Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CONDITIONALS Teoría Cuadros
Uploaded by
Maria Iranzo Esteban0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views5 pagesThe document outlines the different types of conditional sentences in English:
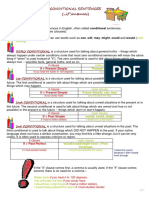
1) Zero conditional sentences describe permanent or repeated situations using the present simple tense.
2) First conditional sentences describe likely future situations using "if" with the present simple and the future simple.
3) Second conditional sentences describe unlikely or hypothetical present situations using "if" with the past simple and the conditional.
4) Third conditional sentences describe impossible past situations using "if" with the past perfect and the perfect conditional.
5) Mixed conditionals combine tenses from more than one conditional type to describe inconsistent or hypothetical past and present situations.
Original Description:
CONDITIONALS Teoría Cuadros
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the different types of conditional sentences in English:
1) Zero conditional sentences describe permanent or repeated situations using the present simple tense.
2) First conditional sentences describe likely future situations using "if" with the present simple and the future simple.
3) Second conditional sentences describe unlikely or hypothetical present situations using "if" with the past simple and the conditional.
4) Third conditional sentences describe impossible past situations using "if" with the past perfect and the perfect conditional.
5) Mixed conditionals combine tenses from more than one conditional type to describe inconsistent or hypothetical past and present situations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views5 pagesCONDITIONALS Teoría Cuadros
Uploaded by
Maria Iranzo EstebanThe document outlines the different types of conditional sentences in English:
1) Zero conditional sentences describe permanent or repeated situations using the present simple tense.
2) First conditional sentences describe likely future situations using "if" with the present simple and the future simple.
3) Second conditional sentences describe unlikely or hypothetical present situations using "if" with the past simple and the conditional.
4) Third conditional sentences describe impossible past situations using "if" with the past perfect and the perfect conditional.
5) Mixed conditionals combine tenses from more than one conditional type to describe inconsistent or hypothetical past and present situations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
ZERO CONDITIONAL
Conditional clause Main clause (result) Use
- Permanent situations, unchangeable
IF / WHEN / UNLESS + PRESENT SIMPLE Subject + PRESENT SIMPLE truths.
(if not) - Repeated actions when a determined
condition appears.
Examples: If I heat ice, it melts.
My granny can’t read unless she has her glasses on.
When I drink too much coke, I can’t sleep
FIRST CONDITIONAL: real situations
Conditional clause Main clause (result) Use
Subject + FUTURE SIMPLE (WILL) - The situation is likely to happen if the
IF / UNLESS + PRESENT SIMPLE IMPERATIVE + base condition takes place. We also use it in
(if not) MODAL SIMPLE form orders (imperative).
Examples: If you study harder, you will get better results.
If you see the English teacher, tell her that I’m looking for her.
Unless you study harder, you will fail (if you don’t study harder, you will fail).
If you lose your documents in London, you have to go to the police station.
TIME CLAUSES: When we talk about the future, we use AS SOON AS, WHEN, BY THE MOMENT…
These clauses use the same structure as the 1st conditional.
As soon as you pass the bank, you will see the museum (when you pass the bank…)
SECOND CONDITIONAL: unreal/hypothetical situations
Conditional clause Main clause (result) Use
- The situation is not likely to happen in
IF / UNLESS + PAST SIMPLE Subject + SIMPLE CONDITIONAL (WOULD) + base the present, given the current situation
(if not) COULD/MIGHT (minor possibility) form
Careful: with the verb to be, we always use
WERE.
Examples: If I won 5 million dollars, I would buy a tiny mobile phone.
If I were you, I would read more and talk less.
My friend Ana may come to visit me more often if she lived in Spain.
THIRD CONDITIONAL: impossible situations
Conditional clause Main clause (result) Use
- The situations are “impossible”,
IF / PAST PERFECT (HAD + P.P) Subject + PERFECT CONDITIONAL (WOUL HAVE) + P.P because they have already happened.
COULD/MIGHT HAVE We cannot change it anymore.
Examples: if I had studied more, I would have passed the test.
You could have seen the sunrise if you had woken uo earlier.
If you hadn’t downloaded a trojan virus, it wouldn’t have erased all the information in your computer.
MIXED CONDITIONALS
Conditional clause Main clause (result) Use
- Situation that is inconsistent with reality, both
Subject + SIMPLE CONDITIONAL (WOULD) + base form in the past and at the present. None of the
IF / PAST PERFECT (HAD + P.P) COULD/MIGHT (less likely to occur) clauses are factual reality:
If I had studied at school, now I’s have a better
job
- Hypothetical situation that would have had a
IF + PAST SIMPLE Subject + PERFECT CONDITIONAL (WOUL HAVE) + P.P probable result, but it’s not the case now.
COULD/MIGHT HAVE (if I wasn’t scared of rats, I’d have chosen that
room)
Las oraciones subordinadas CONDICIONALES MIXTAS están integradas por proposiciones que se refieren a momentos distintos.
La primera expresa una situación que es contraria a la realidad, tanto en el pasado como en el momento actual. No podemos cambiar la condición, por
tanto, el resultado es hipotético.
La segunda se refiere a una situación real / hipotética presente que, de haberse cumplido, hubiera tenido un resultado probable en el pasado.
You might also like
- Wiley S Mathematics For IIT JEE Main and AdvancedTrigonometry Vector Algebra Probability Vol 2 Maestro Series Dr. G S N Murti Dr. U M Swamy PDFDocument620 pagesWiley S Mathematics For IIT JEE Main and AdvancedTrigonometry Vector Algebra Probability Vol 2 Maestro Series Dr. G S N Murti Dr. U M Swamy PDFDavid Tallat Ibrahim Wasef100% (4)
- Conditional TensesDocument3 pagesConditional TensesMuhammad yousafNo ratings yet
- TEFL Course Opt PDFDocument147 pagesTEFL Course Opt PDFWAWAN SAHIBNo ratings yet
- Clauses of ResultDocument5 pagesClauses of ResultMaria Iranzo Esteban0% (1)
- J.M. Synge Riders To The SeaDocument18 pagesJ.M. Synge Riders To The SeaAmna Arbi100% (2)
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentAlllioNo ratings yet
- Training ManagerDocument13 pagesTraining ManagerMathew JcNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 0 1 2 3Document2 pagesConditionals 0 1 2 3gocan12-1No ratings yet
- Life of Pi SummaryDocument3 pagesLife of Pi SummarydeathmouseNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsPetra StefanescuNo ratings yet
- 2 - Fce - Conditional 0123 Rules 2015Document10 pages2 - Fce - Conditional 0123 Rules 2015Alba Fortuny HueteNo ratings yet
- Reader. Contemporary Critical TheoriesDocument226 pagesReader. Contemporary Critical TheoriesIoana Munteanu100% (1)
- Storytelling - ReflectionDocument3 pagesStorytelling - ReflectionMaria Iranzo Esteban100% (1)
- Conditional Sentences Zero FirstDocument21 pagesConditional Sentences Zero FirstJosé Henrique Tobias PereiraNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences 1Document1 pageConditional Sentences 1Bozhidara KaragyozovaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument23 pagesConditionalsFatïma ZohraNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 9, Q1 - LAS, WK 4 Day 1-5Document5 pagesENGLISH 9, Q1 - LAS, WK 4 Day 1-5kenNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsКоля МогильниковNo ratings yet
- Conditionals ProjectDocument7 pagesConditionals ProjectIon PopescuNo ratings yet
- Conditional Clauses - Grammar PDFDocument2 pagesConditional Clauses - Grammar PDFAdrián Gutiérrez SanzNo ratings yet
- Conditionals in Expressing Arguments: Lady Fe Castro-AbreaDocument23 pagesConditionals in Expressing Arguments: Lady Fe Castro-AbreaLADY FE ABREANo ratings yet
- Conditional-Easy ExplanationDocument1 pageConditional-Easy ExplanationFernanda Shine SantosNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences: Zero, First, Second and Third ConditionalDocument6 pagesConditional Sentences: Zero, First, Second and Third ConditionalAmjad EshteiNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalsYol Anda San Roman FiolNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALSbDocument8 pagesCONDITIONALSbalexander celyNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences: Teacher: Vladimir Ajon JironDocument6 pagesConditional Sentences: Teacher: Vladimir Ajon JironVladimir AjonNo ratings yet
- Cream Cute Illustrative Mind Map BrainstormDocument1 pageCream Cute Illustrative Mind Map BrainstormRoman Gonzalez MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Zero ConditionalDocument1 pageConditionals: Zero ConditionalHajar DajajNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesGrace Gesto RubillosNo ratings yet
- Conditional ClausesDocument2 pagesConditional ClausesAli MalikNo ratings yet
- Zero Conditional First Conditional: Type Structure ExplanationDocument3 pagesZero Conditional First Conditional: Type Structure ExplanationSoledad BaltarNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence 0 and 1Document17 pagesConditional Sentence 0 and 1exuuu698No ratings yet
- Happen, What Might Be Happened and What What We Wish To HappenDocument1 pageHappen, What Might Be Happened and What What We Wish To HappenTer RisaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals - Theory (B1)Document2 pagesConditionals - Theory (B1)damianNo ratings yet
- Future Events or Situations (That Will Happen, or Are Likely To Happen) and Their Possible or Likely ResultsDocument7 pagesFuture Events or Situations (That Will Happen, or Are Likely To Happen) and Their Possible or Likely ResultsbelbachirNo ratings yet
- Conditionals B2 (Full Version)Document3 pagesConditionals B2 (Full Version)Gigi GuastellaNo ratings yet
- B Inggris XiDocument24 pagesB Inggris XiAsep SaepulNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument10 pagesConditional Sentencemedia kreasiNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument2 pagesConditionalKasia KasiaNo ratings yet
- Situation Result Situation Result Situation Result: Sentences With IFDocument1 pageSituation Result Situation Result Situation Result: Sentences With IFKenia AquinoNo ratings yet
- The Zero and First Conditional For SharingDocument7 pagesThe Zero and First Conditional For SharingabielgtgNo ratings yet
- Conditionals PDFDocument2 pagesConditionals PDFminimunhozNo ratings yet
- 1st ConditionalDocument9 pages1st ConditionalSneider CardonaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals SummaryDocument2 pagesConditionals SummaryAnca ȘtefănescuNo ratings yet
- 0 1st 2nd 3rd ConditionalDocument28 pages0 1st 2nd 3rd ConditionalCristian Omar Cano CruzNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences: Type Patterns DescriptionDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences: Type Patterns DescriptionYoga PramudanaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument3 pagesConditionalsVera AtanasovaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalsLauragaestNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalstamaraNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument3 pagesConditional Sentencesabdellah dandoumNo ratings yet
- English ConditionalsDocument2 pagesEnglish Conditionalshd25252No ratings yet
- If Clause + Main Clause: Condicionals SentencesDocument1 pageIf Clause + Main Clause: Condicionals SentencesEalex1dNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalsEzequiel MartínezNo ratings yet
- First Conditional Real Situations in The Present/ Future. Second Conditional Untrue, Unreal or Hypothetical Situations inDocument3 pagesFirst Conditional Real Situations in The Present/ Future. Second Conditional Untrue, Unreal or Hypothetical Situations inDanny MillerNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument12 pagesConditional Sentencesniko_blue55No ratings yet
- Chapther 4 Conditional SentencesDocument1 pageChapther 4 Conditional Sentencesganis galuhNo ratings yet
- Conditionals DefinitionDocument6 pagesConditionals Definitionlarisa jamiesonNo ratings yet
- 0 Conditional 1 Conditional 2 Conditional 3 ConditionalDocument3 pages0 Conditional 1 Conditional 2 Conditional 3 ConditionalAnda AdaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument9 pagesConditional SentenceIRMAN AMINUDINNo ratings yet
- Conditionals All InfographicsDocument8 pagesConditionals All Infographicsamajida fadia rNo ratings yet
- Conditional and Subjunctive MoodsDocument20 pagesConditional and Subjunctive MoodsCyndi De VriesNo ratings yet
- Conditional ClausesDocument1 pageConditional Clausesrafaelbalbuena06No ratings yet
- CONDITIONALS - Review PresentationDocument1 pageCONDITIONALS - Review PresentationGabriellaReneeNo ratings yet
- Zero Conditional First Conditional Second ConditionalDocument1 pageZero Conditional First Conditional Second ConditionalDiana EncinasNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Unit 4Document9 pagesConditionals: Unit 4Sara Vaquero GomezNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentense: SubjuntiveDocument10 pagesConditional Sentense: SubjuntiveAhmad MuqoddimNo ratings yet
- By N. F. Novian Paiman, S.PDDocument9 pagesBy N. F. Novian Paiman, S.PDDavid WilliamNo ratings yet
- Apples To Apples - Card BacksDocument1 pageApples To Apples - Card BacksMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- How To Describe An Animal THEORYDocument1 pageHow To Describe An Animal THEORYMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- How To Describe An Animal THEORYDocument1 pageHow To Describe An Animal THEORYMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument7 pagesExercisesMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- What Have I LearntDocument1 pageWhat Have I LearntMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- Reflection Communicative ActivityDocument5 pagesReflection Communicative ActivityMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- 05 03 18 ComparativesandsuperlativesDocument4 pages05 03 18 ComparativesandsuperlativesMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- Why Is This A Communicative ActivityDocument1 pageWhy Is This A Communicative ActivityMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- Tasks List Resources 14-15Document1 pageTasks List Resources 14-15Maria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- Teaching Arts Through EnglishDocument6 pagesTeaching Arts Through EnglishMaria Iranzo EstebanNo ratings yet
- The Doctrine of SatanDocument41 pagesThe Doctrine of Satanemmanueloduor100% (2)
- Academic Writing and Critical Thinking (IMPORTANT) PDFDocument37 pagesAcademic Writing and Critical Thinking (IMPORTANT) PDFShilpi DeyNo ratings yet
- Refraction and ReflectionDocument4 pagesRefraction and Reflectionsyafiq157No ratings yet
- N113 Syllabus W 11-1-1Document23 pagesN113 Syllabus W 11-1-1Minh PhungNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument25 pagesPhilosophyMoniq MaresNo ratings yet
- Brian McCall - Unprofitable Lending ChapterDocument65 pagesBrian McCall - Unprofitable Lending ChapterRh2223dbNo ratings yet
- The Place Called Zero: (Based On A True Story)Document43 pagesThe Place Called Zero: (Based On A True Story)LETCHUMY A/P MARIPAN MoeNo ratings yet
- A Student's History of PhilosphyDocument540 pagesA Student's History of PhilosphyNhuan Tu - TuanNo ratings yet
- The Sin Against The Holy SpiritDocument16 pagesThe Sin Against The Holy SpiritBill EnsslenNo ratings yet
- School Name My Family - Listening Comprehension NameDocument2 pagesSchool Name My Family - Listening Comprehension NameDelia ChiraNo ratings yet
- m1 Dynamics FmaDocument7 pagesm1 Dynamics FmadrkhansacademyNo ratings yet
- Opción 1 Read The Text and The Instructions To The Questions Very Carefully. Answer All The Questions in EnglishDocument6 pagesOpción 1 Read The Text and The Instructions To The Questions Very Carefully. Answer All The Questions in EnglishAisha HenniNo ratings yet
- Director of TourismDocument4 pagesDirector of TourismKimmy2010No ratings yet
- Legend of Eternal LoveDocument3 pagesLegend of Eternal LoveCyber TeenNo ratings yet
- Ibn Katheer IntroDocument14 pagesIbn Katheer IntroAishah Muhammad100% (1)
- MCS Weekly Paper - Control Tightness and Control Cost System KP YDocument25 pagesMCS Weekly Paper - Control Tightness and Control Cost System KP YJorgi PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Aberca v. Fabian-Ver, GR L-69866, 15 April 1988, en Banc, Yap (J)Document3 pagesAberca v. Fabian-Ver, GR L-69866, 15 April 1988, en Banc, Yap (J)Latjing SolimanNo ratings yet
- Bentzen, Aage - The Old Testament and The New CovenantDocument15 pagesBentzen, Aage - The Old Testament and The New CovenantcwbeardNo ratings yet
- GRE Essay Toppics MagooshDocument5 pagesGRE Essay Toppics MagooshraazahmadNo ratings yet
- BF Alignment Creators Kit r3Document4 pagesBF Alignment Creators Kit r3vscribNo ratings yet
- Elections and Voters A Comparative Introduction - Compressed PDFDocument45 pagesElections and Voters A Comparative Introduction - Compressed PDFMónica López100% (1)
- Productive Homework PDFDocument12 pagesProductive Homework PDFJames FarnhamNo ratings yet
- Self AwarenessDocument66 pagesSelf Awareness9986212378No ratings yet