Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecuaciones Homogeneas
Uploaded by
Juanjo Rlloz Gl0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageecuaciones matematicas
Original Title
ECUACIONES HOMOGENEAS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentecuaciones matematicas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageEcuaciones Homogeneas
Uploaded by
Juanjo Rlloz Glecuaciones matematicas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
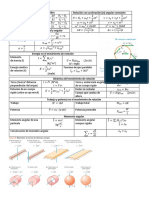
ECUACIONES HOMOGENEAS
Formas Sustitución
Coeficientes Constantes Ay ’ ’ + By ’+C y=0 y=erx
Cauchy-Euler x 2 y ’ ’ + xy ’ + y=0 y=x r
Reducción de Ecuaciones y’ y y=x r
y ’ ’+ + 2 =0
x x
Coeficientes Constantes Cauchy-Euler
r1x r2 x rnx 2
Raíces diferentes y=C 1 e + C2 x e +C n e … y=C 1 x r +C 2 x r ln ( x ) +C 2 x r [ ln ( x ) ]
Raíces iguales y=C 1 er x + C2 xer x + Cn e r x …
1 1 n
y=C 1 x r +C 2 x r +C 3 x r + …
1 2 3
Raíces imaginarias y=eax (C ¿ ¿1 cos (bx )+C 2 sin (bx))¿
r =a ±bi
Raíces imaginarias iguales y=eax (C ¿ ¿1 cos (bx )+C 2 sin (bx))+e ax (C ¿ ¿ 3 cos (bx) +C 4 sin (bx ))¿ ¿
3 raíces con imaginarias y=C 1 er x + e ax (C 2 cos (bx )+C3 sin ( bx))
1
ECUACIONES NO HOMOGENEAS POLINOMIOS SUSTITUCIÓN DE POLINOMIO
x
e x Ax+ B
Para ecuaciones Sen (θ ) ó cos(θ)
que contengan x 2+ x A x 2+ Bx+ C
polinomios en función de x x 3 + x2 + x A x 3+ B x 2+ Cx+ D
Sen(θ) A∗sin ( θ ) + B∗cos (θ)
cos (θ) A∗sin ( θ ) + B∗cos (θ)
e bx Aebx
x 2 e bx e bx ( A x 2 + Bx++C)
x 3 sin (bx ) ( A x 3 +B x 2 +Cx+ D ) sin ( bx ) + ( E x3 + F x2 +Gx+ H ) cos ( bx )
e ax sin (bx) ( Asin ( bx ) +bCos ( bx ))e ax
x 2 e bx sin (cx ) ( A x 2+ Bx +C ) e bx sin ( cx ) +(E x 2 + Fx+G)e bx cos(bx)
You might also like
- HT3: Proyección Oferta y Demanda: Escuela de Ingeniería CivilDocument3 pagesHT3: Proyección Oferta y Demanda: Escuela de Ingeniería CivilJuanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Tipos de ServidumbreDocument7 pagesTipos de ServidumbreJuanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Formulario Fisica 1Document2 pagesFormulario Fisica 1Juanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Tipos de ServidumbreDocument7 pagesTipos de ServidumbreJuanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Arquitectura de Von NeumannDocument4 pagesArquitectura de Von NeumannJuanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Arquitectura de Von NeumannDocument4 pagesArquitectura de Von NeumannJuanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Reciclar Es El Proceso Mediante El Cual Los Productos de Desecho Son Nuevamente UtilizadosDocument1 pageReciclar Es El Proceso Mediante El Cual Los Productos de Desecho Son Nuevamente UtilizadosJuanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Reset AsDocument9 pagesReset AsJuanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Parte 2 Glosario EstadisticoDocument8 pagesParte 2 Glosario EstadisticoJuanjo Rlloz GlNo ratings yet
- Instrucciones (Contraseña para Descomprimir)Document4 pagesInstrucciones (Contraseña para Descomprimir)Juanjo Rlloz Gl100% (1)
- El Átomo Como Principio de Nuestra RealidadDocument5 pagesEl Átomo Como Principio de Nuestra RealidadBernd Andres VockentänzerNo ratings yet
- MGAN1 Planeación U4Document8 pagesMGAN1 Planeación U4kikionte08No ratings yet
- DERECHO ADMINISTRATIVO - Principio de Legalidad y Potestades AdministrativasDocument8 pagesDERECHO ADMINISTRATIVO - Principio de Legalidad y Potestades AdministrativasivanluisdiazNo ratings yet
- SylabussDocument9 pagesSylabussCristhian Taramuel GuerreroNo ratings yet
- El Parque Acuático Los Chorros Es Un Lugar Muy Popular Entre Todos Los Salvadoreños y Es Identificado Por La Mayoría de Ellos Como Un Lugar de DiversionesDocument4 pagesEl Parque Acuático Los Chorros Es Un Lugar Muy Popular Entre Todos Los Salvadoreños y Es Identificado Por La Mayoría de Ellos Como Un Lugar de Diversionesnoecito lobosNo ratings yet
- Funcionamiento y Caracteristicas Bomba CentrifugaDocument4 pagesFuncionamiento y Caracteristicas Bomba CentrifugaGustavo HanccoNo ratings yet
- Teoría Del Aprendizaje ConductistaDocument12 pagesTeoría Del Aprendizaje Conductistaiglesia evangélica trinitariaNo ratings yet
- Absurdos VisualesDocument15 pagesAbsurdos VisualesAndreaSepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Calculadora GeoestacionariaDocument8 pagesCalculadora GeoestacionariaJuan C Sandoval CNo ratings yet
- Inte Iso 7010 2022Document346 pagesInte Iso 7010 2022Pilar Castro Soto100% (1)
- Psicología Del Niño - PiagetDocument124 pagesPsicología Del Niño - PiagetCatalina BalNo ratings yet
- RESUMEN TEXTO Obligaciones IndivisiblesDocument10 pagesRESUMEN TEXTO Obligaciones IndivisiblesCarolina Riadi SaffieNo ratings yet
- Triptico EspañolDocument2 pagesTriptico EspañolMondragón Valdez Kevin RamsésNo ratings yet
- El Poder en La Organizacion.Document32 pagesEl Poder en La Organizacion.Luz María López67% (3)
- Teoría Básica de La Seguridad IDocument46 pagesTeoría Básica de La Seguridad IArmando Enrique Rodriguez TorresNo ratings yet
- Lecturas Proceso Contencioso AdministrativoDocument181 pagesLecturas Proceso Contencioso AdministrativoAntonio EscobedoNo ratings yet
- Pydi A2 T1 Cruz Casango Luis JeffetDocument2 pagesPydi A2 T1 Cruz Casango Luis JeffetGammer XxZ3taxXNo ratings yet
- Memoria DescriptivaDocument58 pagesMemoria DescriptivaJesus Percy Garro EspinozaNo ratings yet
- SENA Estimulacion Neuroauditiva en La Optometria .Jorde GalceránDocument11 pagesSENA Estimulacion Neuroauditiva en La Optometria .Jorde GalceránAnonymous g8P3dNxNo ratings yet
- La Funcion Del PlaneamientoDocument13 pagesLa Funcion Del PlaneamientoSCRISVANo ratings yet
- Caso de La BallenaDocument41 pagesCaso de La BallenagabandpaulaNo ratings yet
- Carpeta Actuarial 1Document250 pagesCarpeta Actuarial 1Joseph Cunningham100% (2)
- El Poder de Tu Mente PDFDocument29 pagesEl Poder de Tu Mente PDFlastre01No ratings yet
- Tema PT 21Document16 pagesTema PT 21saraypablo100% (1)
- Cuadro Comparativo Teoría CelularDocument4 pagesCuadro Comparativo Teoría Celularmariarmrez50% (2)
- Ejemplos-Elasticidad-Grupo 01Document9 pagesEjemplos-Elasticidad-Grupo 01Harolstiven MamaniaguilarNo ratings yet
- Rendir Examen MedicoDocument2 pagesRendir Examen MedicoLipe BaressiNo ratings yet
- 3-2-002 Pavimentos Concreto Asfáltico. EspecificacionesDocument12 pages3-2-002 Pavimentos Concreto Asfáltico. EspecificacionesLaboratorio Nacional de Ensayos SAS100% (2)
- GUÍA ÓPtica Relfectiva - Refractiva.Document15 pagesGUÍA ÓPtica Relfectiva - Refractiva.Miguel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Examen Final - Semana 8 - Segundo Bloque-Teorico - Fundamentos de Psicologia - (Grupo6)Document10 pagesExamen Final - Semana 8 - Segundo Bloque-Teorico - Fundamentos de Psicologia - (Grupo6)Nicole Sierra33% (3)