Professional Documents
Culture Documents
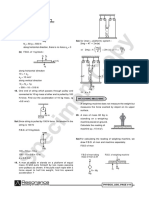
(B) Tension:: - KX K Spring
Uploaded by
SadguruOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(B) Tension:: - KX K Spring
Uploaded by
SadguruCopyright:
Available Formats
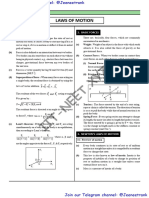
3.
Two blocks are kept in contact on a smooth surface as
F = 0 spring in natural
shown in figure. Draw normal force exerted by length does not exerts
A on B. any force on its ends
x
Fext
F F
F = – kx ;k = spring
Sol. In above problem, block A does not push block B, so constant or stiffness
constant (unit = N/m)
there is no molecular interaction between A and B. x = extension in spring
Hence normal force exerted by A on B is zero.
x
Note : F
F
• Normal is a dependent force it comes in role when Fext
one surface presses the other. F = – kx
x = compression in spring
(b) Tension : Note : Spring force is also electromagnetic in nature :
Tension is the magnitude of pulling force exerted by a
(d) Friction force :
string, cable, chain, rope etc. W hen a string is
connected to a body and pulled out, the string said to When a body is moving on a rough surface resistance
be under tension. It pulls the body with a force T, whose
to the motion occurs because of the interaction
direction is away from the body and along the length of
the string. Usually strings are regarded to be massless between the body and its surroundings. We call such
and unstretchable, known as ideal string. resistance as force of friction. Friction is also
considered as component of contact force which acts
parallel to the surfaces in contact.
(i) Origin of friction : The frictional force arises due to
molecular interactions between the surfaces at the
points of actual contact. When two bodies are placed
one over other, the actual area of contact is much
Note : (i) Tension in a string is an electromagnetic smaller then the total surface areas of bodies. The
force and it arises only when string is pulled. If a molecular forces starts operating at the actual points
massless string is not pulled, tension in it is zero.
of contact of the surfaces. Molecular bonds are formed
(ii) String can not push a body in direct contact.
at these contact points. When one body is pulled over
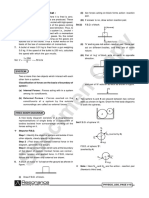
(c) Force Exerted by spring : the other, these bonds are broken, and the material
A spring is made of a coiled metallic wire having a get deformed and new bonds are formed. The local
definite length. When it is neither pushed nor pulled deformation sends vibrations into the bodies. These
then its length is called natural length.
Vibrations ultimately dumps out and energy of
At natural length the spring does not exert any force on
vibrations appears as heat. Hence to start or carry on
the objects attached to its ends.f the spring is pulled
at the ends, its length becomes larger than its natural the motion, there is a need of force.
length, it is known as stretched or extended spring.
Extended spring pulls objects attached to its ends. Body 1
A B
Normal spring
Body 2
Spring force on A Spring force on B
A B Actual area of contact
Stretched spring
Spring force on A Spring force on B (ii) Statics and Kinetic Frictions :
A B
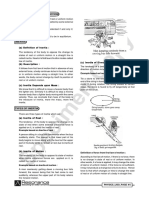
• Experiment :
Compressed spring
If the spring is pushed at the ends, its length becomes (A) Consider a block placed on a table, and a small
less than natural length. It is known as compressed force F1 is acted on it. The block does not move. It
spring. A compressed spring pushes the objects indicates that the frictional force fs starts acting in
attached to its ends.
opposite direction of applied force and its magnitude
is equal of F1(figure b). That is for the equilibrium of
PHYSICS_IJSO_PAGE #33
You might also like
- Class IX Vistaar ExpertDocument100 pagesClass IX Vistaar ExpertSrinivas VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Resonance Class 9 Ijso Study MaterialDocument100 pagesResonance Class 9 Ijso Study MaterialSaransh Goyal80% (25)
- Chapter 5 Laws of Motion Notes Manoj SirDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Laws of Motion Notes Manoj SirSTUDY WITH MADHAVNo ratings yet
- Force Is A Push or Pull Which TriesDocument37 pagesForce Is A Push or Pull Which TriesSantoshKumarNo ratings yet
- Force 8Document20 pagesForce 8Liana Belle0% (1)
- Laws of Motion: Inertia. The Inertia of A Body Is Related To What We Can Think of As The Amount of Matter It ContainsDocument8 pagesLaws of Motion: Inertia. The Inertia of A Body Is Related To What We Can Think of As The Amount of Matter It ContainsEduard Benjamin LauronNo ratings yet
- Resonance Class 9 Ijso Study MaterialDocument127 pagesResonance Class 9 Ijso Study MaterialSarvesh Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- (A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceDocument1 page(A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceSadguruNo ratings yet
- Friction TheoryDocument19 pagesFriction TheorySubbu SarabuNo ratings yet
- Forces Lecture NotesDocument37 pagesForces Lecture NotesWee Chee LimNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton LawsDocument37 pagesForces and Newton LawsRavenSkullNo ratings yet
- Etoos Short NoteDocument5 pagesEtoos Short NoteRudra PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument23 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Force Mass AccelerationDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Force Mass AccelerationAivan SaberonNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion. Byju'sDocument135 pagesLaws of Motion. Byju'sjimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument98 pagesForcesWee Chee LimNo ratings yet
- AND Classification of ForcesDocument40 pagesAND Classification of ForcesSandeep JaiswalNo ratings yet
- B16 Statics - Force Definition ClassificationDocument40 pagesB16 Statics - Force Definition ClassificationRaymart BulagsacNo ratings yet
- Unit1 ElasticityDocument7 pagesUnit1 ElasticityAnupama MohananNo ratings yet
- Plan For Today: Dry Friction Belt FrictionDocument17 pagesPlan For Today: Dry Friction Belt FrictionMr. JoestarNo ratings yet
- IJSO PlusDocument73 pagesIJSO PlusResonance Dlpd82% (34)
- WEEK 4 Forces and Newton LawsDocument36 pagesWEEK 4 Forces and Newton LawsShare linkNo ratings yet
- Topic111Newtons Second and Third Lawswith Key 1Document16 pagesTopic111Newtons Second and Third Lawswith Key 1serenity xxNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Thermal ExpansionDocument24 pagesElasticity and Thermal ExpansionAyush SrivastavNo ratings yet
- 03 Friction Revision Notes QuizrrDocument38 pages03 Friction Revision Notes QuizrrTech me BroNo ratings yet
- 65cd8cf91234170018fb40af - ## - Laws of Motion Short Notes JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2.0 2024Document1 page65cd8cf91234170018fb40af - ## - Laws of Motion Short Notes JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2.0 2024Krishanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- 09 Elasticity Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument7 pages09 Elasticity Formula Sheets QuizrrmaruthuNo ratings yet
- Inertia and Mass: Newton's Laws NameDocument11 pagesInertia and Mass: Newton's Laws NameAlexander Van TilNo ratings yet
- Topic07 08 Forces Friction Static EquilibriumDocument24 pagesTopic07 08 Forces Friction Static EquilibriumjgsNo ratings yet
- 2b.+Elementary+Mechanics+-+Statics Lecture+2b 14+feb+2014Document7 pages2b.+Elementary+Mechanics+-+Statics Lecture+2b 14+feb+2014lcy199541No ratings yet
- PHYS101 Lesson 2 Dynamics Part 2 - PDFDocument21 pagesPHYS101 Lesson 2 Dynamics Part 2 - PDFYour SageNo ratings yet
- Phy 2. Force and Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesPhy 2. Force and Laws of MotionShreyash MauryaNo ratings yet
- Types of Load Failure and Properties of MaterialDocument5 pagesTypes of Load Failure and Properties of Materialdummy staticNo ratings yet
- Mechanical System Isolation:: Free-Body DiagramDocument33 pagesMechanical System Isolation:: Free-Body DiagramChristian DelfinNo ratings yet
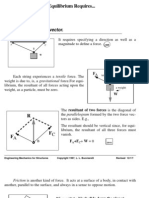
- Equilibrium Requires... : 2.1 Force Is A VectorDocument4 pagesEquilibrium Requires... : 2.1 Force Is A VectorGemarajuSreeTejaSimhaNo ratings yet
- 5 G8 Science Q1 - Week 2 - ForcesDocument27 pages5 G8 Science Q1 - Week 2 - ForcesMary Ann BarquioNo ratings yet
- Physgen Cu4Document16 pagesPhysgen Cu4emji miraNo ratings yet
- Elasticity 11th (MFA)Document10 pagesElasticity 11th (MFA)Sachin JainNo ratings yet
- CSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Mechanics 1 - StaticsDocument10 pagesCSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Mechanics 1 - StaticsCinderella WhiteNo ratings yet
- Physics Friction ModuleDocument7 pagesPhysics Friction ModuleFRANCES VISAYANo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Mechanics of MaterialsDocument50 pagesChapter 02 Mechanics of Materialspanave3104No ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument37 pagesElasticityTetsuya OkazakiNo ratings yet
- IctionDocument7 pagesIctionFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- NLM (WithOUT Ans) 2020 - Satveer SirDocument95 pagesNLM (WithOUT Ans) 2020 - Satveer SirGamerAWXNo ratings yet
- PHM031 - Modern Mechanics - Lecture 4Document23 pagesPHM031 - Modern Mechanics - Lecture 4Mohammed ZaitounNo ratings yet
- 2 ForcesDocument35 pages2 Forcesschiliza1975No ratings yet
- 003 Force and Motion PDFDocument9 pages003 Force and Motion PDFRachelle AndradeNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 2Document65 pagesMechanics 2abhist singhNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument14 pagesLaws of MotionSiva Chaitanya SunkuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 FrictionDocument7 pagesChapter 8 FrictionTOS CCLNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document36 pagesChapter 3sigitNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of Motion Class 11, IIT-JEE, NEET NotesDocument39 pagesNewton Laws of Motion Class 11, IIT-JEE, NEET NotesAshutosh Pareek100% (1)
- 10 1425 Web Lec 24 MoreStaticsDocument13 pages10 1425 Web Lec 24 MoreStaticsAK CreationNo ratings yet
- PH8151 - Engineering Physics 01 - by LearnEngineering - inDocument130 pagesPH8151 - Engineering Physics 01 - by LearnEngineering - inRathodNo ratings yet
- Newton S Laws of MotionDocument55 pagesNewton S Laws of MotionNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Motion and ForceDocument3 pagesLesson 3. Motion and ForceUchiha SasukeNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-16Document1 pageIJSO Part-16SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-20Document1 pageIJSO Part-20SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-17Document1 pageIJSO Part-17SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-19Document1 pageIJSO Part-19SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-15Document1 pageIJSO Part-15SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-14Document1 pageIJSO Part-14SadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairDocument1 page(B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairSadguruNo ratings yet
- Newton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaDocument1 pageNewton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunDocument1 pagePrinciple of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-13Document1 pageIJSO Part-13SadguruNo ratings yet
- Translatory Equilibrium: F F F MaDocument1 pageTranslatory Equilibrium: F F F MaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Impulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument1 pageImpulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of MotionSadguruNo ratings yet
- (A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S ExperimentsDocument1 page(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S ExperimentsSadguruNo ratings yet
- Nso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedDocument1 pageNso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-2Document1 pageIJSO Part-2SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-8Document1 pageIJSO Part-8SadguruNo ratings yet
- (A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceDocument1 page(A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceSadguruNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 CH 1 To 4Document4 pagesPaper 1 CH 1 To 4SadguruNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 Electric DipolesDocument9 pagesUnit - 5 Electric DipolesELMURNo ratings yet
- Thermo1 Chapter 04Document110 pagesThermo1 Chapter 04Yasser Hijji80% (15)
- Smart Safety Helmet: K.Sai Sampath, Belvin Benny, K.Avinash, M.Rama KrishnaDocument4 pagesSmart Safety Helmet: K.Sai Sampath, Belvin Benny, K.Avinash, M.Rama KrishnaAnonymous 53KsloNo ratings yet
- FEM Solved ExampleDocument4 pagesFEM Solved ExampleZakria ToorNo ratings yet
- PHY 2 - Problem Solution of CH 1Document10 pagesPHY 2 - Problem Solution of CH 1Mohamed El-GoharyNo ratings yet
- Lighting or Illumination Is The Deliberate Use of Light To Achieve A Practical or Aesthetic EffectDocument4 pagesLighting or Illumination Is The Deliberate Use of Light To Achieve A Practical or Aesthetic EffectasNo ratings yet
- Validation of Process Gas SystemsDocument6 pagesValidation of Process Gas SystemsJuan Manuel Valdez Von FürthNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Matrix Control: Presented by Chinta Manohar D Surya SuvidhaDocument35 pagesDynamic Matrix Control: Presented by Chinta Manohar D Surya SuvidhaManoharChintaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Actinometry IUPAC (Muy Bueno)Document47 pagesChemical Actinometry IUPAC (Muy Bueno)Leo DanNo ratings yet
- Salt Effect in Distillation - A Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesSalt Effect in Distillation - A Literature Reviewcombo162No ratings yet
- HAFTOMDocument67 pagesHAFTOMfanus100% (1)
- Fatigue and FractureDocument187 pagesFatigue and FractureRavishankarNo ratings yet
- Bojan Petkovic-Modeling and Simulation of A Double Pendulum With Pad PDFDocument12 pagesBojan Petkovic-Modeling and Simulation of A Double Pendulum With Pad PDFVeljko MilkovicNo ratings yet
- Link LookupDocument9 pagesLink LookupBobaru MariusNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ProblemsDocument1 pageThermodynamics ProblemsTots HolaresNo ratings yet
- Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner: TriadsDocument5 pagesJohann Wolfgang Döbereiner: TriadsMikeLesterCalolotNo ratings yet
- Volterra SeriesDocument5 pagesVolterra SeriesAnimasahun Olamide HammedNo ratings yet
- Investigating Water Transport Through The Xylem Network in Vascular PlantsDocument10 pagesInvestigating Water Transport Through The Xylem Network in Vascular PlantsverisugiyantoNo ratings yet
- 2 Wave Equations and Their SolutionDocument11 pages2 Wave Equations and Their SolutionPanagiotis StamatisNo ratings yet
- Ipe JR PhysicsDocument144 pagesIpe JR PhysicsSai Varun KruthiventiNo ratings yet
- Ent Sheath Overvoltages in Armoured Power: CablesDocument7 pagesEnt Sheath Overvoltages in Armoured Power: CablesA. HassanNo ratings yet
- Ramiro GpsDocument289 pagesRamiro Gpsbenghy SoporteNo ratings yet
- Random Vibration Best PracticesDocument34 pagesRandom Vibration Best PracticesAlvarohjNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Annular Prediffuser For Marine Gas Turbine Combustor Using CFD - A Study On The Effect of Strut ConfigurationDocument12 pagesModeling of Annular Prediffuser For Marine Gas Turbine Combustor Using CFD - A Study On The Effect of Strut Configurationrajarathnam.kNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Operation Instruction On BT118: Key Is Also MultiDocument7 pagesChapter Two Operation Instruction On BT118: Key Is Also MultiNathaniel TalisayanNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee AitsDocument23 pagesFiitjee Aitsullasagw100% (6)
- Addition of ForcesDocument1 pageAddition of ForcesMargam Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- 09-SAMSS-071 - (2016) Qualification Requirements For Inorganic Zinc Primer (APCS-17A) and (APCS-17B)Document9 pages09-SAMSS-071 - (2016) Qualification Requirements For Inorganic Zinc Primer (APCS-17A) and (APCS-17B)middlepermian100% (1)
- Ris 223Document157 pagesRis 223Rizky FirdausNo ratings yet