Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical Stoker Firing Principles & Types
Uploaded by
Hefni OssyanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanical Stoker Firing Principles & Types
Uploaded by
Hefni OssyanCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanical Stoker Firing:
Even though it is costlier, generally they are used to feed the solid fuels in small and medium size
power plants, because of the following reasons:
1) Combustion is more efficient.
2) Fuel handling is automatic and combustion control is easier.
3) Faster response to load fluctuations.
4) Low quality fuels can be successfully burnt. 5) Suitable for small to high capacity plants.
Principle of Stokers
The different types of stokers work on the following principles.
a) Principle of overfeed stokers
b) Principle of under feed stoker
a) Principle of overfeed stokers
A fully built up overfeed stoker will have the beds of green coal (raw coal), incandescent coke
and ash over the grate. In this the primary air enters the grate from the bottom, which cools the grate
while moving up and gets heated as it passes through hot ash bed.
The hot air then passes through the bed of incandescent coke, where oxygen reacts with the
carbon in the coke to form carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Part of carbon dioxide
formed reacts with carbon in the fuel to form carbon monoxide. The gases leaving the bed of
incandescent coke consist of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen and water. To
these gases, then an additional air termed the secondary air is supplied from the sides to burn the
combustible gases like the carbon monoxide, hydrogen and other volatile matters. The burnt hot
gases entering the boiler consist of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, oxygen, and water. It may also
contain carbon monoxide, if the combustion is incomplete. The primary and secondary air to the
stoker is supplied under pressure with the help of blower
DEPT OF MECHANICAL ENGG, NITR
Principle of under feed stoker
In this the coal is charged from the bottom,
and the primary air under pressure also moves
from the bottom through the holes in the grate.
This stoker has the layers of ash, incandescent
coke bed and raw coal, in the reverse direction
as compared to that of the overfeed stoker. In
operation the primary air entering from the
bottom through the grate holes comes in contact
with the coal and then passes through the bed of
incandescent coke. In operation the primary air
entering from the bottom through the grate
holes comes in contact with the green coal and
then passes through the bed of incandescent
coke. Initially, air reacts with carbon in the coke
to form carbon dioxide, and the moisture in the air reacts to release carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide
and hydrogen. While these gases pass over the ash bed, secondary air is supplied for their complete
combustion. This method is most suitable for semi-bituminous and bituminous coals which have high
volatile-matter.
Types of Stokers
Different types of stokers are
1. Over feed stokers
a) Conveyer stoker
i) Chain grate stoker
ii) Traveling grate stoker
b) Spreader stoker
2. Under feed stokers
a) Single retort stoker
b) Multi-retort stoker
DEPT OF MECHANICAL ENGG, NITR
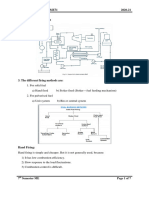
1) Chain & traveling grate stokers:
A chain grate stoker consists of an endless chain which forms the support for the fuel bed.
The chain is made of cast iron links connected by pins. The chain is held over two sprockets as
shown figure, and travels from one end of the furnace to the other end. The sprocket at the front
end is driven by an electric motor. The coal is fed at the front end through a hopper which is
carried by the chain to the other end, hence into the furnace. The air necessary for the combustion
of the fuel is supplied through the air inlets below the traveling grate. The secondary air is supplied
through the openings in the top roof as shown in figure.
The rate of fuel supplied to the grate and hence the heat to the boiler can be controlled by
two means. The first means is to control the depth of the coal bed on the grate by controlling the
feed to the hopper. In the second method, the speed of the chain grate can be adjusted to meet the
boiler operation requirements. The chain grate stokers are widely used for burning non-caking (that
does not form a solid mass while burning), free burning, volatile and high ash content coals.
Advantages of chain grate stokers
1) It is simple in construction and operation.
2) Its initial and maintenance costs very low.
3) It doesn't have ash cleaning problems.
4) Combustion control is simple, by control of feed or chain speed, along with the air supply. 5) Its
combustion efficiency is high.
Disadvantages
1) It is suitable only for small capacity plants.
2) Coal losses are high as the un burnt coal may also move with ash.
3) If caking coal is used ash clinker problems may rise.
• In the traveling grate stoker, the chain grate is replaced by grate bars that support the
burning fuel.
• Also the grate is inclined towards the inlet of the furnace.
• The fuel movement is accomplished and controlled by vibration of the grate.
• The air supply similar to the chain grate stoker
DEPT OF MECHANICAL ENGG, NITR
Spreader or Sprinkler Stoker
In this type stoker, coal from the hopper is fed on to a rotating feeder which in turn feeds the, to a
spreader or sprinkler, and feed according to the requirements. Feeder is a rotating drum fitted with
blades on its periphery. Other type of feeders such as reciprocations, endless belts or spiral worms
can also be used. The feeder continuously supply the coal on to the spreader, a fast moving drum
with blades, which in turn distributes and feeds the coal on to the grate as shown in figure. The fuel
feed rate and the supplied to the boiler can be controlled by controlling the feed to the hopper or by
controlling the spreader speed.
Fig. shows the schematic arrangement of a spreader stoker. In this type stoker, coal from
the hopper is fed on to a rotating feeder which in turn feeds the, to a spreader or sprinkler, and
feed according to the requirements. Feeder is a rotating drum fitted with blades on its
periphery. Other type of feeders such as reciprocating rams, endless belts or spiral worms can
also be used. The feeder continuously supplies the coal on to the spreader, a fast moving drum
with blades, which in turn distributes and feeds the coal on to the grate as shown in figure. The
fuel feed rate and the supplied to the boiler can be controlled by controlling the feed to the
hopper are by controlling the spreader speed.
Advantages of spreader stoker
1) Its operation is simple and economical.
2) A wide variety of low quality coals can be burnt successfully.
3) Preheated air can be used for improving the efficiency of operation.
4) The fuel burns rapidly and hence the caking tendency is very low, even with the use of caking
coals. 5) It can responds quickly to load variations
Disadvantages
1) It is not possible to burn varying sizes of coal and only crushed, sized coal can be used.
2) A part of the charge is burnt in suspension and hence fly ash is discharged with flue
gases. This necessitates a suitable dust (or fly ash) collector system.
3) Un burnt carbon particles may escape through the flues and reduce the combustion efficiency.
DEPT OF MECHANICAL ENGG, NITR
You might also like
- Lubrication For Journal BearingDocument25 pagesLubrication For Journal BearingNguyễn Thanh SơnNo ratings yet
- IEEE Solar Stirling PaperDocument6 pagesIEEE Solar Stirling PaperAli KaiserNo ratings yet
- Oil SeparatorsDocument11 pagesOil Separatorsalan.edwards7282No ratings yet
- Coal Formation ProcessDocument51 pagesCoal Formation ProcessLORDJASON100% (2)
- Lecture 7 - Steam GeneratorsDocument6 pagesLecture 7 - Steam GeneratorsHussain Abbas100% (1)
- RG Integrally Geared CompressorsDocument6 pagesRG Integrally Geared CompressorsSauptik SinhaNo ratings yet
- Indian BOE Coaching Services: Gujarat BOE-2016 Paper-2 (Boiler Engg-2) SolutionDocument7 pagesIndian BOE Coaching Services: Gujarat BOE-2016 Paper-2 (Boiler Engg-2) SolutionAlok DoshiNo ratings yet
- Report on 135 TPH CFBC Boiler Start UpDocument40 pagesReport on 135 TPH CFBC Boiler Start UparvindshuklaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Air PreheatersDocument21 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Air PreheatersVinay DimriNo ratings yet
- Boiler TuBeDocument26 pagesBoiler TuBemdjanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantsDocument47 pagesThermal Power Plantsbbhabal67% (3)
- NORSOK Standard Jacket PipesDocument28 pagesNORSOK Standard Jacket PipesvuongNo ratings yet
- NORSOK Standard Jacket PipesDocument28 pagesNORSOK Standard Jacket PipesvuongNo ratings yet
- Boiler Q ADocument26 pagesBoiler Q AGnanaSekar100% (1)
- Potential of Solar Energy in Developing Countries For Reducing EnergyDocument3 pagesPotential of Solar Energy in Developing Countries For Reducing EnergyPrashannaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power GenerationDocument143 pagesElectrical Power GenerationDhondiram Maruthi Kakre100% (1)
- Overview of RefractoriesDocument54 pagesOverview of Refractoriesssmith2007No ratings yet
- Coal and OilDocument48 pagesCoal and OilAnjaly KumariNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation Engineers Examination Papers Nov 2016Document10 pagesBoiler Operation Engineers Examination Papers Nov 20169766224189No ratings yet
- Module 5 CombustionDocument51 pagesModule 5 CombustionermiasNo ratings yet
- B&W FBC Boiler Opeating Experience With U BeamsDocument9 pagesB&W FBC Boiler Opeating Experience With U BeamsNath BoyapatiNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Boilers - Revised (Table Format)Document11 pages2.2 Boilers - Revised (Table Format)Gajanan JagtapNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plants (System)Document58 pagesSteam Power Plants (System)Hafzal Gani100% (1)
- Clinker Formation in BoilersDocument2 pagesClinker Formation in BoilersArivu100% (3)
- Explosion Occurance in CFBC Boiler and Necessary OperationsDocument6 pagesExplosion Occurance in CFBC Boiler and Necessary OperationsAnudeep ChittluriNo ratings yet
- Materi OperasiDocument27 pagesMateri OperasiDava Abi WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Department Gas Analysis ReportDocument26 pagesChemical Engineering Department Gas Analysis ReportDanice LunaNo ratings yet
- CFBC Boiler DescriptionDocument9 pagesCFBC Boiler Descriptioncmani_bweNo ratings yet
- LPG Energy Efficiency Report PDFDocument50 pagesLPG Energy Efficiency Report PDFFERNANDO JOSE NOVAESNo ratings yet
- Boiler Technology Exam PapersDocument9 pagesBoiler Technology Exam PaperssaurabhshineNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube Leakage Furnace Explosion Clinker Formation in Thermal Power Plant Boiler - Boiler Turbogenerator GT ESP ABT FSS DeaDocument3 pagesBoiler Tube Leakage Furnace Explosion Clinker Formation in Thermal Power Plant Boiler - Boiler Turbogenerator GT ESP ABT FSS DeaRobin BansalNo ratings yet
- Coal Combustion ProcessDocument14 pagesCoal Combustion Processdevilturn70100% (1)
- Iso 10438 1 2003 FR en PDFDocument11 pagesIso 10438 1 2003 FR en PDFHefni Ossyan0% (1)
- CFBC & PFBC Technology OverviewDocument18 pagesCFBC & PFBC Technology OverviewomiitgNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Reforming: 2011 Refining Processes HandbookDocument3 pagesCatalytic Reforming: 2011 Refining Processes HandbookGaspar BlaserNo ratings yet
- 3 Benefites of CFB Boiler Over Pc-Fired BoilerDocument9 pages3 Benefites of CFB Boiler Over Pc-Fired BoilersunitbhaumikNo ratings yet
- Improve Pulverizer PerformanceDocument39 pagesImprove Pulverizer PerformanceRavi Satyapal100% (1)
- Ludeca-A Practical Guide To Shaft Alignment PDFDocument0 pagesLudeca-A Practical Guide To Shaft Alignment PDFDelfinsh100% (1)
- C&I in CFBC-1Document25 pagesC&I in CFBC-1Prudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- Boiler Code Study GuideDocument104 pagesBoiler Code Study Guidearmstrong323590% (10)
- CFBC BoilersDocument11 pagesCFBC BoilersManoj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Fuel and Combustion Lecture NoteDocument40 pagesChapter 2 Fuel and Combustion Lecture NoteHabtamu Tkubet Ebuy100% (1)
- Operation of 300MW CFBC BoilerDocument6 pagesOperation of 300MW CFBC BoilerSoodamany Ponnu PandianNo ratings yet
- Suspension (PC) Combustion: Chungen YinDocument47 pagesSuspension (PC) Combustion: Chungen YinAakash RanjanNo ratings yet
- Boiler Exam Study Guide 1Document10 pagesBoiler Exam Study Guide 1TINHLAING100% (4)
- Boiler Cleaning Technologies - Water Lance VsDocument3 pagesBoiler Cleaning Technologies - Water Lance VsDSGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Fuel Firing SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Fuel Firing SystemBineet Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- Condensate Extraction Pump: GeneralDocument5 pagesCondensate Extraction Pump: GeneralAnonymous DKv8vpNo ratings yet
- Combustion of Pulverised Coal in a Mixture of Oxygen and Recycled Flue GasFrom EverandCombustion of Pulverised Coal in a Mixture of Oxygen and Recycled Flue GasNo ratings yet
- Components of Circulating Fluidized Bed BoilersDocument20 pagesComponents of Circulating Fluidized Bed BoilersTyrelle Joseph ManitiNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument17 pagesBoilerʞǝǝs Uǝ ƎpıɥNo ratings yet
- CFBC BoilerDocument26 pagesCFBC BoilerJustin TaylorNo ratings yet
- The Indian Boilers Act 1923Document16 pagesThe Indian Boilers Act 1923Anand Swami100% (1)
- Firing of DolaCharDocument14 pagesFiring of DolaCharS V NAGESHNo ratings yet
- Quality - Concept of CombustionDocument3 pagesQuality - Concept of CombustionNoviandryNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument36 pagesThermal Power PlantAshvani Shukla100% (1)
- Bed Ash Cooler's in Ir-Cfbc Boilers PDFDocument12 pagesBed Ash Cooler's in Ir-Cfbc Boilers PDFpradeep1987coolNo ratings yet
- Boiler TrainingDocument40 pagesBoiler TrainingHarry Ansari100% (1)
- Training Material for Efficient CFB Boiler OperationsDocument110 pagesTraining Material for Efficient CFB Boiler OperationsgkswaroopNo ratings yet
- MH BOE 2016 Paper 2 SolutionDocument9 pagesMH BOE 2016 Paper 2 SolutionKamleshNo ratings yet
- ME 231 Lecture Material (26!01!2018)Document64 pagesME 231 Lecture Material (26!01!2018)ernest amponsahNo ratings yet
- Syed Ammal Engineering College Power Plant Engineering Question BankDocument16 pagesSyed Ammal Engineering College Power Plant Engineering Question BankNizam MANo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg.: Report On Industrial TrainingDocument44 pagesMechanical Engg.: Report On Industrial TrainingSakshi SanghiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Bed Height Formula - NirmaDocument1 pageBoiler Bed Height Formula - NirmaRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- U BeamsDocument8 pagesU BeamsAmitav MishraNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Fuels & Combustion - Revised (Table Format)Document9 pages2.1 Fuels & Combustion - Revised (Table Format)Gajanan JagtapNo ratings yet
- Pulverized CoalDocument13 pagesPulverized CoalKeioleNo ratings yet
- Top 50 Boiler Information Booster Question Answers - ASKPOWERPLANTDocument19 pagesTop 50 Boiler Information Booster Question Answers - ASKPOWERPLANTRaju MaityNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed BoilerDocument4 pagesFluidized Bed BoilerbobyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Coal Requirement in Steam PlantDocument3 pagesCalculation of Coal Requirement in Steam PlantRavindra K BelapurkarNo ratings yet
- Benson BoilerDocument21 pagesBenson BoilerDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Chandrapur CTPS 15 Days Training ReportDocument21 pagesChandrapur CTPS 15 Days Training ReportUday Wankar0% (1)
- Steam Power PlantDocument56 pagesSteam Power PlantصصNo ratings yet
- Soot BlowingDocument11 pagesSoot BlowingHoncho Abhi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Air PreheaterDocument19 pagesRegenerative Air PreheaterTejas T S Tejas100% (2)
- Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesSteam Power PlantnityanandNo ratings yet
- PPE Unit 2 MaterialDocument27 pagesPPE Unit 2 MaterialEnosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Firing Systems in Power PlantsDocument54 pagesFiring Systems in Power PlantsamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Coal Combustion TechniquesDocument13 pagesCoal Combustion TechniquesAnup NairNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 WteDocument17 pagesUnit 4 Wtevarshh001No ratings yet
- David Snell SafetyDocument8 pagesDavid Snell Safetypower groupNo ratings yet
- Plastic Refractory Instalation RefDocument5 pagesPlastic Refractory Instalation RefHefni OssyanNo ratings yet
- Premium Heavy Duty GreaseDocument2 pagesPremium Heavy Duty GreaseRoger ObregonNo ratings yet
- Shayan 2015Document14 pagesShayan 2015Hefni OssyanNo ratings yet
- Low cement castable for reheating furnacesDocument1 pageLow cement castable for reheating furnacesHefni OssyanNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operations TheoryDocument60 pagesBoiler Operations TheoryHefni OssyanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Performance of Primary and Secondary Air PreheatersDocument5 pagesEvolution of Performance of Primary and Secondary Air PreheatersHefni OssyanNo ratings yet
- 250 TPH Biomass Boiler DesignDocument8 pages250 TPH Biomass Boiler DesignpoloNo ratings yet
- IRENA Future of Solar PV Summary 2019Document8 pagesIRENA Future of Solar PV Summary 2019Diego Alcázar LagunaNo ratings yet
- SGT-500 Industrial Gas Turbine: Answers For EnergyDocument4 pagesSGT-500 Industrial Gas Turbine: Answers For EnergySalim BenlahceneNo ratings yet
- PowerbotsDocument9 pagesPowerbotsAnand SelvaNo ratings yet
- Power Sector Data SetsDocument13 pagesPower Sector Data SetsZakiyah AfrinNo ratings yet
- IC engine question bank covers Otto, Diesel & dual cyclesDocument4 pagesIC engine question bank covers Otto, Diesel & dual cyclesalex aweNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactionsDocument31 pagesNuclear ReactionsKrishnan JagadeesanNo ratings yet
- Press Information: MTU Onsite Energy Unveils New Series 1600 Diesel Generator SetsDocument5 pagesPress Information: MTU Onsite Energy Unveils New Series 1600 Diesel Generator SetsLuis JesusNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Question BankDocument7 pagesRenewable Energy Question BankLovleen GargNo ratings yet
- Circulation of Water Inside Boiler TubesDocument14 pagesCirculation of Water Inside Boiler Tubesمصطفى أحمد عبد الرزاق هاديNo ratings yet
- ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY GeothermalDocument8 pagesENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY GeothermalTegar Putra Adi PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy and Solar TechnologiesDocument2 pagesSolar Energy and Solar TechnologiesRaul OrcigaNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship At: Haldia Petrochemicals LTDDocument11 pagesSummer Internship At: Haldia Petrochemicals LTDJyoti PrakashNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Electric Heat Pump Parts Outdoor MUZ-GE25-80VA (2) - A1, A2 - OBB532E PDFDocument10 pagesMitsubishi Electric Heat Pump Parts Outdoor MUZ-GE25-80VA (2) - A1, A2 - OBB532E PDFTony SavageNo ratings yet
- BSB Solar Series Lead Acid Battery GuideDocument2 pagesBSB Solar Series Lead Acid Battery GuideAdji PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- IGCC For Power Generation: N.T.P.C Gas Plant DadriDocument25 pagesIGCC For Power Generation: N.T.P.C Gas Plant DadriAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Power Sector by MechalogyDocument16 pagesPower Sector by MechalogyAghsbsgNo ratings yet
- Project OverviewDocument3 pagesProject OverviewtungluongNo ratings yet
- Second CheckingDocument12 pagesSecond CheckingKing Cyruz PabloNo ratings yet