Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Smart Tourism Mohanty IEEE-CEM 2018-May ITour
Uploaded by
kontaktblCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Smart Tourism Mohanty IEEE-CEM 2018-May ITour
Uploaded by
kontaktblCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/324691837
iTour: The Future of Smart Tourism: An IoT Framework for the Independent
Mobility of Tourists in Smart Cities
Article in IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine · May 2018
DOI: 10.1109/MCE.2018.2797758
CITATIONS READS
3 1,681
4 authors:
Ajaya Kumar Tripathy Pradyumna Tripathy
Silicon Institute of Technology Silicon Institute of Technology
14 PUBLICATIONS 56 CITATIONS 11 PUBLICATIONS 51 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE
Niranjan Ray Saraju P. Mohanty
Silicon Institute of Technology University of North Texas
8 PUBLICATIONS 11 CITATIONS 360 PUBLICATIONS 3,163 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Memristors: Modeling, Circuit Design, and Applications View project
Topological optimization View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Saraju P. Mohanty on 20 May 2018.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
1
iTour: The Future of Smart Tourism
By A. K. Tripathy, P. K. Tripathy, N. K. Ray, and S. P. Mohanty
Abstract—Smart tourism is an example of the important iTour involves a large variety of stakeholders including
components of smart cities. However, in many cities, city administrative officials and volunteers. The proposed
insecurity, safety, fraud and unavailability of proper in- iTour has been illustrated in Figure 1.
formation about resources are the biggest hurdles towards
independent mobility. The tourists’ issues can be over-
come by proactive participation of local citizens to help
tourists as well as by the cooperation between citizens,
city administration and tourists. As a result, a number
of components of a smart cities can be strengthened,
from the sustainable mobility in tourism development to
economy development. It is very challenging as it requires
a combination of societal input and advanced smart and
effective tools. This article presents viable Internet of
Things (IoT) based solution as a framework for tourist
independent mobility, called iTour. In the process, this
article analyzes the difficulties in initiatives and lessons,
exploring possible roles of IoT.
I. S MART C ITIES AND T OURISM Fig. 1. iTour using Internet-of-Things (IoT).
The concept of smart city has evolved with technology
centric evolution based on Internet, mobile services,
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), smart technologies,
II. T HE I SSUE OF I NDEPENDENT AND S USTAINABLE
and Internet of Things (IoT) [1]–[3]. The key elements
M OBILITY OF T OURISTS IN S MART C ITIES
of a smart community are the proactive participation of
citizens in public life and the ability to create new ways A key requirement of tourism has been to attract more
of association between citizens and city administrations. and more tourists from different parts of the world.
In recent years, many initiatives have been taken with However, insecurity, fraud, lack of proper transportation
different aims and objectives [4]–[6]. It is envisioned and communication facilities are the major concerns.
that the integration of advanced tools and technologies Moreover, the safety concerns in the tourist places have
and societal engagement that can provide the best op- restricted independent mobility of tourists [11].
portunity to deal with some of the hurdles. Tourism is an important component in the revenue of a
Tourist independent mobility in many countries is a country. For example, in India the tourism plays a major
paradigmatic example for a smart city [7]–[9]. Indepen- role in the economical growth. Directly and indirectly,
dent mobility of tourists is limited in many countries due it provides millions of employments. However, it was
to several reasons. Some of the major reasons include: recorded that in year 2013, the number of tourist visits
(1) lack of trust in the ongoing tourism services, (2) lack in India was less than the tourist visits in cities like
of security support, and (3) fraud prone tourist places. Bangkok and London. This may be due to the many
The countries with various physical, religious and social reasons such as (as depicted in Figure 2): (1) lack of
diversities become preferable places to visit for tourists. trust on hotel and travel agencies, (2) lack of support
But due to the above mentioned reasons, tourists limit from government the private bodies, (3) insecurity in
their travels to such countries. As a result, tourism indus- tourist places, and (iv) unavailability of real time help
tries are affected severely. Tourism management plays an centers [11]. These things need to be addressed properly
important role in making smart city more effective [10]. in order to attract the tourists.
The proposed iTour has the ability to establish a new era There are lot of concerns for a tourist while visiting
for smart city functioning. This can overcome challenges to unknown places. It is due to the lack of realistic infor-
in the existing tourism management system. Further, mation, security and other concerns discussed previously.
2
Trust on Travel through IoT enabed devices can communicates among
Agencies each others. IoT based services and applications can
Visa Trust on make tourism resources such as: roadside smart ma-
Processing Hotels chines, police control room (PCR) vans, and mobile
Issues of services more convenient. IoT can also provide these
Government
Real-Time Tourists in tourism resources more secure and reliable.
Support
Help Smart Cities
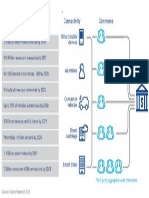
b) Consciousness: By the help of social networks
Private Body and IoT, the awareness for tourist mobility in smart
Tourist Support
Personal Tourist cities and other tourist places can be improved. For
Safety Location example, the information about hotels, and tourist places
Security can be integrated in a smart map. This smart map can be
helpful to all stakeholders such as: traffic police, tourism
Fig. 2. Selected issues of tourists in smart cities.
office, transport services, and hotel services to exchange
information. This facilitates an inclusive support that
For this reason people prefer to travel the known places allows tourists to connect with the real time support
where they feel safe and comfort. team, explore all the probable options to their needs and
One of the major obstacle in tourist independent take knowledgeable decisions.
mobility is the lack of social awareness about the tech- c) Independent Initiatives: IoT can helps different
nologies such as IoT based applications. Many initiatives stakeholders in the detection, design and operation of
have been introduced by the tourism departments. But new ideas on tourist independent mobility. It not only
due to the lack of awareness, those initiatives are not facilitate to investigate for initiatives and join them, but
been utilised as expected. also suggest new initiatives, to evaluate and comment on
Considering the above facts, we introduced a frame- them.
work for tourist independent mobility based on IoT. It d) Tourist attitude towards the problem: IoT solu-
facilitates all stakeholders where they can easily avail tions will help improving tourist responsiveness towards
the required services such as access information and the tourism problem. Further, it can be used for the
manage the tourism services like hotels, public and design of real time model of allocating social scoring.
private transports, traffics, and local volunteers. This social scoring approach will attract and involve
all stakeholders. These processes encourage participa-
tion and forthright behavior through virtual and real
III. T HE ROLE OF I OT TO E NHANCE I NDEPENDENT
incentives. This approach will also increase the effects
AND S USTAINABLE M OBILITY
and duration of the engagement of all stakeholders
The tourism problems can be overcome with the use of in independent mobility campaigns and enhance their
information and communication technology, particularly sustainability in time.
by the IoT. The role of IoT in tourist independent and e) Mining and Monitoring: Further, the tourism
sustainable mobility is depicted in Figure 3. ministry and government authorities can take the help
of data mining and monitoring mechanisms to make the
Convenience and
system effective [12]–[14]. Mainly, the tourism mobility,
Flexibility volunteer availability, pattern in volunteer involvement,
Tourist’s pattern of emergency help request, etc. can be mined
Attitude Consciousness and monitored. Based on the output of the mining and
Towards the Role of IoT
Problem monitoring process, adaptive steps can be taken for
in Tourist betterment of the system.
Mobility
Independent
Mining and IV. I T OUR - T HE PROPOSED F RAMEWORK FOR
Monitoring Initiatives
T OURIST I NDEPENDENT M OBILITY
This article presents a framework for “Tourist Inde-
Fig. 3. Selected roles of IoT in independent and sustainable mobility
of tourists in smart cities. pendent Mobility” called iTour. The iTour platform is
driven by a set of novel ideas, taking into account of
a) Convenience and Flexibility: IoT can be used all stakeholders requirements and needs. It combines the
for convenience and flexibility in tourism domain. It IoT techniques and tools to use the services and data
can integrate various tourist services. All stakeholders available on the way. Further, it allows easy, faithful
3
coordination and co-operation of available resources. It socializing spot managers, and cultural event managers.
makes the use of information exchange to make tourist Volunteers such as on-road tourist helping volunteers,
life easy. Further, the possible resources which can cultural exchange centers, and human interpreter, are also
contribute to the tourism ecosystem has bee identified. a part of this.
b) Non-Human Resources: In tourism management
A. Resources and their Involvement system, both human resources and non-human resources
The iTour Resources and their involvement is shown need to be coordinated. These non-human resources
in Figure 4. In the tourism independent mobility frame- need to be connected to iTour to make the life of
work, most of the resources which are needed are pre- tourist and tourist support team more comfortable. The
existing. If anybody wants to help tourists, there is a iTour framework consists of integration of IoT solutions
trust gap between a tourist and local volunteers due to such as sensors, GPS, WSN, smart devices, smart map,
the fear of getting trapped by dishonest people. Even Internet and different types of services. IoT enbles these
if there is trust, in some cases there is insufficient objects to connect and exchange data using wireless
information, equipments for connection and cooperation protocols.
between them. Therefore, the aim of the framework is c) Services: The iTour provides different types of
to identify such resources and provide them a suitable services. Booking tickets in hotel, reserving the seat in a
platform using IoT solutions (iTour). It is a easy way of taxi, searching for essential services such as banking,
coordination and cooperation in the tourism ecosystem, guide, restaurants and fooding, and posting. can be
with some level of authentication. done through the smart devices. Morever, smart devices
support user authentication and security. It also provides
Services: Ticket
iTour Framework Enabling Technologies: emergency services such as ambulance, fire brigade, and
Booking, Taxi Wireless Sensor
Hiring, Restaurants,
Smart Device Network, LAN, WAN police. In emergency situations such as theft, road rage,
Banking
and medical emergency, the user can use these services.
B. iTour Working Principles
(Smart Technologies)
Each human actor involved in iTour are provided a
Human Resources: Emergency Help:
Tourists, Police, Ambulance, Police Smart Device. Each smart device is uniquely identified
Volunteers, Officials Control Room, by the means of identification. It also has the provision
Officials
of authentication by the help of fingerprint sensors. With
this device, the actor can easily communicate to iTour
and other users within the range. The private partners
Fig. 4. iTour resources and their involvement through IoT. will go through a background verification and then they
will be provided with a smart device. All the stakeholders
Further, the IoT solutions can be used to analyze the will be connected to the iTour by the help of smart
functioning of the system to provide proper feedbacks device. All smart devices are GPS enabled and equipped
from time to time to make it adaptive. Real-time moni- with internet and other services such as RFID, smart
toring of the system by iTour can help in handling crisis lock, bluetooth, smart map, and sensors.
situations and can improve effectiveness of system as The iTour deployed in a WSN environment. It is as-
well. The available resources those can contribute to sumed that nodes on the WSN relaying on central entities
iTour are broadly classified as Human Resources and such as base stations or access points. However, the node
Non-Human Resources. deployment can be ramdom or structure depending upon
a) Human Resources: Based on the interactions, the application area. With the help of the authentication
the people who can contribute towards the improvement and location information that are collected through the
of tourism management system and promotion program WSN and smart device, the iTour will provide various
can be identified. These are the set of people involved functionalities such as smart map, real-time mining and
in the tourist management system to help the tourists monitoring of iTour services. The Smart Map consisting
are categorized as Human Resources. Such a collection of following functionalities: (1) resources at a glance,
of stakeholders includes the public employees such as (2) trace volunteers and resources, (3) real-time travel
officials from home department, tourism department, assistance, (4) volunteer map, (5) vehicle map, and (6)
transport department, police department, PCR van in- emergency help. Different types of actors involved in the
charge, post office, and bank. It also included the pri- iTour framework are represented with a unique symbol.
vate partners such as hotel managers, vehicle drivers, These symbols and their meanings are given in Table I.
4
TABLE I
M AP S YMBOL C HART.
Symbol Meaning
On road volunteer
Road side shop owner volunteer
Volunteer who can contribute some time with
tourist for help
Police control room (PCR) bike for help Fig. 6. Trace volunteer map in iTour.
Police control room (PCR) van for help
On road police for help
Traffic police for Help
Tourist
1) Resources at a Glance: This map can only be
viewed by iTour manager, Tourism department, Home
department and other government officials. Using this
map one can view all resources at real time on the city Fig. 7. Trace vehicle map in iTour.
map. The mining and monitoring reports are available
in this view. The monitoring component can monitor the
effective use of resources like average response time to lice station, post office, bank, hotel, restaurants, shopping
a tourist request, volunteer density near tourists, tourist mall, and socializing spots. Also there is a possibility of
density at a particular place, immediate instruction to online communication through smart devices. The view
nearby volunteers to support in case of emergency. The of this map is shown in Figure 6.
view of this map is shown in Figure 5. 3) Real Time Travel Assistance: In this view, a tourist
can ask for a travel plan from one place to another
place. The map will show some of the best possible
options available at that instant for that request. The
user can select one of them to view in detail, such as
class of vehicle, price per distance, availability of tickets,
direct/connecting travel service, response time, and turn
around time. If the choice matches, then the available
service will be displayed on this view and the tourist can
plan accordingly. By comparing the options, the tourist
can book the vehicle or reserve a seat in vehicle. The
Fig. 5. Resource view at a glance for administrators in iTour. view is depicted in Figure 7.
4) Volunteer Map: In this view, a volunteer can view
2) Trace Volunteers and Resources: With the help the details of a tourist. When a volunteer receives a
of this, the tourist can view nearby volunteers. The request from a tourist, he can verify the details through
volunteers may include on-road volunteers, road-side this view.
volunteers, local volunteers and public officials on duty. 5) Vehicle Map: In this view, the vehicle in-charge
One can get instant assistances from any of the nearby will set the starting and ending point and its route on
volunteers. Before communication, there will be a both the smart map. The on-road sensors will automatically
side fingerprint authentication process by the smart de- update the current position of the vehicle. This will be
vices. In a similar view, one can trace resources like po- used by the iTour to provide vehicle assistance. This can
5
be also used for ticket booking. [2] S. P. Mohanty, “Smart Cities - Demystified,”
6) Emergency Help: With this view, the tourist can http://www.smohanty.org/Presentations/2017/Mohanty_MAMI-
2017_Keynote_Smart-Cities.pdf, Keynote Address, 2nd
use this help option in case of emergency situation. When International Conference on Man and Machine Interfacing,
the help option is pressed, the tourist smart device is con- 2017, Bhubaneswar, India, 23 Decemmber 2017, Last visited
nected to all emergency services such as police control on 01 January 2018.
[3] A. Zanella, N. Bui, A. Castellani, L. Vangelista, and M. Zorzi,
room, hospital, and tourist department. The authority can
“Internet of things for smart cities,” IEEE Internet of Things
take necessary steps as per the need of situation. Journal, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 22–32, Feb 2014.
[4] R. B. Luca Mora and M. Deakin, “The First Two Decades
of Smart-City Research: A Bibliometric Analysis,” Journal of
V. C ONCLUSIONS Urban Technology, pp. 3–27, March 2017.
[5] R. Kazhamiakin, A. Marconi, M. Perillo, M. Pistore, G. Valetto,
Tourism is one of the major component of economy L. Piras, F. Avesani, and N. Perri, “Using Gamification to
growth of many countries in world. Due to the lack Incentivize Sustainable Urban Mobility,” in Proceedings of the
First IEEE International Smart Cities Conference, 2015, pp.
of coordinated services, tourism has suffered a lot. In
1–6.
this article, an IoT framework called iTour has been [6] M. Gerosa, A. Marconi, M. Pistore, and P. Traverso, “An Open
presented which was implemented Java. In iTour, the Platform for Children’s Independent Mobility,” in Proceedings
smart citizens can participate in tourism development. It of the International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT
Systems, 2015, pp. 50–71.
enables the city administrator accountable towards the [7] S. P. Mohanty, “Everything you Wanted to Know about Smart
cooperation and coordination of tourist daily life in a Cities,” https://cesoc.ieee.org/images/files/pdf/Mohanty_IEEE-
city. It can also use data mining techniques to prepare DL_Smart-Cities.pdf, IEEE Distinguished Lecture CE Society
the city for future tourism. The effectiveness of iTour is Webinar, 5 October 2017, Last visited on 01 January 2018.
[8] J. Marc and J. Catudan, “The Impact of Tourist Arrivals,
being proven through in-depth evaluation in a smart city Physical Infrastructures, and Employment, on Regional Output
by involving all stakeholders. Growth,” Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, vol. 219,
no. 4, pp. 175–184, May 2016.
[9] M. Lacinak and J. Ristve, “Smart City, Safety and Security,”
A BOUT THE AUTHORS Procedia Engineering, vol. 192, no. Supplement C, pp. 522 –
527, 2017.
Ajaya K. Tripathy (ajayatripathy1@silicon.ac.in) is [10] P. Mrazovic, J. L. Larriba-Pey, and M. Matskin, “Improving
an Assistant Professor in Department of Computer Sci- Mobility in Smart Cities with Intelligent Tourist Trip Planning,”
in Proceedings of the IEEE 41st Annual Computer Software and
ence and Engineering at Silicon Institute of Technology, Applications Conference (COMPSAC), 2017, pp. 897–907.
Bhubaneswar, India. His research interest is Service [11] S. Kannan, “Why India is Struggling to Attract Tourists,”
Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Machine Learning. http://www.bbc.com/news/business-28796280, BBC News,
Delhi, 19th August, 2014, Last visited on 01 January 2018.
Pradyumna K. Tripathy (ptripathy@silicon.ac.in) [12] J. Borras, A. Moreno, and A. Valls, “Intelligent Tourism Recom-
is an Assistant Professor in Department of Computer mender Systems: A Survey,” Expert Systems with Applications,
Science and Engineering at Silicon Institute of Technol- vol. 41, no. 16, pp. 7370 – 7389, 2014.
ogy, Bhubaneswar, India. His research interest includes [13] A. K. Tripathy and M. R. Patra, “Service based System
Monitoring Framework,” International Journal of Computer
Distributed Computing and Machine Learning. Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications,
Niranjan K. Ray (rayniranjan@gmail.com) is an vol. 3, pp. 924–931, 2011.
Associate Professor in School of Computer Engineering [14] A. K. Tripathy, M. R. Patra, M. A. Khan, H. Fatima, and
P. Swain, “Dynamic Web Service Composition with QoS Clus-
at KIIT University, Odisha, India. His area of interest tering,” in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference
includes wireless sensor networks (WSNs) and Internet on Web Services, 2014, pp. 678–679.
of Things (IoT).
Saraju P. Mohanty (saraju.mohanty@unt.edu) is a
Professor at the University of North Texas. Prof. Mo-
hanty’s research is in “Smart Electronic Systems” which
has been funded by National Science Foundations, Semi-
conductor Corporation, and US Air Force. He authored
250 research articles, 3 books, and invented 4 US patents.
R EFERENCES
[1] S. P. Mohanty, U. Choppali, and E. Kougianos, “Everything
You wanted to Know about Smart Cities,” IEEE Consumer
Electronics Magazine, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 60–70, 2016.
View publication stats
You might also like
- TAX 01 Fundamental Principles of TaxationDocument9 pagesTAX 01 Fundamental Principles of Taxationooagentx44No ratings yet
- Samahan NG Optometrists Sa Pilipinas v. AcebeoDocument2 pagesSamahan NG Optometrists Sa Pilipinas v. AcebeoIvee OngNo ratings yet
- RFP for AIIMS Guwahati Executing AgencyDocument32 pagesRFP for AIIMS Guwahati Executing AgencyAmlan BiswalNo ratings yet
- SBLC Monetizing MOUDocument9 pagesSBLC Monetizing MOUDinni Resa75% (4)
- Assignment On HRMDocument8 pagesAssignment On HRMTapu Z71% (14)
- Pleasantville v. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 79688, February 1, 1996Document2 pagesPleasantville v. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 79688, February 1, 1996Al Jay MejosNo ratings yet
- Group 10 - Eyewear Industry - LenskartDocument46 pagesGroup 10 - Eyewear Industry - LenskartSargun Matta100% (3)
- Artificial Intelligence Term PaperDocument17 pagesArtificial Intelligence Term PapersaadmanNo ratings yet
- Embedded Based Smart City ApplicationsDocument54 pagesEmbedded Based Smart City ApplicationsrvseceplacementNo ratings yet
- Smart City ProjectDocument16 pagesSmart City ProjectSayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- A Survey: Smart Cities For Sustainable FutureDocument4 pagesA Survey: Smart Cities For Sustainable FutureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- IoT Based Smart City Security Issues and Tokenization, Pseudonymization, Tunneling Techniques Used For Data ProtectionDocument4 pagesIoT Based Smart City Security Issues and Tokenization, Pseudonymization, Tunneling Techniques Used For Data ProtectionEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Smart NeighborhoodDocument44 pagesSmart NeighborhoodAr Siddharth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Smart Tourism FrameworkDocument11 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Smart Tourism FrameworkPeat PatcharaNo ratings yet
- Smart Cities: Understanding The Challenges and OpportunitiesDocument24 pagesSmart Cities: Understanding The Challenges and OpportunitiesNidhin RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- السياحةDocument4 pagesالسياحةMoh OhNo ratings yet
- Privacy in The Smart City-Applications, Technologies, Challenges, and SolutionsDocument28 pagesPrivacy in The Smart City-Applications, Technologies, Challenges, and SolutionsEladhio BurgosNo ratings yet
- Current Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Tourism and HospitalityDocument8 pagesCurrent Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Tourism and HospitalityT.U SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Metaverse 3C: Concept, Components, and Challenges in Travel and Tourism SectorDocument15 pagesMetaverse 3C: Concept, Components, and Challenges in Travel and Tourism SectorPoonkuzhali SNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Smart Technologies On Customer Journey in Tourist Attractions Within The Smart Tourism Management FrameworkDocument18 pagesThe Influence of Smart Technologies On Customer Journey in Tourist Attractions Within The Smart Tourism Management FrameworkJessica IlaidaNo ratings yet
- Financing Smart CitiesDocument4 pagesFinancing Smart CitiesArthur BenedictNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security in Smart CitiesDocument3 pagesCyber Security in Smart CitiesMili SharmaNo ratings yet
- Developing Smart Tourism Destinations With The Internet of Things: Managerial Approaches, Techniques, and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesDeveloping Smart Tourism Destinations With The Internet of Things: Managerial Approaches, Techniques, and ApplicationsDulan lakjith WijenayakaNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Smart City ApplicationsDocument4 pagesA Survey of Smart City ApplicationsGiovanni PintoNo ratings yet
- Io TDriven Smart CitiesDocument20 pagesIo TDriven Smart CitiesR Naveen BabuNo ratings yet
- Application For E-Tourism: Intelligent Mobile Tourist GuideDocument6 pagesApplication For E-Tourism: Intelligent Mobile Tourist GuideshitalNo ratings yet
- Advance City Surveillance Using Data AnalysisDocument7 pagesAdvance City Surveillance Using Data AnalysisIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Smart CityDocument7 pagesSmart CityStArK ツKuNuNo ratings yet
- Out 6Document15 pagesOut 6ANDI SETIAWAN [AB]No ratings yet
- Research Article Design and Implementation of Smart Tourism Service Platform From The Perspective of Artificial IntelligenceDocument12 pagesResearch Article Design and Implementation of Smart Tourism Service Platform From The Perspective of Artificial IntelligenceAmnah MagdyNo ratings yet
- Introductionto Smart Citiesand Selected Literature ReviewDocument10 pagesIntroductionto Smart Citiesand Selected Literature ReviewBahi AliNo ratings yet
- Car_PilepicStifanich_Simunic_IoTDocument14 pagesCar_PilepicStifanich_Simunic_IoTRina RadmilovNo ratings yet
- Smart City - Marsudi W KisworoDocument16 pagesSmart City - Marsudi W KisworoNico Saibort JuniorNo ratings yet
- Miramap: A We-Government Tool For Smart Peripheries in Smart CitiesDocument20 pagesMiramap: A We-Government Tool For Smart Peripheries in Smart CitiesshitalNo ratings yet
- A Literature Study on the Role of IoT in Developing Smart CitiesDocument5 pagesA Literature Study on the Role of IoT in Developing Smart CitiesPooja GowdaNo ratings yet
- Aplicatio Smart CityDocument27 pagesAplicatio Smart CityLouNo ratings yet
- The Role of An Information and Communication Technology in Smart CityDocument9 pagesThe Role of An Information and Communication Technology in Smart CityIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Smart CityDocument7 pagesSmart CityJean Paul Herrera MoncayoNo ratings yet
- Smart City Master ThesisDocument8 pagesSmart City Master Thesissaraharrismilwaukee100% (2)
- Fintech Agents Technologies and TheoriesDocument30 pagesFintech Agents Technologies and TheoriesHarman iNo ratings yet
- Social Scientist Social Scientist: This Content Downloaded From 130.209.6.61 On Mon, 30 Apr 2018 07:03:31 UTCDocument21 pagesSocial Scientist Social Scientist: This Content Downloaded From 130.209.6.61 On Mon, 30 Apr 2018 07:03:31 UTCSiddharthNo ratings yet
- Blockchain and ID Systems (See Part 2) USAID IDENTITY - IN - A - DIGITAL - AGE PDFDocument80 pagesBlockchain and ID Systems (See Part 2) USAID IDENTITY - IN - A - DIGITAL - AGE PDFniccookNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Smart CityDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Smart Cityafnhkvmnemelfx100% (1)
- Exploring Tourism With Virtual and Augmented RealityDocument7 pagesExploring Tourism With Virtual and Augmented RealityIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 02190 v2Document15 pagesMathematics 10 02190 v2Vũ Ngọc Minh ThuNo ratings yet
- Rough DraftDocument4 pagesRough Draftjayraj daveNo ratings yet
- Future Generation Computer Systems: Tai-Hoon Kim, Carlos Ramos, Sabah MohammedDocument4 pagesFuture Generation Computer Systems: Tai-Hoon Kim, Carlos Ramos, Sabah MohammedMinh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Role of Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact On The Tourism Industry of IndiaDocument13 pagesRole of Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact On The Tourism Industry of IndiaVanshika BajajNo ratings yet
- Smart City DissertationDocument7 pagesSmart City DissertationPayForPaperSingapore100% (1)
- Financial GrowthDocument68 pagesFinancial GrowthNadia MurtazaNo ratings yet
- "Smart City" Definition and ITS Practice in India: Vinay Prakash Shrivastava, Jagdish SinghDocument11 pages"Smart City" Definition and ITS Practice in India: Vinay Prakash Shrivastava, Jagdish SinghDarth FrootLoopsNo ratings yet
- Crossover To Crypto Currency Using E-RUPIDocument8 pagesCrossover To Crypto Currency Using E-RUPIIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Activity4 Kurt Medina BSIT-3B DCIT65Document1 pageActivity4 Kurt Medina BSIT-3B DCIT65Kurt MedinaNo ratings yet
- UGE-1 Practice SetDocument1 pageUGE-1 Practice SetJhanna Vee DamaleNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Context On Privacy Concern in Smart Tourism DestinationsDocument12 pagesThe Influence of Context On Privacy Concern in Smart Tourism DestinationsGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal Tour ManagementDocument9 pagesProject Proposal Tour ManagementJJ SumtNo ratings yet
- Mohanty IEEE-CEM 2016-July Smart-CitiesDocument16 pagesMohanty IEEE-CEM 2016-July Smart-CitiesMohammad Nouman KakarNo ratings yet
- Sadowski & Pasquale - The Spectrum of Control A Social Theory of The Smart CityDocument21 pagesSadowski & Pasquale - The Spectrum of Control A Social Theory of The Smart Cityanton.de.rotaNo ratings yet
- Revelando Tendencias en La Investigación en Turismo Digital Un Análisis Bibliométrico deDocument10 pagesRevelando Tendencias en La Investigación en Turismo Digital Un Análisis Bibliométrico dezuridaiNo ratings yet
- Discussion 3Document2 pagesDiscussion 3Lucia LeiNo ratings yet
- 10.2478 - RSC 2023 0004Document13 pages10.2478 - RSC 2023 0004Uday pooniaNo ratings yet
- Fin TechDocument11 pagesFin TechIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Transfer in Smart Tourism DestinationsDocument6 pagesKnowledge Transfer in Smart Tourism DestinationsvineethkmenonNo ratings yet
- Smart Cities and Tourist Destinations Indicators Applied in Foz Do Iguaçu, BrazilDocument9 pagesSmart Cities and Tourist Destinations Indicators Applied in Foz Do Iguaçu, BrazilIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Tourism Network and Information and Communication Technologies in The South of Morocco: A Case StudyDocument5 pagesTourism Network and Information and Communication Technologies in The South of Morocco: A Case StudyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- The Smart City Odyssey: Unveiling the Secrets to Traveller-Centric SoftwareFrom EverandThe Smart City Odyssey: Unveiling the Secrets to Traveller-Centric SoftwareNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmekontaktblNo ratings yet
- Title in Times New Roman 14 Point - Caps LockDocument1 pageTitle in Times New Roman 14 Point - Caps LockkontaktblNo ratings yet
- Net IDDocument1 pageNet IDkontaktblNo ratings yet
- HubIT-MakerLab EventsDocument1 pageHubIT-MakerLab EventskontaktblNo ratings yet
- MailboxDownloader Exe ConfigDocument1 pageMailboxDownloader Exe ConfigkontaktblNo ratings yet
- Forntal SpeakerDocument1 pageForntal SpeakerkontaktblNo ratings yet
- License AgreementDocument2 pagesLicense AgreementkontaktblNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmekontaktblNo ratings yet
- Open Garage Door SchematicDocument1 pageOpen Garage Door SchematickontaktblNo ratings yet
- Ubkc BLDocument1 pageUbkc BLkontaktblNo ratings yet
- Aosong Electronics Co.,LtdDocument10 pagesAosong Electronics Co.,Ltdnagagop930No ratings yet
- Yog DocumentDocument2 pagesYog DocumentkontaktblNo ratings yet
- Telstra Research 2015Document1 pageTelstra Research 2015kontaktblNo ratings yet
- Server Side ImagesDocument1 pageServer Side ImageskontaktblNo ratings yet
- MPT Whitepaper v4Document7 pagesMPT Whitepaper v4kontaktblNo ratings yet
- How To Buy AGuitarDocument22 pagesHow To Buy AGuitarennio888No ratings yet
- Honda BF45ADocument2 pagesHonda BF45AkontaktblNo ratings yet
- Pogledajte Semafor 29.03.2010.Document5 pagesPogledajte Semafor 29.03.2010.kontaktblNo ratings yet
- ASUS RT - N10E ManualDocument52 pagesASUS RT - N10E ManualkontaktblNo ratings yet
- Delta Programmable Logic Controller DVP Series: Automation For A Changing WorldDocument52 pagesDelta Programmable Logic Controller DVP Series: Automation For A Changing WorldelkimezsNo ratings yet
- BTC - AUTOPILOT - METHOD - Make 700$-1000$Document4 pagesBTC - AUTOPILOT - METHOD - Make 700$-1000$john renoldNo ratings yet
- WTO Philippines Spirits AnalysisDocument11 pagesWTO Philippines Spirits Analysisodin_siegreicher100% (1)
- Logistics Expenses - Seminar Paper II.Document8 pagesLogistics Expenses - Seminar Paper II.PetraNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research - An Applied Orientation 6th EditionDocument2 pagesMarketing Research - An Applied Orientation 6th Editionstefany AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 DB U2000429Document3 pagesTutorial 3 DB U2000429Haikal HaziqNo ratings yet
- Dustbin SensorsDocument12 pagesDustbin SensorsNikitha PaulsonNo ratings yet
- FINAL WORK Sesi 1-3Document127 pagesFINAL WORK Sesi 1-3Fanli KayoriNo ratings yet
- Unit-Department IT DRPDocument22 pagesUnit-Department IT DRPllm oodNo ratings yet
- Global Business - Unit 4Document86 pagesGlobal Business - Unit 4GauravTiwariNo ratings yet
- The Investment Process: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument40 pagesThe Investment Process: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwinobaidah j98No ratings yet
- Name: Tamzid Ahmed Anik ID:1911031 Code: HRM 370 Submitted To: Dr. SHIBLY KHAN Date: 5 July, 2022Document8 pagesName: Tamzid Ahmed Anik ID:1911031 Code: HRM 370 Submitted To: Dr. SHIBLY KHAN Date: 5 July, 2022Tamzid Ahmed AnikNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument13 pagesProject ManagementAnnaNo ratings yet
- Bartertrade - Io - WhitepaperDocument41 pagesBartertrade - Io - WhitepaperRandall FlaggNo ratings yet
- Return: Return What Is GST ReturnDocument3 pagesReturn: Return What Is GST ReturnNagarjuna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Report Sample-Supplier Factory AuditDocument24 pagesReport Sample-Supplier Factory AuditCarlosSánchezNo ratings yet
- Bobcat Compact Excavator E16 Operation Maintenance Manual 6989423Document14 pagesBobcat Compact Excavator E16 Operation Maintenance Manual 6989423andrewshelton250683psa100% (67)
- Abigail Gunlock: 7657 Athenia Drive, Cincinnati OH, 45244 Gunlocal@mail - Uc.edu 513.473.1285Document2 pagesAbigail Gunlock: 7657 Athenia Drive, Cincinnati OH, 45244 Gunlocal@mail - Uc.edu 513.473.1285api-340013835No ratings yet
- Building New Boxes WorkbookDocument8 pagesBuilding New Boxes Workbookrohit11dec99No ratings yet
- BUAD 807 SummaryDocument6 pagesBUAD 807 SummaryZainab Ibrahim100% (1)
- Error RegconitionDocument15 pagesError RegconitionNguyễn Trần Hoài ÂnNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Hospitality Management: Waseem Ul Hameed, Qasim Ali Nisar, Hung-Che WuDocument15 pagesInternational Journal of Hospitality Management: Waseem Ul Hameed, Qasim Ali Nisar, Hung-Che WuShoaib ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Harvard PDP - Teams Under Pressure-MergedDocument8 pagesHarvard PDP - Teams Under Pressure-Mergedapi-551397274No ratings yet