Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CVS Tables Franz
Uploaded by
Cole GoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CVS Tables Franz
Uploaded by
Cole GoCopyright:
Available Formats
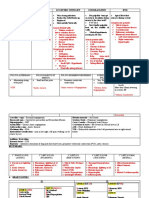
CLINMED – CVS NOTES – 2017
CONCENTRIC ECCENTRIC ECCENTRIC WITH LIFT LVH DILATATION RVH
Strong forceful Displaced apical Very strong pulsation Not palpable Apical Beat that retracts during
pulsation/impulse beat horizontally Pushes the *turn pt. on lateral systole
5th ICS MCL/10cm 5th ICS LAAL/12cm steth/Hands up decubitus-bring
Thick wall Thick wall Displaced nearer to the chest
Small cavity Thick septum Horizontally/Vertically wall* Symptomatic patients:
5th/6th ICS Mitral stenosis
Seen in Patient with : Seen in Patient with : Seen in Patient with : Very faintly palpable Congested heart disease
Chronic HPN Chronic HPN Volume overload beat on the middle Cor pulmonale
due to vulvular of axilla Pulmonary embolism
disease Rheumatic heart disease
Mitral regurgitation *Global hypokinesia o Left atrial enlargement
Aortic regurgitation moving in 2D echo o Right ventricular
Congenital Heart hypertrophy
Disease Seen in patient with :
Eg. Patent Ductus Cardiomyopathy
Arteriosus (PDA) CAD
Chronic Ischemia
Symptomatic patients: Heart Disease
DOB Coronary Bypass
Orthopnea Cox Virus
Peripheral edema Echo virus-viral
w/ jugular vein cardiomyopathy
distention Use of alcohol
On ECG Taking illicit drugs
o Small QRS-
Hypokinetic
On Xray
o Markedly
enlarged heart
FRANZ MIKKAEL AGAS, MD (FMAMD) 1
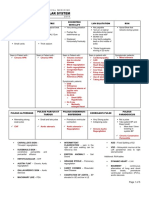
CLINMED – CVS NOTES – 2017
PULSUS ALTERRANS PULSUS PARVUS ET TARDUS PULSUS BIGEMINUS/ CORRIGAN’S PULSE PULSUS PARADOXICUS
BISFRIENS
Alternating strong Small and late pulse Premature Very Strong pulse Not a pulse
weak pulse ventricular Collapsing pulse Take pt BP and Deep breath
contraction -More than 10mm lowering in
*CHF *Aortic stenosis systolic BP
*Aortic stenosis + *Chronic Aortic
Regurgitation Regurgitation *Chronic Constrictive Pericarditis
Carvallos’s sign – Tricuspid regurgitation Ebstein Anomaly – Sail Sound
Kussmauls sign – Constrictive pericarditis and Pericardial effusion Graham Steele – Pulmonary regurgitation
Hepatojugular – CHF Carey Coombs – Rheumatic heart Disease
Austin Flint – Chronic Aortic regurgitation Coartation of Aorta – BP elevated in UE and low in LE
Gallavardin’s sign – Aortic Stenosis ASD – Fixed Splitting of S2
Machinary like – PDA VSD – Holosystolic murmur at the Left parasternal area to right sternal
border
Intermittent Claudication – pain in the right calf upon walking can be
relieve by rest
Addtion: RAA tables
Dynamic heart – LVH
Bigeminy - continuous alternation of long and short heart beats, premature ventricular contraction (PVC), aortic stenosis
FRANZ MIKKAEL AGAS, MD (FMAMD) 2
CLINMED – CVS NOTES – 2017
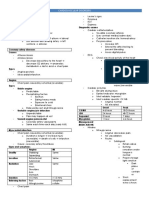
BEST HEARD:
2nd RIGHT ICS PSL 2nd LEFT ICS PSL 3rd LEFT ICS 4th LEFT ICS PSB 5th LEFT ICS MAL
(AORTIC) (PULMONIC) (ERB’S POINT) (TRICUSPID) (MITRAL)
1. Paradoxical 1. Physiologic 1. Mitral Valve Prolapse 1. Tricuspid 1. Mitral Regurgitation
Splitting of S2 Splitting of S2 (MVP) Regurgitation 2. Mitral Stenosis
2. Aortic Stenosis 2. Persistent Splitting 2. Vetricular Septal 2. ASD 3. S3
3. Aortic Aneurysm of S2 - Defect (VSD) 3. Physiologic 4. S4
3. Pulmonic 3. Aortic Regurgitation Splitting of S1 5. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Aneurysm 4. Quadruple Rhythm 4. Ebstein Anomaly
4. Pulmonary 5. Hypertrophic
Stenosis Cardiomayopathy
5. PDA
6. ASD
A. HEART SOUNDS
S1 S2
LOUD S1 (TIM)
LOUD A2 (LA-SA) LOUD P2 (LP-PA)
Tachycardia
Systemic HPN Pulmonary HPN
Increased Temp
Aortic Dilatation ASD
Mitral Stenosis
SOFT S1 (VAMCC) SOFT A2 SOFT P2
Vol. Overload Aortic Stenosis Pulmonary Stenosis
A-FIB
Mitral Regurgitation
CHF
CAD
FRANZ MIKKAEL AGAS, MD (FMAMD) 3
CLINMED – CVS NOTES – 2017
B. HEART SOUND
S1 S2
SPLITTING 1st-Closure of mitral valve 1st – Aortic
2nd – Pulmonic
WIDENING Complete RBBB RBBB
Delayed onset of RV pressure pulse Delayed closure of PV
Mitral regurgitation
REVERSED Severe mitral stenosis
LBBB
Left atrial myxoma
PHYSIOLOGIC Delayed closure not vary with
pulmonic valve
ASD
RBBB
FIXED Does not vary with respiration
ASD
RVF
PARADOXICAL Does not vary on expiration and
disappears on inspiration
Delayed closure at AV
Aortic stenosis
LBBB
Hypertropic Cardiomyopathy
SYSTOLIC SOUND
EJECTION SOUNDS NON-EJECTION SOUND/MIDSYSTOLIC CLICK
-HIGH PITCH SOUND (DAPE) MVP
Dilatation of Aorta Barlow’s Syndrome
Aortic Stenosis
Pulmonic Stenosis
Early Systole
FRANZ MIKKAEL AGAS, MD (FMAMD) 4
CLINMED – CVS NOTES – 2017
DIASTOLIC SOUND
OPENING SNAP S3 S4
- Brief high pitch - Low pitched - Low pitched
- LLSB - Normal in children - Pre-systolic sound
- Radiates to the base of heart
AV Stenosis Early Diastole Absent in AF
Cardiac tamponade Systemic HPN
Tricuspid regurgitation Aortic Stenosis
Constrictive pericarditis *vol. overload Hypertropic Cardiomyopathy
Ventricular Gallop After S2 Ischemic Heart Disease
Heart Failure Mitral Regurgitation
Aortic Regurgitation
Weak Contractility
REVIEW:
Normla
Apex: Loud S1 Soft S2
Based: Loud S2 Soft S1
The intensity of first heart sound is being affected by heart rate. In patient with very fast heart (FEVER, PREGNANCY, and HYPERTHYROIDISM –
S1 becomes loud all over
Physiologic Splitting of S2 in Normal Breathing
Persistent Splitting of S2 in Pulmonic Stenosism Atrial Septal Defect
Paradoxical Splitting: P2 Louder than A2 (in comparison to physiologic and persistent splitting which has louder A2 than P2)
S3
-Mitral Regurgitation
-Hypertropic Cardiomyopathy
-Restrictive in early diastole (ventricular filling)
FRANZ MIKKAEL AGAS, MD (FMAMD) 5
CLINMED – CVS NOTES – 2017
HEART MURMUR
Systolic Diastolic
MITRAL VALVE REGURGITATION STENOSIS
TRICUSPID VALVE (Holocystolic) (MID SYSTOLIC MURMUR)
AORTIC VALVE STENOSIS REGURGITATION
PULMONIC VALVE (Midsystolic/Systolic Ejection Murmur) (EARLY DIASTOLIC MURMUR)
SYSTOLIC DIASTOLIC
MIDSYSTOLIC (APAH) EARLY DIASTOLIC (APA)
- Aortic Stenosis - AORTIC REGURGITATION
- Pulmonic stenosis - PULMONIC REGURGITATION
- ASD - AUSTIN FLINT
- HOCM – Hypertropic Cardiomyopathy
HOLOSYSTOLIC (MTV) MID-LATE DIASTOLIC (MT)
- Miral Valve Regurgitation - Mitral Stenosis
- Tricuspid Regurgitation - Tricuspid Stenosis
- VSD
LATE SYSTOLIC
- MVP
CONTINOUS MURMUR VENOUS HUM – Loudest in Diastole : PERICARDIAL FRICTION RUB –
PDA- MACHINERY LIKE MURMUR Humming or Rearing Sound Scartchy, scraping sound at Erb’s
point
Austin Flint – Soft rumbling murmur. Late systolic
FRANZ MIKKAEL AGAS, MD (FMAMD) 6
CLINMED – CVS NOTES – 2017
POSITIONING
Valsalva Increase hypertrophic cardiomyopathy murmur
Deep breathing Right sided murmur
Hand grip Left sided murmur
Standing from squatting MVP
Squatting from standing Decrease hypertrophic cardiomyopathy murmur
Squatting and leg raising Increase venous return to the heart
AUSCULTATION
Sitting and leaning Mild aortic regurgitation
HEART
Aortic Stenosis Ejection systolic murmur transmitted into carotids
Crescendo-decrescendo murmur
Ejection click or sound
Paradoxical splitting of S2
Aortic regurgitation Diastolic blowing murmur
Wide systolic pressure
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Atrial septal defect Fixed/persistent splitting of S2
Ventricular septal defect Holosystolic murmur Heard at Erb’s, transmitted to the right sternal border
Tricuspid regurgitation 4th ICS parasternal line
Pulmonic stenosis RBBB
Mid-diastolic murmur radiates to left shoulder
Crescendo-decrescendo
Persistent splitting of S2
Pulmonic regurgitation
Mitral stenosis Opening snap
Diastolic murmur
Loud S1
Mitral regurgitation Holosystolic murmur displaced to the left axilla/infrascapular
Diminished S1
Rumbling murmur
Mitral valve prolapse Mid-systolic click
Late systolic murmur
Non-ejection sound
Coarctation of aorta Greater BP in the UE compared to LE
FRANZ MIKKAEL AGAS, MD (FMAMD) 7
You might also like
- REVIEWER2Document6 pagesREVIEWER2Lorielyn Ashlee GaiteNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Left and Right Heart Failure: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument118 pagesDifferences Between Left and Right Heart Failure: Diagnosis and TreatmentMirza Thaariq HapsitoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine CVS Tabulated 2019Document5 pagesClinical Medicine CVS Tabulated 2019Justin TayabanNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- ch28 Notes Part 2Document9 pagesch28 Notes Part 2Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- IM Part 1Document48 pagesIM Part 1sasghfdgNo ratings yet
- IM Part 1 and 2 CombinedDocument100 pagesIM Part 1 and 2 CombinedsasghfdgNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument8 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseSanthosh.S.U100% (3)
- ACC Jimmy AsafDocument152 pagesACC Jimmy AsafFikriYTNo ratings yet
- 5 Pericarditis and Its Complications ICMPDDocument22 pages5 Pericarditis and Its Complications ICMPDmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: 10 July 2013Document8 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: 10 July 2013Michelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- Sudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesSudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart Diseasenmyza89No ratings yet
- Word Association PANCEDocument31 pagesWord Association PANCEnevmerka100% (1)
- PT Management & Problems of The CV System - Part 3 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPT Management & Problems of The CV System - Part 3 Cheat SheetGayle MarieNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument2 pagesMitral StenosisitsmailbbkNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) : Pathogenesis RFDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (CAD) : Pathogenesis RFJennyu Yu100% (1)
- High Risk AdultDocument7 pagesHigh Risk AdultJen IlaganNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Defect Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 pagesCongenital Heart Defect Diagnosis and TreatmentPrincess LegansonNo ratings yet
- MateriDocument39 pagesMateriDR BASUKINo ratings yet
- Endocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Document8 pagesEndocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Eben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Acute Heart Failure PDFDocument18 pagesAcute Heart Failure PDFRiaak ImNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Physical ExaminationDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System: Physical ExaminationMiguel C. DolotNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsDocument3 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- Hi-Yield Notes in Im & PediaDocument20 pagesHi-Yield Notes in Im & PediaJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- VALVULAR HEART DISEASES Transes PrelimsDocument3 pagesVALVULAR HEART DISEASES Transes PrelimsRichell CatianNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart FailureErin MarieNo ratings yet
- Approach To Chest Pain 1Document5 pagesApproach To Chest Pain 1Sonu CanNo ratings yet
- Anak 2Document107 pagesAnak 2Nency PurmayaNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Lec Prelim NotesDocument35 pagesNCM 114 Lec Prelim Notesmblanco.dchNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DisordersDocument35 pagesCardiac DisordersNaomi Anne AsuntoNo ratings yet
- Cardio PathDocument6 pagesCardio PathPranay ManiarNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument40 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromesandi siregarNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument39 pagesShockCut Ristina OlviaNo ratings yet
- PANCE Word Associations PDFDocument27 pagesPANCE Word Associations PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Parameter 0 1 2 Activity Pulse GrimaceDocument2 pagesParameter 0 1 2 Activity Pulse GrimaceAnna BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Aortic StenosisDocument8 pagesAortic Stenosisdr.moni.co.ukNo ratings yet
- MCQ 1. Heart Sound Heart Sound S1 S2Document7 pagesMCQ 1. Heart Sound Heart Sound S1 S2Atirah AaNo ratings yet
- PT Management & Problems of The CV System - Part 4 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPT Management & Problems of The CV System - Part 4 Cheat SheetKat KatNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock and HemodynamicsDocument18 pagesCardiogenic Shock and HemodynamicsfikriNo ratings yet
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDocument5 pagesPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument48 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasenabillagusrinaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Critically Ill PatientDocument5 pagesAssessment of The Critically Ill PatientCris John RicoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure CHF: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimDocument94 pagesCongestive Heart Failure CHF: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimDella DevegaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Dysfunction: (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)Document6 pagesCardiovascular Dysfunction: (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)Jc MacujaNo ratings yet
- Syok Kardiogenik Dr. Rani Maliawan, SP JPDocument59 pagesSyok Kardiogenik Dr. Rani Maliawan, SP JPLuh Leni AriniNo ratings yet
- Understanding Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument54 pagesUnderstanding Congenital Heart DiseaseYemata HailuNo ratings yet
- CARDIODocument5 pagesCARDIORayana UbasNo ratings yet
- IM-Heart Failure Concept MapDocument16 pagesIM-Heart Failure Concept MapTrisNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Cardio-Vascular ExaminationDocument43 pagesCardio-Vascular ExaminationDimas FrasesaNo ratings yet
- Valvular DiseasesDocument8 pagesValvular DiseasesBeryl Ben MergalNo ratings yet
- Stroke Summary Document For Medical StudentsDocument3 pagesStroke Summary Document For Medical StudentsDeclan O'KaneNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCDocument25 pagesCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCYUSRIL ZUMADINSYAHNo ratings yet
- Aortic Regurgitation CaseDocument38 pagesAortic Regurgitation CaseIka MagfirahNo ratings yet
- AkshayDocument35 pagesAkshaySheryl VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Reviewer CardiovascularDocument4 pagesPediatric Nursing Reviewer CardiovascularnieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ExaminationDocument10 pagesCardiovascular ExaminationSaurabh PaudyalNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- JournalsDocument10 pagesJournalsCole GoNo ratings yet
- Journal (Ophtha)Document3 pagesJournal (Ophtha)Cole GoNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Cammayo, Alden R. Canlas, Joy Marie Canezal, Raiyah Members: Caluag, Elaine Caluag, Janssen Canlas, JamesDocument37 pagesGroup 1: Cammayo, Alden R. Canlas, Joy Marie Canezal, Raiyah Members: Caluag, Elaine Caluag, Janssen Canlas, JamesCole GoNo ratings yet
- Long Term Care ServicesDocument8 pagesLong Term Care ServicesCole GoNo ratings yet
- PSMID COVID TX Guidelines V.3.31.20a PDFDocument62 pagesPSMID COVID TX Guidelines V.3.31.20a PDFRenz Marion AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- Journal (Ophtha)Document3 pagesJournal (Ophtha)Cole GoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Beyond The Data-E-cigarettes: An Emerging Public Health ChallengeDocument1 page2017 Beyond The Data-E-cigarettes: An Emerging Public Health ChallengeCole GoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Journal Analysis: What Are The Basic InformationDocument1 pageGuidelines On Journal Analysis: What Are The Basic InformationCole GoNo ratings yet
- Journal (Ophtha)Document3 pagesJournal (Ophtha)Cole GoNo ratings yet
- Med Block ScheduleDocument1 pageMed Block ScheduleCole GoNo ratings yet
- Med Block ScheduleDocument1 pageMed Block ScheduleCole GoNo ratings yet
- Revolutionizing Via RoboticsDocument7 pagesRevolutionizing Via RoboticsSiddhi DoshiNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Students Pronounciation Errors Made by Ninth Grade of Junior High School 1 TengaranDocument22 pagesAn Analysis of Students Pronounciation Errors Made by Ninth Grade of Junior High School 1 TengaranOcta WibawaNo ratings yet
- Tennessee Inmate Search Department of Corrections LookupDocument9 pagesTennessee Inmate Search Department of Corrections Lookupinmatesearchinfo50% (2)
- SCMReport Group4 MilmaDocument10 pagesSCMReport Group4 MilmaJyotsna Gautam0% (1)
- Digi-Notes-Maths - Number-System-14-04-2017 PDFDocument9 pagesDigi-Notes-Maths - Number-System-14-04-2017 PDFMayank kumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Love? - Osho: Sat Sangha SalonDocument7 pagesWhat Is Love? - Osho: Sat Sangha SalonMichael VladislavNo ratings yet
- 12.1 MagazineDocument44 pages12.1 Magazineabdelhamed aliNo ratings yet
- Research PhilosophyDocument4 pagesResearch Philosophygdayanand4uNo ratings yet
- Structural Works - SharingDocument37 pagesStructural Works - SharingEsvimy Deliquena CauilanNo ratings yet
- MA CHAPTER 2 Zero Based BudgetingDocument2 pagesMA CHAPTER 2 Zero Based BudgetingMohd Zubair KhanNo ratings yet
- MBA Third Semester Model Question Paper - 2009: Management and Organization Development-MU0002 (2 Credits)Document11 pagesMBA Third Semester Model Question Paper - 2009: Management and Organization Development-MU0002 (2 Credits)ManindersuriNo ratings yet
- BICON Prysmian Cable Cleats Selection ChartDocument1 pageBICON Prysmian Cable Cleats Selection ChartMacobNo ratings yet
- Classification of Boreal Forest Ecosystem Goods and Services in FinlandDocument197 pagesClassification of Boreal Forest Ecosystem Goods and Services in FinlandSivamani SelvarajuNo ratings yet
- Product Packaging, Labelling and Shipping Plans: What's NextDocument17 pagesProduct Packaging, Labelling and Shipping Plans: What's NextShameer ShahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing (COMP-01102) Telecom 1 Semester: Lab Experiment No.05Document7 pagesIntroduction To Computing (COMP-01102) Telecom 1 Semester: Lab Experiment No.05ASISNo ratings yet
- 05 Gregor and The Code of ClawDocument621 pages05 Gregor and The Code of ClawFaye Alonzo100% (7)
- ISA standards, materials, and control room conceptsDocument8 pagesISA standards, materials, and control room conceptsGiovanniNo ratings yet
- Midgard - Player's Guide To The Seven Cities PDFDocument32 pagesMidgard - Player's Guide To The Seven Cities PDFColin Khoo100% (8)
- Canine Guided Occlusion and Group FuntionDocument1 pageCanine Guided Occlusion and Group Funtionlittlestar35100% (3)
- Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Areas Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Areas Teaching Dates and Time QuarterKhesler RamosNo ratings yet
- Irony in Language and ThoughtDocument2 pagesIrony in Language and Thoughtsilviapoli2No ratings yet
- Ghaziabad Resume Amresh Kumar Upadhyay Desktop EngineerDocument2 pagesGhaziabad Resume Amresh Kumar Upadhyay Desktop EngineerRipunjay MishraNo ratings yet
- Astrology - House SignificationDocument4 pagesAstrology - House SignificationsunilkumardubeyNo ratings yet
- MiQ Programmatic Media Intern RoleDocument4 pagesMiQ Programmatic Media Intern Role124 SHAIL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Equity Valuation Concepts and Basic Tools (CFA) CH 10Document28 pagesEquity Valuation Concepts and Basic Tools (CFA) CH 10nadeem.aftab1177No ratings yet
- February / March 2010Document16 pagesFebruary / March 2010Instrulife OostkampNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Globalization of World EconomicsDocument17 pagesLesson 2 Globalization of World EconomicsKent Aron Lazona Doromal57% (7)
- MinePlan Release NotesDocument14 pagesMinePlan Release NotesJuanJo RoblesNo ratings yet
- Tong RBD3 SheetDocument4 pagesTong RBD3 SheetAshish GiriNo ratings yet
- RA 4196 University Charter of PLMDocument4 pagesRA 4196 University Charter of PLMJoan PabloNo ratings yet