Plot Area and Computation of FSIsarangNo ratings yet
- NO Pekerjaan SAT Harga Satuan (RP.) Harga SATUAN (RP.) Jumlah Harga (RP.)Document50 pagesNO Pekerjaan SAT Harga Satuan (RP.) Harga SATUAN (RP.) Jumlah Harga (RP.)Bagus IqbalNo ratings yet
- Carpenters MetalworkDocument5 pagesCarpenters MetalworkJFAFPNo ratings yet
- A10530 Te Whatu Ora Lakes Project Mauri Ora SoQ March 2023 Excel Spreadsheet NOT A Contract DocumentDocument262 pagesA10530 Te Whatu Ora Lakes Project Mauri Ora SoQ March 2023 Excel Spreadsheet NOT A Contract DocumentcesarNo ratings yet
- Alphakit PDFDocument24 pagesAlphakit PDFNASWAHATIN MAHARANINo ratings yet
- Hill Architecture. Dagshai 16608Document26 pagesHill Architecture. Dagshai 1660833 Gunna RaviNo ratings yet
- Thermal Bypass: The Impact Upon Building PerformanceDocument8 pagesThermal Bypass: The Impact Upon Building PerformanceMark Siddall100% (5)
- Indo-Saracenic ArchitectureDocument14 pagesIndo-Saracenic ArchitectureGagandeep Kaur100% (1)
- Module 3 Part 3Document32 pagesModule 3 Part 3ANAS ANVERNo ratings yet
- Formwork in Building ConstructionDocument24 pagesFormwork in Building Constructionbharat verma100% (1)
- Method StatementDocument13 pagesMethod Statementchandu100% (1)
- BaroqueDocument2 pagesBaroqueMalasaga Trading CorporationNo ratings yet
- PZ Wall Column Formwork Systems 2019Document40 pagesPZ Wall Column Formwork Systems 2019Derek HeaneyNo ratings yet
- Technobond Insulation BRANZ Appraisl No 693 Ceiling and Wall PDFDocument5 pagesTechnobond Insulation BRANZ Appraisl No 693 Ceiling and Wall PDFJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Weyerhauser TJ-9001Document19 pagesWeyerhauser TJ-9001Andrew PooleNo ratings yet
- Estimation & Quantity SurveyingDocument20 pagesEstimation & Quantity Surveyingdraj1875977No ratings yet
- Biomimicry in Architecture: Hindu School of Architecture SONIPAT 131001Document47 pagesBiomimicry in Architecture: Hindu School of Architecture SONIPAT 131001Abhey Verma100% (1)
- Renson ConceptDocument10 pagesRenson ConceptdrugalediNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Discontinuous Puf Panels Using Cyclopentane As A Blowing AgentDocument6 pagesProject Report On Discontinuous Puf Panels Using Cyclopentane As A Blowing AgentEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Construction Document Phase Document Checklist: Project Name: Prepared By: SBC No.: DateDocument1 pageConstruction Document Phase Document Checklist: Project Name: Prepared By: SBC No.: DateZineddine ALICHENo ratings yet
- Case Study 01, Kantana Film SchoolDocument30 pagesCase Study 01, Kantana Film SchoolScoobee Doo100% (2)
- Code Check Plmbg-Mech PDFDocument124 pagesCode Check Plmbg-Mech PDFRessy PrayogiNo ratings yet
- Cluster Housing and Planned Unit Development PudDocument71 pagesCluster Housing and Planned Unit Development PudRoi KimssiNo ratings yet
- DC Valuation Gujranwala With Kahsra NumberDocument27 pagesDC Valuation Gujranwala With Kahsra NumberJavaid Ashraf0% (1)
- GFRG Design Manual - December 2012Document168 pagesGFRG Design Manual - December 2012venkieeNo ratings yet