Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis On Connection of Urbanized City and Employment in Malaysia (Universiti Utara Malaysia)
Uploaded by
NoranizaYusoff0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views10 pagesUrban rate economies in operation are the fundamental for big cities to subsist whereas diseconomies in life restricts sizes and that there is an urban structure where little cities incline to specialize in standardized operation of distinct manufacturing and facility activities. Whereas larger cities have higher different economic foundations, that are concentrated on high tech manufacturing and specific commercial facilities (Boer, 2015).
Original Title
ANALYSIS ON CONNECTION OF URBANIZED CITY AND EMPLOYMENT IN MALAYSIA (UNIVERSITI UTARA MALAYSIA)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentUrban rate economies in operation are the fundamental for big cities to subsist whereas diseconomies in life restricts sizes and that there is an urban structure where little cities incline to specialize in standardized operation of distinct manufacturing and facility activities. Whereas larger cities have higher different economic foundations, that are concentrated on high tech manufacturing and specific commercial facilities (Boer, 2015).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views10 pagesAnalysis On Connection of Urbanized City and Employment in Malaysia (Universiti Utara Malaysia)
Uploaded by
NoranizaYusoffUrban rate economies in operation are the fundamental for big cities to subsist whereas diseconomies in life restricts sizes and that there is an urban structure where little cities incline to specialize in standardized operation of distinct manufacturing and facility activities. Whereas larger cities have higher different economic foundations, that are concentrated on high tech manufacturing and specific commercial facilities (Boer, 2015).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
You are on page 1of 10
ANALYSIS ON CONNECTION OF
URBANIZED CITY AND EMPLOYMENT IN
MALAYSIA
Noraniza Yusoff
Senior Lecturer, School of Government, UUM
COLGIS, Universiti Utara Malaysia, 06010
Sintok,
Kedah, Malaysia
IASTEM – ICSSH 2018, 5 February 2018, Putrajaya, Malaysia
INTRODUCTION
Urban rate economies in operation are the fundamental for big cities to
subsist whereas diseconomies in life restricts sizes and that there is an urban
structure where little cities incline to specialize in standardized operation of
distinct manufacturing and facility activities. Whereas larger cities have
higher different economic foundations, that are concentrated on high tech
manufacturing and specific commercial facilities (Boer, 2015).
LITERATURE REVIEW
Highly urbanized cities are regarded the most developed location in each
area. Even though urbanization is drive for modernization, economic
expansion and growth, there is growing attention regarding the impact of
enlarging cities, especially on human health, subsistence and environment.
The effect of fast urbanization and demographic patterns of occupation, food,
safety, a supply of water, housing and sewerage, primarily the spillage of
rubbish namely solid and effluent that the cities create are remarkable (De
Guzman and Caballero, 2015).
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research designed to perform this study is basic research with the primary
target is to explain on the association among the rise of consumption and
income polarization. The examination of information on the subject matters
in this study undertook at one point in time or cross sectional research. This
research utilized quantitative method for data collection and analysis. Data
collection used survey technique through questionnaire involved a large
number of inhabitant in the study areas as the samples in the study. Stratified
sampling that is probability sampling utilized for samples selection. Research
location involved three cities in north area of Peninsular Malaysia namely
Sungai Petani City in Kedah, Georgetown City in Penang and Ipoh City in
Perak.
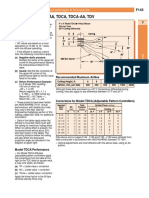
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Urbanized city Employment
Fig. 1: Relationship between urbanized city and employment
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Scatterplot shows zero correlation coefficient and the points have no
direction as well as a line does not fit to the points on the graph.
The rs (434) = - 0.55, p > 0.05 and there is no relationship between urbanized
city and employment. This interpreted that accept the Null hypothesis.
The difference between two log likelihoods namely the chi square has an
observed significance level of more than 0.05 (p > 0.05). This interpreted that
accept the Null hypothesis that the model without predictors is as good as the
model with the predictors.
The p value for the goodness of fit is lower than 0.05 (p < 0.05), reject the
Null hypothesis that the model fits and the observed significance level for the
goodness of fit statistics is small.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Significance value of chi square of the difference between the two log
likelihood of test of parallel lines that reject the Null hypothesis that is p =
0.000 (p < 0.05).
The findings differ with Clark and Moonen (2014) that represented Mumbai
started to generate bigger range of occupation chances in finance, services as
well as Information and Communication Technology (ICT), with produce
impacts on the firm, music and travel sectors.
These findings also differ with Priemus (2014) that as a result of
overpopulation of office space, the declining amount of working population
and the rising renown of the so called recent working systems, the position of
offices in urban regions is growing rapidly.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
These findings also differ with van Ham, Findlay, Manley and Feijten (2012)
that represented attempts to undone the difficult association among a
population’s migration conduct, dwelling and occupational achievement in
the Scottish manpower market among the year 1991 and 2001.
CONCLUSION
Results represent that there is no relationship between urbanize city and
employment through scatterplot and Spearman correlation analyses. Ordinal
regression indicates that the model without predictors is as good as the model
with the predictors. Recommendation on the finding is reemployment
attempts according to Brand (2015) should be concentrated on acquiring
discharged manpower in occupations that create the outlook of durable
occupation, preferably in an occupation in pre unemployment industry or one
that is an acceptable fit to skills.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author wish to thank the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia in
funding this study under the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS),
S/O code 13228, and Research and Innovation Management Centre,
Universiti Utara Malaysia, Kedah for the administration of this study.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Massey Ferguson MF7600 Technician Workshop ManualDocument798 pagesMassey Ferguson MF7600 Technician Workshop Manualgavcin100% (5)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Drill Bit Classifier 2004 PDFDocument15 pagesDrill Bit Classifier 2004 PDFgustavoemir0% (2)
- Bill of Quantity: Supply of Pipes and FittingsDocument3 pagesBill of Quantity: Supply of Pipes and FittingssubxaanalahNo ratings yet
- Astm D2265-00 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm D2265-00 PDFOGINo ratings yet
- Hybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and DemonstratedDocument4 pagesHybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and Demonstratedmohamad theibechNo ratings yet
- VDRL - Press. GaugesDocument9 pagesVDRL - Press. GaugesSourav RayNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal DraftDocument1 pageProject Proposal DraftCarl Axel M. FajardoNo ratings yet
- UniFi Quick GuideDocument2 pagesUniFi Quick GuideAndhika TharunaNo ratings yet
- Manual Bms8n2 e LowDocument58 pagesManual Bms8n2 e Lowzoranbt80_324037655No ratings yet
- STS Reviewer FinalsDocument33 pagesSTS Reviewer FinalsLeiNo ratings yet
- EHR StandardsIndia - August 2013-32630521Document54 pagesEHR StandardsIndia - August 2013-32630521kartiksinhNo ratings yet
- Impeller Velocity TrianglesDocument2 pagesImpeller Velocity TrianglesLorettaMayNo ratings yet
- CE Laws L8 L15Document470 pagesCE Laws L8 L15Edwin BernatNo ratings yet
- C305 - QTO Workshop PDFDocument90 pagesC305 - QTO Workshop PDFJason SecretNo ratings yet
- PD750-01 Engine Data Sheet 12-29-20Document4 pagesPD750-01 Engine Data Sheet 12-29-20Service Brags & Hayes, Inc.No ratings yet
- FO - Course Transition Info - Acknowledgement - SIT50422 - Dip Hospitality Management - V1Document2 pagesFO - Course Transition Info - Acknowledgement - SIT50422 - Dip Hospitality Management - V1nitesh.kc06No ratings yet
- BF254 BF255Document3 pagesBF254 BF255rrr2013No ratings yet
- Englis 123Document39 pagesEnglis 123Cindy EysiaNo ratings yet
- 88 Year Old Man Missing in SC - Please ShareDocument1 page88 Year Old Man Missing in SC - Please ShareAmy WoodNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper DementiaDocument1 pageReaction Paper DementiaElla MejiaNo ratings yet
- A Control Method For Power-Assist Devices Using A BLDC Motor For Manual WheelchairsDocument7 pagesA Control Method For Power-Assist Devices Using A BLDC Motor For Manual WheelchairsAhmed ShoeebNo ratings yet
- Munchies BrochureDocument28 pagesMunchies BrochureIbrahim Diaz LazoNo ratings yet
- I - Pronunciation Choose The Word Whose Stress Pattern Is Different From The Other Three in The Following QuestionsDocument6 pagesI - Pronunciation Choose The Word Whose Stress Pattern Is Different From The Other Three in The Following QuestionsHaNo ratings yet
- The Incidence of COVID-19 Along The ThaiCambodian Border Using Geographic Information System (GIS), Sa Kaeo Province, Thailand PDFDocument5 pagesThe Incidence of COVID-19 Along The ThaiCambodian Border Using Geographic Information System (GIS), Sa Kaeo Province, Thailand PDFInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Titus Selection of DiffuserDocument14 pagesTitus Selection of DiffuserhanyassawyNo ratings yet
- Job Sheet 1Document5 pagesJob Sheet 1Sue AzizNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Naac PPT 07-12Document13 pagesCH 4 Naac PPT 07-12Arshad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Micro Fibra Sintetica at 06-MapeiDocument2 pagesMicro Fibra Sintetica at 06-MapeiSergio GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Market Challengers StrategiesDocument19 pagesMarket Challengers Strategiestobbob007100% (20)
- NCP81205Document1 pageNCP81205Tom TomNo ratings yet