Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Department of Anatomy: - Endocrine Glands
Uploaded by
hermain raisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Anatomy: - Endocrine Glands
Uploaded by
hermain raisCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY
SECOND YEAR MBBS
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION OF HISTOLOGY PRACTICAL FOR II
MODULE
- ENDOCRINE GLANDS
-
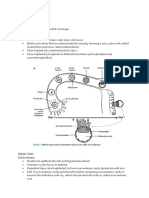
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR PITUITARY GLAND
It consists of 3 parts.
1. pars distalis, consists of two cell types; chromophobes (poorly stained and have no
cytoplasmic granules) , chromophils (deeply stained and have granules)….It is further divided
into two sub-types ; acidophils and basophils.
2. Pars intermedialis, contains colloid filled vesicles surrounded by cells of pars intermedialis.
3 . Pars nervosa, look whitish in colour because of unmyelinated axons. It also contains
supporting pituicytes .
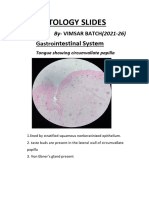
-POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR THYROID GLAND
1. Consists of numerous follicles filled with colloid. It is lined by simple cuboidal epithelium.
2. Connective tissue septa extend in a gland and divide it into lobules. Numerous blood vessels
are also seen in connective tissue septa.
3. Parafollicular cells are seen between basal lamina and epithelium of two follicles.
-POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR PARATHYROID GLAND
1. Surrounded by thin connective tissue capsule which radiate septa and provide
demarcation between thyroid and parathyroid gland.
2. Have two types of cells; OXYPHIL and CHIEF CELLS (principle cells).Cells are
arranged in anastomosing cords and clumps.
-POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR ADRENAL GLAND.
1. It consists of an outer cortex and inner medulla, surrounded by thick connective tissue
capsule that contains blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves.
2. Cortex has three parts ; Zona Glomerulosa-cells arranged in ovoid groups.
Zona Fasiculata-cells arranged in radial plates
Zona Reticularis-cells form anastomosing cords surrounded by sinusoidal capillaries.
3. Cells of medulla stains with chromium salts and are called chromaffin cells.Mdulla also
contain sympathetic neurons that are present in small groups.
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR TESTIS
1. Thick connective tissue tunica albuginea surrounds testis and form mediastinal
testis from where the thin connective tissue separates testis into testicular lobule
which contain coiled seminiferous tubules lined with germinal epithelium.
2. Germinal epithelium contains spermatogenic cells and sertoli cells (supportive cells).
Between seminiferous tubules are interstitial cells (cells of leydig).
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR EPIDIDYMIS
1. It is surrounded by connective tissue and a thin smooth muscle layer.It is lined by
pseudostratified epithelium.
2. The epithelium consists of tall columnar (principle) cells with long non motile stereo
cilia and small Basal cells.
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR VAS DEFERENS
1. It exhibit narrow, irregular lumen with longitudinal mucosal folds.It is lined by
pseudo stratified columnar epithelium. Below epithelium, lamina propria is present.
2. Thick muscularis layer consist of thin inner longitudinal, thick middle circular layer,
thin outer longitudinal layer. The muscularis is surrounded by adventitia.
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION OF SEMINAL VESICLE
1. It exhibit highly convoluted and irregular lumina. Lined by pseudo stratified and low
columnar epithelium.
2. The muscularis contain inner circular and outer longitudinal layer. The muscularis is
surrounded by Adventitia.
POINTS OF IDENTIDICATION OF PROSTATE GLAND
1. Characterized by fibromuscular stroma and prostatic concretions in gland.
2. Has 3 parts in males Prostatic part, Membranous part and Penil part.Transitional
epithelium lines the protatic part of urethra.
URINARY SYSTEM
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR KIDNEY
1. It has 2 parts;(A) Outer cortex- gives granular appearance due to the presence of
corpuscles (part of nephron)
2. (B) Inner Medulla – gives striated appearance because it lodges partially arranged
blood vessels and loops of henle.
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION OF URETER
1. The wall of ureter consists of mucosa, muscularis, and adventitia. The ureter mucosa
consists of Trasitional epithelium below which lamina propria is present.
2. Muscularis contain inner longitudinal smooth muscle and outer circular smooth
muscle. Muscularis is surrounded by adventitia
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR URINARY BLADDER
1. It consists of transitional epithelium. In empty bladder it consists of 6 to 8 layers
Basal layer-cuboidal cells
Middle layer-polygonal cells
When bladder gets distended, epithelium shows 2 to 3 layers
2. The lamina propria contain venule and arteriole and Muscularis contain 3 indistinct
layers as smooth muscle bundle.
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR INACTIVE MAMMARY GLAND.
1. Characterized by abundance of connective tissue and by a scarcity of glandular
element.
2. The glandular lobule contain ducts and they are surrounded by Myoepithelial cells.
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR LACTATING MAMMARY GLAND
1. They exhibit large number of distended alveoli filled with secretions and
vacuoles.The active alveoli are lined with low epithelium and filled with milk.
2. Surrounding the alveoli in mammary gland are myoepithelial cells, present between
alveolar cells and basal lamina.
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION FOR OVARY
1. Germinal epithelium overlies connective tissue tunica albuginea. It consists of outer
cortex and inner medulla without distinct boundaries. Cortex contains follicles,
fibrocytes, collagenous and reticular fibers.
Medulla is contious with mesovarium.
2. Its primordial cells exhibit simple cuboidal layer .
3. Secondary follicle exhibit liquid accumulations between granulosa cells or antrum.
POINTS OF IDENTIFICATION OF UTERINE TUBE.
1. Extend from ovaries into the uterus and exhibit infundibulum with fimbrae,
ampulla, isthmus, intramural region. Its mucosa contain extensive folds and form
irregular lumen.
2. Epithelium is simple columnar with ciliated and non ciliated secretory (peg) cells.
Ciliated cells create current towards uterus and become predominant in
proliferative phase. Secretory cells provide nutrition for oocyte, fertilized ovum, and
developing embryo.
IDENTIFICATION POINT OF UTERUS
1. Consists of body, fundus, and cervix.
2. Wall consists of outer perimetrium, middle myometrium, and inner endometrium.
3. Endometrium is divided into stratum functionalis which sheds with menstrual flow
and sratium basalis.
IDENTIFICATION POINTS FOR VAGINA
1. The vaginal mucosa is irregular and shows mucosal folds. It does not have glands
and is lined by non cornified stratified squamous epithelium.
You might also like
- B 28-MIBS-Histology Log Book - Model DiagramDocument27 pagesB 28-MIBS-Histology Log Book - Model DiagramSANTHIYA A/P MOHANA SUNDARAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Histology Slides (Batch 2021-26)Document42 pagesHistology Slides (Batch 2021-26)ranjit.mohapatra1968No ratings yet
- Bio 11 UPD Third Lec Exam ReviewerDocument111 pagesBio 11 UPD Third Lec Exam ReviewerMedjugorje Beltran DalanNo ratings yet
- Course 4Document9 pagesCourse 4bordinessrineNo ratings yet
- Micronatomy pt2Document35 pagesMicronatomy pt2poopziNo ratings yet
- Epithelium SummaryDocument7 pagesEpithelium SummaryElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument75 pagesAnimal TissuesFaithlyn Riche YocorNo ratings yet
- Histology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.SC., RewaDocument26 pagesHistology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.SC., RewaDiahNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Tissues PDFDocument70 pagesLesson 6 - Tissues PDFVjay Payumo100% (1)
- AnaPhyLec Midterms TissueDocument4 pagesAnaPhyLec Midterms TissueSoul YuNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AdhyapakDocument50 pagesAnatomy AdhyapakChief Nike - Clash RoyaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMary Rose Jose GragasinNo ratings yet
- 2ND Year Histology QUICK RECAPDocument12 pages2ND Year Histology QUICK RECAPMarya Safdar100% (2)
- Histology AssignmentDocument4 pagesHistology AssignmentNico LokoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument72 pagesTissuesFrelyn Tamba AndresNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIAL TISSUE (Defn, Classification & Functions - PDFDocument29 pagesEPITHELIAL TISSUE (Defn, Classification & Functions - PDFnikitachaudhary1220No ratings yet
- Glandular Epithelium: Endocrine GlandsDocument10 pagesGlandular Epithelium: Endocrine GlandsDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- Histology of The EarDocument10 pagesHistology of The EarmohamadNo ratings yet
- Histology 2018 1Document38 pagesHistology 2018 1Marvin Ndashimye100% (1)
- Histology Work-1Document11 pagesHistology Work-1siddharth.roy26587No ratings yet
- Histology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDocument8 pagesHistology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- PPT14-Histology of Urinary SystemDocument17 pagesPPT14-Histology of Urinary SystemElvie ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Lab Act 3 HistologyDocument15 pagesLab Act 3 HistologydiithandariNo ratings yet
- Week 2 The Tissues MembranesDocument60 pagesWeek 2 The Tissues MembranesJeqtopher RoaNo ratings yet
- Human Cell TypesDocument75 pagesHuman Cell Typesmegamemory14No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- Basic Histology: Moderator - Dr. Ganga S PilliDocument42 pagesBasic Histology: Moderator - Dr. Ganga S PillicoollNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTDocument124 pagesEpithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy IntroDocument4 pagesAnatomy IntroAlex HirschNo ratings yet
- Histology of Urinary System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.Sc. & A.H., RewaDocument35 pagesHistology of Urinary System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.Sc. & A.H., RewaMike AnnisNo ratings yet
- Meth IntestDocument2 pagesMeth IntestJames Masela LMNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- HISTOLOGY Connective Tissue (Components)Document16 pagesHISTOLOGY Connective Tissue (Components)faariyaabdullah03No ratings yet
- Cytology, Histology, EmbryologyDocument53 pagesCytology, Histology, Embryologyagostino.93.sommaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Small Intestine 3Document17 pagesHistology of Small Intestine 3ShizraNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument27 pagesNothingyoussef zareaNo ratings yet
- Crissman Epithelial ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCrissman Epithelial Objectiveskkonci01No ratings yet
- 03-Epithelial TissuesDocument9 pages03-Epithelial TissuesRehab OmerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 2013 Animal TissuesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - 2013 Animal TissuesSiti Juwairiah ZainurinNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: SquamousDocument4 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Squamousazouz jaboobiNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Histology of Normal Tissues: Connective, Muscle and Nervous. These Four Classes Respect TheDocument11 pagesHistology of Normal Tissues: Connective, Muscle and Nervous. These Four Classes Respect TheFatima AbdelRahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review TissueDocument4 pagesChapter Review TissueGeorge IvyNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument11 pagesEpithelial TissueFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument72 pagesSweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDr Daulat Ram DhakedNo ratings yet
- Histology (Tissue Organisation) Animal Tissues: Arthur Kugonza HDocument14 pagesHistology (Tissue Organisation) Animal Tissues: Arthur Kugonza HAnonymous M7aBZl100% (1)
- Structural Organization in AnimalsDocument7 pagesStructural Organization in AnimalsVedant BondeNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueSagar GavasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument39 pagesLaboratory ManualChelsea Chadwick100% (1)
- Mirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Document5 pagesMirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- Test CaseDocument54 pagesTest CaseEmil BoseNo ratings yet
- Sivajith P R - LAST MINUTE HISTOLOGY - Quick Review of Histology and Cell Biology For Medical and Nursing Students (1st Edition) - Wolfrum (2021)Document172 pagesSivajith P R - LAST MINUTE HISTOLOGY - Quick Review of Histology and Cell Biology For Medical and Nursing Students (1st Edition) - Wolfrum (2021)Yiannis AlatsathianosNo ratings yet
- 6 - Histology Lecture, Structure of The Epithelium 1Document52 pages6 - Histology Lecture, Structure of The Epithelium 1AMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- التشريح والفسلجة نظريDocument16 pagesالتشريح والفسلجة نظريem2200139No ratings yet
- Act05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionDocument9 pagesAct05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionPaula Nicole AlanoNo ratings yet
- PBL 2 - Angelica Reyes: 1. Describe The Anatomy, Histology and Function of The Thyroid Gland and Related StructuresDocument4 pagesPBL 2 - Angelica Reyes: 1. Describe The Anatomy, Histology and Function of The Thyroid Gland and Related StructuresabdulNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDocument6 pagesTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- Broken DollsDocument77 pagesBroken DollsGene FogertyNo ratings yet
- Classification Theory QPDocument28 pagesClassification Theory QPVivehaNo ratings yet
- My First English Exam PDFDocument86 pagesMy First English Exam PDFCiprian PetcuNo ratings yet
- Stitch: Stitch 2023 of 1 12 Instagram @rin - Meow21Document12 pagesStitch: Stitch 2023 of 1 12 Instagram @rin - Meow21loan100% (2)
- Bahasa Inggris.....Document10 pagesBahasa Inggris.....Apta HapsariNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord - Gross AnatomyDocument2 pagesSpinal Cord - Gross AnatomyshreyasNo ratings yet
- Print and Go Esl-eBook-3Document14 pagesPrint and Go Esl-eBook-3ozkankilic100% (5)
- Robinson Crusoe: Zooloretto The Dice GameDocument5 pagesRobinson Crusoe: Zooloretto The Dice GameMuneeb ArshadNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary - 4 Dinosaur DiscoveryDocument1 pageVocabulary - 4 Dinosaur DiscoveryAlifa Prima Budiarga, S.Pd.No ratings yet
- Navitas English Pretest FceDocument13 pagesNavitas English Pretest FceThanh GiangNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972Document3 pagesWildlife Protection Act, 1972sushmithaNo ratings yet
- FM Suppliers Outsourcing of Food Prep PDFDocument5 pagesFM Suppliers Outsourcing of Food Prep PDFAlagendranNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFvarshasharma05No ratings yet
- PSY315 Assignment 2Document4 pagesPSY315 Assignment 2Moham SyafikNo ratings yet
- Viking Pride Hat PatternDocument5 pagesViking Pride Hat Patternjillianebrandt7208100% (1)
- Alphabetical List of English Proverbs - L-ZDocument5 pagesAlphabetical List of English Proverbs - L-ZHendra TaufikNo ratings yet
- Early Embryology Week OneDocument14 pagesEarly Embryology Week OnelukesqueNo ratings yet
- CLINIC CASE Histoplasmosis SoluciónDocument2 pagesCLINIC CASE Histoplasmosis SoluciónCarolina Mueses0% (1)
- Sound Symbolism in 00 CiccDocument302 pagesSound Symbolism in 00 CiccbudisanNo ratings yet
- BI - Modul Cemerlang Amanjaya SPM 2017Document106 pagesBI - Modul Cemerlang Amanjaya SPM 2017sylent goh93% (14)
- Spitz, R. A. (1955) - The Primal CavityDocument27 pagesSpitz, R. A. (1955) - The Primal CavitycabaretdadaNo ratings yet
- Francisco FrondaDocument2 pagesFrancisco FrondaAva BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Cells JeopardyDocument55 pagesCells Jeopardyapi-308745623No ratings yet
- Flora and Fauna in Guru Nanak's Bani - Dr. Jasbir Singh SarnaDocument65 pagesFlora and Fauna in Guru Nanak's Bani - Dr. Jasbir Singh SarnaSikhDigitalLibraryNo ratings yet
- Dungeons & Dragons 3.5 Edition Index - Monsters - Sorted by HDDocument63 pagesDungeons & Dragons 3.5 Edition Index - Monsters - Sorted by HDWanderley MarçalNo ratings yet
- PRONUNCIATION PRACTICE For Grade 5Document1 pagePRONUNCIATION PRACTICE For Grade 5Hien DamNo ratings yet
- Olivia The Big GiraffeDocument13 pagesOlivia The Big GiraffeGraciela Acuña100% (4)
- Rhymes For Class I IIDocument19 pagesRhymes For Class I IIBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- The Hiram W Bleeker Coat of Arms NarrativeDocument26 pagesThe Hiram W Bleeker Coat of Arms Narrativeapi-366143603No ratings yet
- GA HuntingDocument72 pagesGA HuntingEnrique HernandezNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (393)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (116)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsFrom EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignFrom EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet