Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Approaches in A Qualitiative Research Design
Uploaded by
Hyde Park0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views3 pagesThe document discusses several qualitative research approaches:
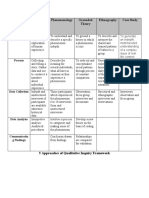
[1] Ethnography aims to describe a culture's characteristics and features through fieldwork and key informant interviews.
[2] Grounded theory develops theories from patterns in interview and observational data, with parallel data collection and analysis.
[3] Phenomenology describes lived experiences from subjects' point of view through interviews and observations to identify themes in individual realities.
Original Description:
Original Title
Approaches_QualiRes.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several qualitative research approaches:
[1] Ethnography aims to describe a culture's characteristics and features through fieldwork and key informant interviews.
[2] Grounded theory develops theories from patterns in interview and observational data, with parallel data collection and analysis.
[3] Phenomenology describes lived experiences from subjects' point of view through interviews and observations to identify themes in individual realities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views3 pagesThe Approaches in A Qualitiative Research Design
Uploaded by
Hyde ParkThe document discusses several qualitative research approaches:
[1] Ethnography aims to describe a culture's characteristics and features through fieldwork and key informant interviews.
[2] Grounded theory develops theories from patterns in interview and observational data, with parallel data collection and analysis.
[3] Phenomenology describes lived experiences from subjects' point of view through interviews and observations to identify themes in individual realities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1
John Ryan M. Jacot | 11 – HumSS
An Introduction to Qualitative Research
School Year 2018 – 2019
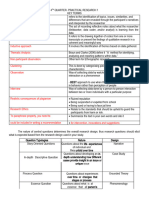
THE APPROACHES IN A QUALITIATIVE RESEARCH DESIGN
A qualitative research design is a general way of thinking about conducting qualitative research. It
describes, either explicitly or implicitly, the purpose of the qualitative research, the role of the
researcher(s), the stages of research, and the method of data analysis. (Trochim, 2006)
Approach Purpose Method Analysis Outcome
Ethnography To describe a Fieldwork and Detailed and rich “Description of
culture: its immersion in the description of Culture”
characteristics culture culture
and features Key informant
interviews and
observations
Grounded To develop Interviews and “Concept Theory backed by
Theory theories from Observations formation” evidences from
analysis of Data collection “Concept data
patterns, themes and analysis are Development” by
and categories done in parallel. looking into
Data are analyzed literature and
as they come. “sampling of
Patterns and subjects”
themes are “Concept
validated and Modification and
disproved by Integration”
further data
collection.
Phenomenolo To describe Seek persons who Classify and rank Findings
gy experiences as understand study data described from
they are lived and are willing to Sense of subject’s point-of-
To examine the express inner wholeness view
uniqueness of feelings and Examine Research
individual’s lived experiences experiences identifies themes
situations Describe beyond human Structural
To describe that experiences of awareness or that explanation of
each person has phenomenon cannot be findings is
own reality; Write experiences communicates developed.
reality is of phenomenon
subjective Direct
Observation
Audio or
Videotape
Narrative To describe Interviews and Analysis of Narrative
Analysis experiences observations Content accounts from
Research Looking into form individual s
participants are and function of
encouraged to stories
share stories.
Discourse To describe Interviews and Analysis of Discourses that
Analysis discourse present Observations content and reflect beliefs,
in a phenomenon meaning behind principles, and
the conversation perspectives
Historical To describe and Formulate idea – Synthesis of all Select means of
Approach examine events of select topic after data; accept and presentation –
the past to reading related reject data; biography,
understand the literature reconcile chronology, issue
present and Develop research conflicting paper
anticipate questions evidence
potential future Develop an
effects inventory of
resources –
archives, private
libraries, papers
Clarify validity
and reliability of
data – primary
sources,
authenticity,
biases
Develop research
outline to
organize
investigative
process
Collect data
Case Study Describe in-depth Direct observation Synthesis of In-depth
the experience of and interaction Experience description of the
one person, with the subject experience
family, group,
community or
institution
You might also like
- The Approaches in A Qualitiative Research DesignDocument3 pagesThe Approaches in A Qualitiative Research DesignHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Research Lec1Document2 pagesResearch Lec1angela verayeNo ratings yet
- Qualitative ResearchDocument61 pagesQualitative Researchrmm0415No ratings yet
- Narrative Study Phenomenology Grounded Theory Ethnography Case StudyDocument1 pageNarrative Study Phenomenology Grounded Theory Ethnography Case StudyAISHA SOOMRONo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research Designs: 1. PhenomenologyDocument5 pagesQualitative Research Designs: 1. Phenomenologynoramin89No ratings yet
- Handout On Qualitative ResearchDocument58 pagesHandout On Qualitative Researchchingferdie_111No ratings yet
- Qualitative Research by J.I. AniDocument23 pagesQualitative Research by J.I. Ani'Yemi AwofalaNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Assumptions and Interpretive Frameworks: Jessline 717182008Document53 pagesPhilosophical Assumptions and Interpretive Frameworks: Jessline 717182008melissaacehNo ratings yet
- Padillo, Bea S. Grade 11 - Leo II Activity 1: Comparison of The Kinds of Qualitative ResearchesDocument2 pagesPadillo, Bea S. Grade 11 - Leo II Activity 1: Comparison of The Kinds of Qualitative ResearchesBea PadilloNo ratings yet
- Advance Qualitative ReserachDocument27 pagesAdvance Qualitative Reserachnestor castanos jrNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Researchers Use:: The Characteristics of ResearchDocument5 pagesQualitative Researchers Use:: The Characteristics of ResearchErica Rose RamalesNo ratings yet
- PR 1 Module 2Document26 pagesPR 1 Module 2olivaresjirah7No ratings yet
- Reviewer For Practical Research 1 PrelimDocument5 pagesReviewer For Practical Research 1 PrelimMaureen ElumbaringNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research: Asistensi 2Document14 pagesQualitative Research: Asistensi 2Priandi Imaduddin SudarmaNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 1.2Document8 pagesResearch in Daily Life 1.2Roberto F. JavalNo ratings yet
- Types of Qualitative ResearchDocument14 pagesTypes of Qualitative ResearchKEAN CHRISTOPHER A NUNEZNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 SLHT Week 3Document8 pagesPractical Research 1 SLHT Week 3rodulfo capangpanganNo ratings yet
- Research 1Document6 pagesResearch 1Emmanuelle CalleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative StudyDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative StudyDr. Muhammad Sofwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- EPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchDocument5 pagesEPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research DesignsDocument2 pagesQualitative Research DesignsCHRISTINA LLAUDERESNo ratings yet
- Midterm Prac Research Session 3 PDFDocument19 pagesMidterm Prac Research Session 3 PDFCaine de LeonNo ratings yet
- Navia, Ma. Sharlyn - Activity 3Document2 pagesNavia, Ma. Sharlyn - Activity 3Ma Sharlyn Ariego NaviaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design - Choosing Among Five Approaches (PDFDrive) - 84-91Document8 pagesQualitative Inquiry & Research Design - Choosing Among Five Approaches (PDFDrive) - 84-91-'aku Cliquers'-No ratings yet
- Qualitative Research: Methods and Practical Tips: References: Methodology BooksDocument40 pagesQualitative Research: Methods and Practical Tips: References: Methodology Bookska ming chu100% (1)
- Group 10 - Narratives Research DesignDocument12 pagesGroup 10 - Narratives Research DesignChelsea Chahya NingratNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Assumptions and Interpretive Frameworks1Document12 pagesPhilosophical Assumptions and Interpretive Frameworks1Rashard AlexanderNo ratings yet
- PR1 - Lesson 2 - Qualitative ResearchDocument2 pagesPR1 - Lesson 2 - Qualitative ResearchAnatanya TironaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR1Document3 pagesReviewer PR1daniel.jungwon06No ratings yet
- Qualitative Vs Quantitative ResearchDocument6 pagesQualitative Vs Quantitative ResearchJelly Mae PeñaNo ratings yet
- A Characteristics of Five Qualitative ApproachesDocument3 pagesA Characteristics of Five Qualitative ApproachestesfaNo ratings yet
- General Forms of ResearchDocument25 pagesGeneral Forms of ResearchJa FloresNo ratings yet
- Doing Research in A Way That Counts: Research and The Research ProcessDocument28 pagesDoing Research in A Way That Counts: Research and The Research ProcessArnold Magdalita FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Conceptualization of Research: What? Why? How?Document68 pagesConceptualization of Research: What? Why? How?pragyasimsNo ratings yet
- Practica L Research 2Document22 pagesPractica L Research 2tan2masNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 Q1 M4Document20 pagesPractical Research 1 Q1 M4dv vargasNo ratings yet
- Conducting Qualitative Research: Writing The MethodologyDocument30 pagesConducting Qualitative Research: Writing The MethodologytamiNo ratings yet
- 02 Qualitative Research MethodsDocument46 pages02 Qualitative Research MethodsAminaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Data AnalysisDocument18 pagesQualitative Data Analysisbsunilsilva100% (2)
- Prac ResDocument5 pagesPrac Rescuasayprincessnicole4No ratings yet
- Research and Types of ResearchDocument6 pagesResearch and Types of ResearchdatujaiysandiganNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument7 pagesResearchLoreanne DamascoNo ratings yet
- Narrative Study - Durratu Fakhria N&Parahat AtabayevDocument18 pagesNarrative Study - Durratu Fakhria N&Parahat AtabayevNun100% (1)
- 7 QUALITATIVE DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS 26112020 100055am 22062021 042520pmDocument89 pages7 QUALITATIVE DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS 26112020 100055am 22062021 042520pmthewarriorprincess02No ratings yet
- Research Methods New EditionDocument28 pagesResearch Methods New EditionStiffany Rose Nillama TinambunanNo ratings yet
- MPPU 1024 Research Methods in Education: (Comparison Between Grounded Theory, Ethnography, Narrative & Case Study)Document3 pagesMPPU 1024 Research Methods in Education: (Comparison Between Grounded Theory, Ethnography, Narrative & Case Study)Kamarul KhamisNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 10 - Qualitative ResearchDocument12 pagesStudy Guide 10 - Qualitative Researchtheresa balaticoNo ratings yet
- Doing Qualitative Research - OverviewDocument29 pagesDoing Qualitative Research - OverviewTram AnhNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research DesignDocument3 pagesQualitative Research DesignBea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Module 2Document5 pagesPractical Research Module 2Andrielle Keith Tolentino MantalabaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Approach and EtcDocument26 pagesQualitative Approach and EtcCarl Jay Dag-umanNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument6 pagesActivityDizon Yevgeny Dre NovalNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 Ethnographic Research LeCompte Schensul 2010Document15 pagesChapter6 Ethnographic Research LeCompte Schensul 2010LAZET618294No ratings yet
- Written Texts Across DisciplinesDocument2 pagesWritten Texts Across DisciplinesGlyzeea Lawansi CandidoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research DesignsDocument24 pagesQualitative Research DesignsPaolo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- L2 NOTES Importance of Quali RSRCH in Daily LifeDocument9 pagesL2 NOTES Importance of Quali RSRCH in Daily Lifecar tadzNo ratings yet
- Dr. Yati Afiyanti, SKP., MN PresentDocument39 pagesDr. Yati Afiyanti, SKP., MN PresenttienNo ratings yet
- AOBTBCResearch 10 Q1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesAOBTBCResearch 10 Q1 ReviewerReizhelle AbisNo ratings yet
- AngeloDocument5 pagesAngeloRyan Cadorna Fontanilla100% (1)
- CreativeNonfiction NotesDocument10 pagesCreativeNonfiction NotesHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Creative Imagination, Especially in The Production of Decorative Objects." However, The ThingDocument4 pagesCreative Imagination, Especially in The Production of Decorative Objects." However, The ThingHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Mary - Luminary of Missio Ad GentesDocument2 pagesMary - Luminary of Missio Ad GentesHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- The Personal Is SocialDocument2 pagesThe Personal Is SocialHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Biological EvolutionDocument3 pagesBiological EvolutionHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Ivan Pavlov'S Theory On Classical ConditioningDocument2 pagesIvan Pavlov'S Theory On Classical ConditioningHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- GODis LoveDocument1 pageGODis LoveHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- CN LitGenresDocument3 pagesCN LitGenresHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- JiveDocument10 pagesJiveHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Topic: Decision Making 1. SWOT AnalysisDocument10 pagesTrends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Topic: Decision Making 1. SWOT AnalysisHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Entrep SpeechDocument3 pagesEntrep SpeechHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- 21st CENTURY LITERATURE FROM THE PHILIPPINES AND THE WORLDDocument3 pages21st CENTURY LITERATURE FROM THE PHILIPPINES AND THE WORLDHyde Park50% (4)
- Into The World of ChristianityDocument15 pagesInto The World of ChristianityHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Intro To ReligionDocument31 pagesIntro To ReligionHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- EAPP StudyQuestionsDocument1 pageEAPP StudyQuestionsHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- UCSP ReviewDocument2 pagesUCSP ReviewHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Significance of The Study: Practical Research 1 2018 - 2019Document14 pagesSignificance of The Study: Practical Research 1 2018 - 2019Hyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Land of BondageDocument1 pageLand of BondageDuke GonzagaNo ratings yet
- QualitativeDocument2 pagesQualitativeHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- The Human Person and His EnvironmentDocument12 pagesThe Human Person and His EnvironmentHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument5 pagesOrigin of LifeHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and GovernanceDocument5 pagesPhilippine Politics and GovernanceHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- OralComm NotesDocument3 pagesOralComm NotesHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- HinduismDocument6 pagesHinduismJohn Ryan JacotNo ratings yet
- A Case On Marketing Strategy of Xiaomi IndiaDocument39 pagesA Case On Marketing Strategy of Xiaomi IndiaSoumyajeet Rout0% (1)
- Seizure Control Status and Associated Factors Among Patients With Epilepsy. North-West Ethiopia'Document14 pagesSeizure Control Status and Associated Factors Among Patients With Epilepsy. North-West Ethiopia'Sulaman AbdelaNo ratings yet
- Backwards Design - Jessica W Maddison CDocument20 pagesBackwards Design - Jessica W Maddison Capi-451306299100% (1)
- Multimedia System DesignDocument95 pagesMultimedia System DesignRishi Aeri100% (1)
- Bgrim 1q2022Document56 pagesBgrim 1q2022Dianne SabadoNo ratings yet
- Manual de Operacion y MantenimientoDocument236 pagesManual de Operacion y MantenimientoalexNo ratings yet
- Tài Liệu Hướng Dẫn Cài Đặt Rơ Le MPS 3000Document55 pagesTài Liệu Hướng Dẫn Cài Đặt Rơ Le MPS 3000nguyenquangtonNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 13th Edition Miller Test BankDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Science 13th Edition Miller Test Bankmarykirbyifsartwckp100% (14)
- Play ClawDocument2 pagesPlay ClawFrenda SeivelunNo ratings yet
- DR S GurusamyDocument15 pagesDR S Gurusamybhanu.chanduNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe - Medical - CPIN - v2.0 - GOV - UKDocument39 pagesZimbabwe - Medical - CPIN - v2.0 - GOV - UKsammy redganjiNo ratings yet
- PetrifiedDocument13 pagesPetrifiedMarta GortNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Psychology of Health and Health Care A Canadian Perspective 5th EditionDocument36 pagesTest Bank For The Psychology of Health and Health Care A Canadian Perspective 5th Editionload.notablewp0oz100% (37)
- Guncha Arora: Professional Profile Career HistoryDocument1 pageGuncha Arora: Professional Profile Career HistoryNitin MahawarNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Online TestingDocument6 pagesEmbedded Systems Online TestingPuspala ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- UAV Design TrainingDocument17 pagesUAV Design TrainingPritam AshutoshNo ratings yet
- Xtype Power Train DTC SummariesDocument53 pagesXtype Power Train DTC Summariescardude45750No ratings yet
- Lesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446Document9 pagesLesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446BruntNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Interim ProjectDocument4 pagesOperations Management Interim ProjectABAYANKAR SRIRAM (RA1931201020042)No ratings yet
- Science and Technology in Ancient India by NeneDocument274 pagesScience and Technology in Ancient India by NeneAshok Nene100% (1)
- Operator'S Manual Diesel Engine: 2L41C - 2M41 - 2M41ZDocument110 pagesOperator'S Manual Diesel Engine: 2L41C - 2M41 - 2M41ZMauricio OlayaNo ratings yet
- Ancient Sumer Flip BookDocument9 pagesAncient Sumer Flip Bookapi-198624210No ratings yet
- MCQ Floyd ElexDocument87 pagesMCQ Floyd ElexnicoleNo ratings yet
- Reaserch On Effect of Social Media On Academic Performance: Study On The Students of University of DhakaDocument27 pagesReaserch On Effect of Social Media On Academic Performance: Study On The Students of University of DhakaFatema Tuz Johoora88% (114)
- Dessler HRM12e PPT 01Document30 pagesDessler HRM12e PPT 01harryjohnlyallNo ratings yet
- Accounting Students' Perceptions On Employment OpportunitiesDocument7 pagesAccounting Students' Perceptions On Employment OpportunitiesAquila Kate ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ismb ItpDocument3 pagesIsmb ItpKumar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Sermon Manuscript Galatians 5:16-26Document9 pagesSermon Manuscript Galatians 5:16-26Nathaniel ParkerNo ratings yet
- Preparing For CPHQ .. An Overview of Concepts: Ghada Al-BarakatiDocument109 pagesPreparing For CPHQ .. An Overview of Concepts: Ghada Al-BarakatiBilal SalamehNo ratings yet
- Brosur YSIO X.preeDocument20 pagesBrosur YSIO X.preeRadiologi RSUD KilisuciNo ratings yet