Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 3 Assignment PDF
Uploaded by
api-445871188Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 3 Assignment PDF
Uploaded by
api-445871188Copyright:
Available Formats
1.
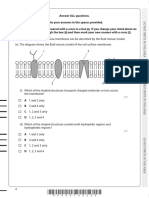
Based on the information from the notes describe why calcium is so important
in muscle contraction? (2pts)
To expose the actives sites during muscle contraction you need calcium to
move the tropomyosin (which changes the shape of the tropomyosin), which allows
people to move there muscles. When you stop, calcium stops going to the
tropomyosin and allows the active sights to be covered, and your muscles relax. When
we contract and relax our muscles, raid change of the amount of calcium change
inside of our bodies. If you have too little or too much calcium this can cause muscle
symptoms, and problems. Calcium is so important in the movement of our muscles
and how they work correctly.
2. In your own words, try to explain the entire process of muscle contraction as if
you were trying to explain it to the players on your team. (4pts)
What happens is that you decide you want to move your muscles. Since these
are skeletal muscles, you have to think about using them. For these muscles to move,
myosin and actin need to be able to bind. Myosin and actin are pretty famous, so they
have bodyguards in there way, and can’t be together. Actin’s bodyguards are the
protein troponin and tropomyosin. Troponin really likes calcium and binds with the
calcium which pulls tropomyosin open. The tropomyosin changes shape and opens the
active sights that contain actin, but myosin isn’t perfect to bind with actin just yet.
Myosin binds with ATP, because she wants to look pretty. Like a girl putting on
makeup. Myosin then changes the ATP into ADP and phosphate. This causes myosin
to change shape, and it moves into an extended position. This makes the myosin ready
to bind with actin, and the myosin releases all of it’s stored energy. After the myosin
releases all of its energy it changes shape. The myosin pulls on the actin strand, which
shrinks the muscle. Then now that the myosin has used up all of the energy that has
from the ATP, it unbinds from the ADP and phosphorus. That then changed the shape
of the myosin, and a new fresh ATP binds in its place. That binding causes another
shape change, and the myosin releases from the actin. The myosin then breaks down
it’s new ATP molecule to ADP and phosphate. Which moves it into the extended
position again to get ready to bind with the actin strand again. Meanwhile, the calcium
pumps are working hard to restock the calcium, and the calcium unbinds with the
troponin. This causes the shape change of the tropomyosin. This process continues to
allow us to move our muscles.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lecture Notes General BiologyDocument34 pagesLecture Notes General BiologyLester Eslava Orpilla100% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Neuromuscular Disorders - A. Zaher (Intech, 2012) WW PDFDocument280 pagesNeuromuscular Disorders - A. Zaher (Intech, 2012) WW PDFDaianaNo ratings yet
- Rigor MortisDocument2 pagesRigor Mortisapi-238242929No ratings yet
- Pathology A - The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseDocument13 pagesPathology A - The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseYui VainNo ratings yet
- 100 Concepts - MCBDocument316 pages100 Concepts - MCBNisreen SalameNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDDocument73 pagesBIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDJowe VarnalNo ratings yet
- Ovine Meat Inspection PDFDocument337 pagesOvine Meat Inspection PDFShannon Hill100% (3)
- Caler, 2000Document9 pagesCaler, 2000samannosheenNo ratings yet
- Learning Express AP Biology Exam 1Document26 pagesLearning Express AP Biology Exam 1Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Concise Histology Gartner, Leslie PDFDocument478 pagesConcise Histology Gartner, Leslie PDFLexsshNo ratings yet
- Histology 3 - Cytoplasm 4 & NucleusDocument8 pagesHistology 3 - Cytoplasm 4 & NucleusShariffa KhadijaNo ratings yet
- Lectures 8-10 NotesDocument15 pagesLectures 8-10 Notesapi-3721438No ratings yet
- Muscles Lab Report - NoDocument3 pagesMuscles Lab Report - Noapi-3801039No ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Protein Function Part I: Myoglobin and HemoglobinDocument27 pagesChapter 7: Protein Function Part I: Myoglobin and HemoglobineliNo ratings yet
- PHCG 201 CytologyDocument113 pagesPHCG 201 CytologyIbn HaarūnNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NotesDocument49 pagesUnit 5 Notesbody fayezNo ratings yet
- Biochem Report Muscle and CytoskeletonDocument87 pagesBiochem Report Muscle and CytoskeletonKate Lynne CamonayanNo ratings yet
- Abstracts Ls 06Document79 pagesAbstracts Ls 06AkoKhalediNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Filaments at TheDocument19 pagesIntermediate Filaments at TheMaria Laura VilchezNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Movements: Types of Muscles Structure of Skeletal MusclesDocument16 pagesMuscles and Movements: Types of Muscles Structure of Skeletal MusclesMahin FatimaNo ratings yet
- CYTOSKELETON The Discovery of The Prokaryotic CytoskeletonDocument2 pagesCYTOSKELETON The Discovery of The Prokaryotic CytoskeletonYunn ZhangNo ratings yet
- Biological Science 5Th Edition Freeman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesBiological Science 5Th Edition Freeman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFElizabethRuizrxka100% (11)
- Self-Organization in Biological Systems PDFDocument9 pagesSelf-Organization in Biological Systems PDFMati dell'ErbaNo ratings yet
- 3D. Muscle TissueDocument47 pages3D. Muscle Tissuejaf123xyNo ratings yet
- LPT 321Document103 pagesLPT 321rahul roshanNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience and Cell Bio Cheat SheetDocument13 pagesNeuroscience and Cell Bio Cheat SheetAbdNo ratings yet
- Dr. Niranjan Murthy H L: Asst. Prof., Dept. of Physiology Sree Siddhartha Medical College & Hospital, TumkurDocument29 pagesDr. Niranjan Murthy H L: Asst. Prof., Dept. of Physiology Sree Siddhartha Medical College & Hospital, Tumkurnirilib100% (6)
- Bio 50Document28 pagesBio 50Mohammad Shahidullah ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 SummaryDocument11 pagesChapter 16 SummaryCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Q # The Girl Which Won The Lottery Was On T.V.: EnglishDocument12 pagesQ # The Girl Which Won The Lottery Was On T.V.: EnglishDileep KumarNo ratings yet