Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uploaded by
Manju ANOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uploaded by
Manju ANCopyright:
Available Formats
CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
KR PURAM, BENGALURU-560036.
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Question Bank for I Internals (Feb 2019)
Subject name : Mechanical Measurements & Metrology Semester : IV
Subject code : 17ME46B Section: A, B, C
MODULE-1 (Introduction to Metrology) - CO1
1. Define Measurement.
2. Discuss the objectives of Metrology.
3. Explain Imperial Standard Yard.
4. List out the need of inspection in Metrology.
5. Explain the Wave length Standard.
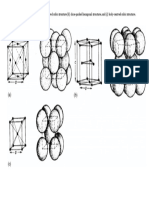
6. Explain with neat diagram, International Prototype Meter.
7. What is Metrology?
8. What care should be taken in use of slip gauges?
9. Select the arrangement of minimum angle gauges required to obtain the fallowing angles
(i) 37˚ 16′ 42″ (ii) 102˚ 8′42″ (iii) 35o 32′ 36″.
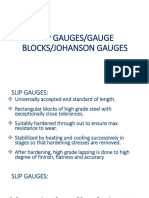
10. Define slip gauge.
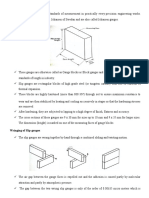
11. Illustrate with neat diagram wringing phenomenon in slip gauges.
12. Select slip gauge combination using M112 set, build the fallowing dimensions (i) 49.3115
(ii) 68.208 (iii) 52.498.
13. Define angle gauges.
14. Explain with a neat diagram working principle of sine bar and mention limitations of sine
bar.
15. Explain the principle of autocollimator.
16. What are optical flats?
17. Explain with a neat diagram working and use of clinometer.
18. Select slip gauge combination for the given dimensions using M112 set. Use two
protector gauges of 2.5mm each. Show the slip gauge combination.
(i) 35.4875 (ii) 58.975 (iii) 92.357.
19. What are line and end standards.
20. Explain sub division of Standards.
21. Three 100mm end bars are measured on a level comparator by first wringing them
together and comparing with a 300mm bar. The 300mm bar has a known error of +40µm
and the three bars together measure 64µm less than the 300 mm bar. Bar A is 18µm
longer than bar B and 23µm longer than bar C. Find the actual length of each bar.
MODULE-2 (Systems of Limits, Fits, Tolerance and Gauging) - CO2
1. Define Tolerance.
2. Explain tolerance accumulation or tolerance “Build-up”.
3. Discuss upper deviation, lower deviation and fundamental deviation for hole and shaft system.
4. Define limits and fits.
5. Explain the terms such as Basic Size, Nominal Size, and Actual size.
6. Explain compound tolerance, with a suitable example.
7. What are unilateral dimensions?
8. Discuss with neat sketch, different types of fits.
9. Distinguish between interchangeability and selective assembly.
10. What are bilateral dimensions?
11. Explain Positional Tolerance.
12. Describe Hole Basis and Shaft Basis System and its significance.
******************
You might also like
- ETL Testing ProcessDocument2 pagesETL Testing ProcessManju ANNo ratings yet
- What Is BIDocument1 pageWhat Is BIManju ANNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 120229065309 Phpapp02Document25 pagesChapter5 120229065309 Phpapp02Manju ANNo ratings yet
- When We Talk About A Second PriorDocument1 pageWhen We Talk About A Second PriorManju ANNo ratings yet
- What Is BIDocument1 pageWhat Is BIManju ANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Abrasive Jet MachiningDocument1 pageIntroduction To Abrasive Jet MachiningManju ANNo ratings yet
- Measurement Reading Technique For MicrometerDocument1 pageMeasurement Reading Technique For MicrometerManju ANNo ratings yet
- Model QP VTU 15ME554QP2Document2 pagesModel QP VTU 15ME554QP2Manju ANNo ratings yet
- Forging New Generations of EngineersDocument20 pagesForging New Generations of Engineers80ALLA86iNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurements and Measuring Devices 6-25-08Document58 pagesMechanical Measurements and Measuring Devices 6-25-08Oliver RubioNo ratings yet
- Model QP - 1 VTU15ME554Document2 pagesModel QP - 1 VTU15ME554Manju ANNo ratings yet
- System of Limits, Fits, Tolerance and Gauging PDFDocument32 pagesSystem of Limits, Fits, Tolerance and Gauging PDFPraveen MohapatraNo ratings yet
- LBM 05-Nov-2019 10-58-36Document1 pageLBM 05-Nov-2019 10-58-36Manju ANNo ratings yet
- 215 Sample ChapterDocument23 pages215 Sample ChapterSreekumar RajendrababuNo ratings yet
- Stroke EngineDocument2 pagesStroke EngineManju ANNo ratings yet
- Quadcopter 140410021020 Phpapp02Document17 pagesQuadcopter 140410021020 Phpapp02SalahAL-HakimiNo ratings yet
- Non Conventional Machining.Document40 pagesNon Conventional Machining.paul gichukiNo ratings yet
- Usual Crystal Structures: Close Packed Metal StructuresDocument2 pagesUsual Crystal Structures: Close Packed Metal StructuresManju ANNo ratings yet
- Usm 2Document1 pageUsm 2Manju ANNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Jute Fiber Reinforced Chemically Functionalized High Density Polyethylene (JF/CF-HDPE) Composites Developed by Palsule ProcessDocument12 pagesThermal Properties of Jute Fiber Reinforced Chemically Functionalized High Density Polyethylene (JF/CF-HDPE) Composites Developed by Palsule ProcessManju ANNo ratings yet
- Figure 3: AB Packing of Spheres. Notice That Layer B Spheres Fit in The Holes in TheDocument3 pagesFigure 3: AB Packing of Spheres. Notice That Layer B Spheres Fit in The Holes in TheManju ANNo ratings yet
- MseschsyllDocument16 pagesMseschsyllSAMEERANo ratings yet
- IgnitionDocument3 pagesIgnitionManju ANNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Atoms in (A) Face-Centred Cubic Structure (B) Close-Packed Hexagonal Structure, and (C) Body-Centred Cubic StructureDocument1 pageArrangement of Atoms in (A) Face-Centred Cubic Structure (B) Close-Packed Hexagonal Structure, and (C) Body-Centred Cubic StructureManju ANNo ratings yet
- ME349 Engineering Design Projects: Introduction To Materials SelectionDocument6 pagesME349 Engineering Design Projects: Introduction To Materials SelectionMehul KaklotarNo ratings yet
- TQM Questions and Answers Unit 2Document8 pagesTQM Questions and Answers Unit 2Manju ANNo ratings yet
- 11Document18 pages11yumiko_sebastian2014No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Machining Process: AdvantagesDocument2 pagesUltrasonic Machining Process: AdvantagesManju ANNo ratings yet
- Reasons For The Downfall of Kingfisher AirlinesDocument6 pagesReasons For The Downfall of Kingfisher AirlinesManju ANNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- MM Interview QuestionsDocument28 pagesMM Interview QuestionsVivek BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Map16 Full 2016Document680 pagesMap16 Full 2016dungdhtsNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document4 pagesModule 4sathiaNo ratings yet
- Cp-005-Calibration of Internal MicrometerDocument5 pagesCp-005-Calibration of Internal MicrometerSUNILNo ratings yet
- 1182 01Document11 pages1182 01Anonymous y3tPCbVrNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Unit Wise Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesUNIT-1: Unit Wise Important Questionssai mohanNo ratings yet
- TB 9-5210-207-24 - Micrometer ISDocument16 pagesTB 9-5210-207-24 - Micrometer ISJose Hernandez DiazNo ratings yet
- EMG 1203 Manufacturing Processes 1-Dimensional Analysis Notes 2020Document71 pagesEMG 1203 Manufacturing Processes 1-Dimensional Analysis Notes 2020kennedyjembezNo ratings yet
- 75 Questions of MetrologyDocument8 pages75 Questions of MetrologyVivek BajpaiNo ratings yet
- BU-00038-Grinding - Polishing - Brochure - BU Automet250Document36 pagesBU-00038-Grinding - Polishing - Brochure - BU Automet250Atul KumarNo ratings yet
- Edoc - Pub Occult ScienceDocument4 pagesEdoc - Pub Occult ScienceSaraswantoNo ratings yet
- Technology of Machine Tools: Inside-, Depth-, and Height-Measuring InstrumentsDocument22 pagesTechnology of Machine Tools: Inside-, Depth-, and Height-Measuring InstrumentsAnibal DazaNo ratings yet
- Angle Measurement PDFDocument85 pagesAngle Measurement PDFSnigdhaNo ratings yet
- Catalogue-Clamping ElementsDocument22 pagesCatalogue-Clamping Elementsanujkumartyagi9275No ratings yet
- CP-003 Calibration of Vernier CaliperDocument6 pagesCP-003 Calibration of Vernier CaliperSUNILNo ratings yet
- GagesDocument81 pagesGagesdaramaha100% (4)
- Common Mistakes in Dimensional Calibration MethodsDocument16 pagesCommon Mistakes in Dimensional Calibration MethodssujudNo ratings yet
- Me1304 - Engineering Metrology and MeasurementsDocument13 pagesMe1304 - Engineering Metrology and MeasurementsKeval PatelNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Warangal Department of Mechanical Engineering Warangal - 506 004Document50 pagesNational Institute of Technology Warangal Department of Mechanical Engineering Warangal - 506 004Venu Gopal AnneNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Complete MitutoyoDocument666 pagesCatalogue Complete MitutoyoJuan Manuel Barcia Diaz100% (2)
- Fitter Sem3 TTDocument134 pagesFitter Sem3 TTPooja7 7No ratings yet
- LMS6048 LowresDocument4 pagesLMS6048 LowrestamanogNo ratings yet
- Caliper Calibration ProcedureDocument3 pagesCaliper Calibration ProcedureQuality VenusNo ratings yet
- Gauge Blocks Reference GaugesDocument32 pagesGauge Blocks Reference GaugesFernando SanezNo ratings yet
- MetrologyDocument157 pagesMetrologyVishwajit HegdeNo ratings yet
- Gauge Block SetDocument19 pagesGauge Block SetSyawatulshuhada SyawalNo ratings yet
- Slip Gauges/Gauge Blocks/Johanson GaugesDocument9 pagesSlip Gauges/Gauge Blocks/Johanson GaugesVinothNo ratings yet
- Angle MeasurementDocument10 pagesAngle MeasurementsumikannuNo ratings yet
- Angle Measurement Using Sine BarDocument4 pagesAngle Measurement Using Sine Barsameerkhan_mhsscoe0% (1)
- Gauge BlocksDocument40 pagesGauge BlocksJean RojasNo ratings yet