Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effects of Protein Excess: 5. Effect of Protein Deficiency On Dental Caries
Uploaded by
Harissa De laraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effects of Protein Excess: 5. Effect of Protein Deficiency On Dental Caries
Uploaded by
Harissa De laraCopyright:
Available Formats
PROTEIN Defect in matrix of tooth enamel
1. effects of protein excess: 5. Effect of protein deficiency on dental caries
A. Kidney problem: Alteration of salivary gland
Proteinuria Defect in enamel matrix
Production of excess Uric Acid -> Kidney Stones Protein deficiency may also mean incease in carb ingestion -> increase
caries susceptibility.
B. Liver problem
6. Protein deficiency in perio disease:
2. Inborn Error of protein metabolism- PHENYLKETONURIA
Protein = negative effect on the activity of fibroblasts, osteoblasts,
cementoblasts
3. Difference of Kwashiorkor and Marasmus:
Manifested through:
- atrophy of connective tissue of the gingiva and perio ligament
A. Kwashiorkor- deficiency in proteins only!
- retardation of cementum matrix
B. Marasmus- defiency in all things like proteins, carbohydrates, fats
- cancellous bone spaces are increased
4. effects of protein deficiency in jaws and teeth
WATER
Crowded and rotated teeth
7. major positive ion outside the cell- SODIUM
Hypoplasia of teeth
8. Major positive ion inside the cell: POTASSIUM C. Antibacterial Action
FLUORIDE - fluoride ion has inhibitory effect on ENOLASE- enzyme invloved in carb
metabolism
9. Fluoride treatment used in the clinic:
a. 2.7% Acydulated Phosphate Fluoride
b. 2% Sodium Fluoride
10. Post operative treatment after fluoridization:
- do not eat for 3 hours
- do not brush teeth for 30 mins
- do not rinse with mouth wash for 4-6 hours
11. Mechanisms for anticaries action of fluorides:
A. Decrease in acid solubiity- fluoride increases enamel resistance to dental
caries
- formation of fluoroapatite-> acid resistant
B. Remineralization
-fluoride can remineralize demineralized/hypomineralized enamel
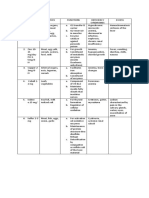
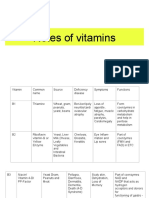
DEFINITION OF
MINERAL DEFICIENCY/ TOXICITY
DEFIENCY* TOXICITY
-osteoporosis *reduction of bone
quantity
CALCIUM
-fatigue
IRON -anemia
-low blood hgb level
*goiter * thyroid gland
enlargement, swelling in
IODIDE -mental retardation
front of the neck
-poor growth in infancy
-increase risk in dental
caries
FLUORIDE
*xerophthalmia *thickening of lens
VIT. A
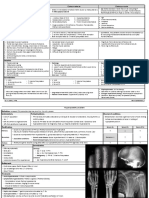
Rickets- kids Osteomalacia- softening of
bone
VIT. D Osteomalacia- adults
VIT. E *hemolytic anemia * rupture/ destruction of
RBC
- nerve degeneration
*Beriberi * nervous tingling
VIT. B1- thiamin *poor coordination
*edema
*megaloblastic anemia
*heart changes
FOLIC ACID (FOLATE)
*weakness
*Pellagra * 4D:
VIT. B3- Niacin -diarrhea
You might also like
- Nutritional Disorders Guide Explains Protein, Vitamin and Mineral DeficienciesDocument22 pagesNutritional Disorders Guide Explains Protein, Vitamin and Mineral DeficienciesyashichauhanNo ratings yet
- Presentation NeuroDocument33 pagesPresentation NeuroPriya ManimalaNo ratings yet
- Bone, Joint and Soft TissueDocument10 pagesBone, Joint and Soft Tissuesarguss14100% (2)
- Paget Disease, Fibrous Dysplasia, Osteosarcoma DiffrentiationDocument3 pagesPaget Disease, Fibrous Dysplasia, Osteosarcoma Diffrentiationreason131No ratings yet
- Deficiency Disorders of Vitamins ExplainedDocument43 pagesDeficiency Disorders of Vitamins ExplainedRENJINIRP100% (1)
- RicketsDocument3 pagesRicketsSaloni GanganNo ratings yet
- Hematology SummaryDocument9 pagesHematology SummaryJovielle Hayden100% (1)
- Missing Links of Molar Incisor Hypomineralization: A ReviewDocument11 pagesMissing Links of Molar Incisor Hypomineralization: A ReviewShinta Dewi NNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument11 pagesBiochemmanahilkhan3103No ratings yet
- nutritional disordersDocument3 pagesnutritional disordersmanar.alaneziNo ratings yet
- Lanat - Bsfi-3a - Module 6-Self-AssessmentDocument2 pagesLanat - Bsfi-3a - Module 6-Self-AssessmentLemark Galban LanatNo ratings yet
- Dr. A. Samy TAG Bone Diseases - 1Document2 pagesDr. A. Samy TAG Bone Diseases - 1Herato MenaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin's Name Function Deficiency Requirements: Retinal RetinolDocument4 pagesVitamin's Name Function Deficiency Requirements: Retinal RetinolAsem AlmeerabiNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and nutritional deficiency diseasesDocument2 pagesVitamins and nutritional deficiency diseasesGhubaya CopNo ratings yet
- Dr Garcia's Lecture on Vitamins A DeficienciesDocument16 pagesDr Garcia's Lecture on Vitamins A DeficiencieskrishNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Bone and JointsDocument58 pagesDiseases of Bone and JointsAMIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument1 pageNUTRITIONSidrah SajjadNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument22 pagesDisorders of Fat Soluble Vitaminsbpt2No ratings yet
- Fibro OsseousDocument25 pagesFibro OsseoussadiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document13 pagesChapter 9Zaky DavidiaNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia Musculoskeletal Degenerative DiseaseDocument7 pagesOsteomalacia Musculoskeletal Degenerative Diseasestar shipNo ratings yet
- HAEMATINICSDocument50 pagesHAEMATINICSvimalaNo ratings yet
- Trace-elementsDocument2 pagesTrace-elementsAbc DefNo ratings yet
- OSTEOMALACIADocument16 pagesOSTEOMALACIAlibrian_pallavi39420% (1)
- Vitamin RDA, UL, Function, Sources, StorageDocument5 pagesVitamin RDA, UL, Function, Sources, StorageDanny LeeNo ratings yet
- c8b Vitamin SupplDocument4 pagesc8b Vitamin SupplAlexandra AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Bone & OsteodystrophiesDocument54 pagesDiseases of Bone & OsteodystrophiesShreya singhNo ratings yet
- CC Is A Clinical Condition That Results From An Insufficient Supply of Healthy RedDocument8 pagesCC Is A Clinical Condition That Results From An Insufficient Supply of Healthy Redsunshine151No ratings yet
- The Key Nutrients: Role and FunctionsDocument5 pagesThe Key Nutrients: Role and FunctionsArvin Ian PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Rickets: Figures 1b and 2Document9 pagesRickets: Figures 1b and 2Mrc PhướcDuyNo ratings yet
- Micronutrient Table 0318Document6 pagesMicronutrient Table 0318Nature's ASMRNo ratings yet
- COL1A2 That Encode The A1 and A2Document6 pagesCOL1A2 That Encode The A1 and A2Jason TubeoNo ratings yet
- Georgemar V. Arana Jr. June 20, 2014 Group III Pedia: Anemia 1) Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument6 pagesGeorgemar V. Arana Jr. June 20, 2014 Group III Pedia: Anemia 1) Iron Deficiency AnemiageorgeNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations ShareDocument38 pagesOral Manifestations SharePrachi ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & Minerals: Slam Shraf AhmyDocument5 pagesVitamins & Minerals: Slam Shraf AhmyAfsal Ur FriendNo ratings yet
- Essential IonsDocument3 pagesEssential IonsGermie PosionNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Bone Density Loss and Fracture RiskDocument24 pagesOsteoporosis: Bone Density Loss and Fracture RiskMelinda FiskaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Sources: Two Types of EachDocument15 pagesVitamin Sources: Two Types of EachJhon Vincent Draug PosadasNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia: Softening of Bones Due to Defective MineralizationDocument38 pagesOsteomalacia: Softening of Bones Due to Defective MineralizationAji PrimaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Bone Metabolism and Osteoporosis TreatmentDocument4 pagesPharmacology of Bone Metabolism and Osteoporosis TreatmentFatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Malnutrition _ Vitamin DeficiencyDocument33 pagesTopic 6 Malnutrition _ Vitamin DeficiencyceraNo ratings yet
- Systemic Diseases With Oral Manifestations: AmyloidosisDocument11 pagesSystemic Diseases With Oral Manifestations: AmyloidosismahalramiNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition and Its Oral Outcome - A Review: Abst TDocument3 pagesMalnutrition and Its Oral Outcome - A Review: Abst TNur YanahNo ratings yet
- Nutrients PDFDocument17 pagesNutrients PDFjoanne riveraNo ratings yet
- Formarea Dintelui - Vitamine.4pptxDocument22 pagesFormarea Dintelui - Vitamine.4pptxRuxandra FitaNo ratings yet
- Clinical MicotoxicosisDocument4 pagesClinical MicotoxicosisusaeswotiNo ratings yet
- Blood DisordersDocument3 pagesBlood DisorderswastiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - MineralsDocument18 pagesChapter 6 - MineralsMariane JaymeNo ratings yet
- Macro and Micro Minerals for Cattle Production and ReproductionDocument56 pagesMacro and Micro Minerals for Cattle Production and Reproductionjraj030_2k6No ratings yet
- Systemic Diseases With RPDocument1 pageSystemic Diseases With RPabuahmed&janaNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSNOTESDocument8 pagesVITAMINSNOTESEllyNo ratings yet
- Vitamins NotesDocument8 pagesVitamins NotesEllyNo ratings yet
- Fibrous Dysplasia: DR Bareerah Idrees Resident OMFS 08 May 2021Document37 pagesFibrous Dysplasia: DR Bareerah Idrees Resident OMFS 08 May 2021biaidreesNo ratings yet
- Understanding RicketsDocument43 pagesUnderstanding RicketsYasna KibriaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone DisordersDocument24 pagesMetabolic Bone Disordersbpt20% (1)
- Endocrine Part 2 DRAFTDocument6 pagesEndocrine Part 2 DRAFTPreeti Joan BuxaniNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone Diseases: Dr. R.C.JindalDocument73 pagesMetabolic Bone Diseases: Dr. R.C.JindalpriyankNo ratings yet
- Patho Le2 ReviewerDocument615 pagesPatho Le2 RevieweretomanengNo ratings yet
- Biologically Active Amines Found in Man: Their Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiological ImportanceFrom EverandBiologically Active Amines Found in Man: Their Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiological ImportanceNo ratings yet
- Lesson Worksheet: Taking Care of Teeth: ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Worksheet: Taking Care of Teeth: Sciencefariska amanizataNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterizations of Hydroxyapatite Derived Blood Clam Shells (Anadara Granosa) and Its Potency To Dental RemineralizationsDocument12 pagesSynthesis and Characterizations of Hydroxyapatite Derived Blood Clam Shells (Anadara Granosa) and Its Potency To Dental RemineralizationsThuầnNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Five Beverages Biology Investigatory Project - Akilesh KumarDocument38 pagesAnalysis of Five Beverages Biology Investigatory Project - Akilesh KumarTahsheen FarhatNo ratings yet
- Thesis ImplantDocument194 pagesThesis ImplantKaushik keth100% (1)
- Int J Paed Dentistry - 2019 - Gatón Hernandéz - Minimally Interventive Restorative Care of Teeth With Molar IncisorDocument7 pagesInt J Paed Dentistry - 2019 - Gatón Hernandéz - Minimally Interventive Restorative Care of Teeth With Molar Incisorcamila.vega.vejar93No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1luiperdvrouNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2, Dental Amalgam II (Script)Document11 pagesLecture 2, Dental Amalgam II (Script)JustDen09No ratings yet
- Endo Board Study GuideDocument56 pagesEndo Board Study Guidedentace150% (2)
- Effect of Full Crown Preparation On Pulpal Blood Flow in Man. Marisa Sukapattee. 2016. Archives of Oral BiologyDocument6 pagesEffect of Full Crown Preparation On Pulpal Blood Flow in Man. Marisa Sukapattee. 2016. Archives of Oral BiologyValeria CrespoNo ratings yet
- AmeloglyphicsDocument9 pagesAmeloglyphicsimi4100% (1)
- AMELOGENESIS & DENTINOGENESIS: THE LIFE CYCLES OF AMELOBLASTS AND ODONTOBLASTSDocument19 pagesAMELOGENESIS & DENTINOGENESIS: THE LIFE CYCLES OF AMELOBLASTS AND ODONTOBLASTSshahzeb memonNo ratings yet
- Structure and Properties of Enamel and DentinDocument17 pagesStructure and Properties of Enamel and DentinFile SeffinaNo ratings yet
- Selenoportax Vexillarius From Dhok Pathan, Chakwal District, The Punjab, PakistanDocument7 pagesSelenoportax Vexillarius From Dhok Pathan, Chakwal District, The Punjab, PakistanInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cavity PreparationsDocument31 pagesFundamentals of Cavity PreparationsaakritiNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Gingival Esthetics: A Microscopic Perspective: David J. Clark, DDS and Jihyon Kim, DDSDocument8 pagesOptimizing Gingival Esthetics: A Microscopic Perspective: David J. Clark, DDS and Jihyon Kim, DDSchauphenNo ratings yet
- (David O. Klugh) Principles of Equine Dentistry PDFDocument241 pages(David O. Klugh) Principles of Equine Dentistry PDFJavier CeseñaNo ratings yet
- Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Therapeutic Strategy From Primary To Permanent Dentition Across Case ReportsDocument8 pagesAmelogenesis Imperfecta: Therapeutic Strategy From Primary To Permanent Dentition Across Case ReportsbanyubiruNo ratings yet
- Biomechanical Behavior of Endocrown Restorations With Different CAD-CAM Materials-A 3D Finite Element and in Vitro Analysis-Ziting 2020Document10 pagesBiomechanical Behavior of Endocrown Restorations With Different CAD-CAM Materials-A 3D Finite Element and in Vitro Analysis-Ziting 2020Dan MPNo ratings yet
- Caries PPT - ppt11Document109 pagesCaries PPT - ppt11dr parveen bathlaNo ratings yet
- 1-9 Iadt Guidelines Combined - LR - 11-5-2013Document27 pages1-9 Iadt Guidelines Combined - LR - 11-5-2013Pepo BelovedNo ratings yet
- Icdas Criteria PDFDocument28 pagesIcdas Criteria PDFluisNo ratings yet
- Erosion Abfraction AbrasionDocument5 pagesErosion Abfraction AbrasionAnggy PrayudhaNo ratings yet
- Digital Smile Design Improves Esthetic RehabilitationDocument10 pagesDigital Smile Design Improves Esthetic RehabilitationRoberto PucNo ratings yet
- Dental CariesDocument8 pagesDental CariesThe KittyNo ratings yet
- Dba 170608162539Document122 pagesDba 170608162539GetLyrics100% (1)
- 1 - MOH Exam PaperDocument8 pages1 - MOH Exam PaperMohammed Jabr100% (4)
- Cario - Exam Questions (Midterm)Document6 pagesCario - Exam Questions (Midterm)AbeerDirawi100% (2)
- Animal NutritionDocument51 pagesAnimal NutritionknlsinhaNo ratings yet
- Revista Australiana de OrtodonciaDocument109 pagesRevista Australiana de OrtodonciajoserodrrNo ratings yet
- How Clean' Must A Cavity Be Before Restoration?: E.A.M. KiddDocument9 pagesHow Clean' Must A Cavity Be Before Restoration?: E.A.M. KiddSamuelHpNo ratings yet