Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essay L Hand
Uploaded by
Geraldo Mejillano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesThis document provides information about different types of essays. It discusses the main parts of an essay, including the introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should catch the reader's attention and state the main idea. Each body paragraph should support the main idea with facts, examples, or details. The conclusion should summarize the key points and avoid introducing new information. The document also defines formal, informal, narrative, expository, and persuasive essays and lists their characteristics. It provides tips for writing formal essays, such as avoiding personal pronouns and contractions.
Original Description:
ez
Original Title
Essay l Hand
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about different types of essays. It discusses the main parts of an essay, including the introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should catch the reader's attention and state the main idea. Each body paragraph should support the main idea with facts, examples, or details. The conclusion should summarize the key points and avoid introducing new information. The document also defines formal, informal, narrative, expository, and persuasive essays and lists their characteristics. It provides tips for writing formal essays, such as avoiding personal pronouns and contractions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesEssay L Hand
Uploaded by
Geraldo MejillanoThis document provides information about different types of essays. It discusses the main parts of an essay, including the introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should catch the reader's attention and state the main idea. Each body paragraph should support the main idea with facts, examples, or details. The conclusion should summarize the key points and avoid introducing new information. The document also defines formal, informal, narrative, expository, and persuasive essays and lists their characteristics. It provides tips for writing formal essays, such as avoiding personal pronouns and contractions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
ESSAY l HAND-OUT Work together with the other body paragraphs
to support your essay’s main idea;
An essay is a short non-fiction, non-imaginary Work together with the other body paragraphs
work about a subject. It may be classified by tone to create a clear, cohesive paper (clarity and
and style as formal or informal. coherence can be achieved through the use of
It has many purposes depending on what the transitions)
writer wants to write about and how he/she wants Each body paragraph states and explains a
to affect the readers. different point to help you prove your opinion
An essay is a written collection of prose, organized An opinion is always stronger when it has more
and divided neatly into paragraphs supporting facts (proof)
Always remember that an essay is a written form
of communication and therefore, must be clear, FACT OPINION
organized and easily understandable to those Fact is a true An opinion is one
reading statement individual’s
Facts can be personal belief on
What is the Purpose of an Essay? supported, upheld a subject
An essay is used to state and support an opinion and proven by Everyone is
with proof and explanation evidence welcome to have
Essays can be used to persuade others to agree an opinion, but not
with your opinion every opinion is
based on fact
THREE MAIN PARTS Opinions can be
1. INTRODUCTION based on what a
It is the opening part of the write-up that shows the person has heard
topic sentence of the essay or the thesis from others, and is
statement. It prepares the readers on the essay. therefore subject
Therefore, it should be effective so that the to bias
readers are encourage/motivate to continue make sure that you phrase and word your essays
reading. as if they are FACT, not simply OPINION
Effective introduction should An effective body paragraphs should
• Catch the reader’s attention, which can be • Explain, illustrate, discuss, or provide evidence
done, for example, by using a direct to support the main idea (thesis or claim) of the
announcement, a quotation, a question, a essay;
definition, an unusual comparison, or a • Discuss only one aspect of the main idea
controversial position/opinion; (whenever you move on to a new supporting
• Introduce the topic of the essay, (in other point, start a new body paragraph);
words, inform the reader of and provide a
context for the topic being discussed); 3. CONCLUSION
• Introduce the main idea (otherwise known as An essay ends with a brief conclusion, which
the thesis or claim) of the essay; brings the essay to a logical end. An effective
• Introduce the purpose of the essay (will it conclusion should:
inform, argue, persuade, describe, narrate, brief;
classify, etc.?). predicting an outcome to the main idea
giving an opinion
2. BODY
quotations
An essay includes body paragraphs, which
develop the main idea (thesis or claim) of the
essay.
Remind readers of the primary focus of the NARRATIVE ESSAY
essay, which can be done by restating the It is an essay that tells a story of the writer or
main idea in different words; other’s story. It is usually found in the feature
Avoid introducing new ideas; writing sections of newspaper or magazine
Avoid apologies.
EXPOSITORY ESSAY
TYPES OF AN ESSAY It is an essay that explains something so that
reader can understand.
FORMAL ESSAY
This is known as impersonal essay. The PERSUASIVE ESSAY
content is informative and scientific in nature. It is an essay that convinces the reader to think
The writer uses the “aesthetic” approach in in a certain way.
language and style.
Elements of an Essay
Audience- It refers to whom the essay is
Tips for Writing Formal Essays intended for.
Do not use personal pronouns (I, we, you) Purpose- It refers to the intention or goal in
These suggest your essay is an opinion writing the essay.
instead of factual Subject- It is the topic discussed in the essay.
Write in Present tense Point of view- It is the how the ideas are told
Do not use rhetorical devises or creative to the reader
writing skills Theme- It refers to the lesson or message of
Do not use contractions (Can’t, won’t, couldn’t) the essay.
Do not use slang or informal language Mood- It refers to the feeling which the writer
Avoid using vague language (be specific) would like the reader to experience or get from
In an essay do not simply summarize your the literary work.
novel/play (assume that whoever is reading Tone- It is the attitude of the writer towards
knows the novel/play well) his/her subject
In your body paragraph, be as detailed and Style- This is the special way in which the
specific as possible when explaining and ideas of the essay are developed.
supporting your evidence and quotations
Use transition words to move smoothly from
one idea to the next (in addition, lastly, for
example, therefore)
NEVER bring up new information in your
closing paragraph
INFORMAL ESSAY
It is called familiar or personal essay. It
expresses personal experiences or
observation on human nature. Its purpose is to
entertain rather than to inform.
FORMS OF ESSAY
DESCRIPTIVE ESSAY
It is an essay that illustrates by using sensory
words in order to bring to the reader’s
imagination what is being talked about.
You might also like
- Discursive Writing EssaysDocument33 pagesDiscursive Writing EssaysClaudia Wydler100% (1)
- IASP 2016 Poster Abstracts - Wednesday PDFDocument731 pagesIASP 2016 Poster Abstracts - Wednesday PDFHendriik ViicarloNo ratings yet
- 203 Cat Generalbrochure Topnotch NEWDocument16 pages203 Cat Generalbrochure Topnotch NEWjhienellNo ratings yet
- Essay WritingDocument22 pagesEssay WritingSheraz AliNo ratings yet
- Pointers For EAPP First Quarter ExamDocument6 pagesPointers For EAPP First Quarter ExamMary Grace Sagun86% (7)
- Essay WritingDocument21 pagesEssay Writingannie malikNo ratings yet
- Other Types of EssaysDocument23 pagesOther Types of EssaysStelaMajaNo ratings yet
- Essay Week5 7 1Document19 pagesEssay Week5 7 1Althea DionisioNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing 1Document15 pagesEssay Writing 1Tawakkal HussainNo ratings yet
- Eng ReviewerDocument4 pagesEng ReviewerYasha DumplyngNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument7 pagesEssayMarjun DoldolNo ratings yet
- Thesis StatementDocument6 pagesThesis StatementG10 de Castro Franz ArielleNo ratings yet
- English Presentation-1Document22 pagesEnglish Presentation-1Aimen KhalidNo ratings yet
- What Is An EssayDocument2 pagesWhat Is An EssayJose Ibañez100% (1)
- Cuadro Tipos de TextosDocument2 pagesCuadro Tipos de TextosjungkookmihombreeternamenteNo ratings yet
- APznzaaJ1_eOATa3DOI5h5_lUPPu7SjhX0v2JbLj_akO1AyrFwJWZ6js-LtSAmJiW-eS6E6-hOJ7ABqtCy-deGEGpVHU_4rygOUXVVTQ-wvQJim7GQQUyVTORryUJZS2MqhNMBxz6Vj6xEE9Qrp_a-FSi7LCvatvZVBhpuXVCUutzL6hiwmXRJmP3AWamAUt3IgkJlTqxfKnFISwgeRL2uDocument18 pagesAPznzaaJ1_eOATa3DOI5h5_lUPPu7SjhX0v2JbLj_akO1AyrFwJWZ6js-LtSAmJiW-eS6E6-hOJ7ABqtCy-deGEGpVHU_4rygOUXVVTQ-wvQJim7GQQUyVTORryUJZS2MqhNMBxz6Vj6xEE9Qrp_a-FSi7LCvatvZVBhpuXVCUutzL6hiwmXRJmP3AWamAUt3IgkJlTqxfKnFISwgeRL2uLEOBERTNo ratings yet
- Analytical Exposition: Here Starts The Lesson!Document11 pagesAnalytical Exposition: Here Starts The Lesson!Laras IHNo ratings yet
- Communication For Academic PurposesDocument15 pagesCommunication For Academic PurposesJahnine BaisNo ratings yet
- 4TH QTR Module 7 EssayDocument18 pages4TH QTR Module 7 EssayRose Ann ZimaraNo ratings yet
- Types of EssaysDocument6 pagesTypes of Essaysslsschool100% (6)
- Consider Brainstorming and Outlining As Effective PreDocument5 pagesConsider Brainstorming and Outlining As Effective PreGautham SajuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 02 (Cont. 2.3)Document7 pagesUNIT 02 (Cont. 2.3)salmaNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarterly Exam HandoutsDocument3 pages3RD Quarterly Exam HandoutsJo Maichel MorenoNo ratings yet
- 1-Argumentative EssayDocument1 page1-Argumentative EssayBlueOneGaussNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Essay: Types of Essays Writing SkillsDocument18 pagesDescriptive Essay: Types of Essays Writing SkillsMeraj AliNo ratings yet
- Essay: Definition of An EssayDocument3 pagesEssay: Definition of An Essaymeldianto manugalaNo ratings yet
- Academic WritingDocument3 pagesAcademic WritingMemon MemonNo ratings yet
- RWLS Kel. 2Document9 pagesRWLS Kel. 2Bagus SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Eapp For PTDocument7 pagesEapp For PTAbbyjane MadlangsakayNo ratings yet
- Expository Vs ArgumentativeDocument10 pagesExpository Vs ArgumentativelearningselfNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Q3 NOTESDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Q3 NOTESalexandersoriano453No ratings yet
- What Is An EssayDocument24 pagesWhat Is An EssayCasNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Writing Skills Learning ObjectiveDocument11 pagesUnit-2 Writing Skills Learning ObjectivePrasanna Chamana100% (1)
- Notes Essay WritingDocument10 pagesNotes Essay WritingBhavuk BansalNo ratings yet
- English 10 - Quarter 3Document2 pagesEnglish 10 - Quarter 3Elixa FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Q3 English Reviewer PDFDocument4 pagesQ3 English Reviewer PDFangela louisseNo ratings yet
- Original Paraphrase: Change by Angela Manalang GloriaDocument2 pagesOriginal Paraphrase: Change by Angela Manalang GloriaYhel LantionNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Writing ReviwerDocument5 pagesPhilosophical Writing ReviwerCharles Nathaniel JavierNo ratings yet
- A Road Map To The Argumentative EssayDocument4 pagesA Road Map To The Argumentative Essaygiselacrz24No ratings yet
- Creative Writing Transcript IIDocument4 pagesCreative Writing Transcript IICourtney BaguinatNo ratings yet
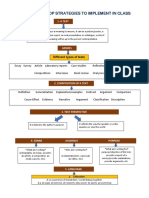
- Egap Workshop Strategies To Implement in Class: 1. A TextDocument3 pagesEgap Workshop Strategies To Implement in Class: 1. A TextAndy ArtNo ratings yet
- AcademicVocabList Argumentative 2018-08-24Document4 pagesAcademicVocabList Argumentative 2018-08-24Grant EwingNo ratings yet
- Writing Research-Based Argumentative EssayDocument12 pagesWriting Research-Based Argumentative EssayEugene Kurt Cahilsot7No ratings yet
- Eapp Reviewer Q1Document5 pagesEapp Reviewer Q1Cindy FloresNo ratings yet
- Morning!: Welcome To Our English ClassDocument18 pagesMorning!: Welcome To Our English ClassRose Ann ZimaraNo ratings yet
- Unit-III: WritingDocument24 pagesUnit-III: WritingRoshin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Thesis StatementDocument2 pagesThesis StatementMylaine Grace Sanchez BacosaNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument24 pagesEssayChristine Joy CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Writing EssayDocument17 pagesWriting EssayAlma AzzuraNo ratings yet
- Writing The Academic Paper: Sebastian Griffin Angel MEI Darapiza Reina PunoDocument15 pagesWriting The Academic Paper: Sebastian Griffin Angel MEI Darapiza Reina PunoMeraflor MiguelNo ratings yet
- Analytical Exposition TextDocument9 pagesAnalytical Exposition TextRAZQA IHSAN YUHENDRYNo ratings yet
- Kinds of EssayDocument16 pagesKinds of EssayAriell EmraduraNo ratings yet
- 11 ReviewerDocument6 pages11 ReviewerjamespaulpannNo ratings yet
- Essay G7 '16-'17Document41 pagesEssay G7 '16-'17Keith Ann KimNo ratings yet
- Essay 2Document2 pagesEssay 2Zamin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Perpertual Succour Academy, Inc.: Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskDocument3 pagesPerpertual Succour Academy, Inc.: Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskCry BeroNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishCherel Joy BolandoNo ratings yet
- Writing Guideline EssayDocument3 pagesWriting Guideline EssayNati AntunezNo ratings yet
- EAPP Handout1Document46 pagesEAPP Handout1Mae MadronaNo ratings yet
- Essay Intros and ConclusionsDocument25 pagesEssay Intros and Conclusionsfarhan talibNo ratings yet
- Acceptance and ContinuanceDocument2 pagesAcceptance and ContinuanceGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Seatplanblindcopy AM Rm4 CBDocument1 pageSeatplanblindcopy AM Rm4 CBGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- R41819 IRR ABD The Accounting Quiz BeesDocument14 pagesR41819 IRR ABD The Accounting Quiz BeesGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Baybayin Writing SheetDocument9 pagesBaybayin Writing SheetGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Audit-1 Course OutlineDocument5 pages2019 Audit-1 Course OutlineGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Postexam Reminders 2019 10 Manila Sept2019Document1 pagePostexam Reminders 2019 10 Manila Sept2019Geraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Apex CrashDocument2 pagesApex CrashVermillion MavisNo ratings yet
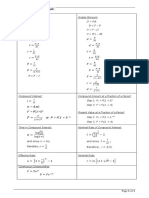
- Formulas in Business MathDocument1 pageFormulas in Business MathGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Formulas in Business MathDocument1 pageFormulas in Business MathGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Garrison FSA Solman PDFDocument39 pagesGarrison FSA Solman PDFGeraldo Mejillano100% (1)
- Formulas in Business MathDocument1 pageFormulas in Business MathGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- IPPF Code of EthicsDocument2 pagesIPPF Code of EthicsHadassahFayNo ratings yet
- Authorization LetterDocument6 pagesAuthorization LetterGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Exceed 2019 Accounting Convention PrimerDocument11 pagesExceed 2019 Accounting Convention PrimerGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- BID Your MATH Bag PrimerDocument1 pageBID Your MATH Bag PrimerGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- AwDocument3 pagesAwGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- ReligionDocument41 pagesReligionSreejith SurendranNo ratings yet
- AA Final Artwork Plan Form 2017-2018Document1 pageAA Final Artwork Plan Form 2017-2018Geraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Authorization LetterDocument2 pagesAuthorization LetterGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- LitformDocument1 pageLitformGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- ABD Waiver FormDocument1 pageABD Waiver FormcykeeNo ratings yet
- WebPage PDFDocument1 pageWebPage PDFGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Go To Inventory ModuleDocument11 pagesGo To Inventory ModuleGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Nature of The FirmDocument1 pageNature of The FirmGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument16 pagesConcept PaperGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Estate and Donor's TaxDocument14 pagesGuidelines On Estate and Donor's Taxkatreena ysabelle89% (9)
- Guidelines On Estate and Donor S TaxDocument2 pagesGuidelines On Estate and Donor S TaxGeraldo MejillanoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Part 2 Solman MillanDocument270 pagesAdvanced Part 2 Solman MillanVenz Lacre80% (25)
- Esci ResultsDocument23 pagesEsci Resultsapi-304738945No ratings yet
- Basic Test 4Document2 pagesBasic Test 4yasser AnwarNo ratings yet
- From " Minister of The Great God" To "Manual Laborer of The Divine Providence": A Peak ExperienceDocument47 pagesFrom " Minister of The Great God" To "Manual Laborer of The Divine Providence": A Peak Experiencenicholas kirimoNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - PDF - Official-Sat-Study-Guide-Command-EvidenceDocument6 pagesChap 3 - PDF - Official-Sat-Study-Guide-Command-EvidenceKriti NyatiNo ratings yet
- Graduate School: Vision RMMC Is An Institution of Innovative Development and ExcellenceDocument7 pagesGraduate School: Vision RMMC Is An Institution of Innovative Development and ExcellenceSWEET GRACE DO-ONGNo ratings yet
- Strawson PresentDocument8 pagesStrawson PresentAnonymous RrgVuPSeYENo ratings yet
- Obligation To Obey The LawDocument89 pagesObligation To Obey The LawJorge Daniel IacovellaNo ratings yet
- PHENOMENOLOGYDocument17 pagesPHENOMENOLOGYSheila Mae LiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson I To III - UTS ReviewerDocument4 pagesLesson I To III - UTS ReviewerZekken Adonai MelekNo ratings yet
- T02Document3 pagesT02awankilat0% (1)
- Habitual Behavior Bridging The Gap BetweDocument8 pagesHabitual Behavior Bridging The Gap BetweAndres Eduardo Del PadroneNo ratings yet
- Ef Academy International Boarding SchoolDocument4 pagesEf Academy International Boarding Schoolapi-277856672No ratings yet
- Definition of A Name GlorifierDocument8 pagesDefinition of A Name GlorifierKristine WhiteNo ratings yet
- Semester - S.Y 2020-2021 - : Module No.Document3 pagesSemester - S.Y 2020-2021 - : Module No.Erwil AgbonNo ratings yet
- 12 The Varieties of Theism and The Openness of God Charles Hartshorne and Free-Will TheismDocument41 pages12 The Varieties of Theism and The Openness of God Charles Hartshorne and Free-Will TheismAaron ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Reading Process Theories: Bottom-Up Model Interactive Model Top-Down ModelDocument2 pagesReading Process Theories: Bottom-Up Model Interactive Model Top-Down ModelBeverly Panganiban CadacioNo ratings yet
- Mage The Ascension (Revised) QuickstartDocument24 pagesMage The Ascension (Revised) Quickstartleprechaun77100% (2)
- Research MethodologyDocument11 pagesResearch MethodologyMPU3412 KHIDMAT MASYARAKAT KaviNo ratings yet
- A Concept Analysis of EmpathyDocument161 pagesA Concept Analysis of EmpathyAlicja RozpendowskaNo ratings yet
- Boff'S Jesus Cristo Libertador: A Review: I Found This Review I Wrote in 2002 For A Christology UnitDocument5 pagesBoff'S Jesus Cristo Libertador: A Review: I Found This Review I Wrote in 2002 For A Christology Unitanonimous40No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Nature of PhilosophyDocument4 pagesLesson 1: The Nature of PhilosophyEunice C. LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Jackson ScottDocument17 pagesJackson ScottNishant MishraNo ratings yet
- Education Final NotesDocument59 pagesEducation Final NotesRajesh Sharma100% (1)
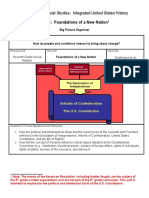
- Unit 1: Foundations of A New Nation: Eighth Grade Social Studies: Integrated United States HistoryDocument5 pagesUnit 1: Foundations of A New Nation: Eighth Grade Social Studies: Integrated United States Historyapi-134134588No ratings yet
- Light Workers by The AbbottsDocument9 pagesLight Workers by The AbbottsmascaNo ratings yet
- Greece Greek Art and LiteratureDocument17 pagesGreece Greek Art and LiteratureLyn ChoiNo ratings yet
- Towards Being HumanDocument12 pagesTowards Being HumanJaymar Magtibay100% (1)
- Nic EthicsDocument29 pagesNic Ethicsrichard100% (1)
- Cover LetterDocument2 pagesCover LetterQazi Zarif Ul IslamNo ratings yet