Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nouveau Document Microsoft Word
Uploaded by
Kaiysse YoukéOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nouveau Document Microsoft Word
Uploaded by
Kaiysse YoukéCopyright:
Available Formats
Work is partially supported by the U.S.
Department of Energy (DOE) National
Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL) under Grant Number DE-FE0002056.
Dr. Paul Glover Petrophysics MSc Course Notes 1 provides a step-by-step reference
for creating the synthetic seismogram and is paraphrased below. This program uses
a data structure that automatically ties all the log curves to the depth as well as the
computed travel time.
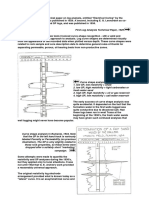
The synthetic seismogram is a seismic trace that has been contructed from well log
data. It represents the idealize trace that should be observed with the seismic method
at the location of the well. The Synthetic Seismic can be compared with the seismic
trace actually measured at the well to improve the picking of seismic horizons, and to
improve the accuracy and resolution of formations of interest.
The observed seismic trace is primarily a record of the ability of interfaces between
formations to reflect elastic waves, which is called the reflection coefficent R. The
reflection coefficient depends on the properties of the rock at the interface of the
beds and in particular on its acoustic impedance. The acoustic impedance is the
product of the seismic velocity and the density of the rock.
The following procedure was performed to create the Synthetic Seismogram in the
Applet,
The synthetic seismogram is constructed from the acoustic travel time (DT)
and the bulk denisty (RHOB) logs, but at a minimun an acoustic travel time
(DT) log must exist for the well of interest.
Convert the depth to the two-way travel time using the acoustic travel time
(DT). The digital Log ASCII Standard (LAS) is generally sampled at 1/2 foot
intervals and it is further assumed that between the interval is the average of
the measured data value. The 2-way travel time at each depth is the sum of
2.0 times the step depth (0.5') times the acoustic travel time (DT) at that depth.
Surface to 1368.5 ft = 172.943 msec
Acoustic Acoustic transit
Depth
transit time time * Step Depth
DEPT DT 2 * DT * 0.5' Time
(ft) (μsec/ft) (μsec) (msec)
1368.5 63.164 63.164 172.943
1369.0 63.164 63.164 173.006
1369.5 63.164 63.164 173.069
1370.0 63.164 63.164 173.132
1370.5 63.164 63.164 173.196
1371.0 63.809 63.809 173.259
1371.5 63.398 63.398 173.323
1372.0 64.102 64.102 173.387
1372.5 70.352 70.352 173.457
1373.0 63.809 63.809 173.521
1373.5 63.77 63.77 173.585
1374.0 63.574 63.574 173.649
1374.5 111.699 111.699 173.76
1375.0 111.426 111.426 173.872
1375.5 115.488 115.488 173.987
1376.0 123.691 123.691 174.111
1376.5 116.719 116.719 174.228
1377.0 108.984 108.984 174.337
1377.5 155.234 155.234 174.492
1378.0 154.072 154.072 174.646
1378.5 148.145 148.145 174.794
1379.0 144.883 144.883 174.939
1379.5 109.941 109.941 175.049
1380.0 114.414 114.414 175.163
1380.5 112.598 112.598 175.276
Compute the wave velocity from the acoustic transit time (DT), V = 10 6/Δt
[ft]/[sec]
You might also like
- Basic Data:: Calculation of Gust Effect FactorDocument4 pagesBasic Data:: Calculation of Gust Effect FactorassadeqNo ratings yet
- Open Foundation SummaryDocument1,816 pagesOpen Foundation SummaryRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Duct SizerDocument26 pagesDuct SizerRaju KsnNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design of Road Crossing: Irrigation EngineeringDocument6 pagesHydraulic Design of Road Crossing: Irrigation EngineeringJouvert TapisNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Circuits Laboratory: Analog Experiment: Common Source AmplifierDocument11 pagesAnalog and Digital Circuits Laboratory: Analog Experiment: Common Source AmplifierSanjai SenthilNo ratings yet
- Design Sheet Sickle PlateDocument15 pagesDesign Sheet Sickle PlatePrashanna BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Calculo Informe BernulliDocument18 pagesCalculo Informe BernullibbustillosiriarteNo ratings yet
- Slope-Degree, Gradient and Slope ConverterDocument14 pagesSlope-Degree, Gradient and Slope ConverterChristopher UcheNo ratings yet
- Roting Waduk (Autorecovered)Document46 pagesRoting Waduk (Autorecovered)irmanovitaNo ratings yet
- Structural PDFDocument5 pagesStructural PDFrouhoNo ratings yet
- 65 65 Table 1 1.25 2 8645 2500 3500 5000 8000 22491Document12 pages65 65 Table 1 1.25 2 8645 2500 3500 5000 8000 22491Muhammad Hakim JaffarNo ratings yet
- HHDocument2 pagesHHunnicyriacNo ratings yet
- HY-8 Analysis Results: Culvert Summary Table - Thesis CulvertDocument1 pageHY-8 Analysis Results: Culvert Summary Table - Thesis CulvertWai linn zawNo ratings yet
- Soil Bearing Capacity CalcuationsDocument26 pagesSoil Bearing Capacity CalcuationsBishal Thapa MagarNo ratings yet
- IPNDocument1 pageIPNarianto32No ratings yet
- Pruebas de Infiltracion (Campo)Document5 pagesPruebas de Infiltracion (Campo)CristianFernandezNo ratings yet
- Pondasi Tiang PancangDocument26 pagesPondasi Tiang PancangTotok HermawanNo ratings yet
- Lare Reservoir CapacityDocument15 pagesLare Reservoir CapacityAbiued EjigueNo ratings yet
- 518kHz Navtex ReceptionDocument18 pages518kHz Navtex ReceptionJose Antonio López FernándezNo ratings yet
- AASHTO A Policy On Geometric Design of Highways and Streets 2018, 7th EditionDocument4 pagesAASHTO A Policy On Geometric Design of Highways and Streets 2018, 7th EditionSara SimoesNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Killing Fluid & Pemompaan: Sepuluh (10) Potensi Bahaya (Hazard) Di Area KerjaDocument4 pagesPerhitungan Killing Fluid & Pemompaan: Sepuluh (10) Potensi Bahaya (Hazard) Di Area KerjaAbdul MuqtadirNo ratings yet
- Stowage Factor CovertionsDocument4 pagesStowage Factor CovertionsPanagiotis RappasNo ratings yet
- Settlement Analysis: Foundation Geometry, GWT & LoadingDocument6 pagesSettlement Analysis: Foundation Geometry, GWT & LoadingUmed ADA-ALSATARNo ratings yet
- Oil Slick Project ReportDocument8 pagesOil Slick Project ReportRobin KimNo ratings yet
- PEHDDocument3 pagesPEHDAthmane HariziNo ratings yet
- ROUND DIFFUSER Single PageDocument9 pagesROUND DIFFUSER Single PageRaed AlmhimdNo ratings yet
- Siemon Tera 600mhz FFTP Cable International - Spec SheetDocument3 pagesSiemon Tera 600mhz FFTP Cable International - Spec SheetJesus LandaetaNo ratings yet
- Conveyanc Table 2020-21Document29 pagesConveyanc Table 2020-21tnadehkjpdNo ratings yet
- Liq Level 1Document5 pagesLiq Level 1DEEP NariyaNo ratings yet
- HY-8 Analysis Results: Culvert Summary Table - Thesis CulvertDocument1 pageHY-8 Analysis Results: Culvert Summary Table - Thesis CulvertWai linn zawNo ratings yet
- HY-8 Analysis Results: Culvert Summary Table - Thesis CulvertDocument1 pageHY-8 Analysis Results: Culvert Summary Table - Thesis CulvertWai linn zawNo ratings yet
- Group28 - Inclined PlaneDocument14 pagesGroup28 - Inclined PlaneAbdul Razak SoaleNo ratings yet
- Fan ResultsDocument1 pageFan ResultsRufus D SNo ratings yet
- (15-16) Double Channel SteelDocument2 pages(15-16) Double Channel SteelTamboli EnergiNo ratings yet
- Roldan PS 3-4Document26 pagesRoldan PS 3-4Charles Warren GoNo ratings yet
- DID 180 Standard Roller Chain: Roller Chains For Power TransmissionDocument1 pageDID 180 Standard Roller Chain: Roller Chains For Power TransmissionJhampol Rosales MuñozNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExperimentDocument10 pagesLaboratory ExperimentladheedhaNo ratings yet
- D3me2b Mochamad Rafi Arya Chadavi PDFDocument7 pagesD3me2b Mochamad Rafi Arya Chadavi PDFrafiNo ratings yet
- Multi-Band 'Linked' Dipole Calculator (For Sota / Portable HF)Document3 pagesMulti-Band 'Linked' Dipole Calculator (For Sota / Portable HF)Andrei PopescuNo ratings yet
- Pengujian Menggunakan Spss - Docx 2Document8 pagesPengujian Menggunakan Spss - Docx 2Candra SartikoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2: (Blasting Technology)Document3 pagesAssignment No. 2: (Blasting Technology)Ayush Anshuman SupakarNo ratings yet
- Vigas PresforzadasDocument15 pagesVigas PresforzadasJulio AmaguaNo ratings yet
- Print Untuk Ujian - Mv. Arawana - Loading ManualDocument11 pagesPrint Untuk Ujian - Mv. Arawana - Loading ManualtperkapalanNo ratings yet
- National Refrigerants, LTD.: Technical GuidelinesDocument2 pagesNational Refrigerants, LTD.: Technical GuidelinesRamadhan Al HaritsNo ratings yet
- Well ControlDocument26 pagesWell ControlAboZaidNo ratings yet
- Kosmos Unit Wise Areas, Pricing and No. of Reserved Car Parking SlotsDocument6 pagesKosmos Unit Wise Areas, Pricing and No. of Reserved Car Parking SlotsGangesh GunjanNo ratings yet
- Print Template - Portland BoltDocument1 pagePrint Template - Portland BoltManik MantalaNo ratings yet
- Name: Bearing Roll No Design Case:: Given Process /operating ConditionsDocument6 pagesName: Bearing Roll No Design Case:: Given Process /operating ConditionsIffatNo ratings yet
- EarethingDocument3 pagesEarethingমোঃ মহসিনNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-5 AD2Document15 pagesExperiment No-5 AD2bad guyNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document6 pagesLab 3Siva EsarapuNo ratings yet
- Hot Roled SectionsDocument58 pagesHot Roled Sectionsmohamed AlasadyNo ratings yet
- Fill-Up Size Components Reference Sheet PDFDocument12 pagesFill-Up Size Components Reference Sheet PDFsubodhasinghNo ratings yet
- Major Design Project BeastDocument26 pagesMajor Design Project BeastPrabakaran MgkNo ratings yet
- Transformer DesignDocument8 pagesTransformer DesignAzminAg100% (1)
- Mueller Equivalent Lengths PDFDocument1 pageMueller Equivalent Lengths PDFkuchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics: SR - No MFR 1-Life of Bulb (In HRS) MFR 2-Life of Bulb (In HRS)Document7 pagesBusiness Statistics: SR - No MFR 1-Life of Bulb (In HRS) MFR 2-Life of Bulb (In HRS)RASHMINo ratings yet
- Squat CalculationDocument4 pagesSquat CalculationXyde JavNo ratings yet
- (Untitled) 2017072508150700Document1 page(Untitled) 2017072508150700Kaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Nouveau Document Microsoft WordDocument2 pagesNouveau Document Microsoft WordKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- (Untitled) 2017072508170100Document1 page(Untitled) 2017072508170100Kaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- (Untitled) 2017072709194800Document1 page(Untitled) 2017072709194800Kaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- (Untitled) 2017072508160500Document1 page(Untitled) 2017072508160500Kaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- (Untitled) 2017072709232600Document1 page(Untitled) 2017072709232600Kaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Inventions That Made Our WorldDocument19 pagesInventions That Made Our WorldKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Recommended Logging ProgramDocument2 pagesRecommended Logging ProgramKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Field DutiesDocument2 pagesJob Description - Field DutiesKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Training and PrerequisitesDocument3 pagesTraining and PrerequisitesKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Nouveau Présentation Microsoft PowerPointDocument18 pagesNouveau Présentation Microsoft PowerPointKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Is Job OneDocument2 pagesQuality Control Is Job OneKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Computer Related DutiesDocument1 pageJob Description - Computer Related DutiesKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Logging in CanadaDocument6 pagesLogging in CanadaKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Physics Across The CenturiesDocument22 pagesPhysics Across The CenturiesKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Physics Across The CenturiesDocument22 pagesPhysics Across The CenturiesKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- The Peak Oil ProblemDocument8 pagesThe Peak Oil ProblemKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- (Untitled) 2017072508133100Document1 page(Untitled) 2017072508133100Kaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas in CanadaDocument1 pageOil and Gas in CanadaKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- RAW Data (SEGD) - SPS Files - Observer Report - Acquisition Report - Upholes & Vertical Electrical Soundings (Sev + Fdem) - VSP - Well LogsDocument2 pagesRAW Data (SEGD) - SPS Files - Observer Report - Acquisition Report - Upholes & Vertical Electrical Soundings (Sev + Fdem) - VSP - Well LogsKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- 2D & 3D Seismic Data AcquisitionDocument2 pages2D & 3D Seismic Data AcquisitionKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- A True History of Oil and GasDocument2 pagesA True History of Oil and GasKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Oil Ain CanadaDocument4 pagesOil Ain CanadaKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Seg yDocument3 pagesSeg yKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- The Recent Years: Saraband Computed Log C.1971 Coriband Computed Log C.1971Document5 pagesThe Recent Years: Saraband Computed Log C.1971 Coriband Computed Log C.1971Kaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- The Middle YearsDocument6 pagesThe Middle YearsKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- The Early Years: Four Electrode Surface Resistivity SystemDocument6 pagesThe Early Years: Four Electrode Surface Resistivity SystemKaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- The Early Years2Document7 pagesThe Early Years2Kaiysse YoukéNo ratings yet
- Ifrs SapDocument6 pagesIfrs Sapravikb01No ratings yet
- Director Product Development Engineering in Detroit MI Resume Brian ThompsonDocument2 pagesDirector Product Development Engineering in Detroit MI Resume Brian ThompsonBrianThompson2No ratings yet
- Siemens - Microsoft Hyper V Case StudyDocument2 pagesSiemens - Microsoft Hyper V Case StudyPaul AdamsNo ratings yet
- 17. ĐỀ SỐ 17 HSG ANH 9 HUYỆNDocument9 pages17. ĐỀ SỐ 17 HSG ANH 9 HUYỆNHồng Hoàn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cerita BugisDocument14 pagesCerita BugisI'dris M11No ratings yet
- PTE Self Study - Lfib v3.0Document57 pagesPTE Self Study - Lfib v3.0Jewel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument69 pagesLab ManualPradeepNo ratings yet
- Questions: Comma PlacementDocument8 pagesQuestions: Comma PlacementZarbibi Hussain khelNo ratings yet
- WEEK8 VI MAPARAAN WHLP Q2 - March1 4 2021Document8 pagesWEEK8 VI MAPARAAN WHLP Q2 - March1 4 2021Arjay M. VirayNo ratings yet
- Absolute Duo 1 PDFDocument219 pagesAbsolute Duo 1 PDFAgnieškaRužičkaNo ratings yet
- Taylor Linker ResumeDocument2 pagesTaylor Linker ResumeTaylor LinkerNo ratings yet
- Making Things: The Essence and Evolution of The Toyota Production SystemDocument2 pagesMaking Things: The Essence and Evolution of The Toyota Production Systemkt44974085No ratings yet
- English 4 Realistic FictionDocument5 pagesEnglish 4 Realistic FictionRose Marie RebutaNo ratings yet
- D062/D063/D065/D066 Service Manual: (Book 1 of 2) 004778MIU MainframeDocument1,347 pagesD062/D063/D065/D066 Service Manual: (Book 1 of 2) 004778MIU MainframeevpsasaNo ratings yet
- Stone ChapaisDocument6 pagesStone ChapaisMaría GallardoNo ratings yet
- Fruits Basket - MemoryDocument1 pageFruits Basket - Memorywane10132100% (1)
- MCQ in Engineering Economics Part 11 ECE Board ExamDocument19 pagesMCQ in Engineering Economics Part 11 ECE Board ExamDaryl GwapoNo ratings yet
- Earth Pressure At-Rest PDFDocument7 pagesEarth Pressure At-Rest PDFvpb literaturaNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Class Notes1 PDFDocument6 pagesTopic 8 Class Notes1 PDFMuhammad Adnan LaghariNo ratings yet
- IMS - General MBA - Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesIMS - General MBA - Interview QuestionsRahulSatputeNo ratings yet
- Astm D448Document3 pagesAstm D448Mutyaba Johnson100% (5)
- School of Education - Writing A Research Proposal - Durham UniversityDocument2 pagesSchool of Education - Writing A Research Proposal - Durham UniversityRussasmita Sri PadmiNo ratings yet
- Confidence Limits in StatisticsDocument30 pagesConfidence Limits in StatisticsaassmmrrNo ratings yet
- 3D CL Correction S1223RTLDocument7 pages3D CL Correction S1223RTLakatsuki.exeNo ratings yet
- DTC Induction Motor DriveDocument13 pagesDTC Induction Motor Drivesarav03100% (2)
- Success Story of Amit Kumar Singh UPSC 2010 BatchDocument5 pagesSuccess Story of Amit Kumar Singh UPSC 2010 BatchvishalkkkkNo ratings yet
- Research Methods SESSIONS STUDENTS Abeeku PDFDocument287 pagesResearch Methods SESSIONS STUDENTS Abeeku PDFdomaina2008100% (3)
- Hawk RoostingDocument11 pagesHawk RoostingMOKIBUL ISLAM MOKIPSNo ratings yet
- Forecasting The Return Volatility of The Exchange RateDocument53 pagesForecasting The Return Volatility of The Exchange RateProdan IoanaNo ratings yet